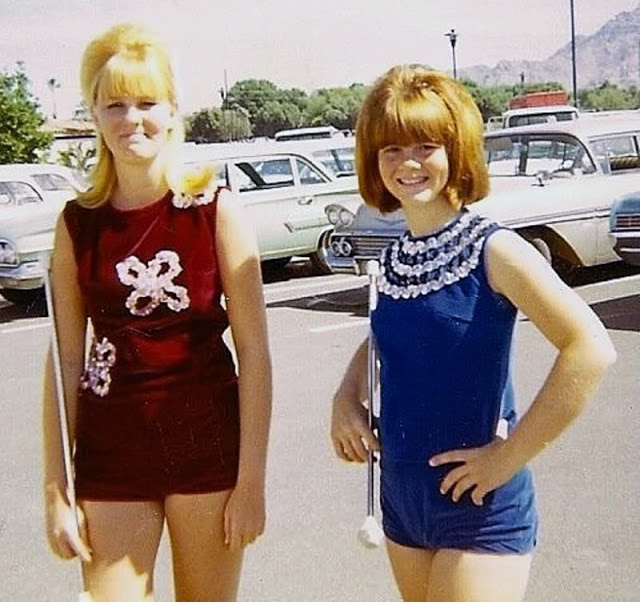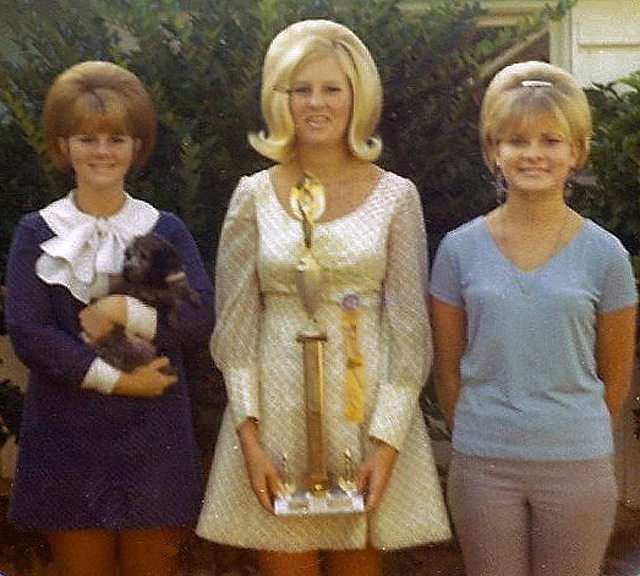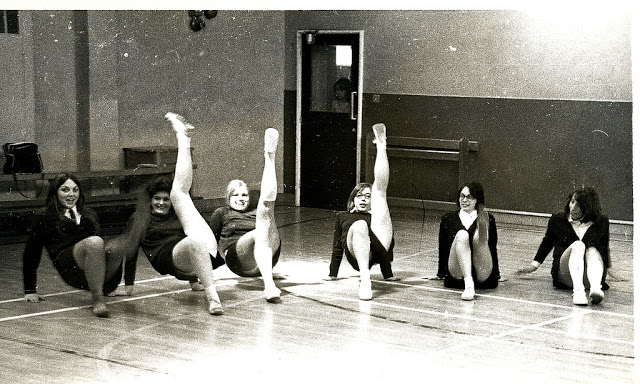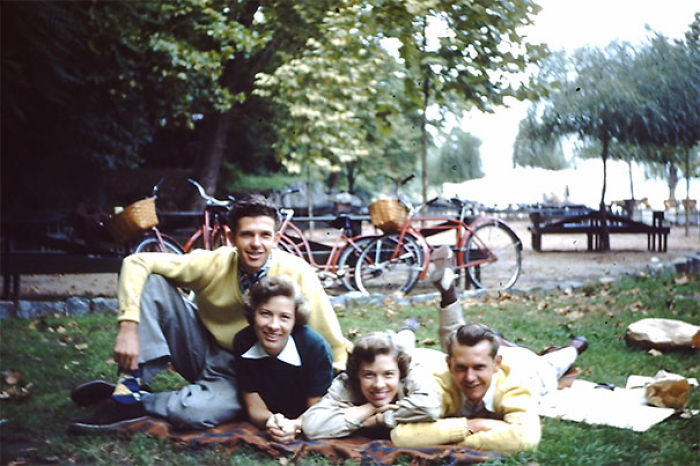






















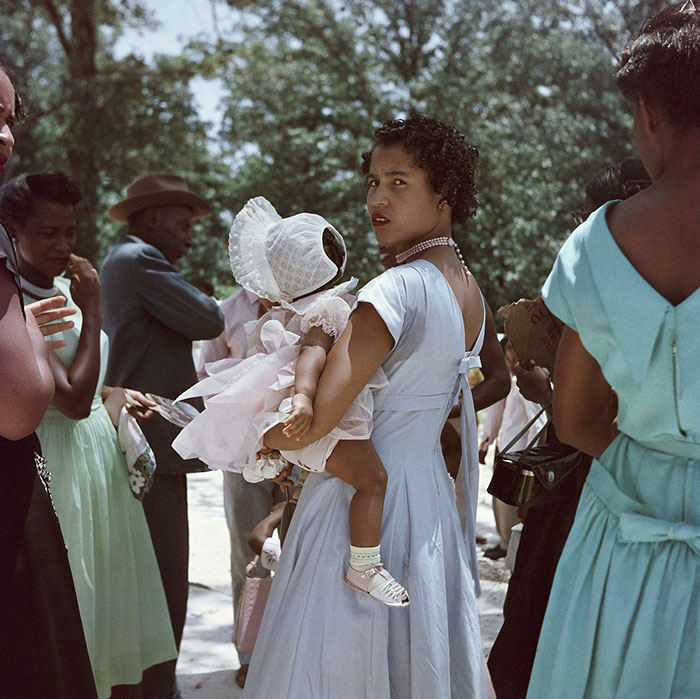

















Bringing You the Wonder of Yesterday – Today
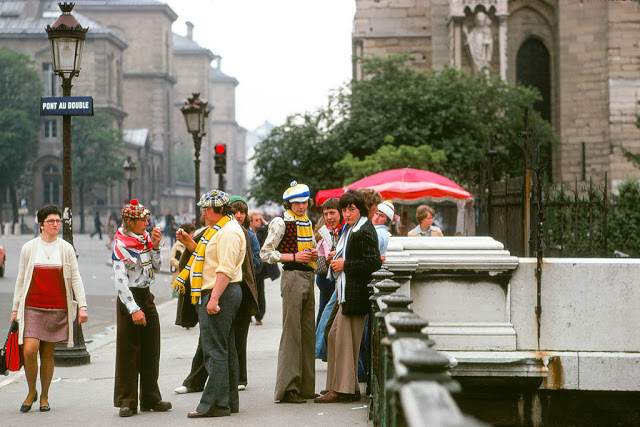










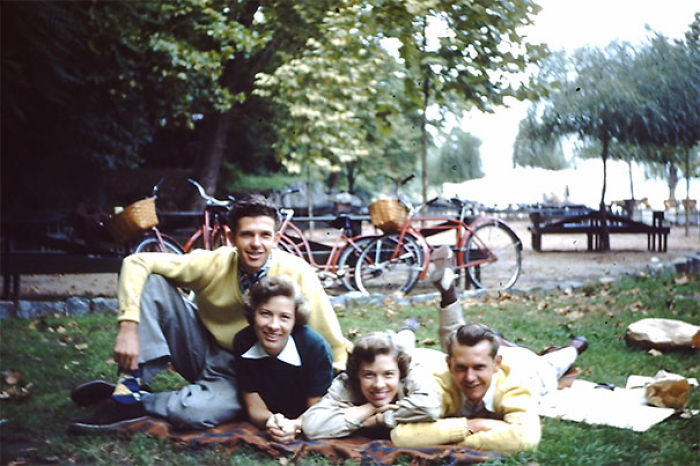






















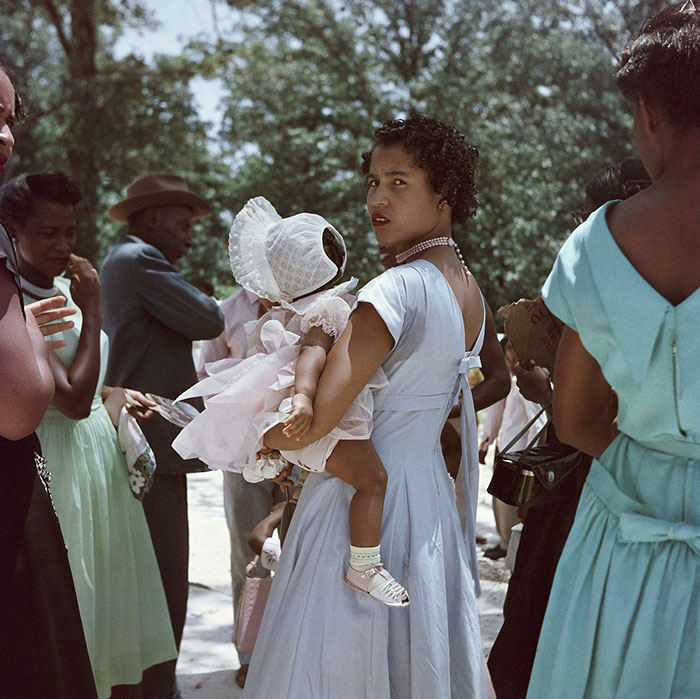


















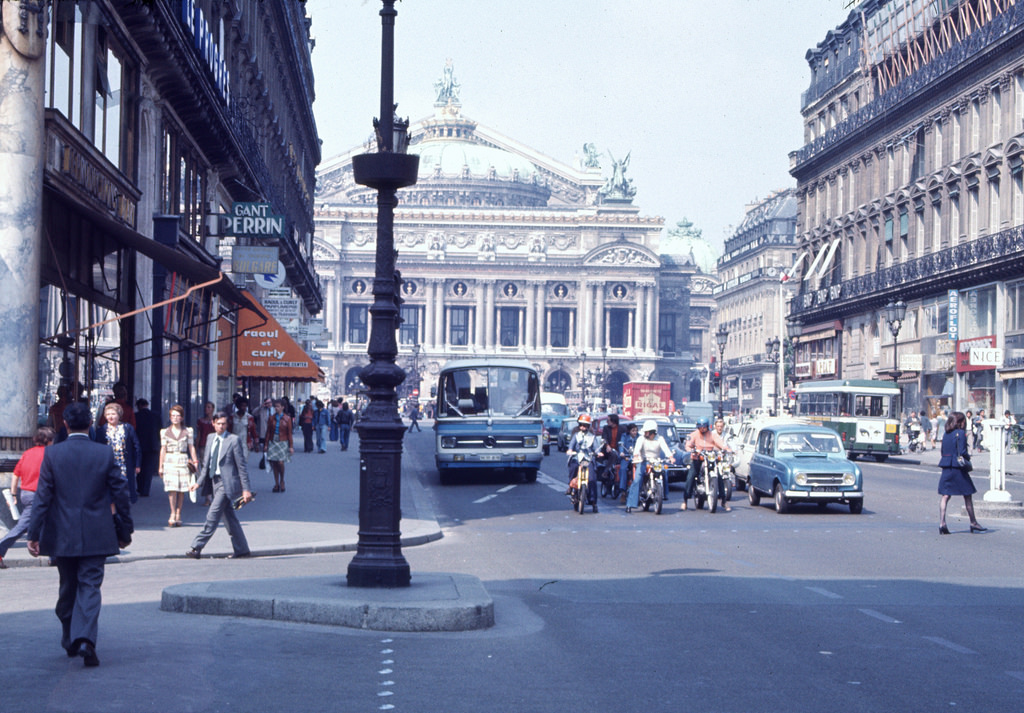
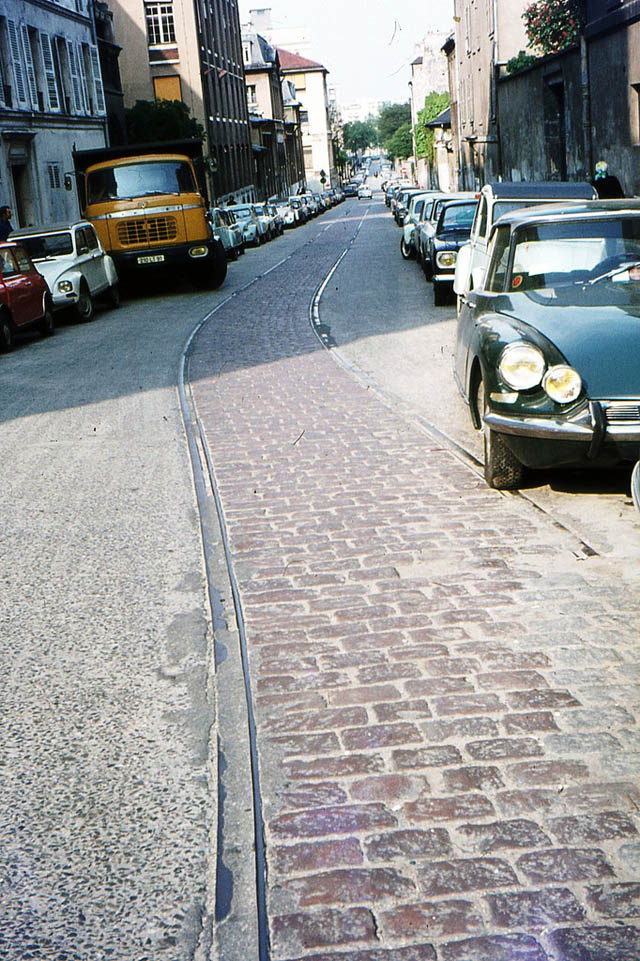
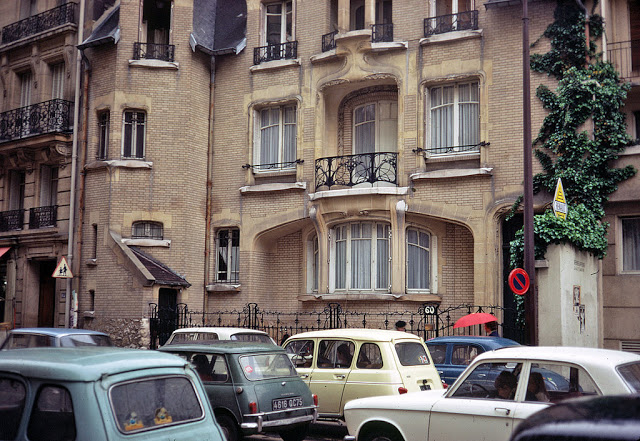
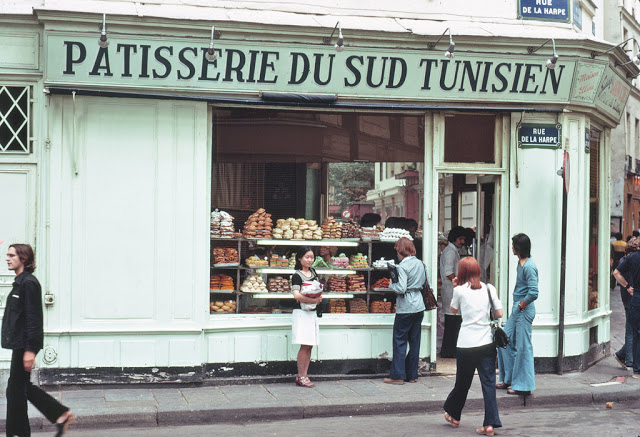
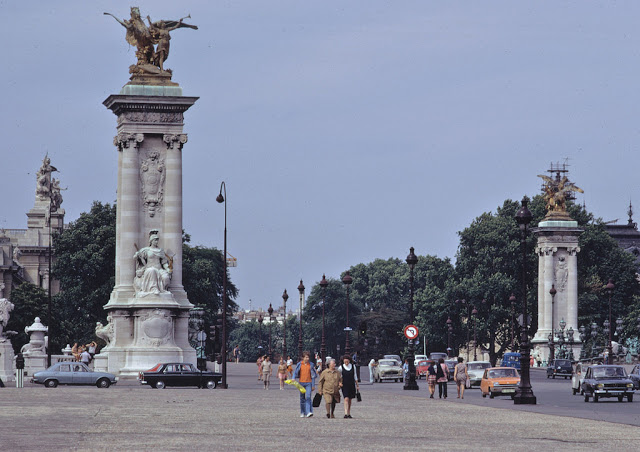
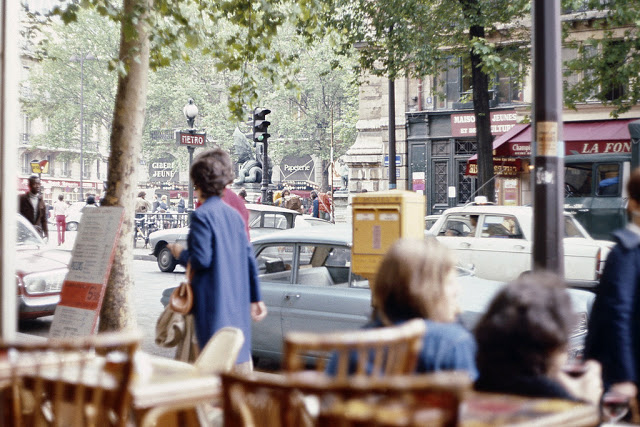
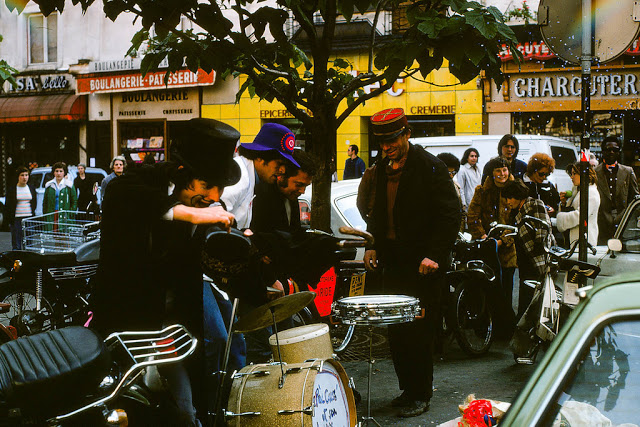
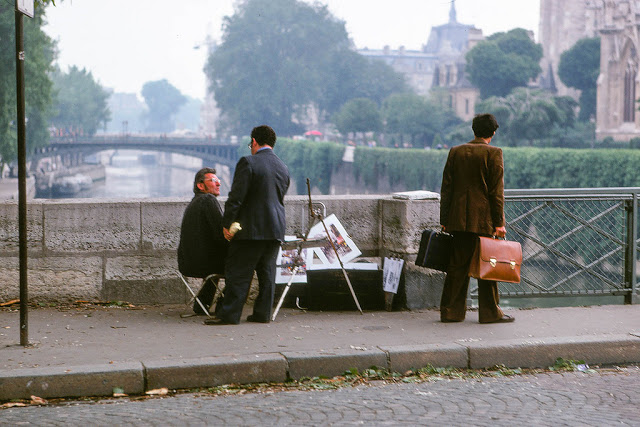
Paris is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents as of 1 January 2022 in an area of more than 105 square kilometres (41 square miles). Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of Europe’s major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, science, and arts. The City of Paris is the centre and seat of government of the region and province of Île-de-France, or Paris Region, which has an estimated population of 12,174,880, or about 18 percent of the population of France as of 2017. The Paris Region had a GDP of €709 billion ($808 billion) in 2017. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit Worldwide Cost of Living Survey in 2018, Paris was the second most expensive city in the world, after Singapore and ahead of Zürich, Hong Kong, Oslo, and Geneva. Another source ranked Paris as most expensive, on par with Singapore and Hong Kong, in 2018.
