
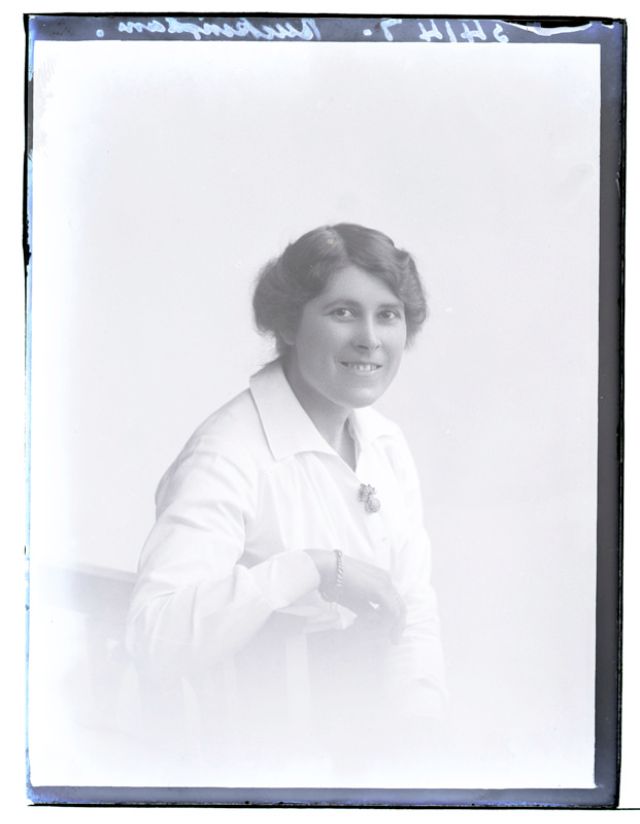
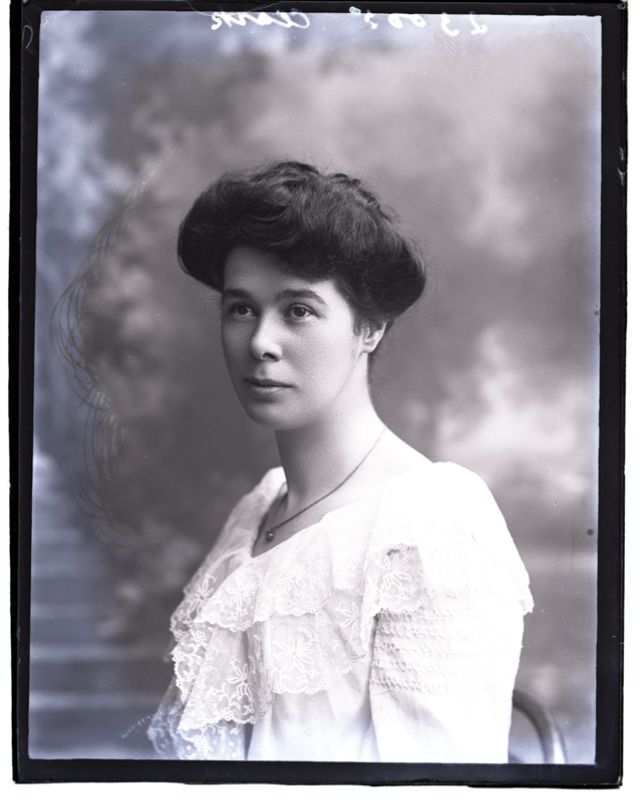
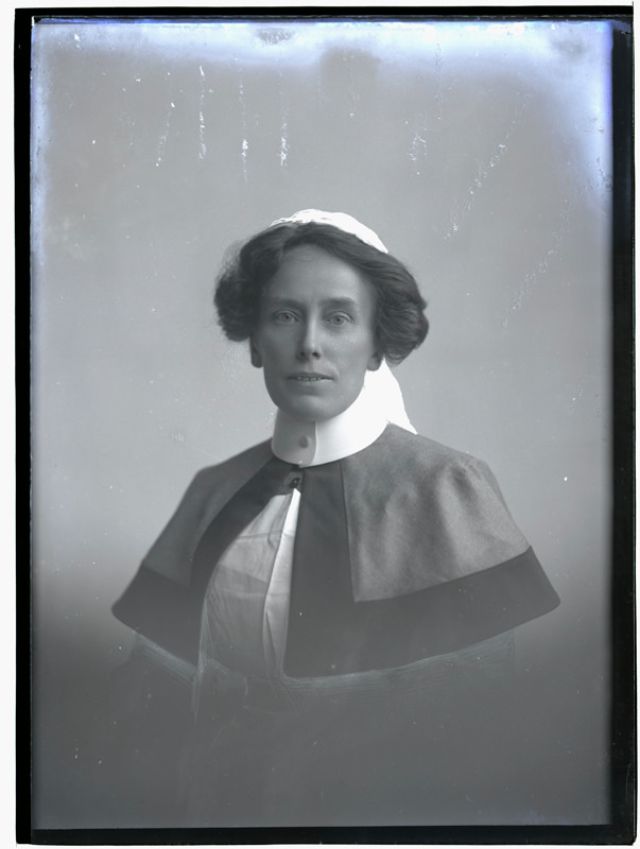
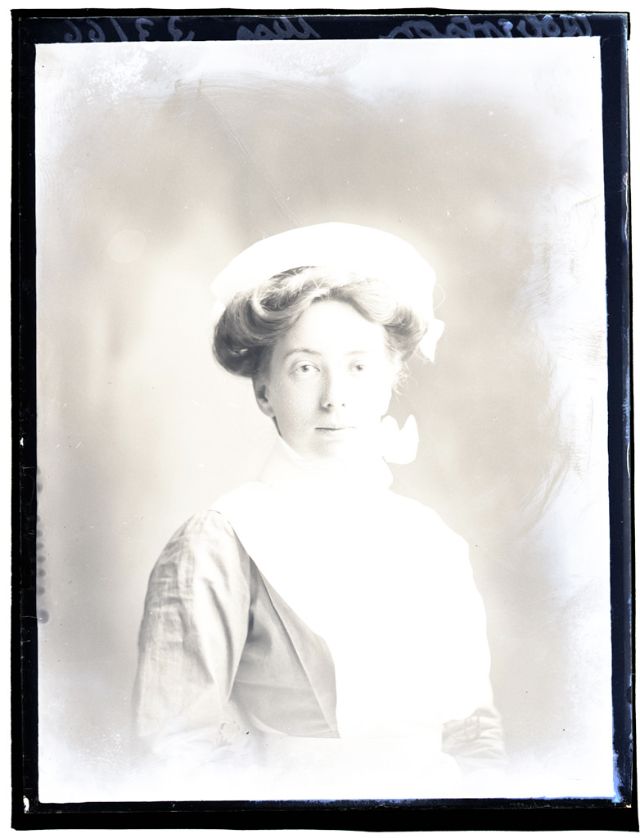
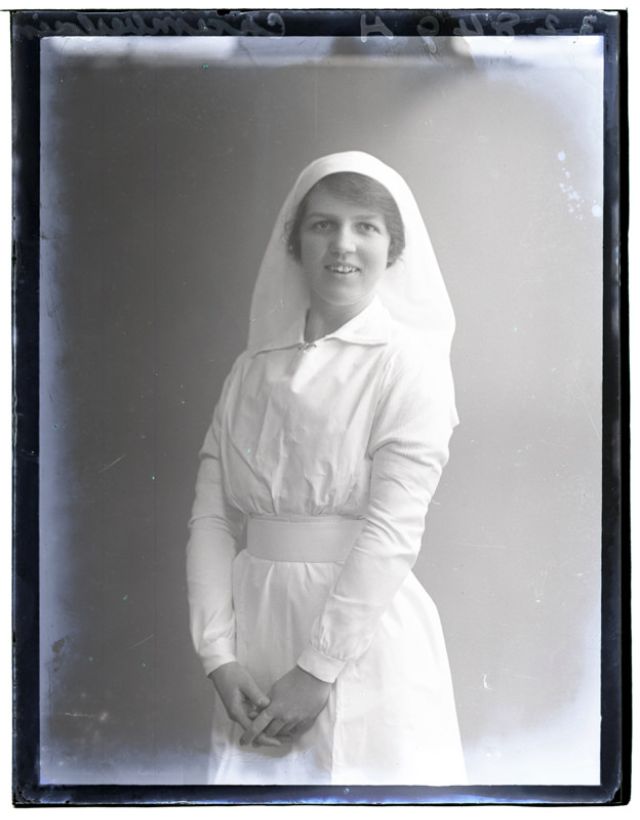
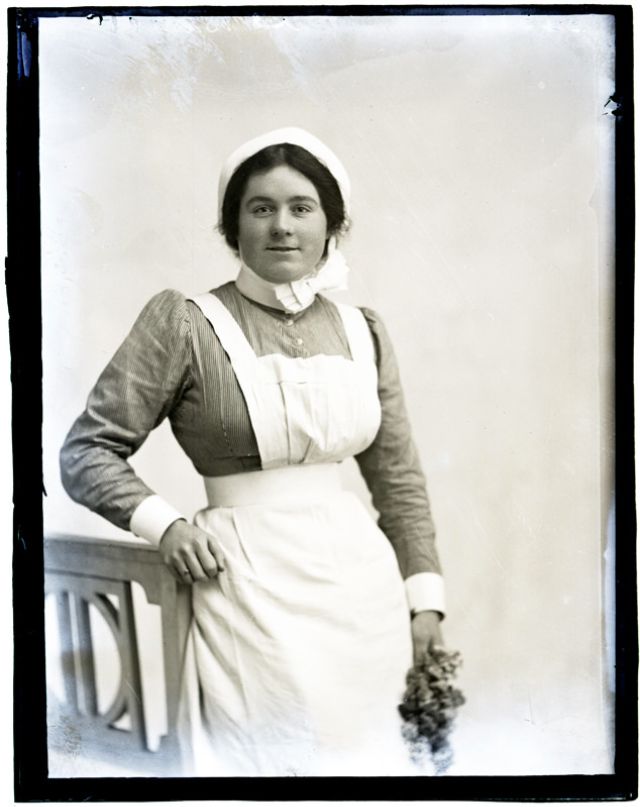
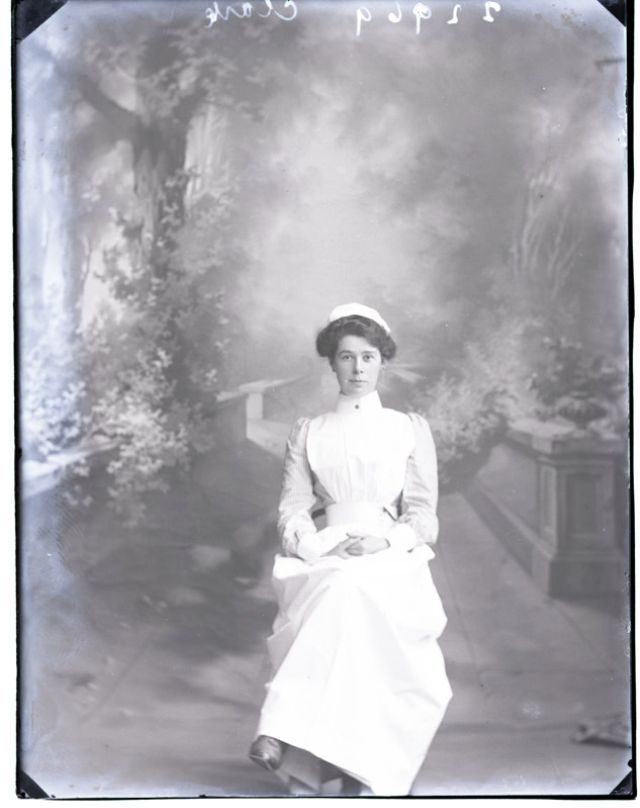
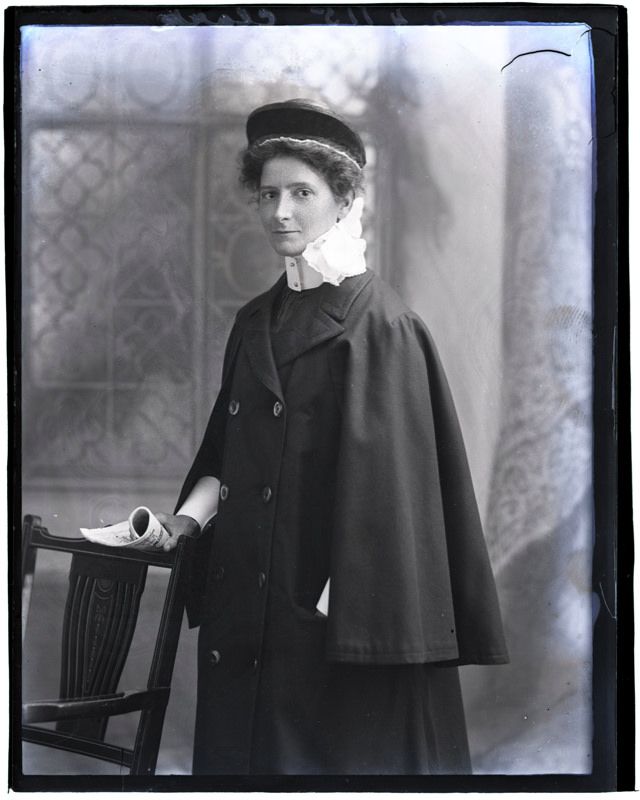