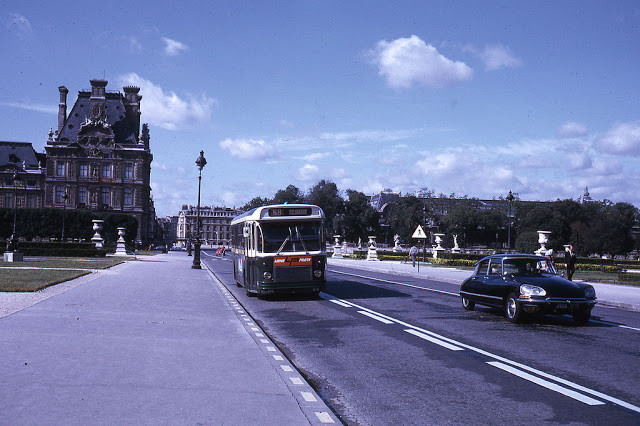
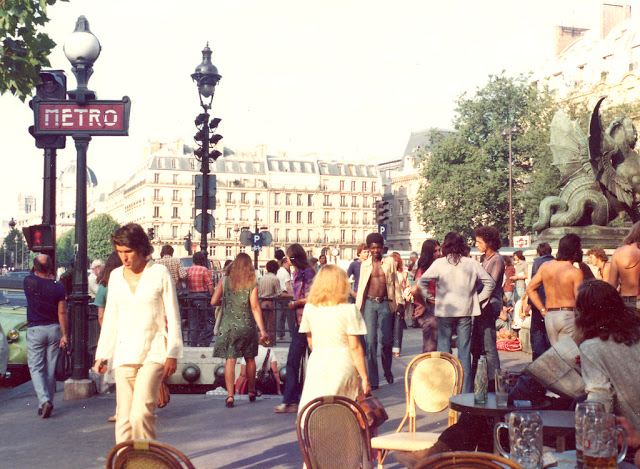
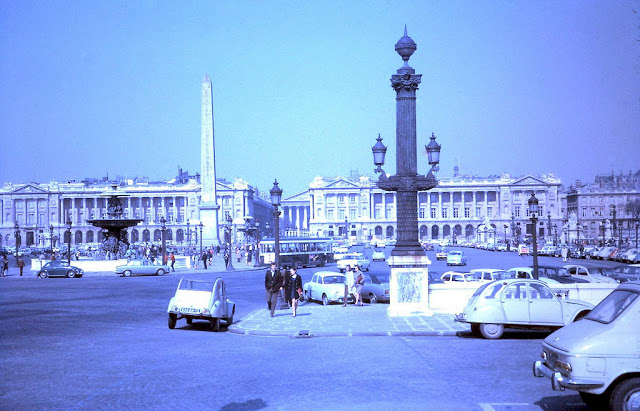
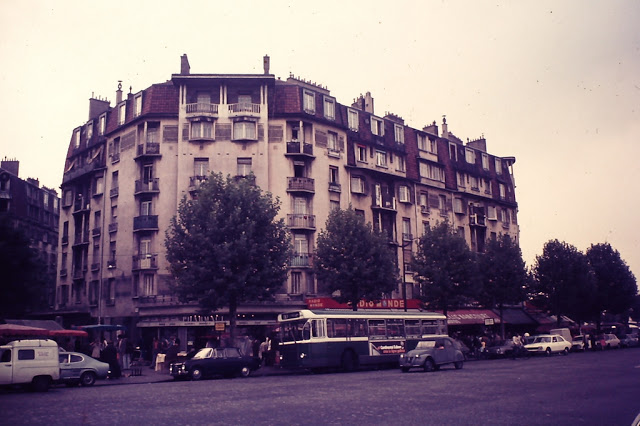
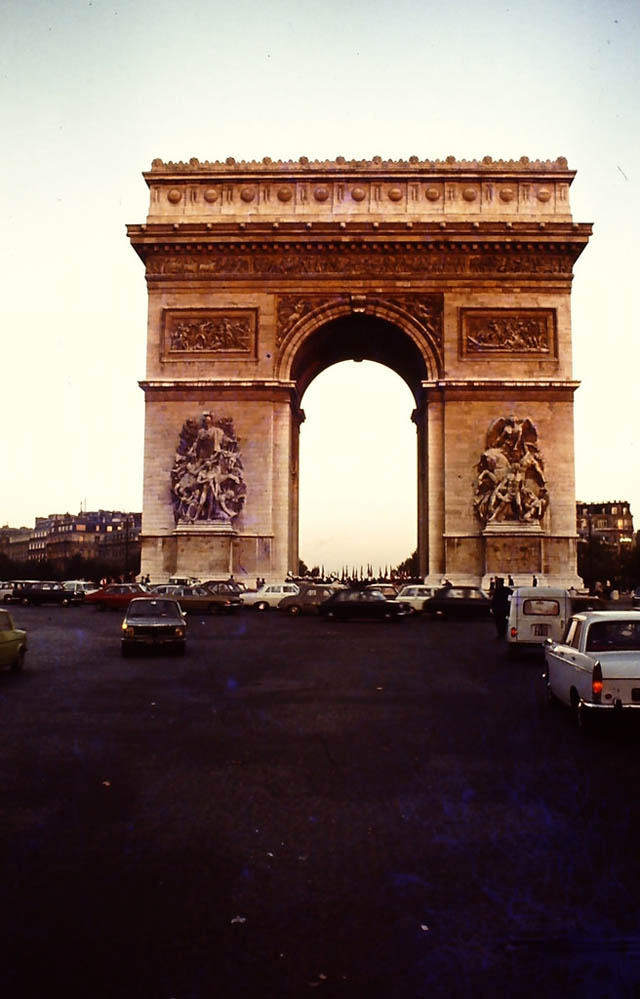
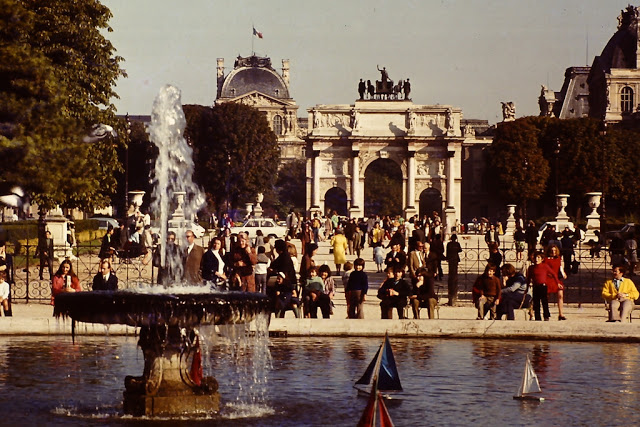
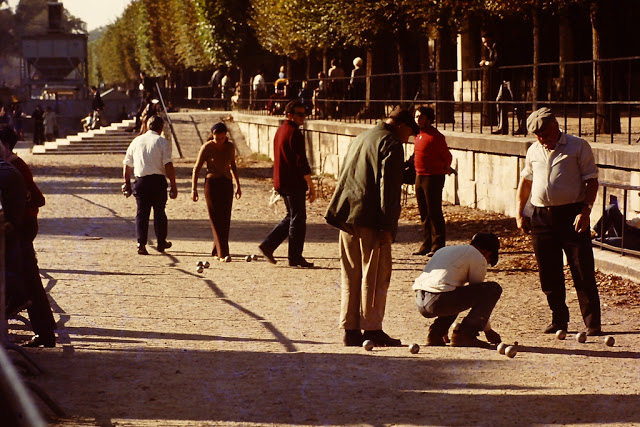
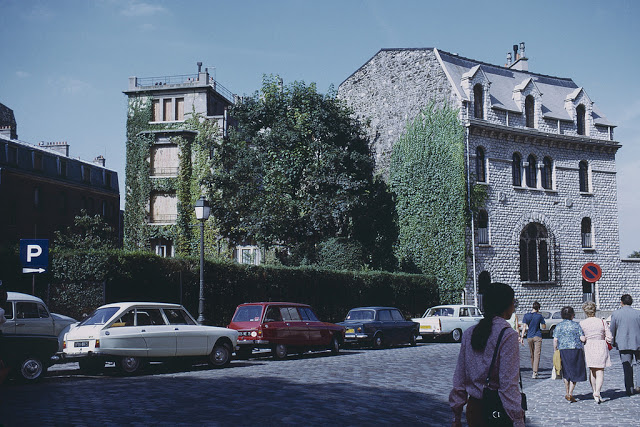
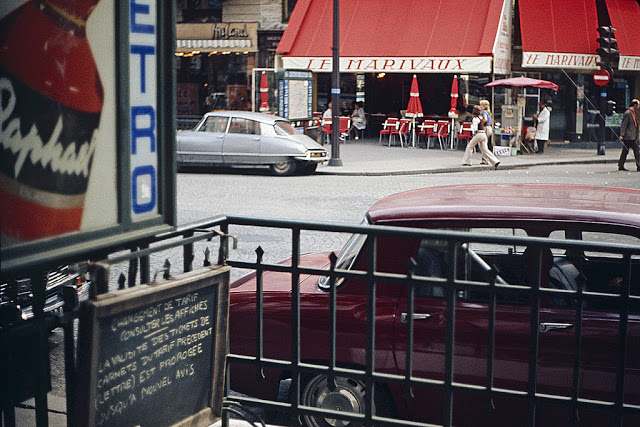
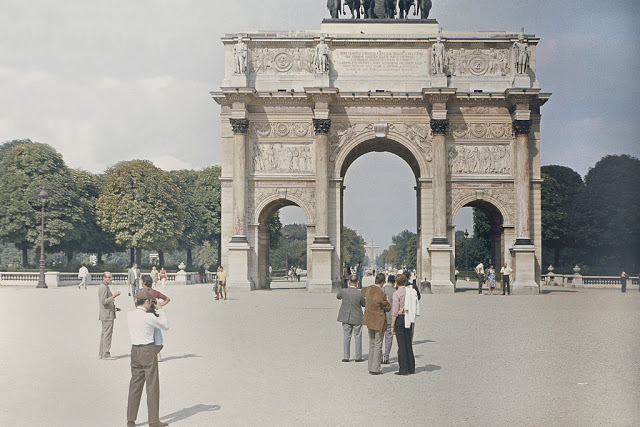
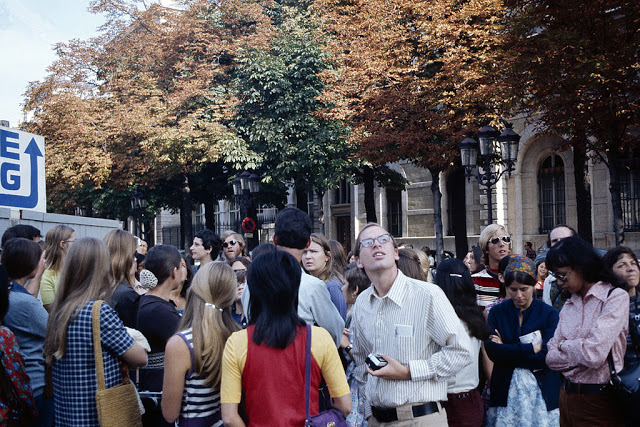
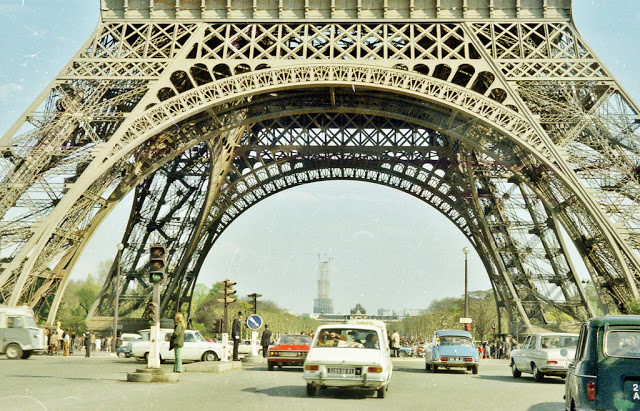
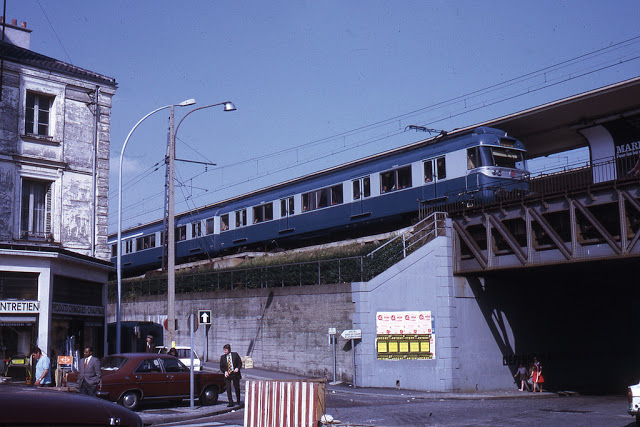
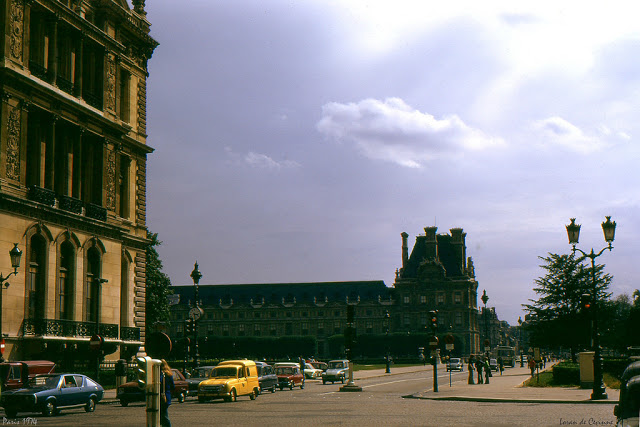
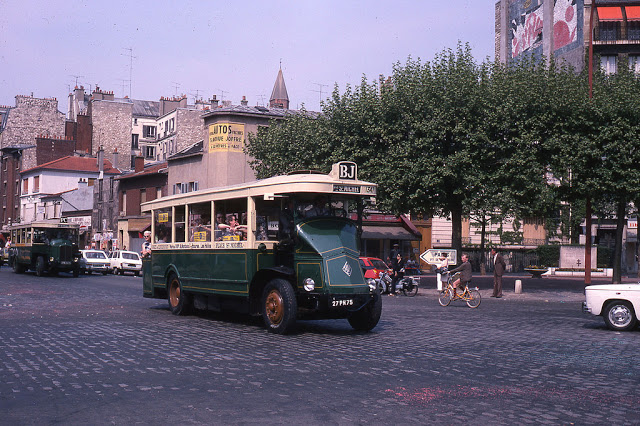
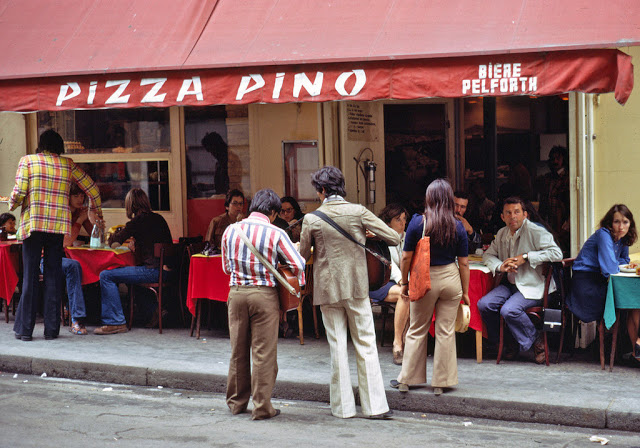
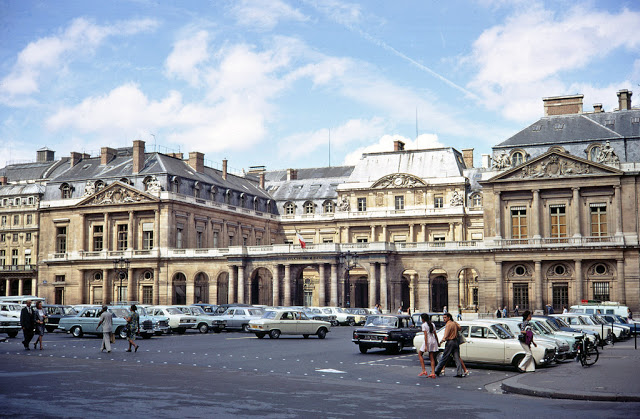
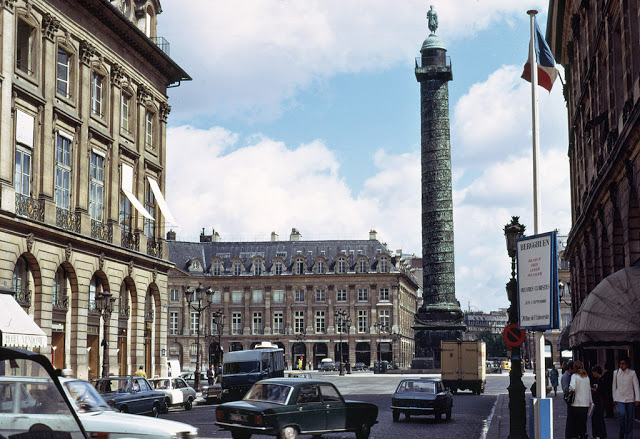
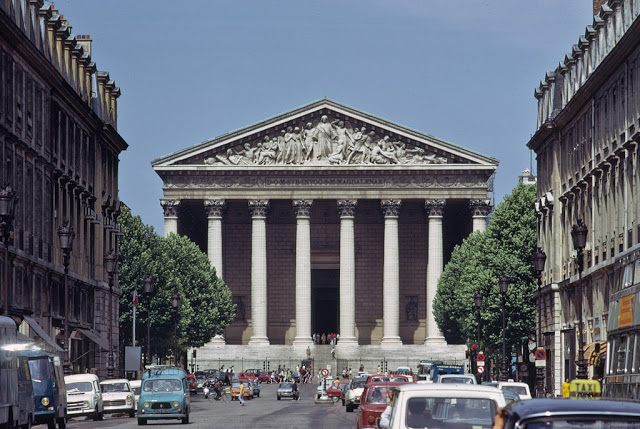
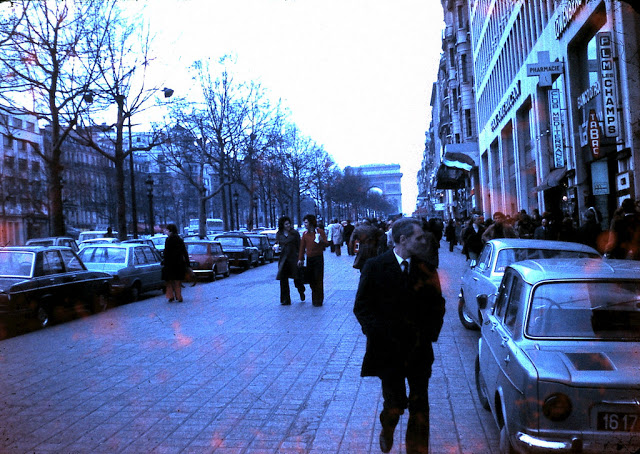
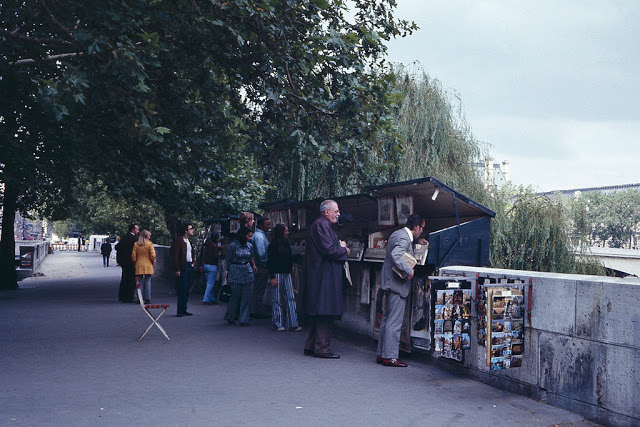
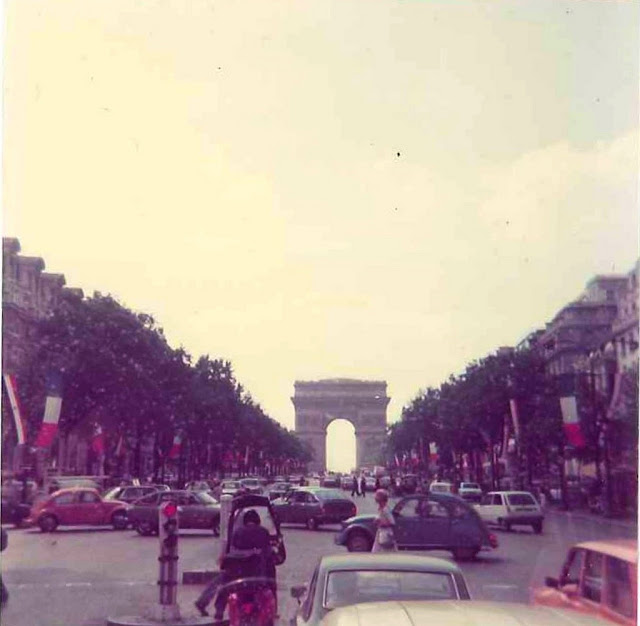
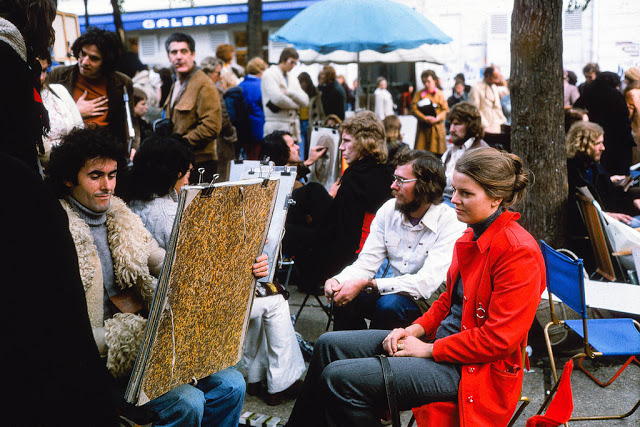
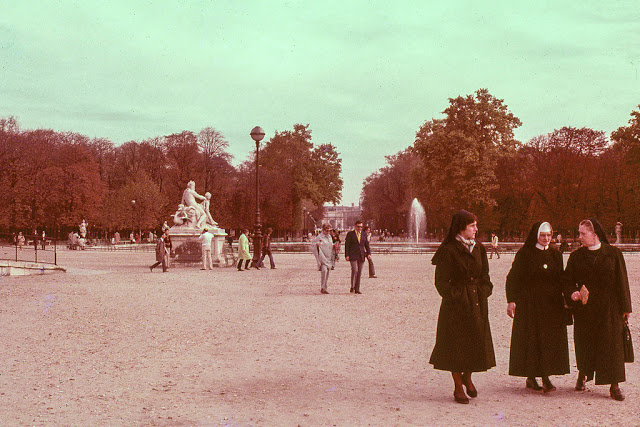
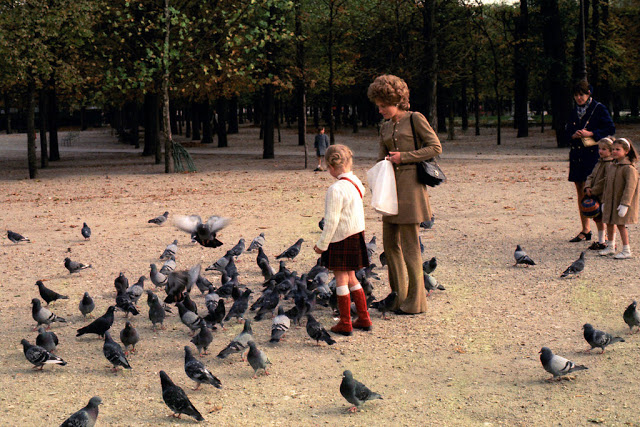
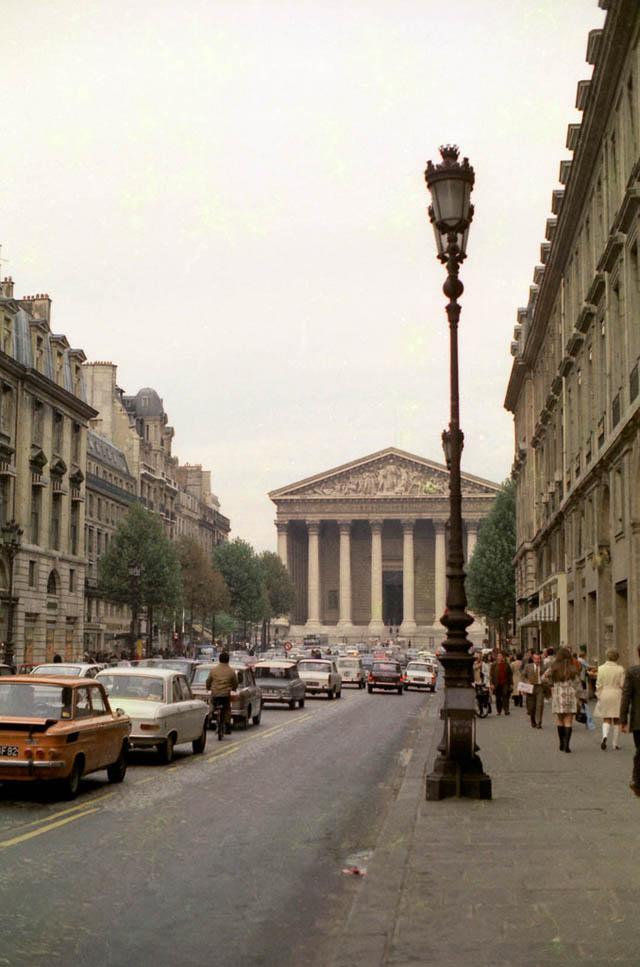
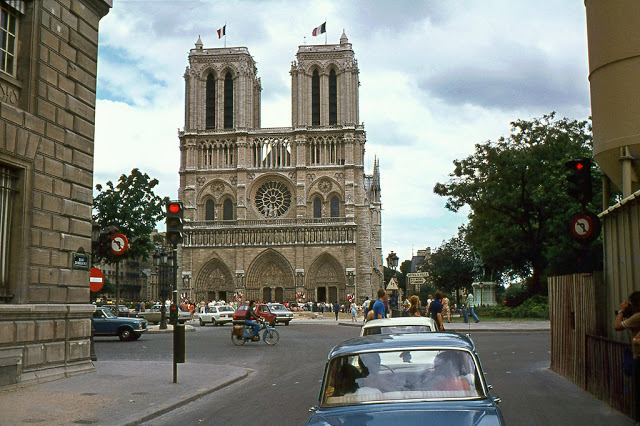
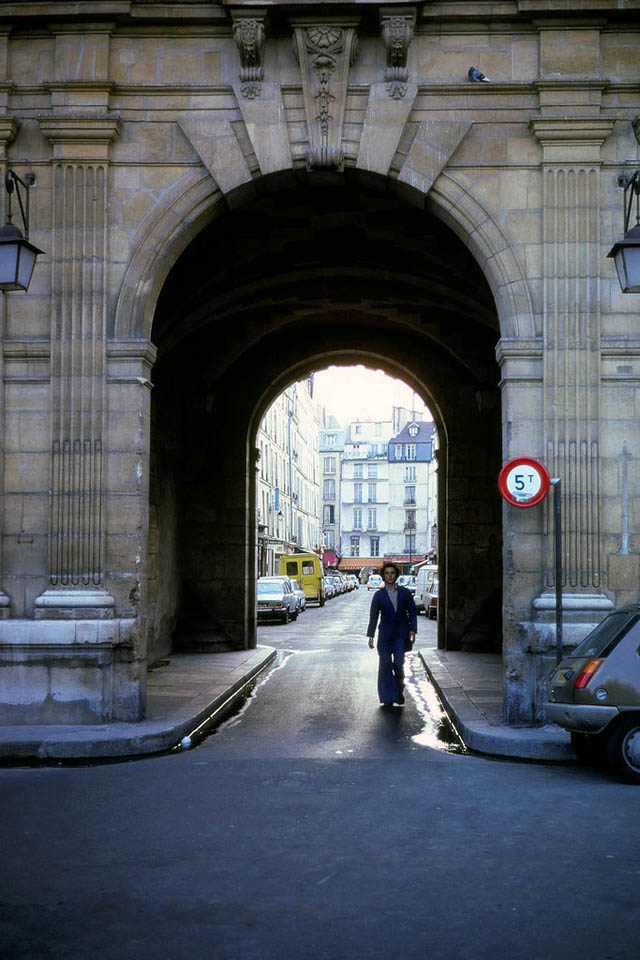
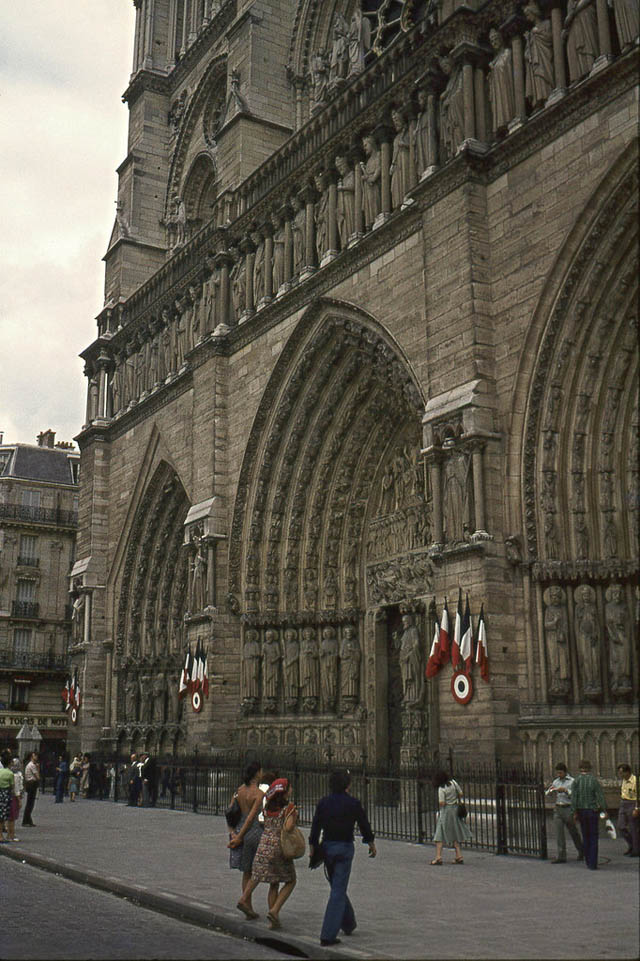
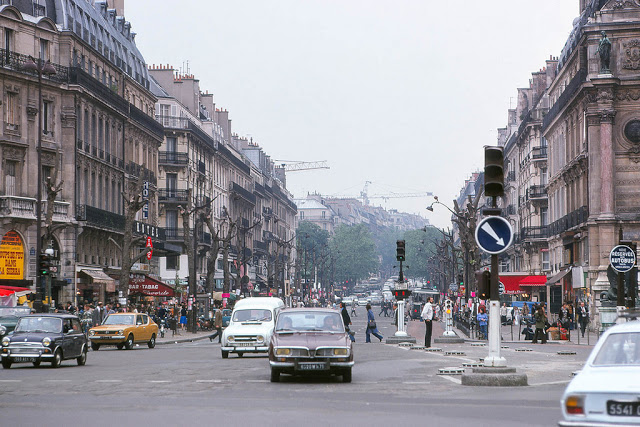
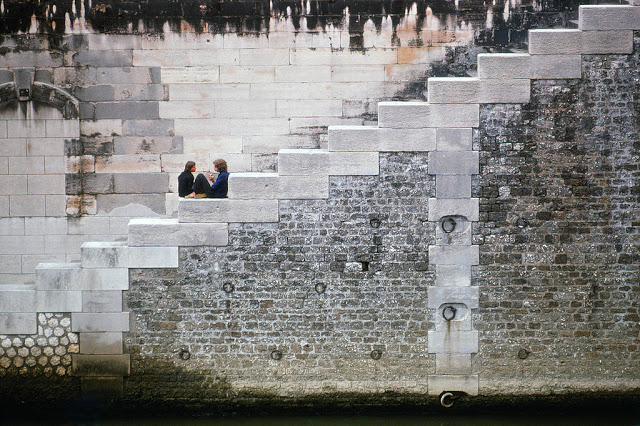
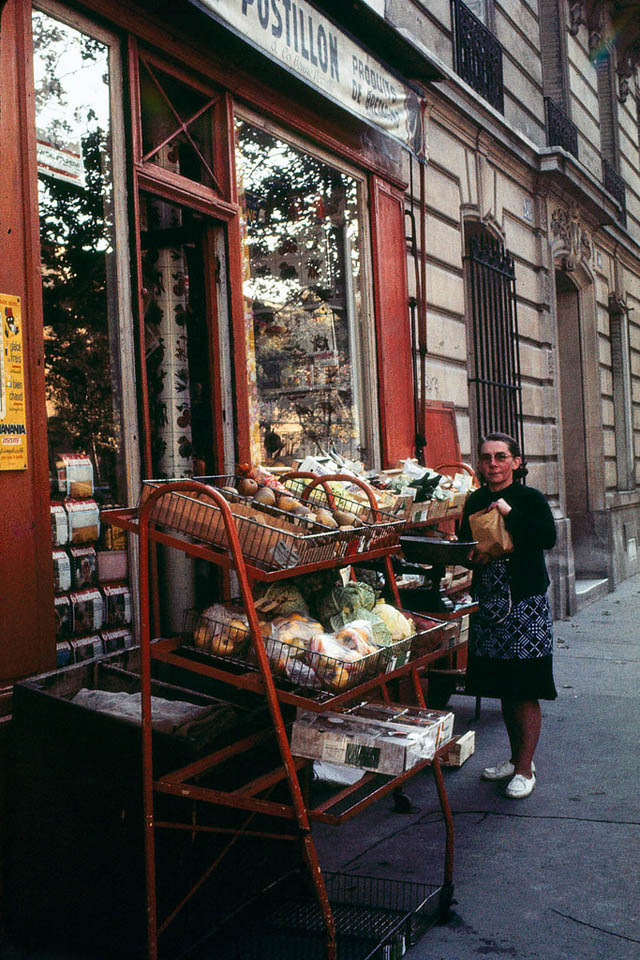
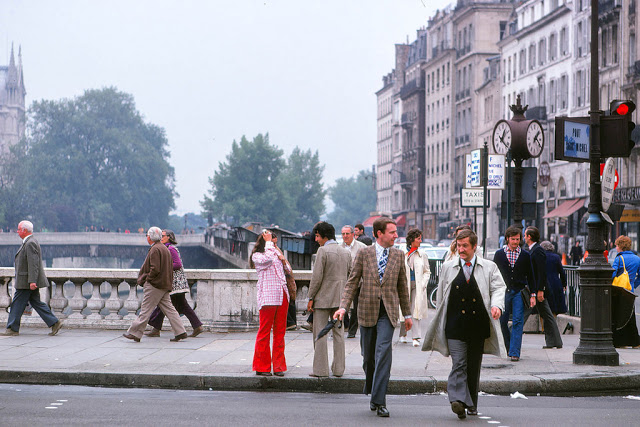
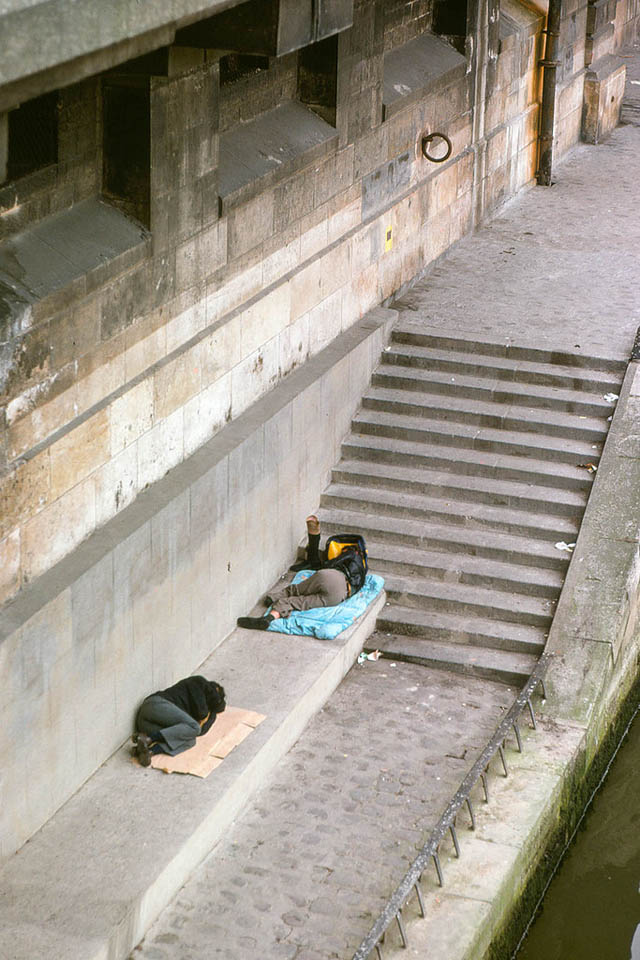
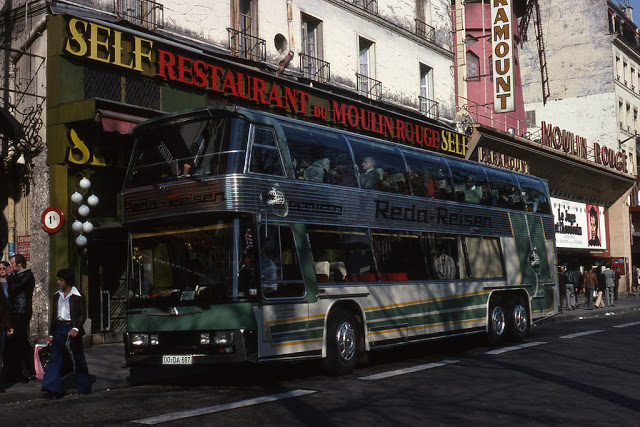
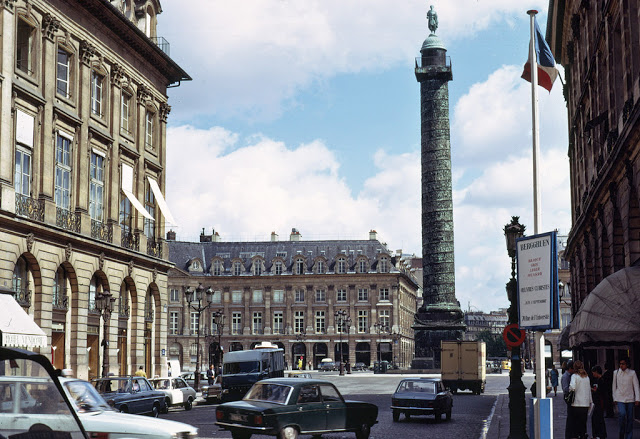
Paris is a major railway, highway, and air-transport hub served by two international airports: Paris–Charles de Gaulle (the second-busiest airport in Europe) and Paris–Orly. Opened in 1900, the city’s subway system, the Paris Métro, serves 5.23 million passengers daily; it is the second-busiest metro system in Europe after the Moscow Metro. Gare du Nord is the 24th-busiest railway station in the world, but the busiest located outside Japan, with 262 million passengers in 2015. Paris is especially known for its museums and architectural landmarks: the Louvre received 2.8 million visitors in 2021, despite the long museum closings caused by the COVID-19 virus. The Musée d’Orsay, Musée Marmottan Monet and Musée de l’Orangerie are noted for their collections of French Impressionist art. The Pompidou Centre Musée National d’Art Moderne has the largest collection of modern and contemporary art in Europe. The Musée Rodin and Musée Picasso exhibit the works of two noted Parisians. The historical district along the Seine in the city centre has been classified as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1991; popular landmarks there include the Cathedral of Notre Dame de Paris on the Île de la Cité, now closed for renovation after the 15 April 2019 fire. Other popular tourist sites include the Gothic royal chapel of Sainte-Chapelle, also on the Île de la Cité; the Eiffel Tower, constructed for the Paris Universal Exposition of 1889; the Grand Palais and Petit Palais, built for the Paris Universal Exposition of 1900; the Arc de Triomphe on the Champs-Élysées, and the hill of Montmartre with its artistic history and its Basilica of Sacré-Coeur.
Paris received 12.6 million visitors in 2020, measured by hotel stays, a drop of 73 percent from 2019, due to the COVID-19 virus. The number of foreign visitors declined by 80.7 percent. Museums re-opened in 2021, with limitations on the number of visitors at a time and a requirement that visitors wear masks.