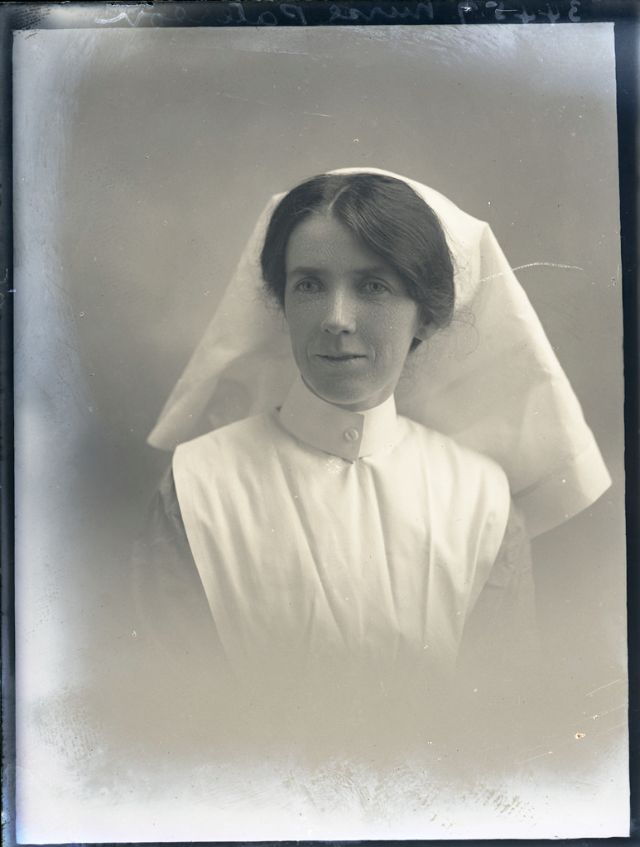
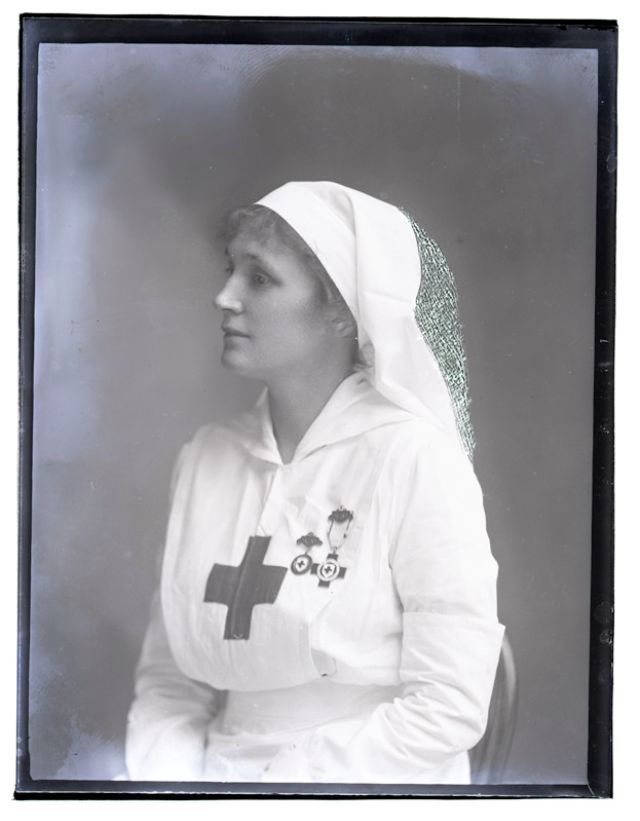
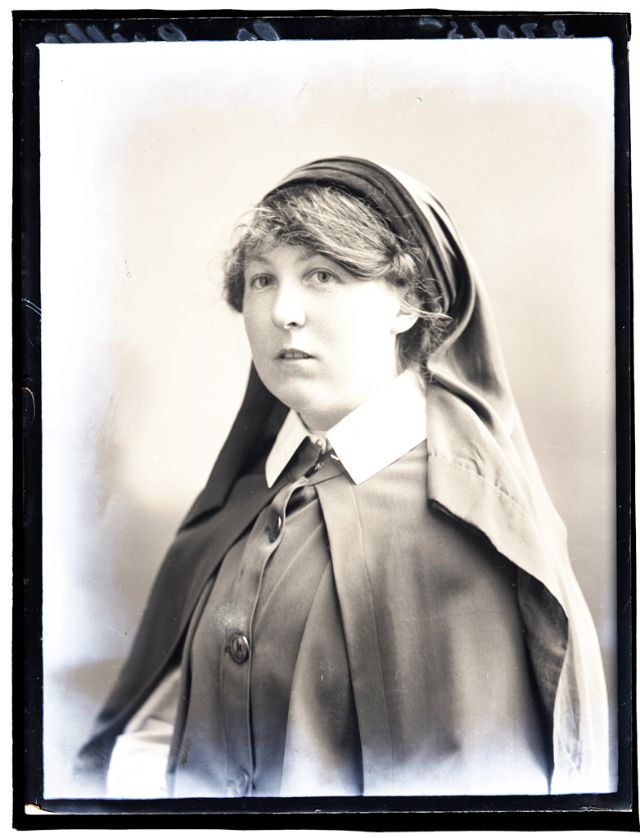
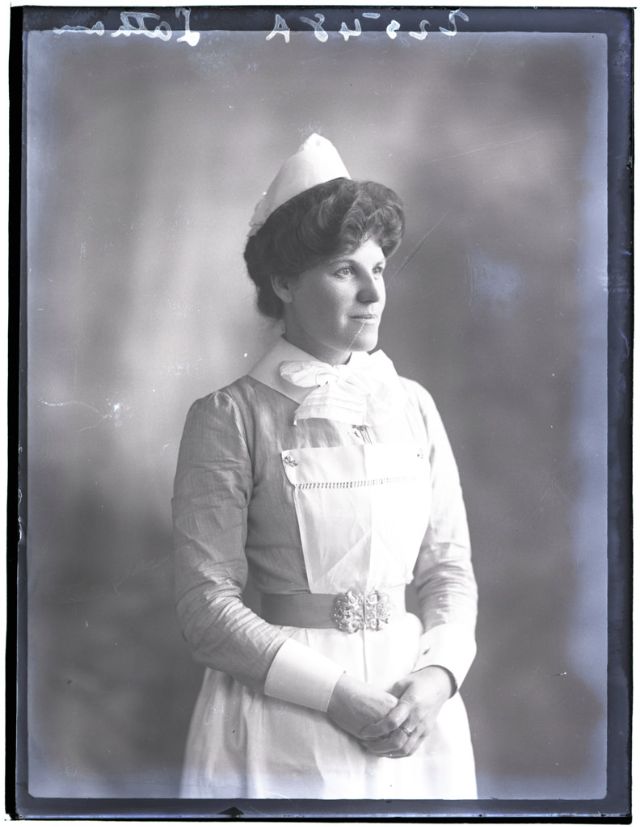
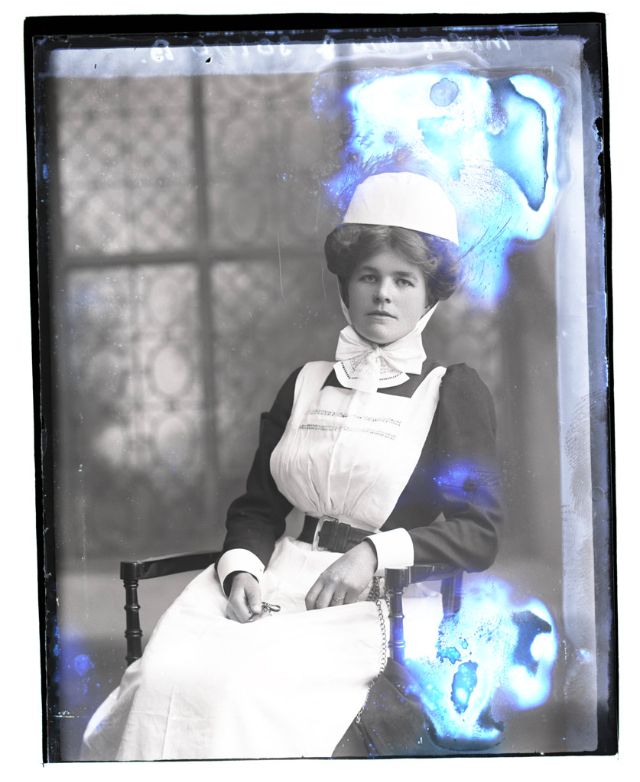
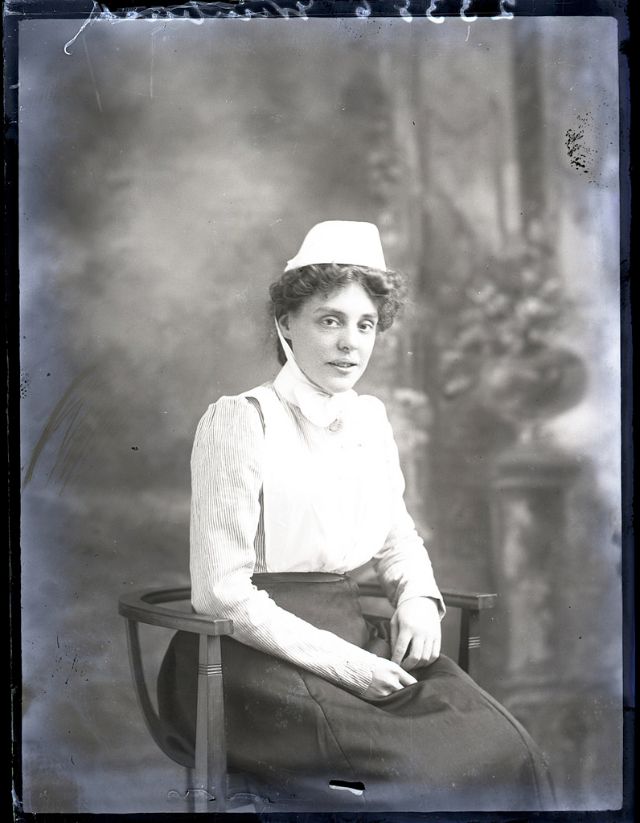
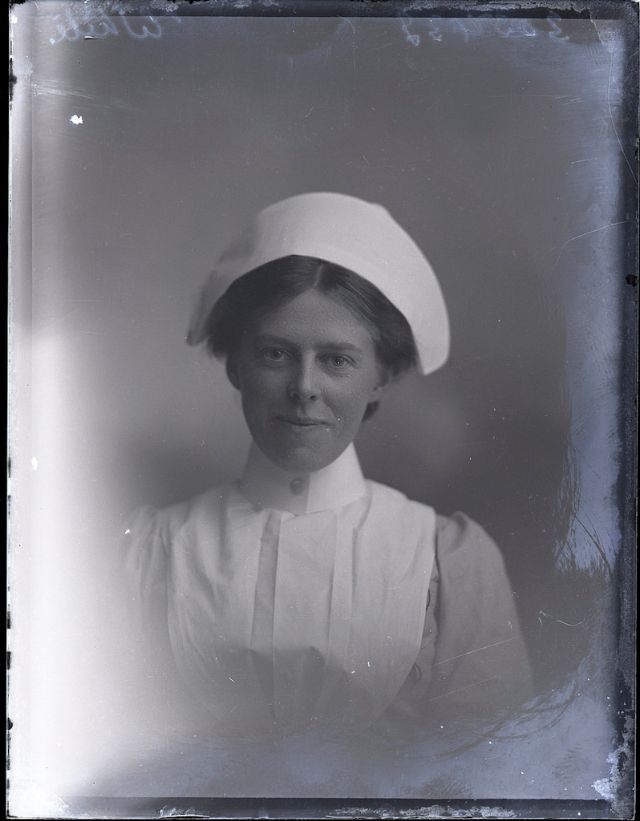
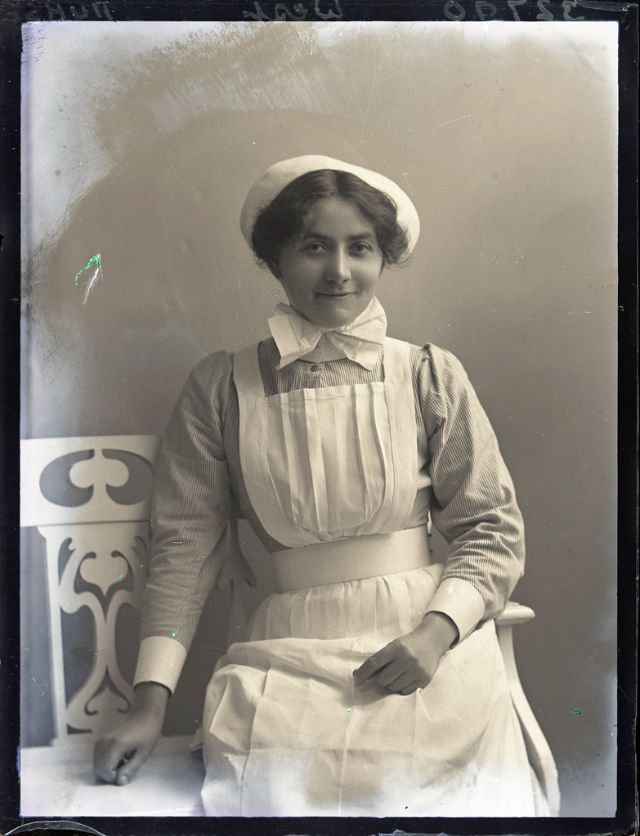
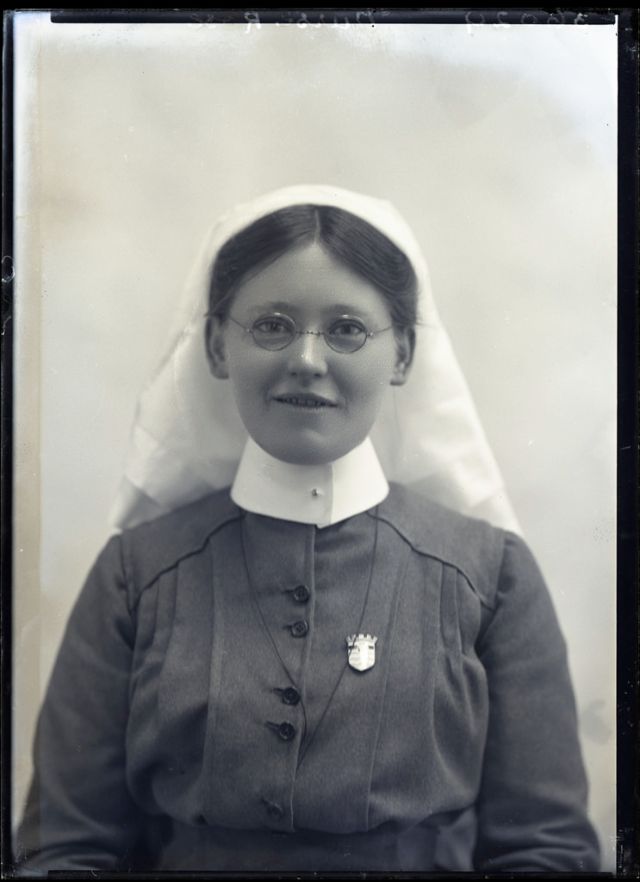