The football club Paris Saint-Germain and the rugby union club Stade Français are based in Paris. The 80,000-seat Stade de France, built for the 1998 FIFA World Cup, is located just north of Paris in the neighbouring commune of Saint-Denis. Paris hosts the annual French Open Grand Slam tennis tournament on the red clay of Roland Garros. The city hosted the Olympic Games in 1900, 1924 and will host the 2024 Summer Olympics. The 1938 and 1998 FIFA World Cups, the 2007 Rugby World Cup, as well as the 1960, 1984 and 2016 UEFA European Championships were also held in the city. Every July, the Tour de France bicycle race finishes on the Avenue des Champs-Élysées in Paris. (Wikipedia)
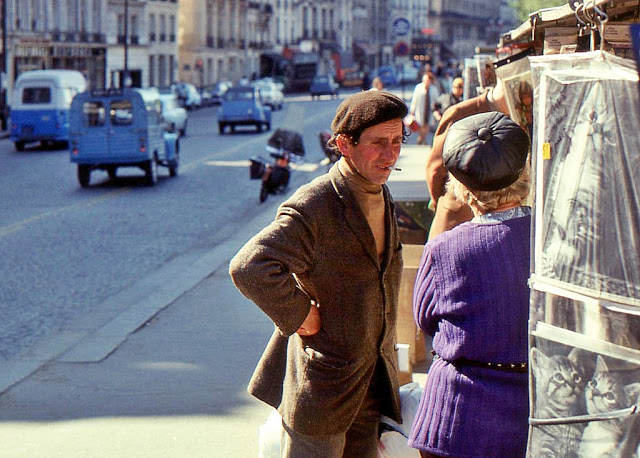
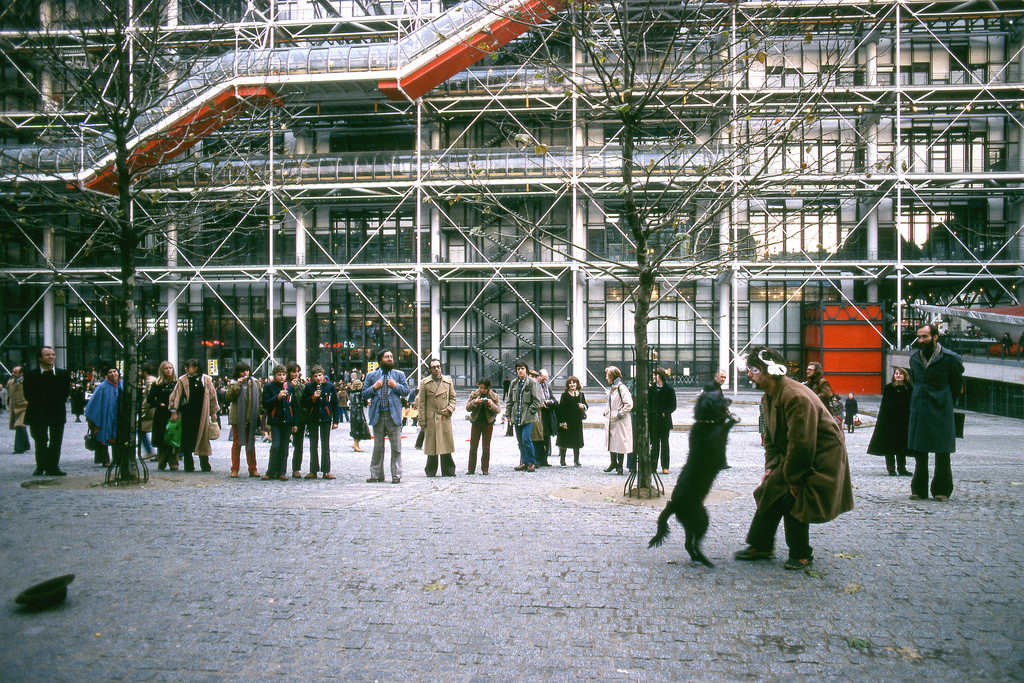
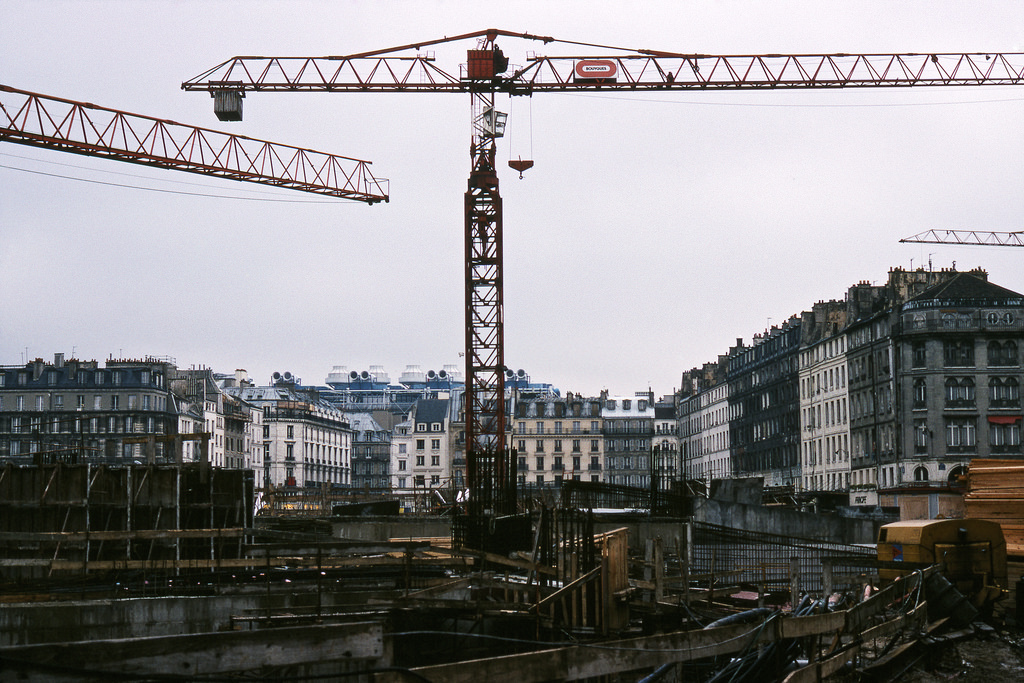
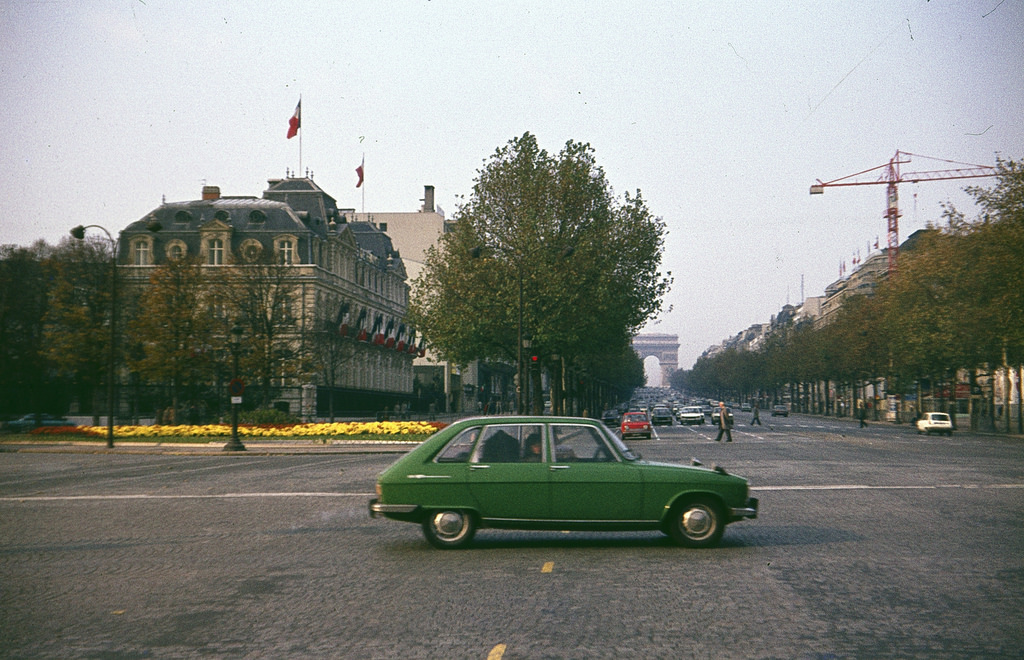
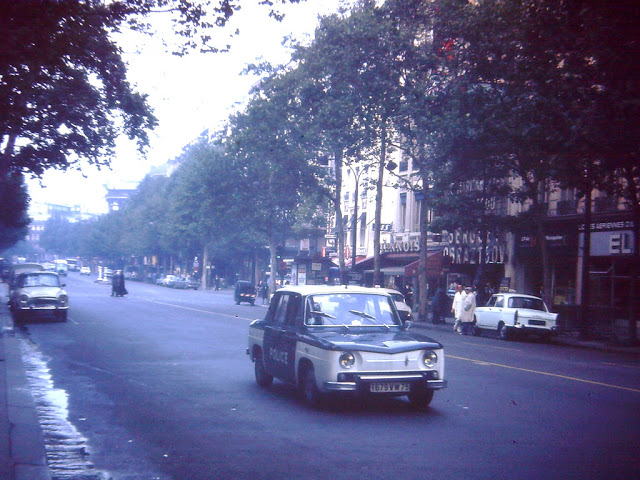
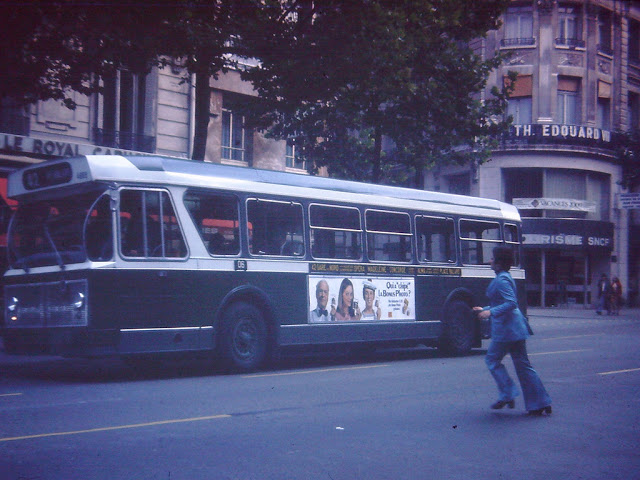
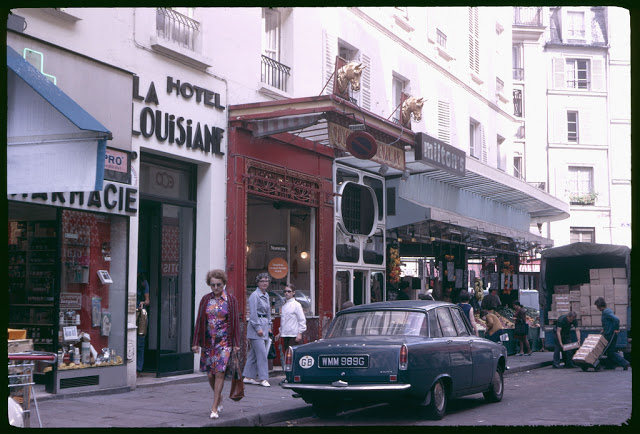
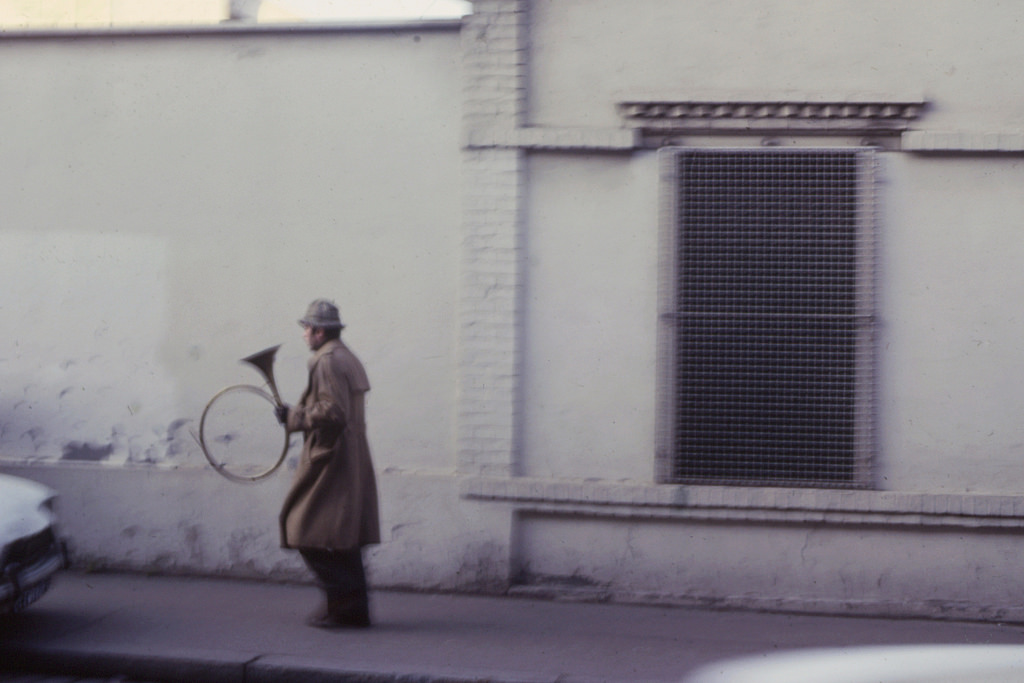
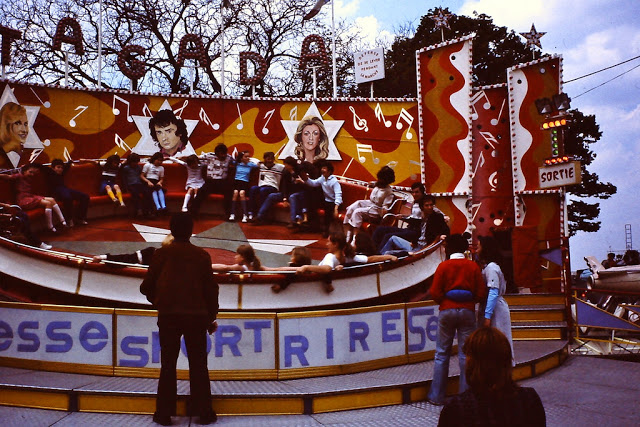
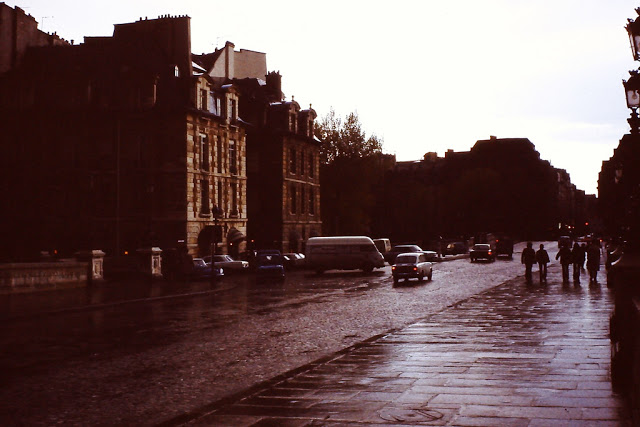
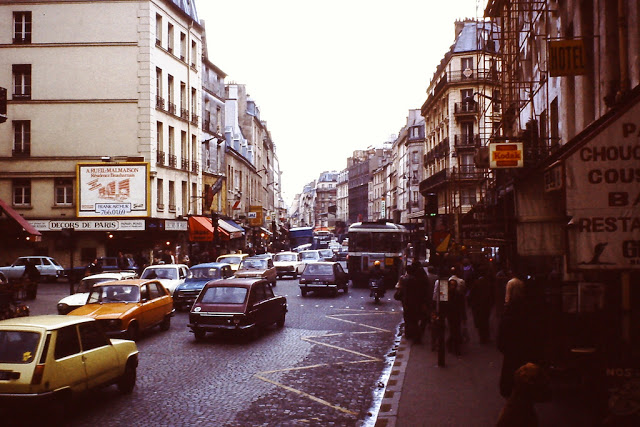
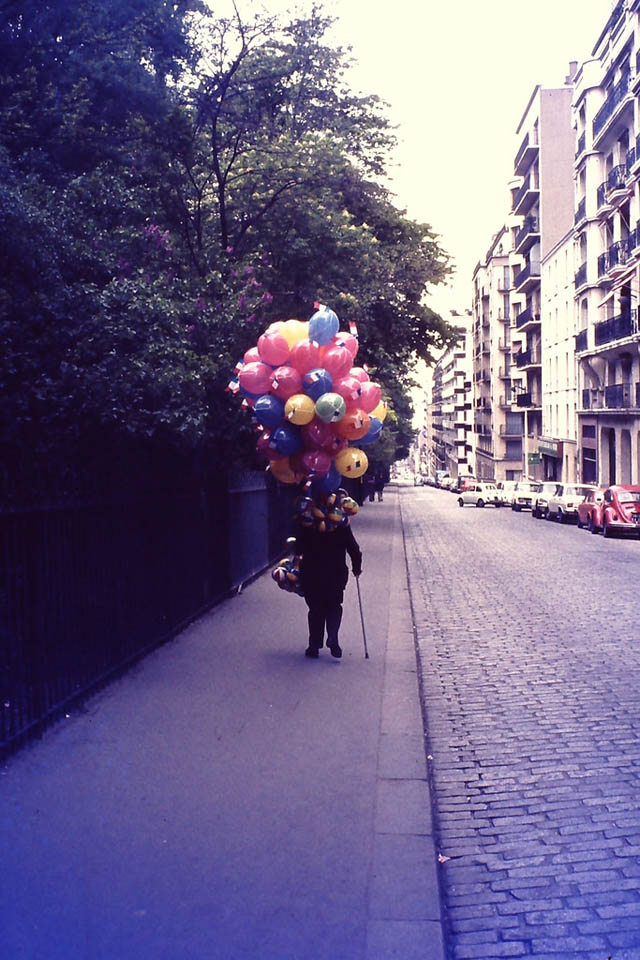










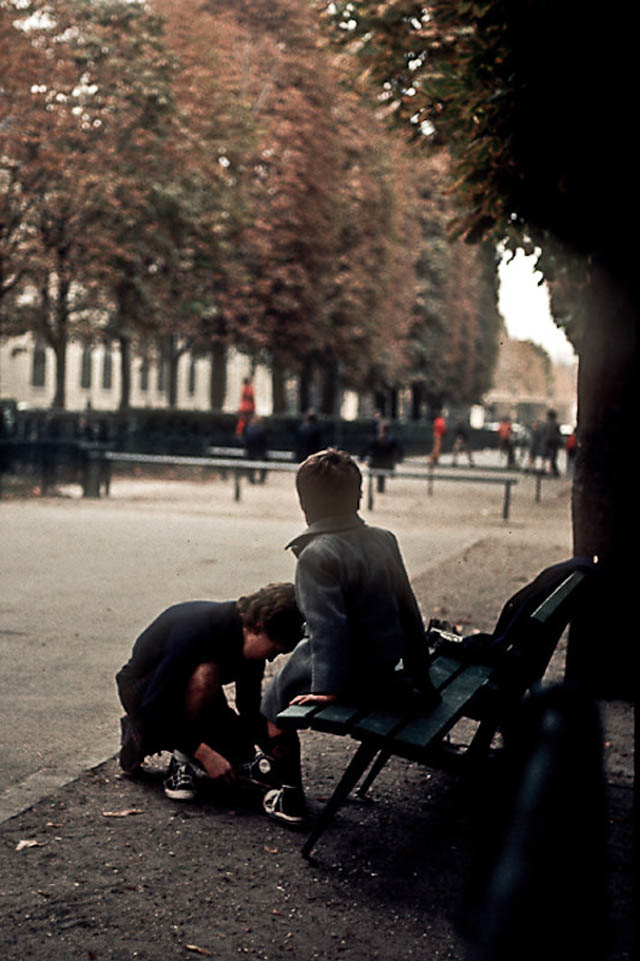


























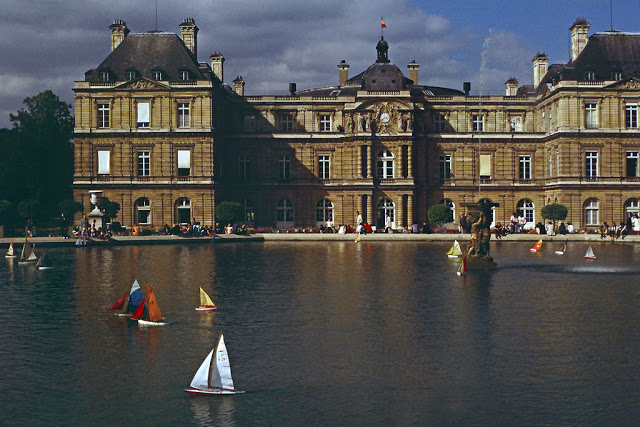







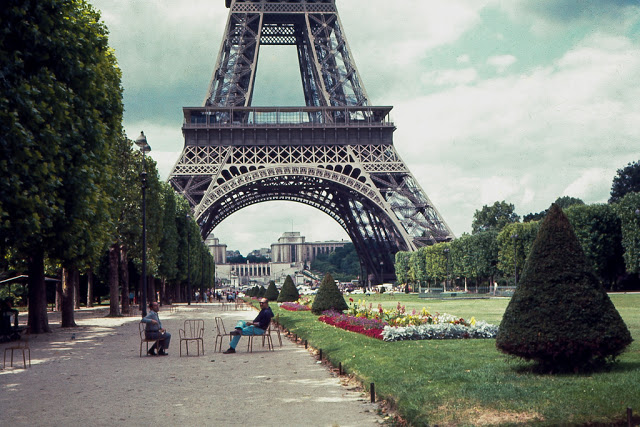



































New Zealand (Maori: Aotearoa) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island (Te Ika-a-Maui) and the South Island (Te Waipounamu)—and over 700 smaller islands, covering a total area of 268,021 square kilometres (103,500 sq mi). New Zealand is about 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country’s varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand’s capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland.
Owing to their remoteness, the islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable landmass to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Maori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Maori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi, which declared British sovereignty over the islands. In 1841, New Zealand became a colony within the British Empire, and in 1907 it became a dominion; it gained full statutory independence in 1947, and the British monarch remained the head of state. Today, the majority of New Zealand’s population of 5 million is of European descent; the indigenous Maori are the largest minority, followed by Asians and Pacific Islanders. Reflecting this, New Zealand’s culture is mainly derived from Maori and early British settlers, with recent broadening of culture arising from increased immigration. The official languages are Maori and New Zealand Sign Language, with English being dominant and a de facto official language.
A developed country, New Zealand ranks highly in international comparisons of national performance, such as quality of life, education, protection of civil liberties, government transparency, and economic freedom. New Zealand underwent major economic changes during the 1980s, which transformed it from a protectionist to a liberalised free-trade economy. The service sector dominates the national economy, followed by the industrial sector, and agriculture. International tourism is also a significant source of revenue. Nationally, legislative authority is vested in an elected, unicameral Parliament, while executive political power is exercised by the Cabinet, led by the prime minister, currently Jacinda Ardern. Queen Elizabeth II is the country’s monarch and is represented by the governor-general. In addition, New Zealand is organised into 11 regional councils and 67 territorial authorities for local government purposes. The Realm of New Zealand also includes Tokelau (a dependent territory); the Cook Islands and Niue (self-governing states in free association with New Zealand); and the Ross Dependency, which is New Zealand’s territorial claim in Antarctica.
New Zealand is a member of the United Nations, Commonwealth of Nations, ANZUS, OECD, ASEAN Plus Six, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, the Pacific Community and the Pacific Islands Forum. (Wikipedia)
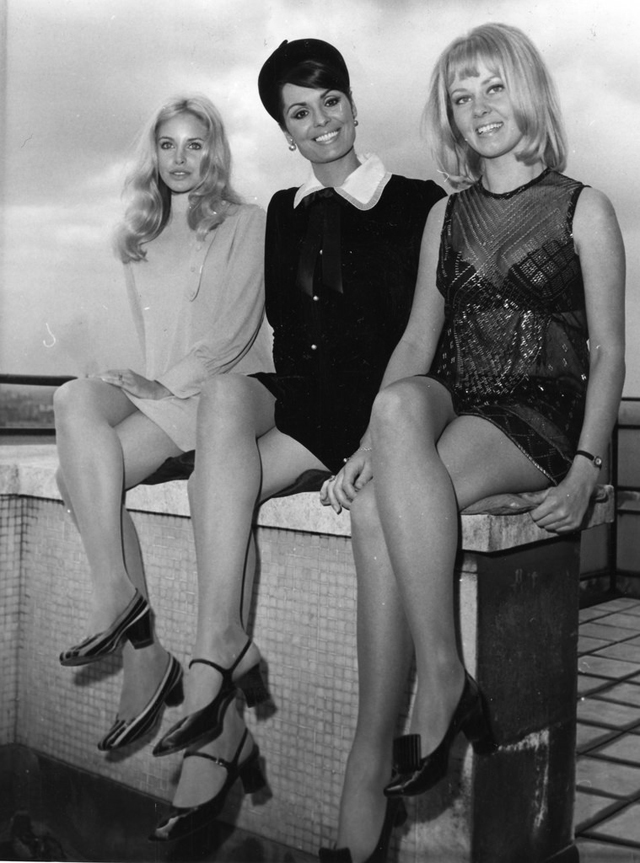
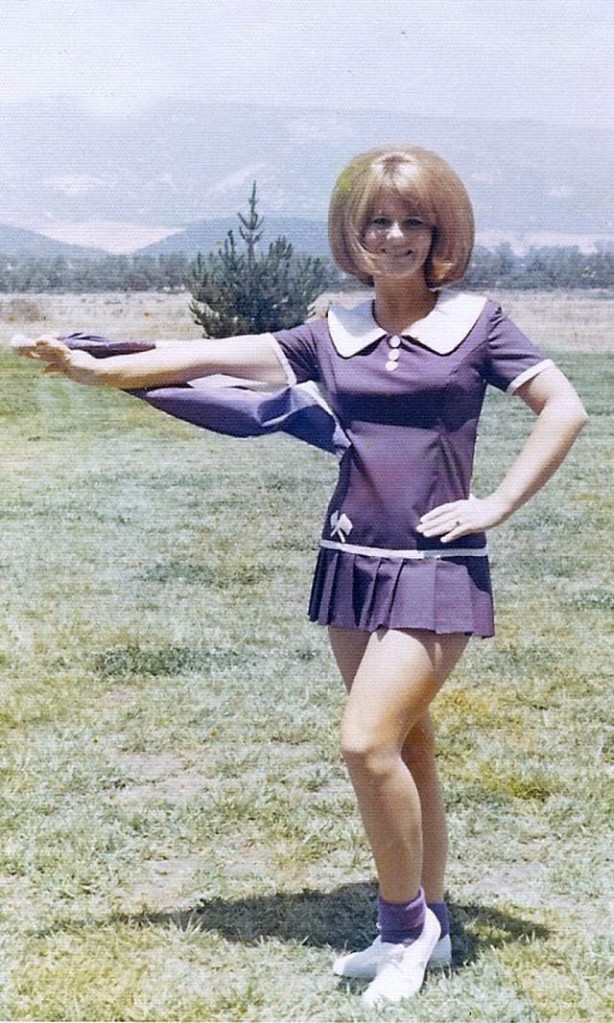
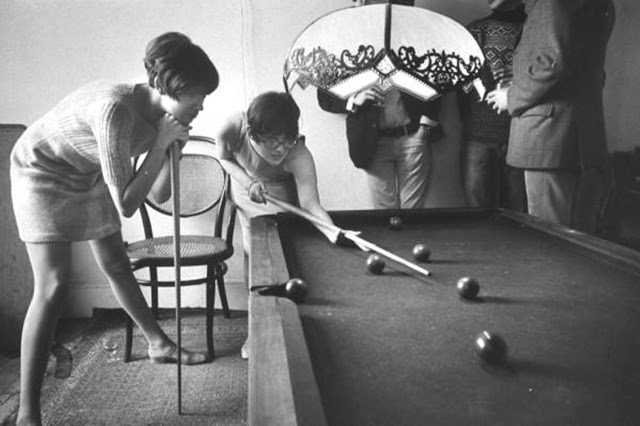
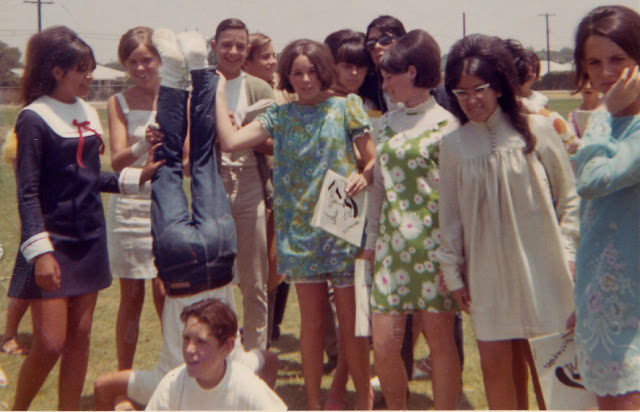
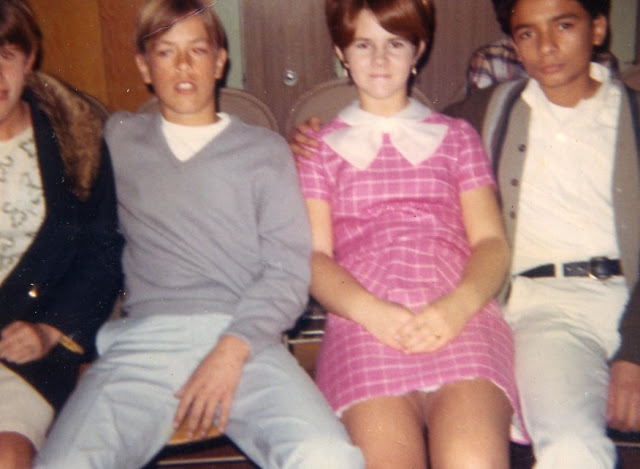
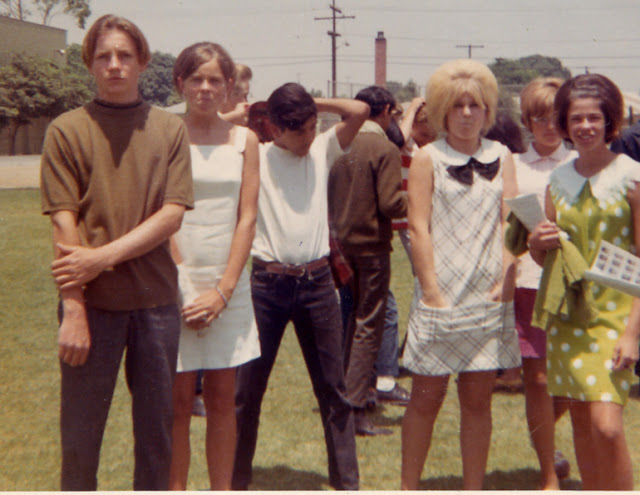
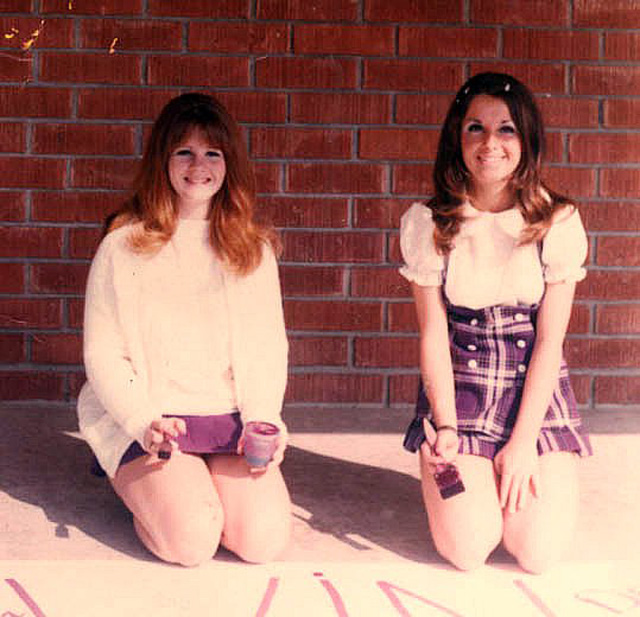
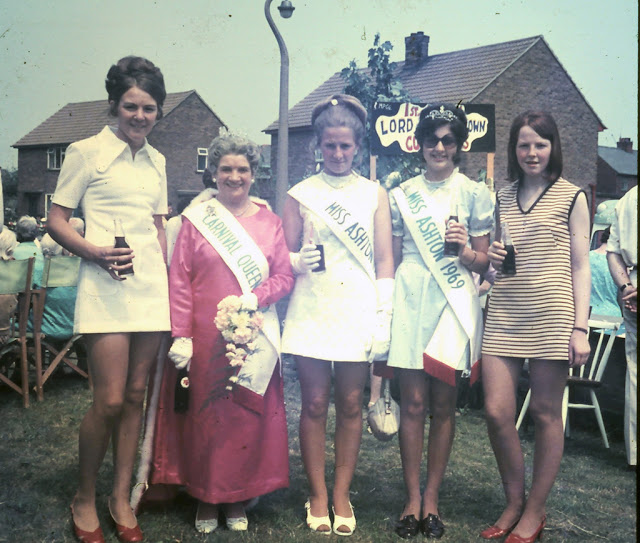