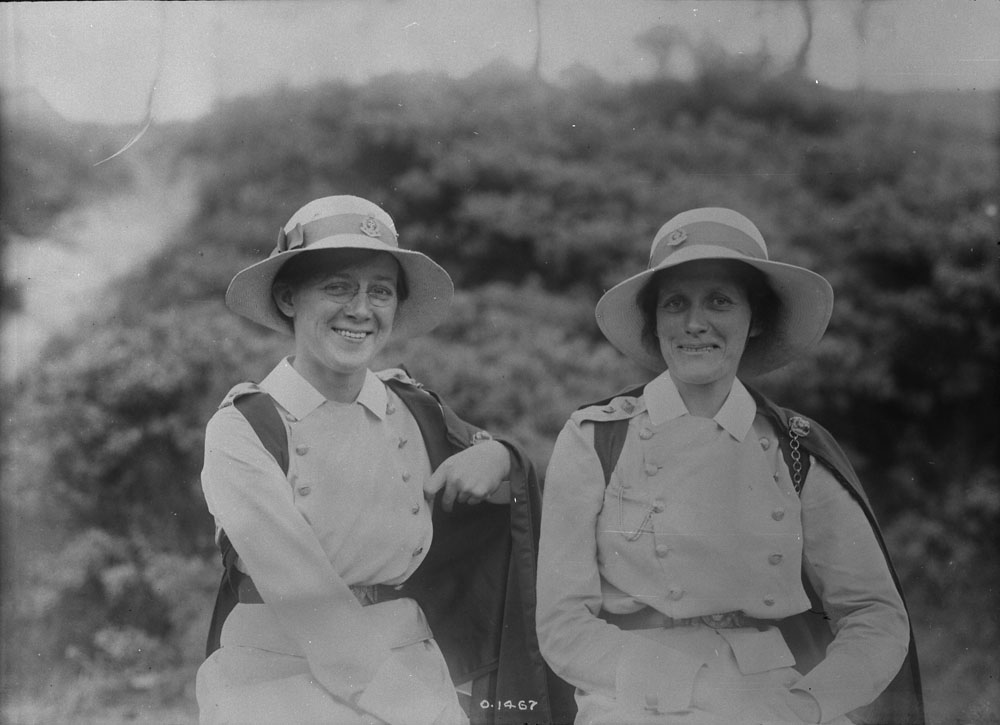
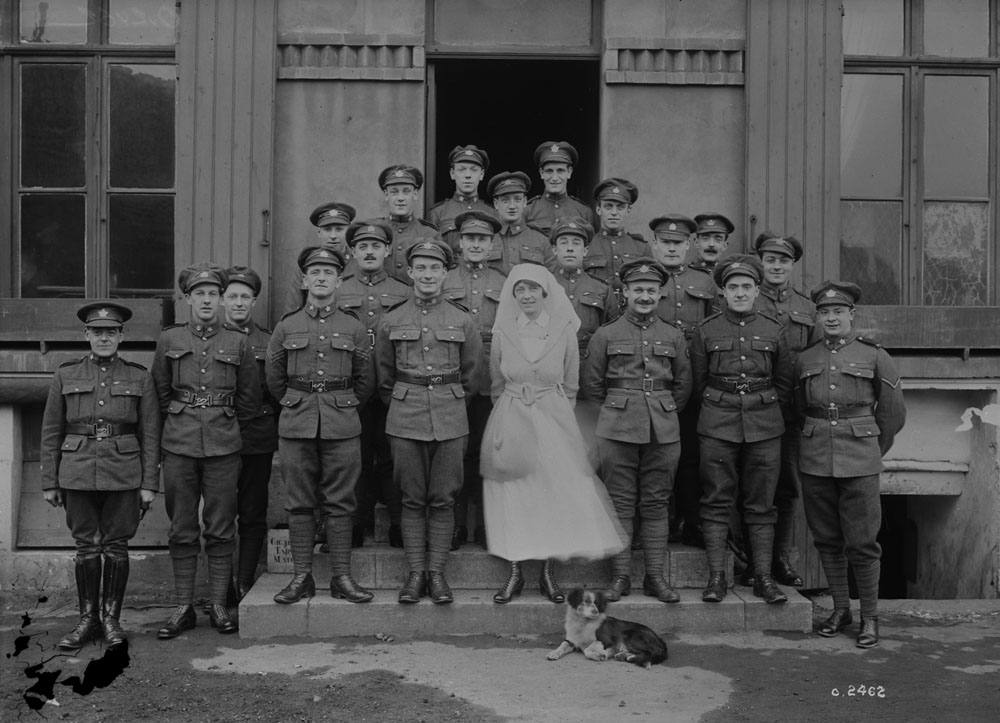
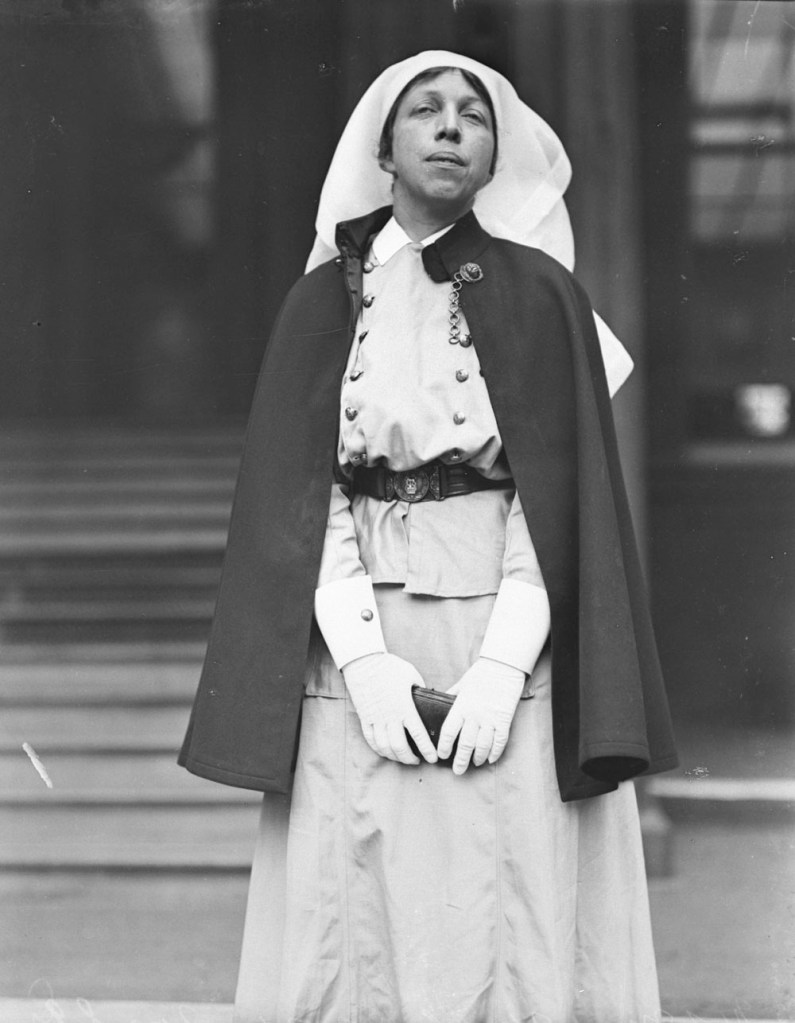
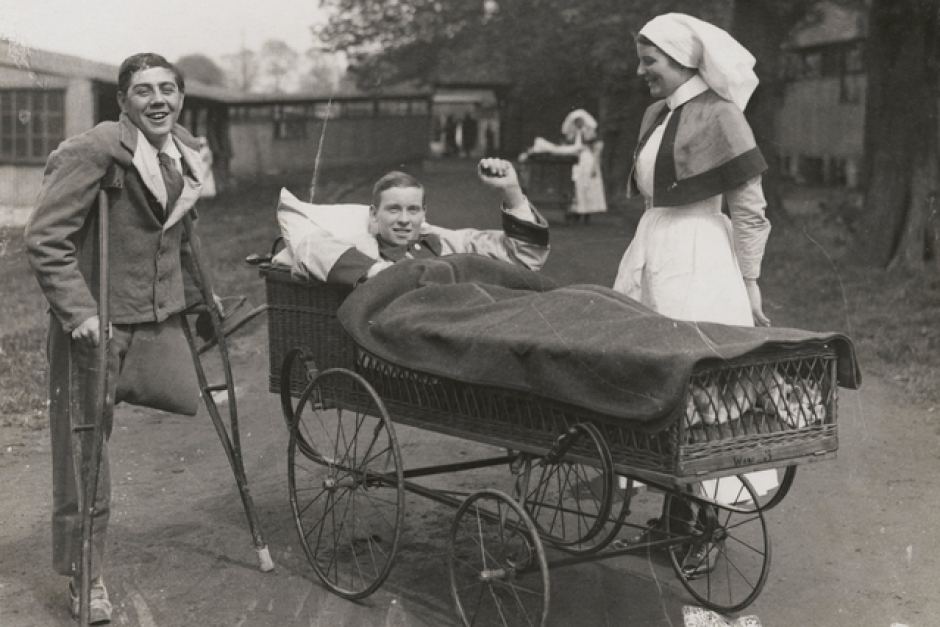
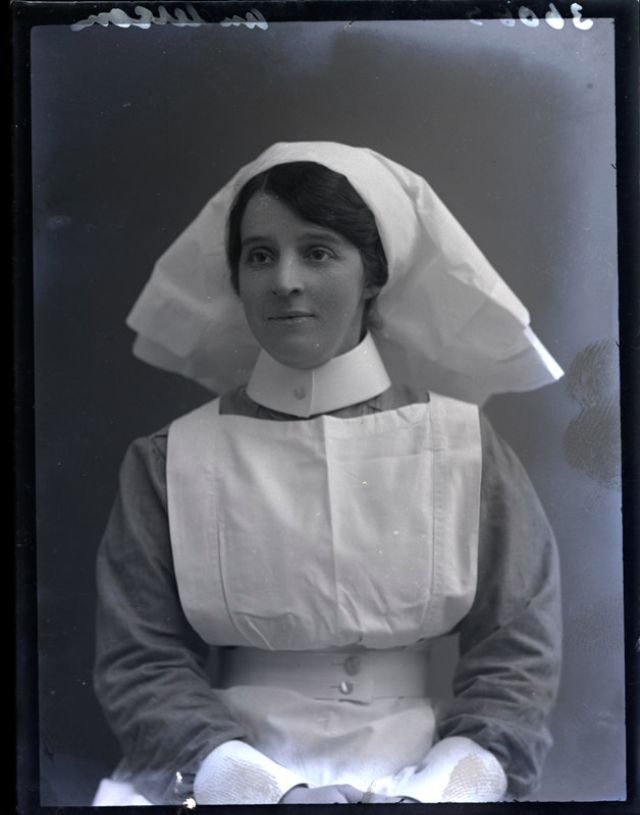
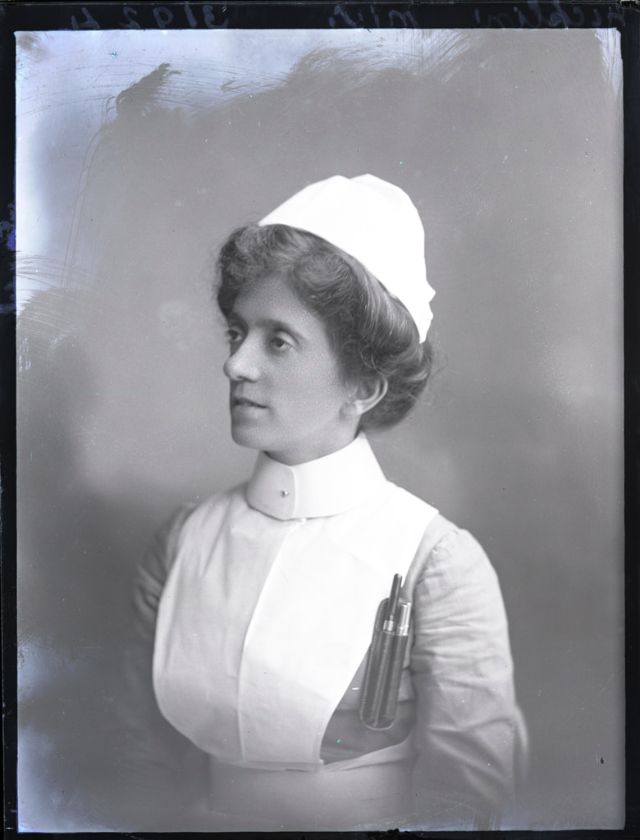
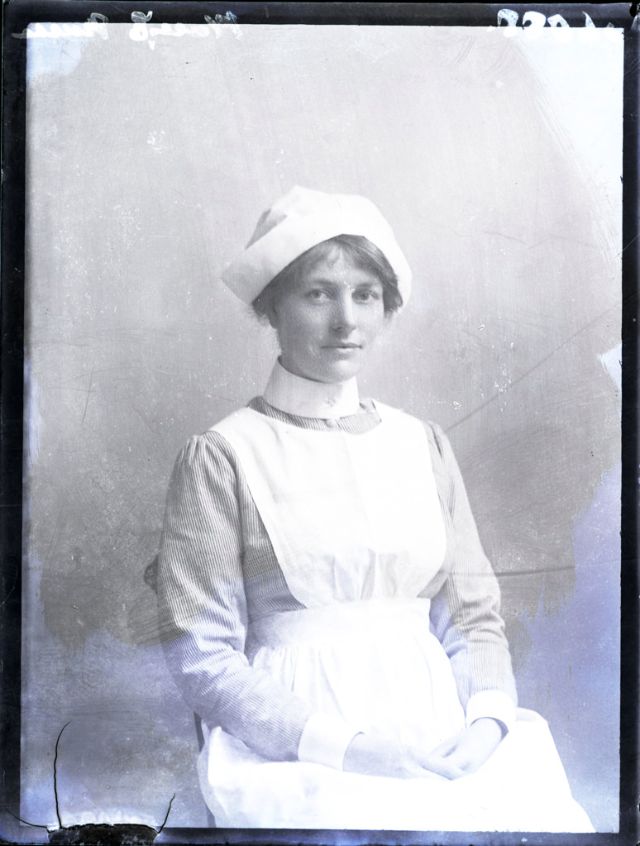