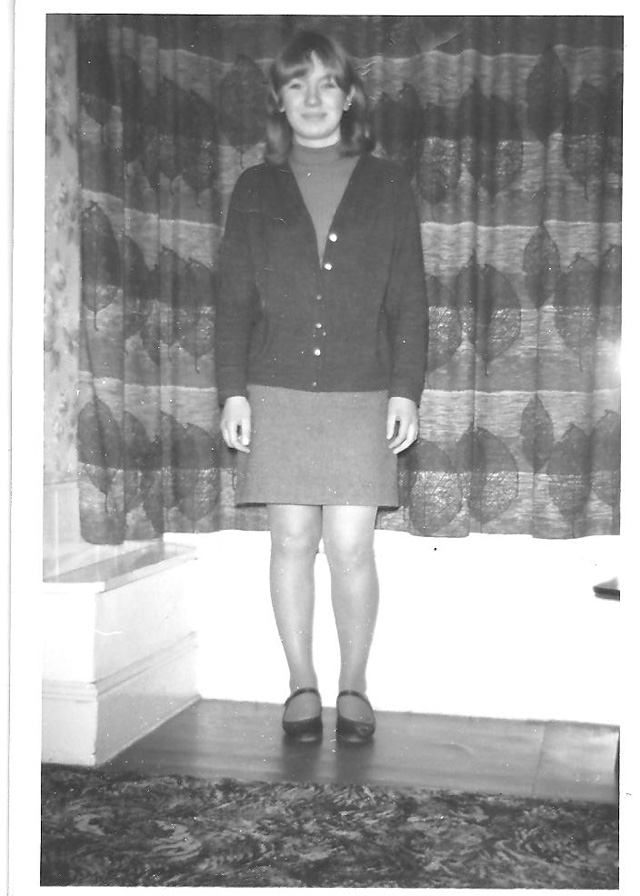
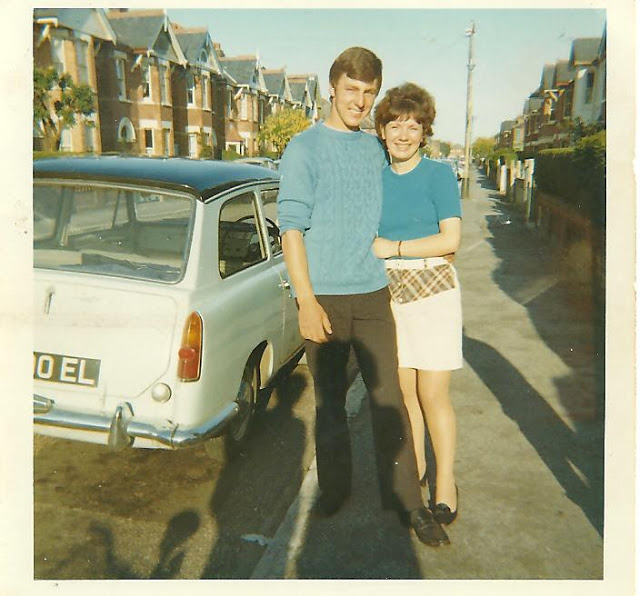
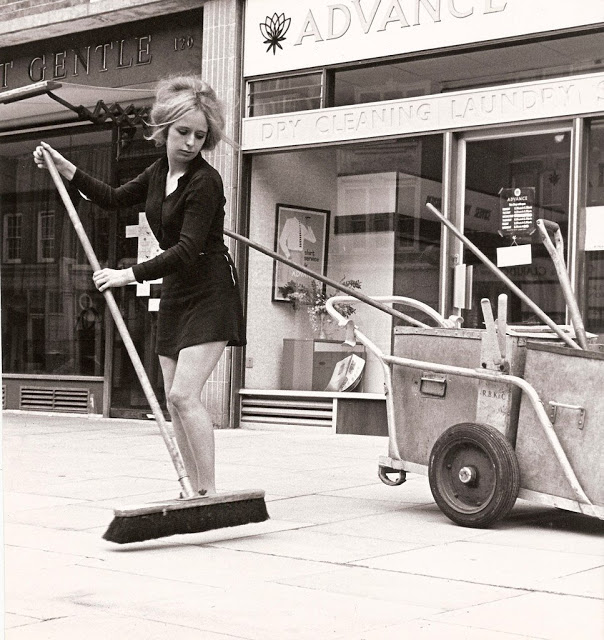
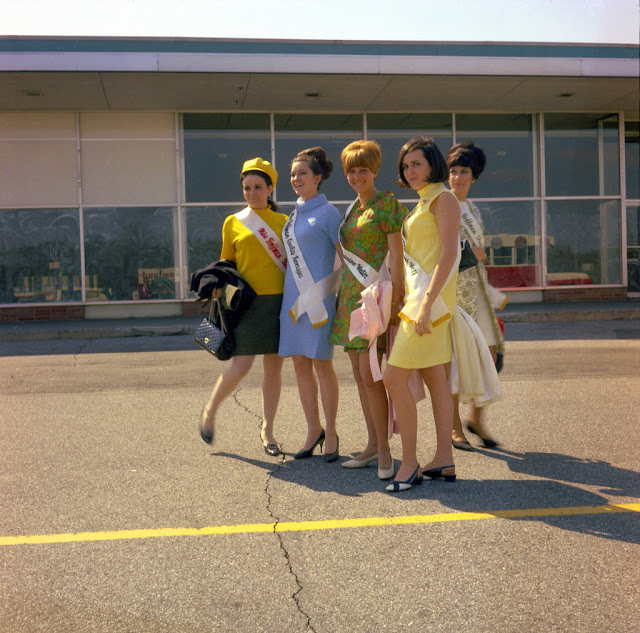
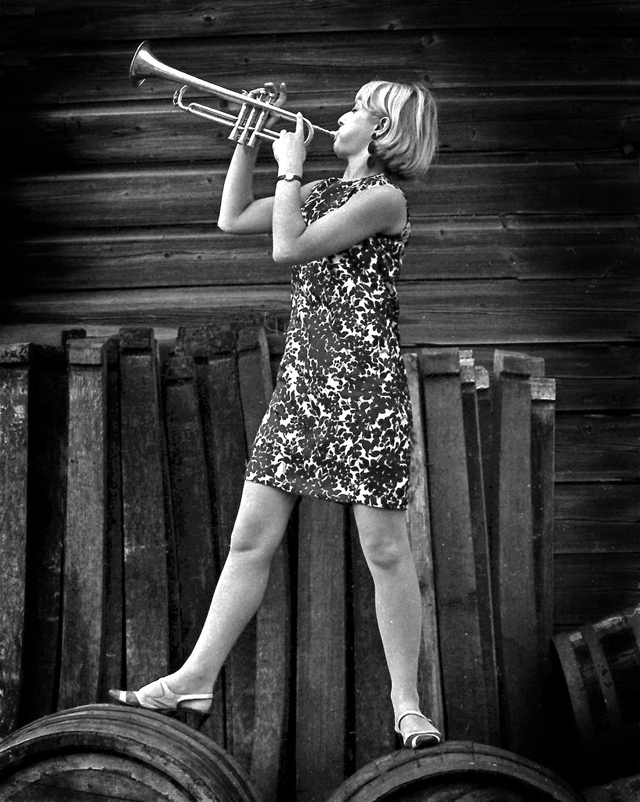
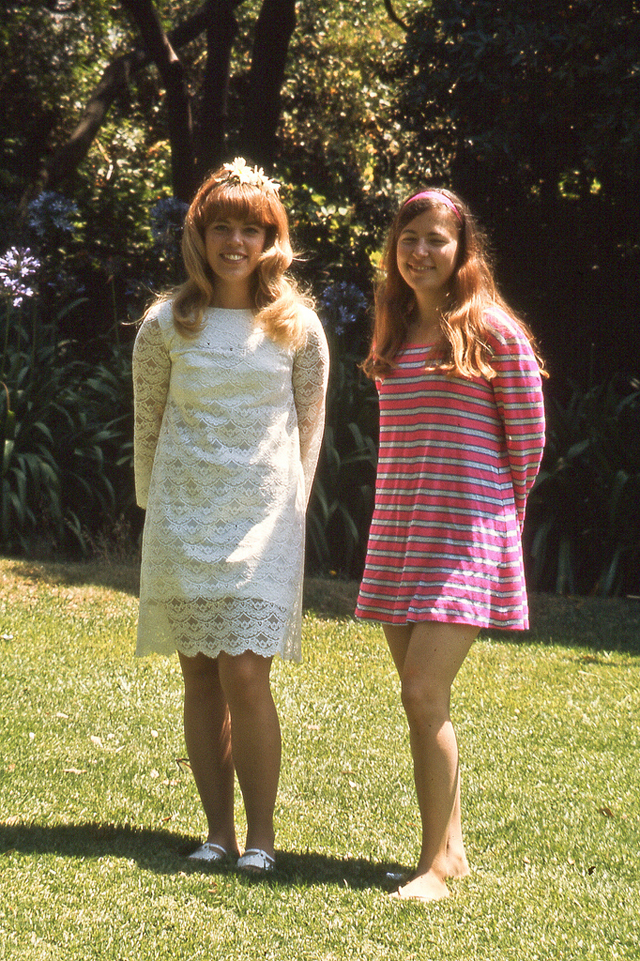
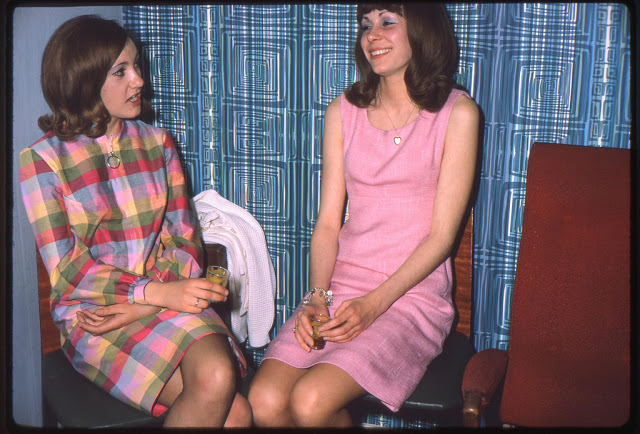
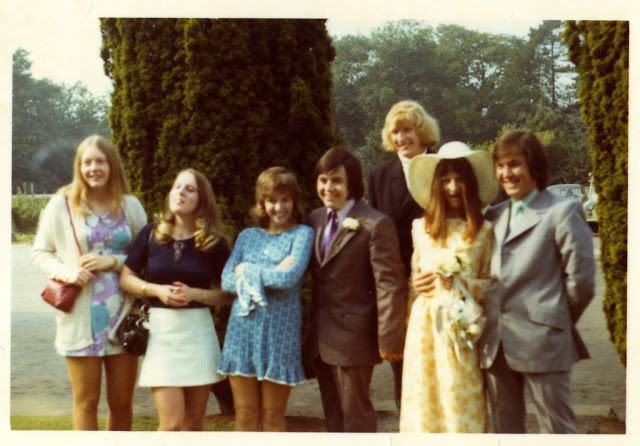
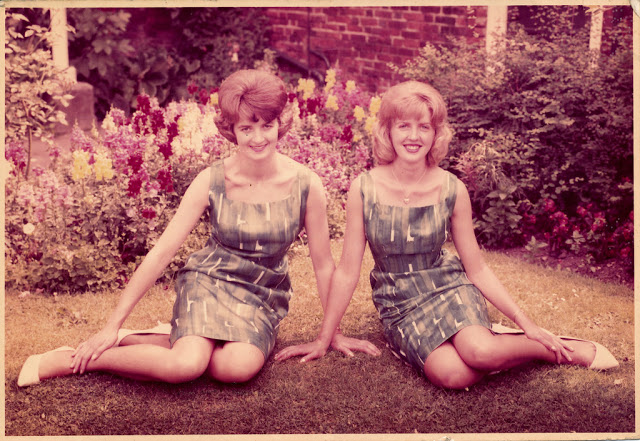
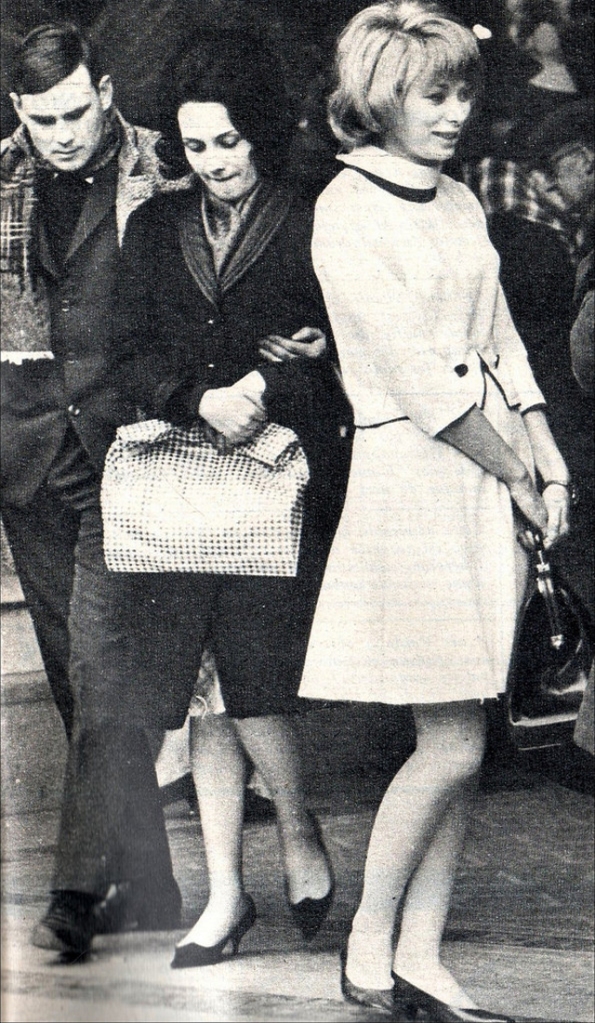
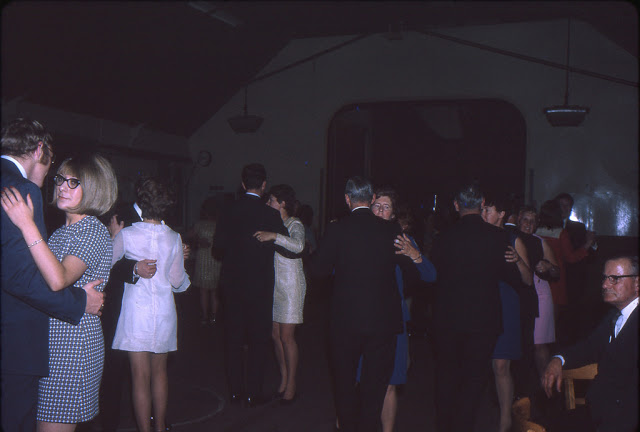
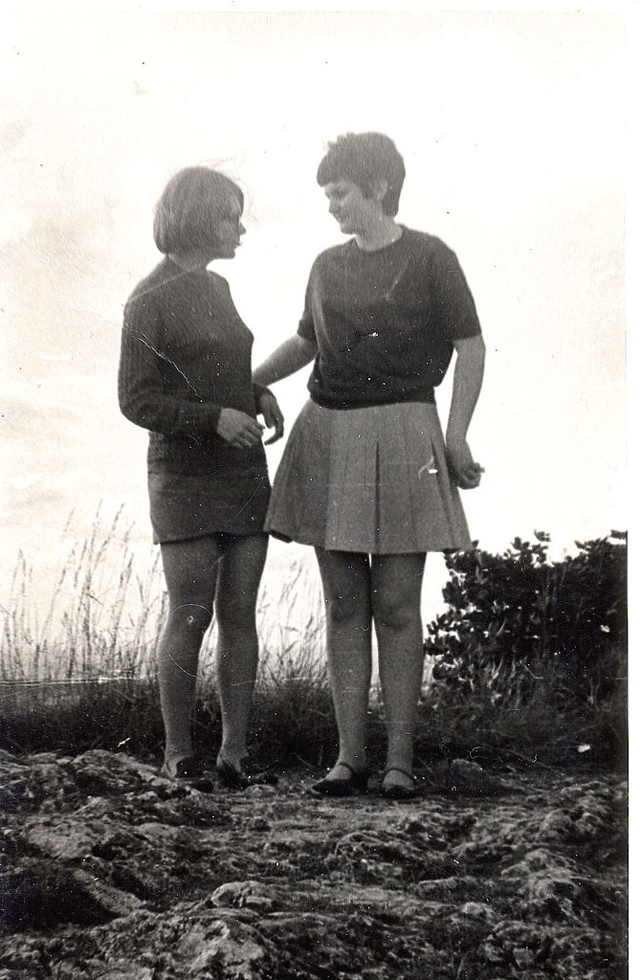
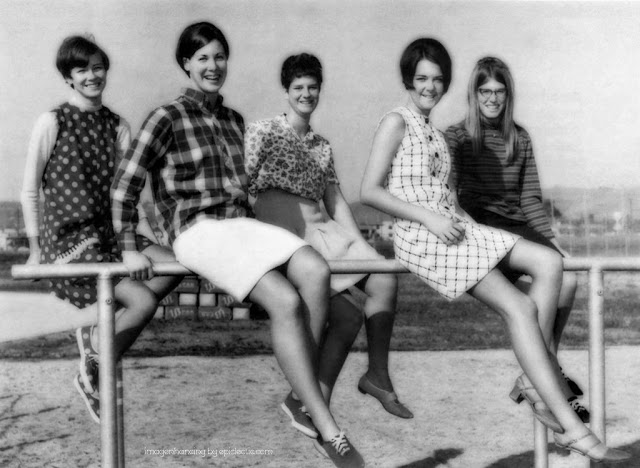
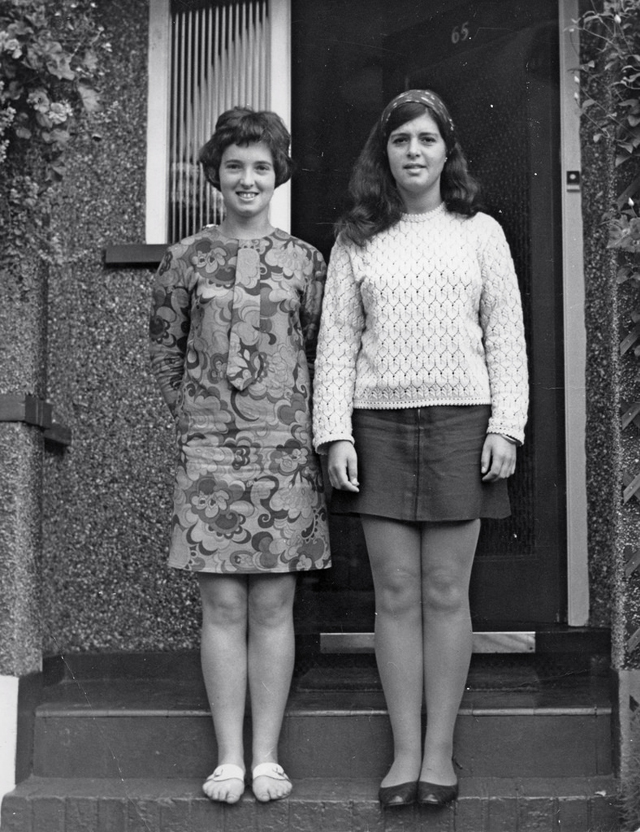
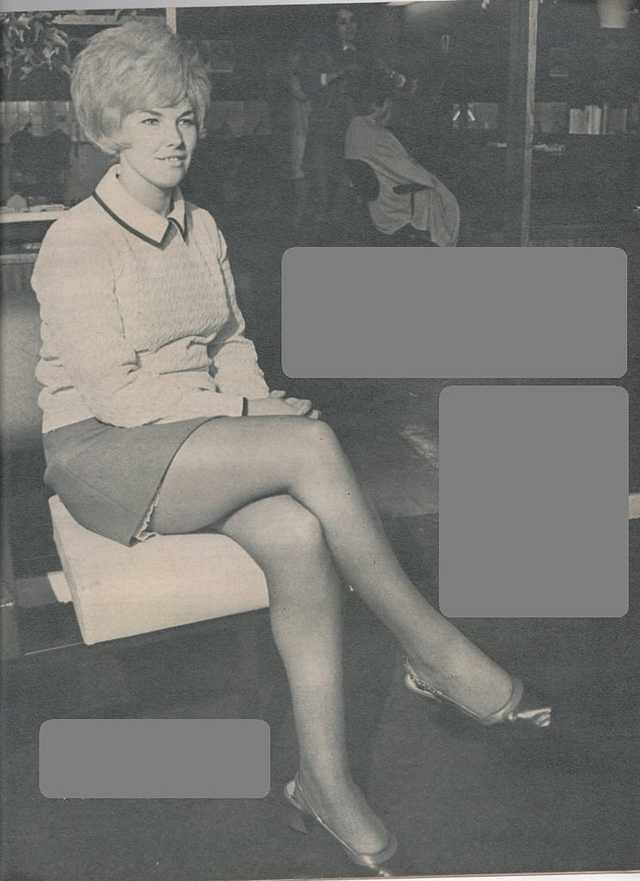
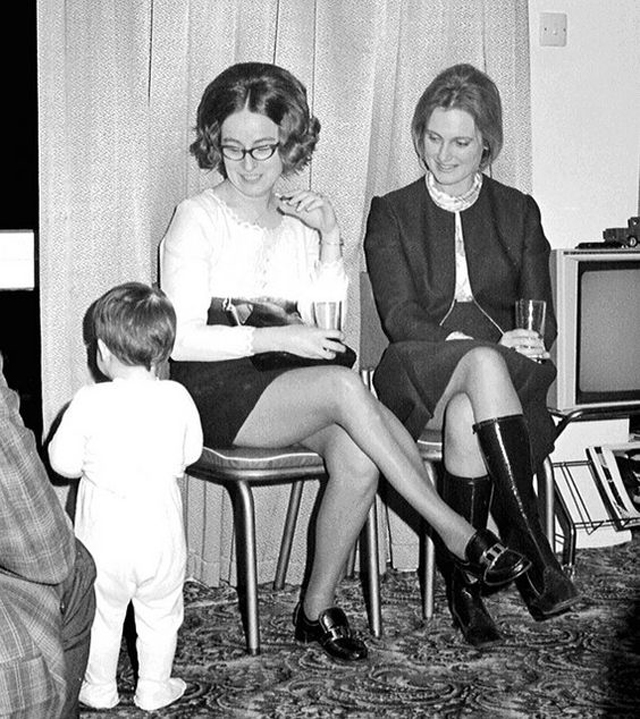
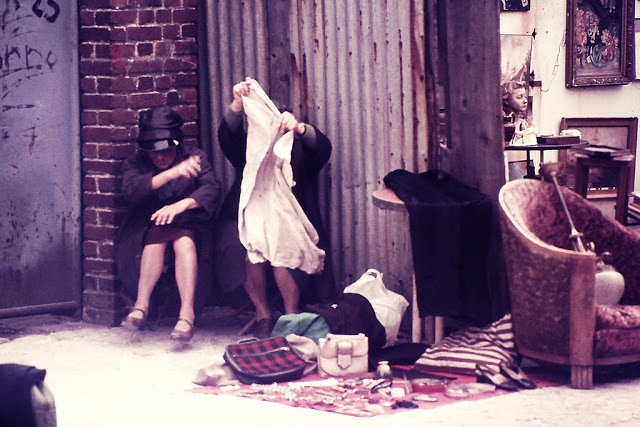
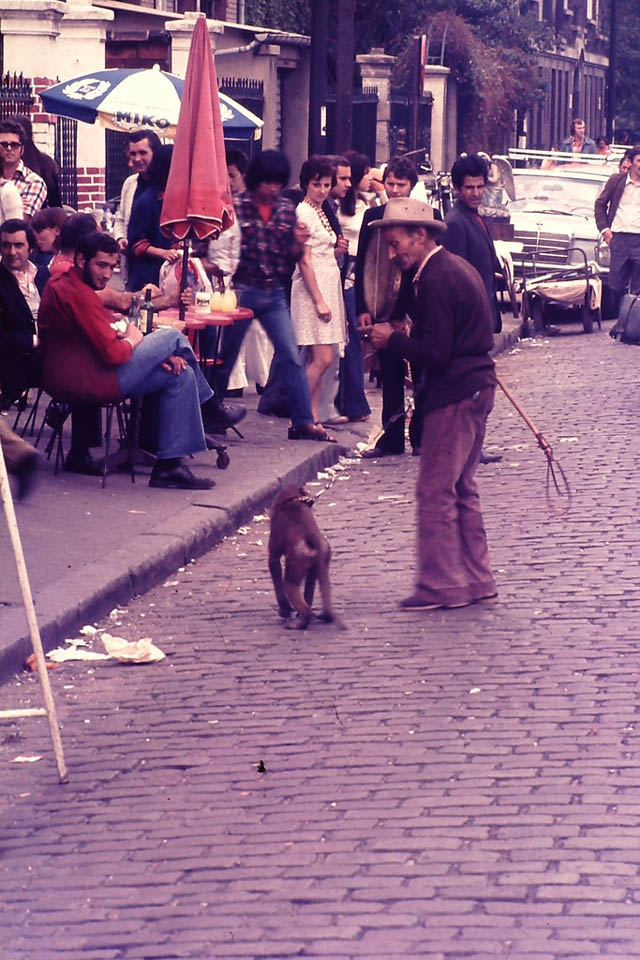
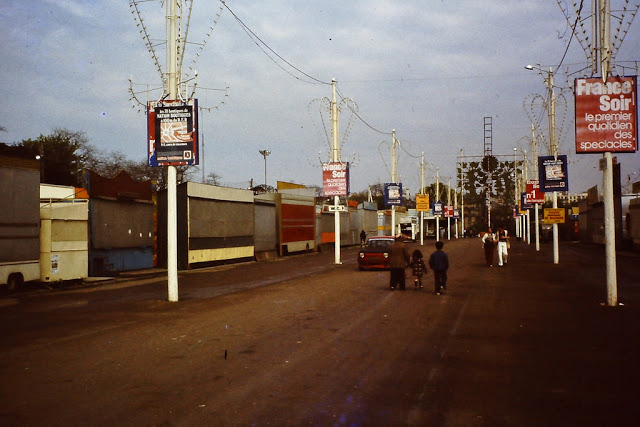
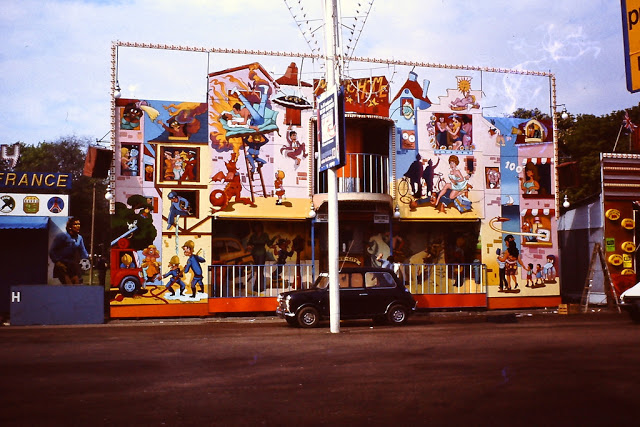
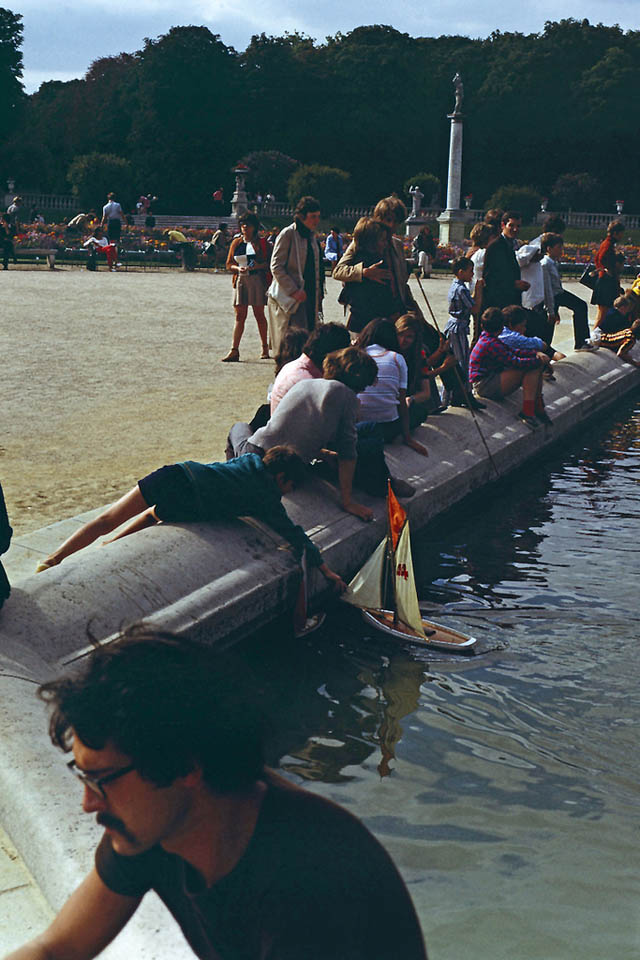
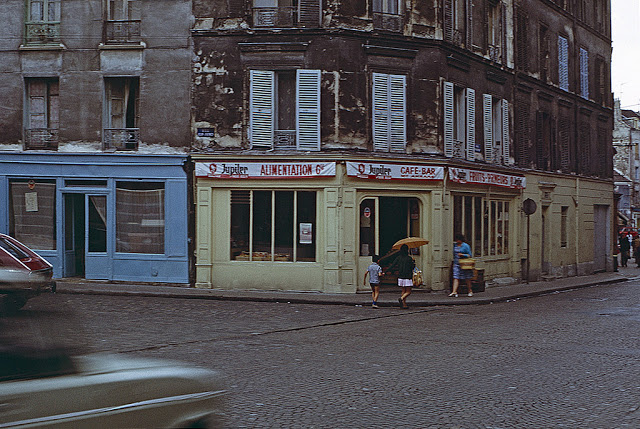
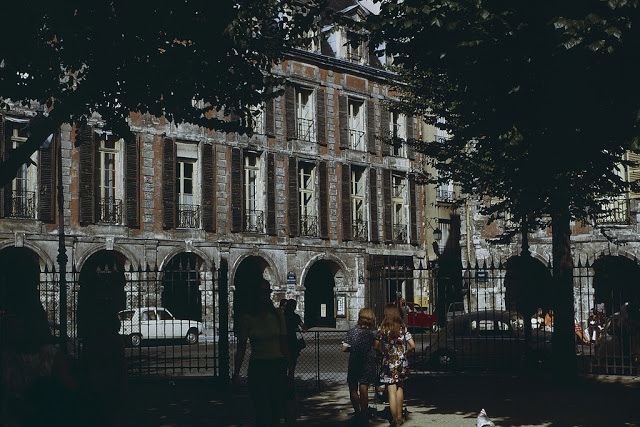
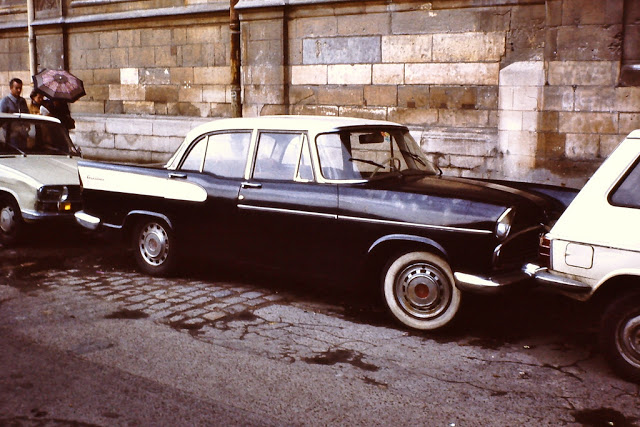
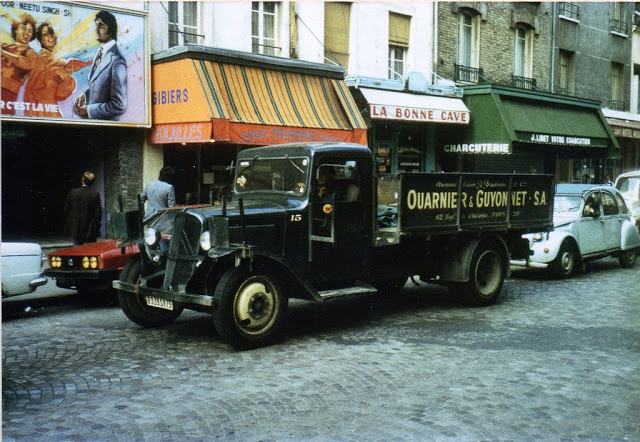
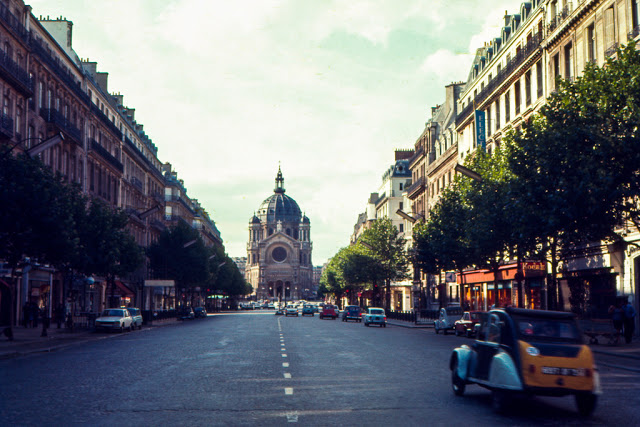
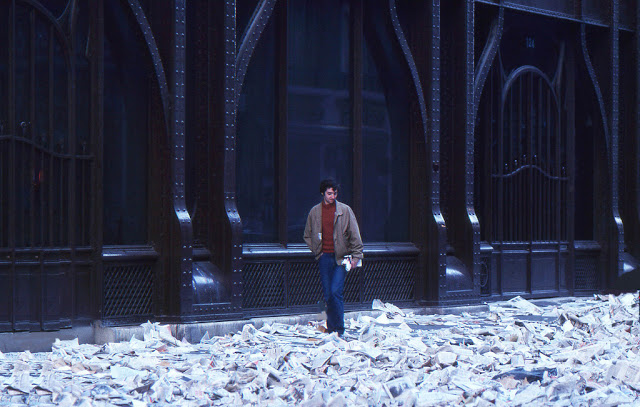
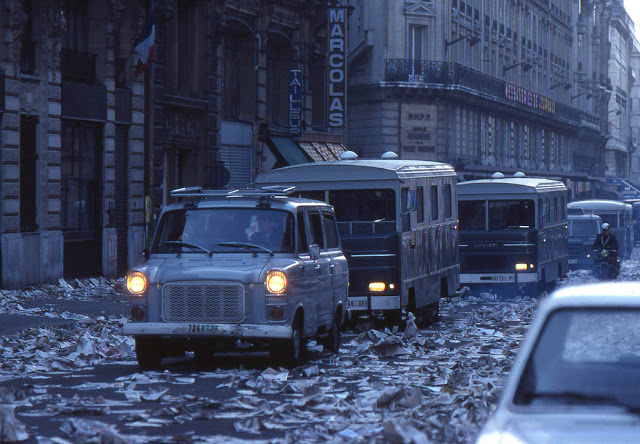
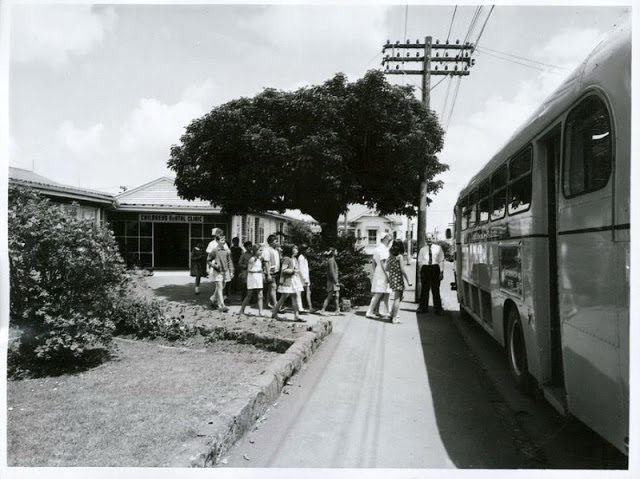
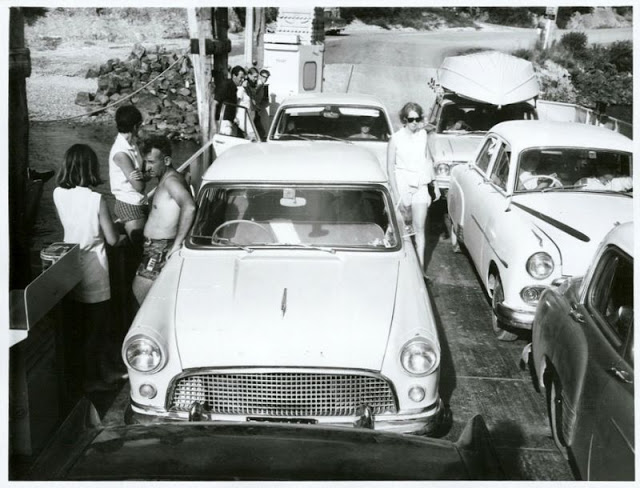
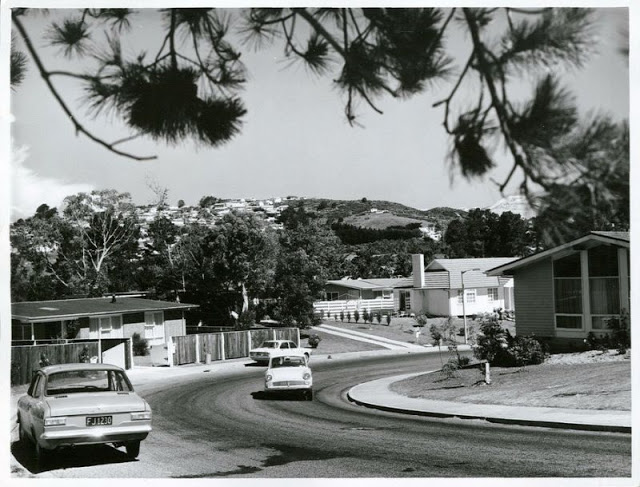
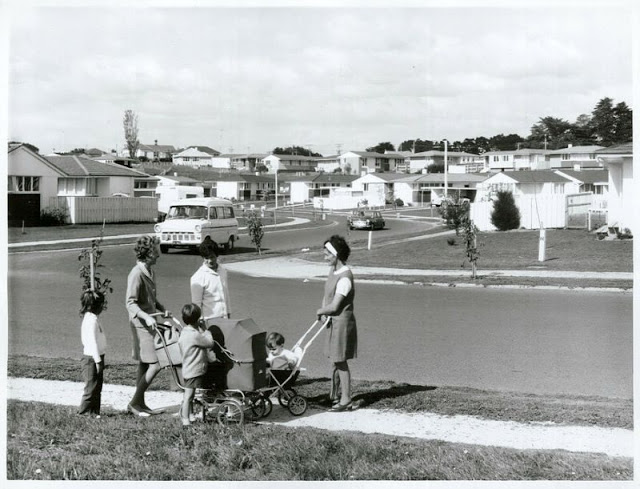