Nursing played a crucial role during the First World War. Emergency medical practices evolved enormously during the war years (1914–1918) and thousands more medical workers were involved than in previous wars. New and innovative practices included blood transfusions, the use of antiseptics, local anesthetics, and painkillers. During the course of the War, membership in the American Red Cross grew from 17,000 to more than 20 million, and 20,000 registered nurses were recruited for military service. In the United Kingdom, 38,000 members of the Voluntary Aid Detachment (VAD) served in hospitals or worked as ambulance drivers and cooks.
Modern medical nursing finds its origins in the remarkable career of Florence Nightingale, the “ministering angel” and “lady with the lamp” who served day and night during the Crimean War (1853–1856). Her understanding of the importance of hygiene saved countless lives and set the stage for nursing as we know it today. Nightingale’s model was followed and greatly expanded upon during the First World War by remarkable women such as Edith Cavell, who saved many lives from both sides of the conflict but ended up before a German firing squad; and the subversive motorbike-riding team of Mairi Chisholm and Elsie Knocker, who left their military medical stations to set up their own clinic closer to the front lines where they could save lives rather than simply provide transportation to the morgue. Similarly, novelist Mary Borden founded a field station that she called “the second battlefield” close to the front lines. https://www.theworldwar.org/explore/exhibitions/past-exhibitions/nurses



















































Discover more from Yesterday Today
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.