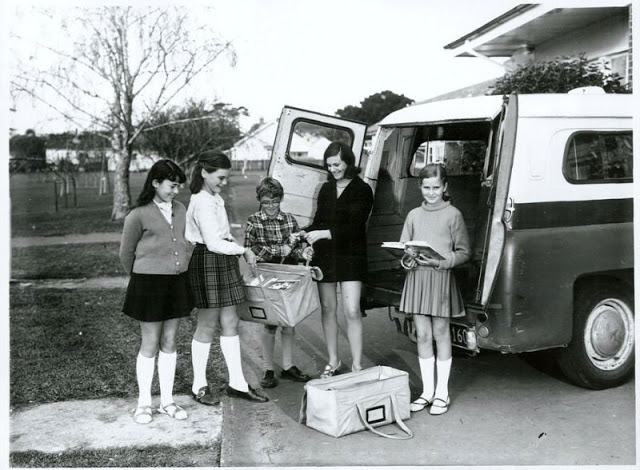
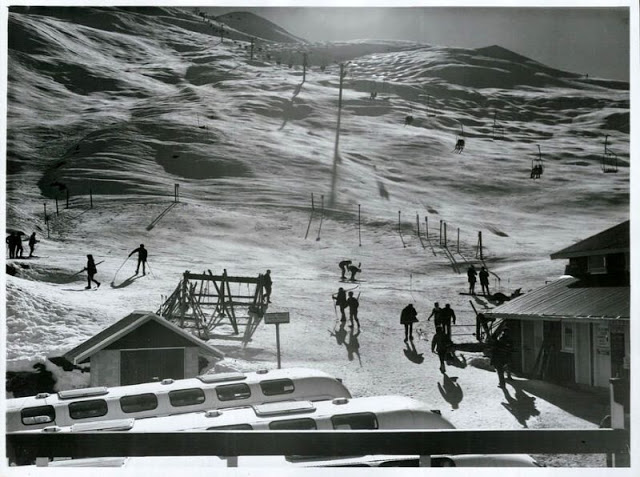
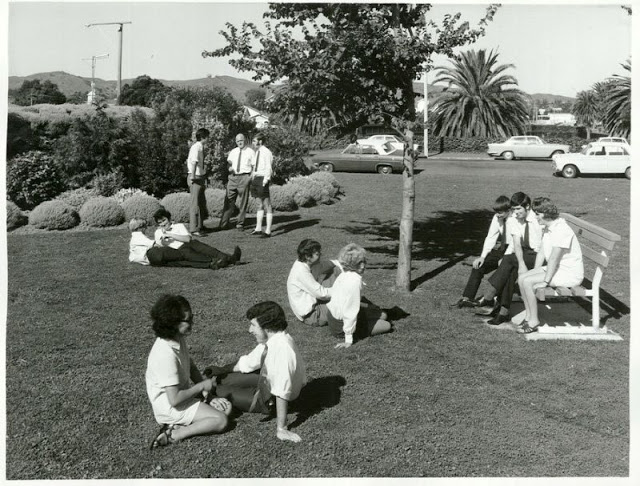
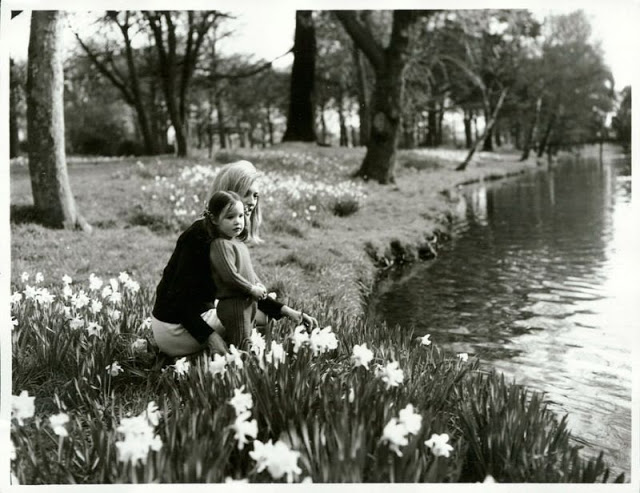
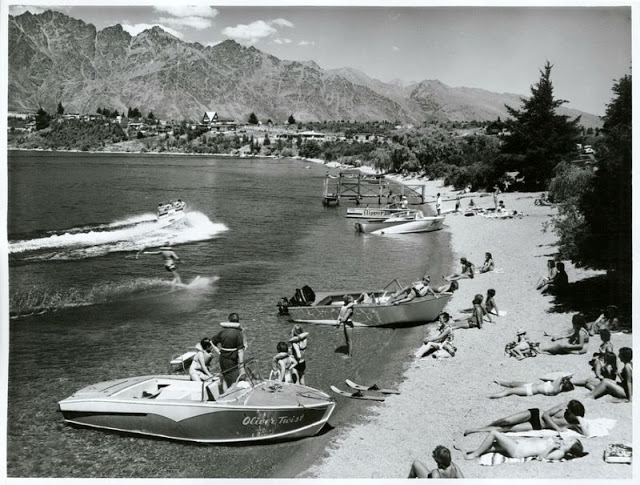
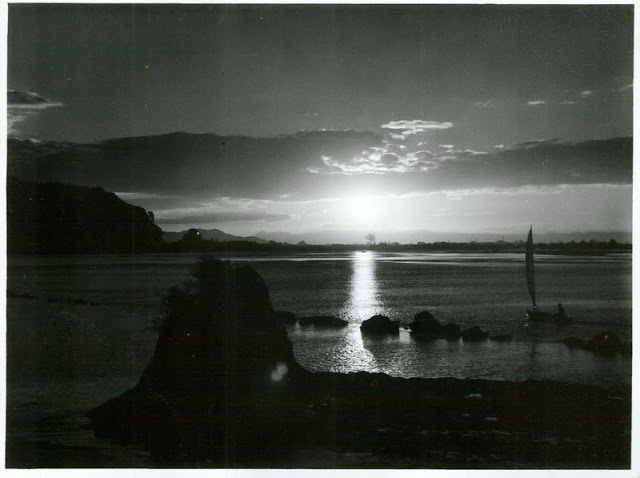
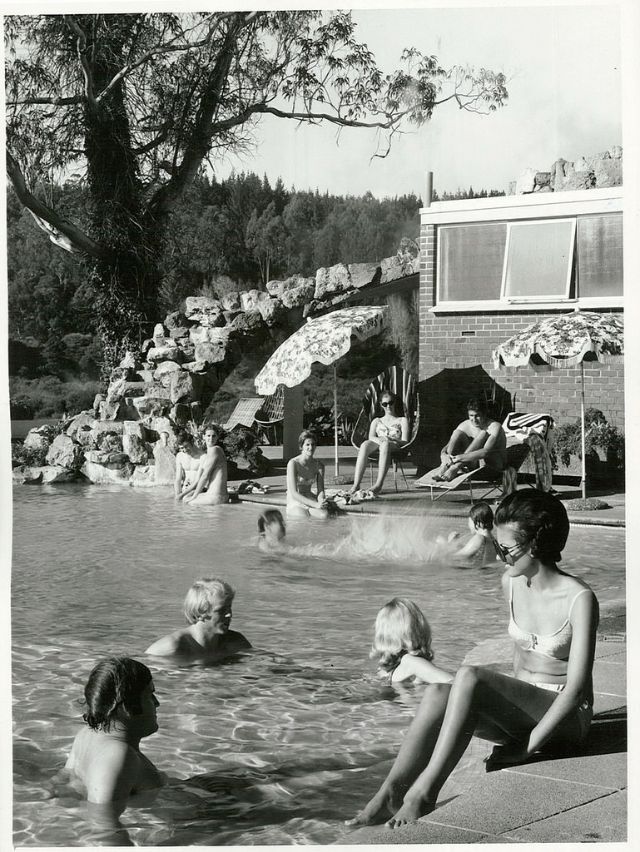
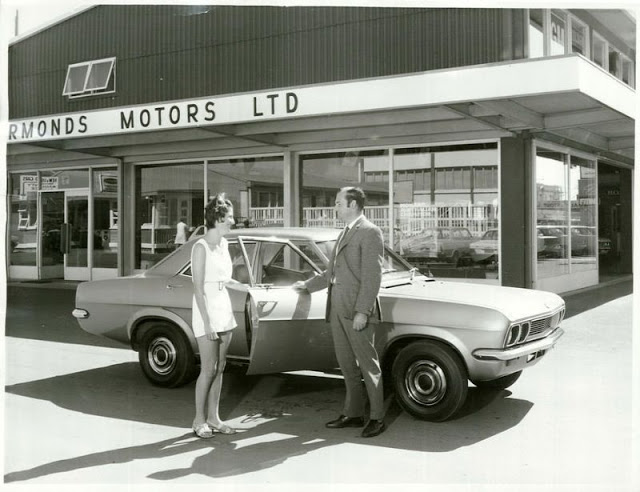
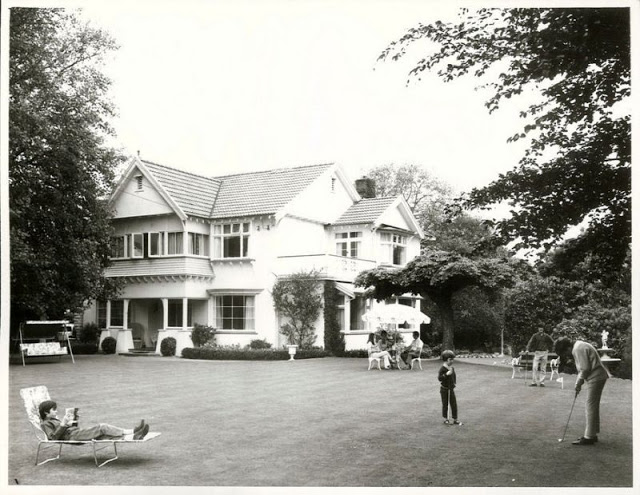
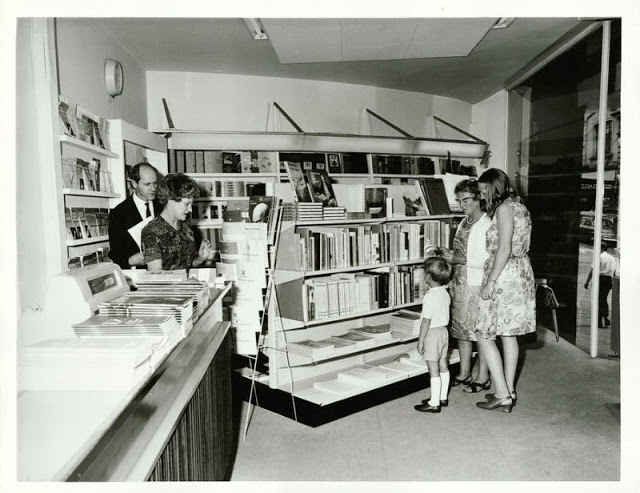
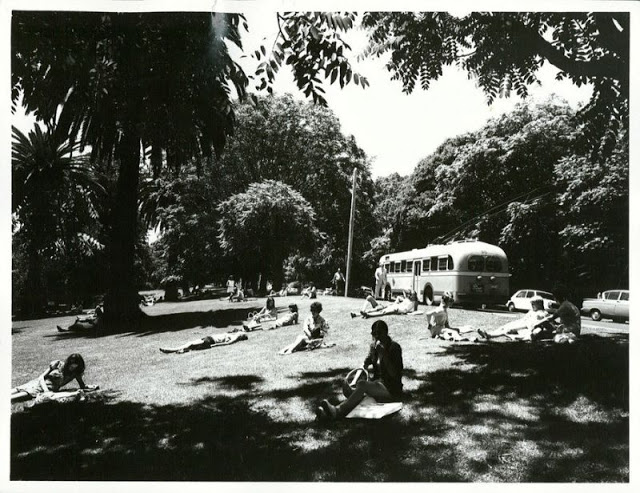
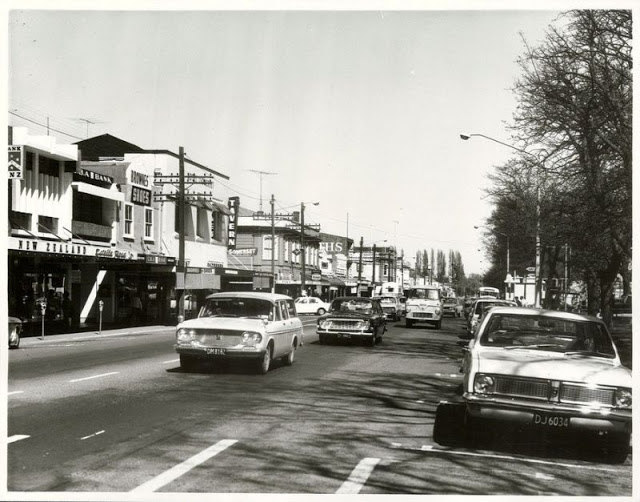
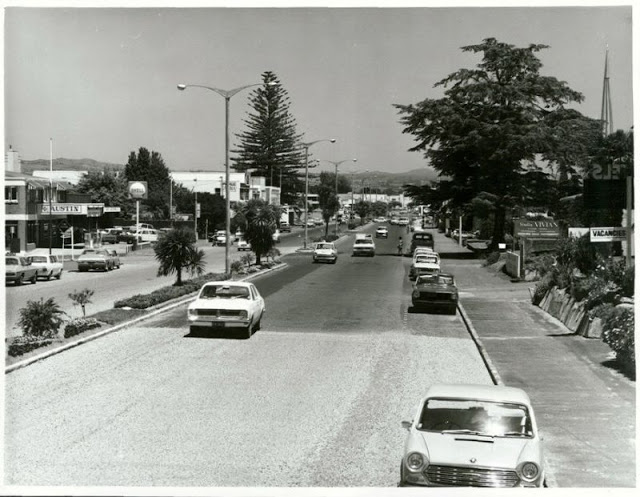
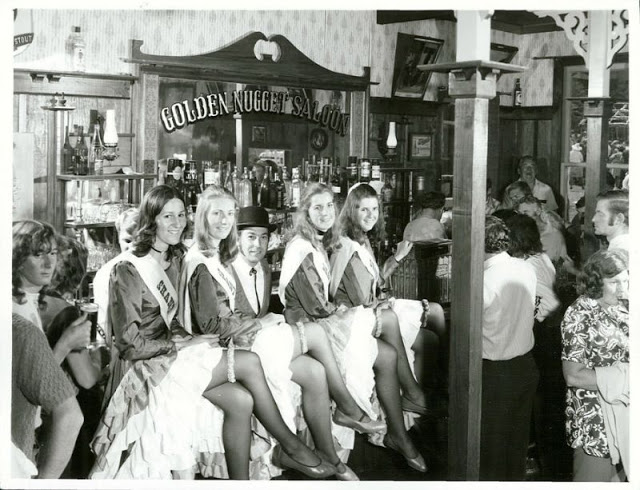
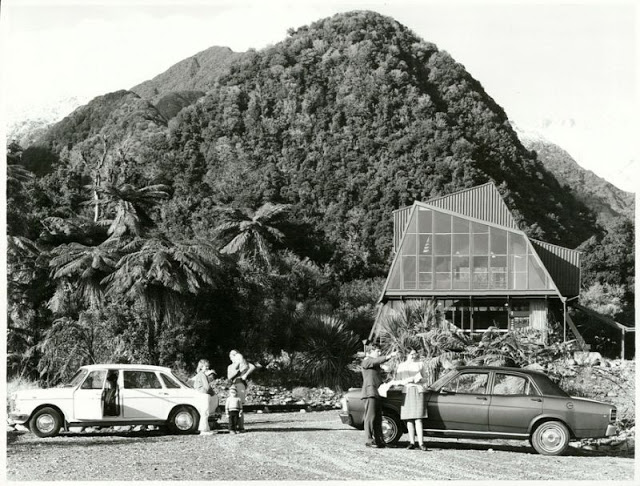
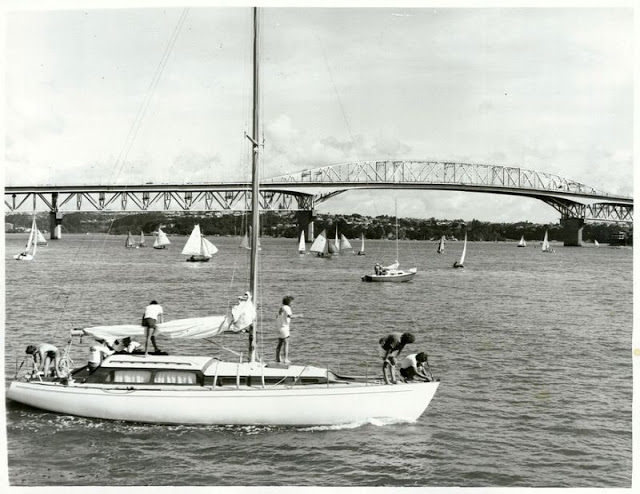
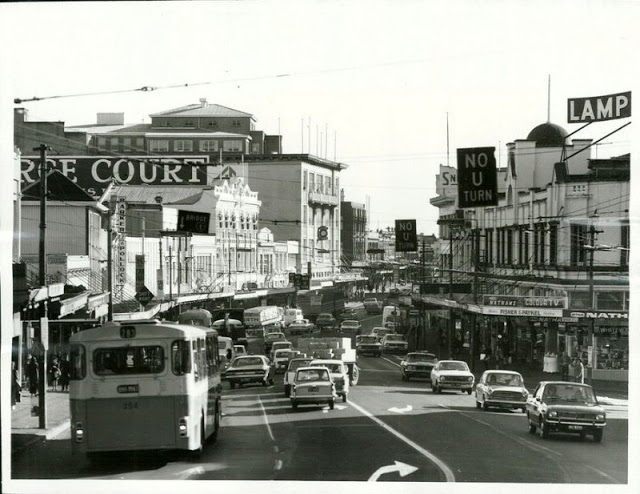
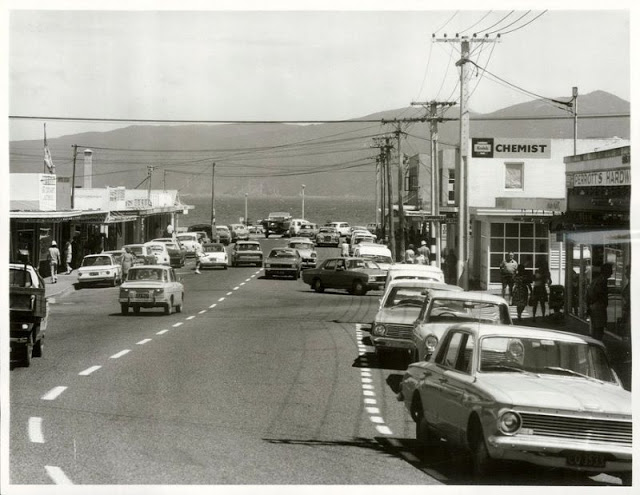
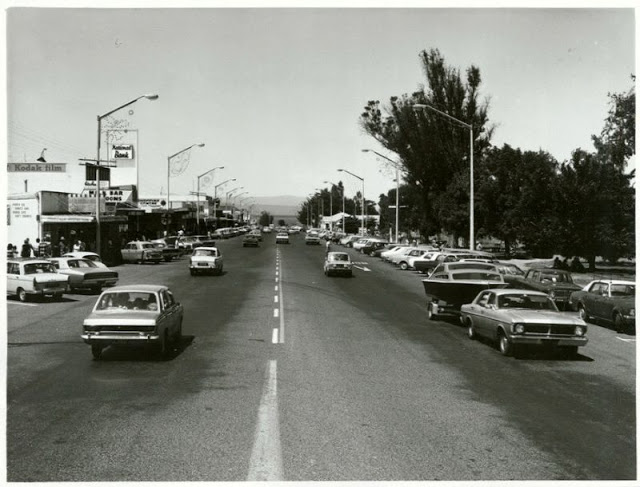
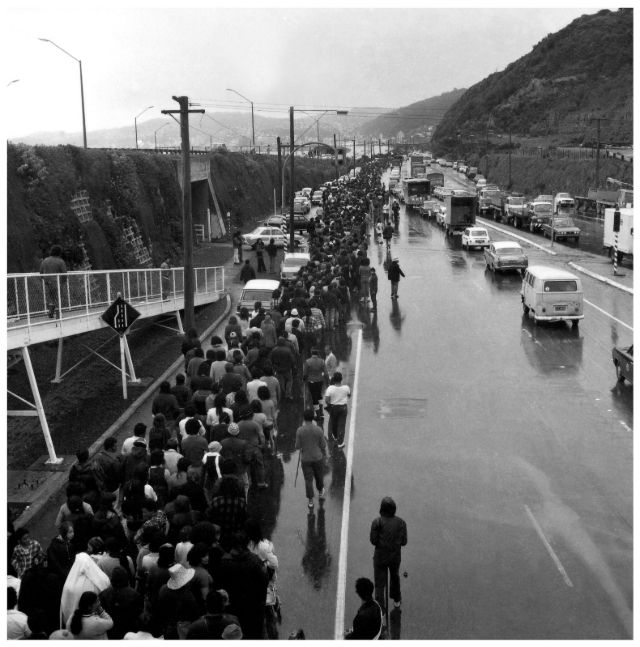
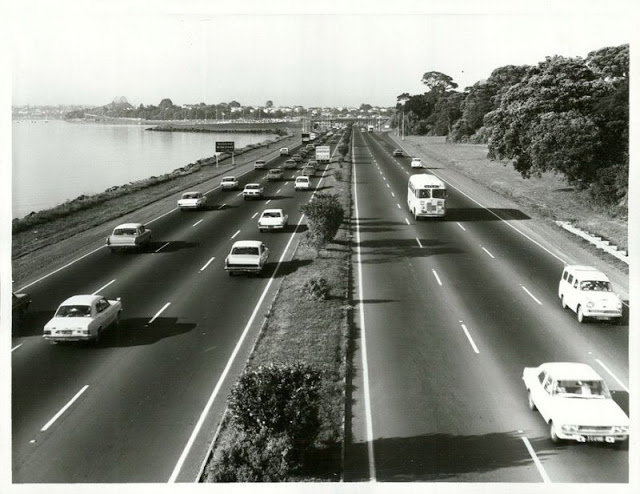
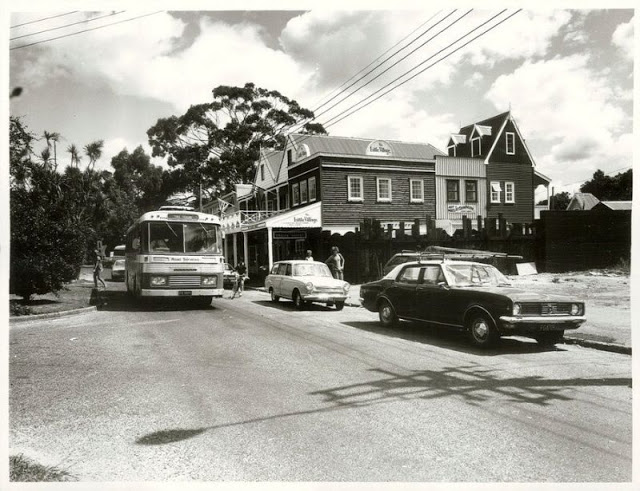
Take a look at these fascinating black and white photos from Archives New Zealand to see the beautiful life of this country in the early 1970s.
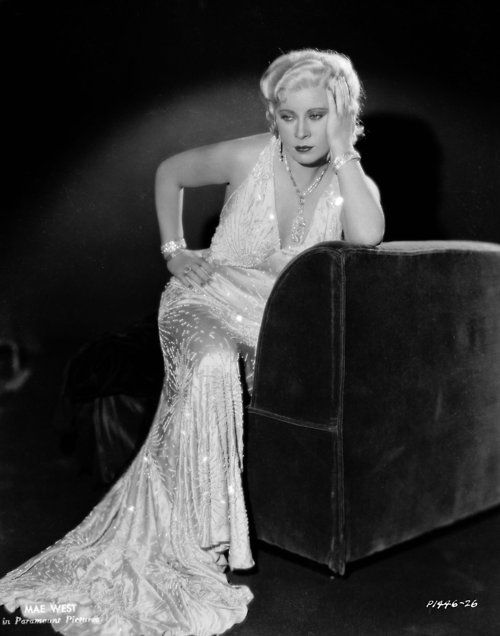
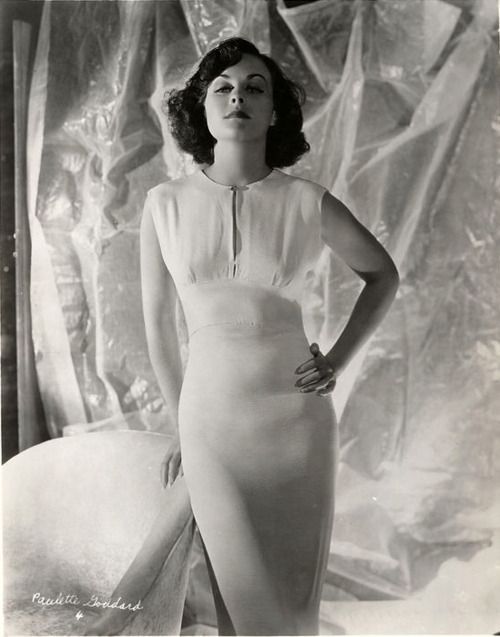
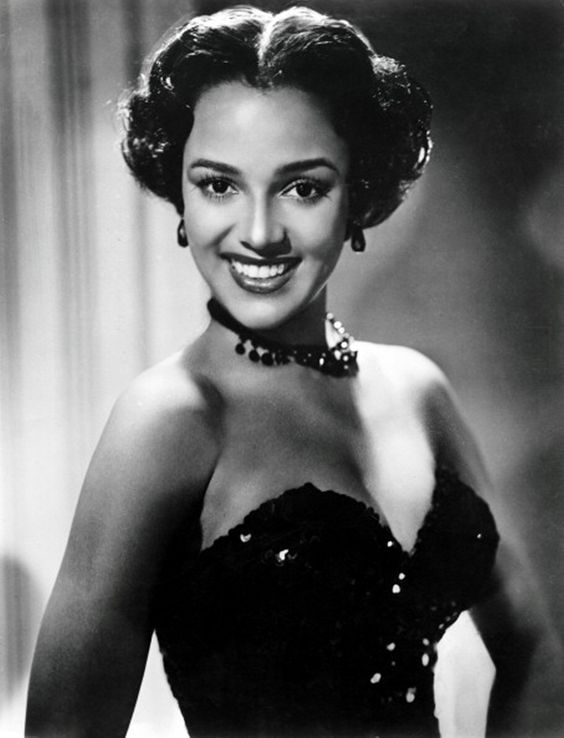
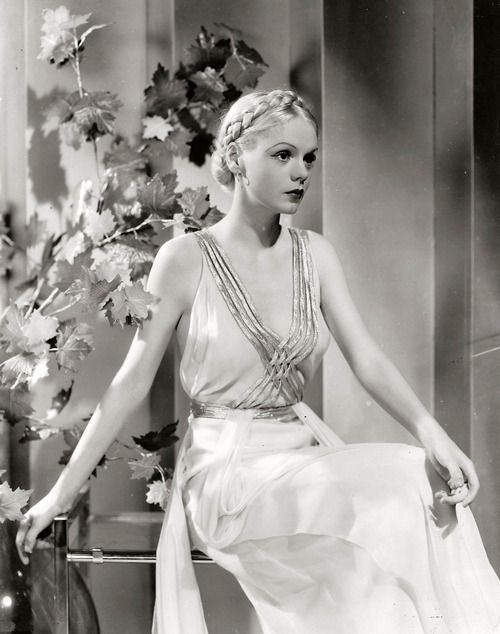
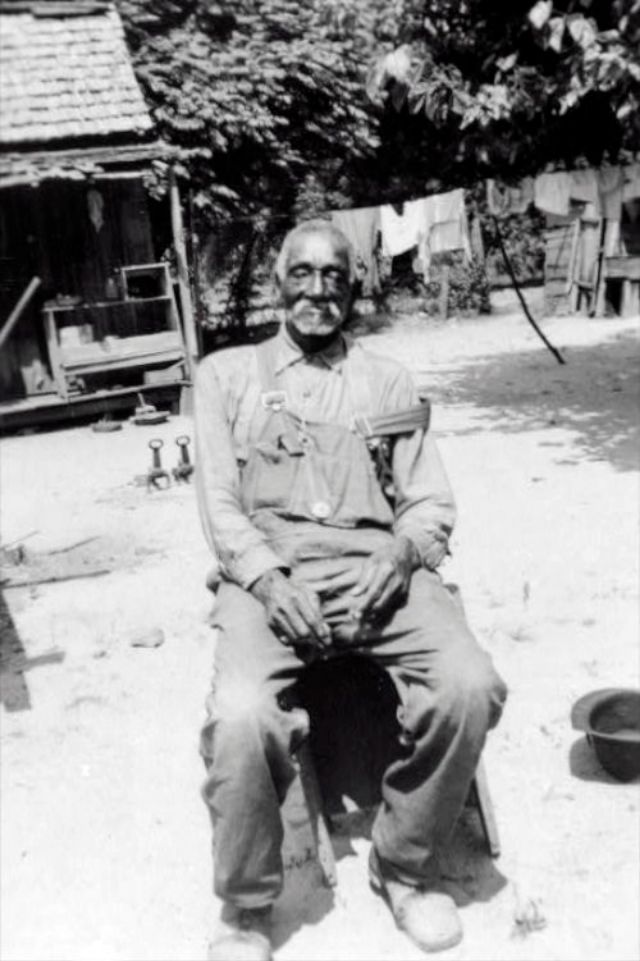

















































































































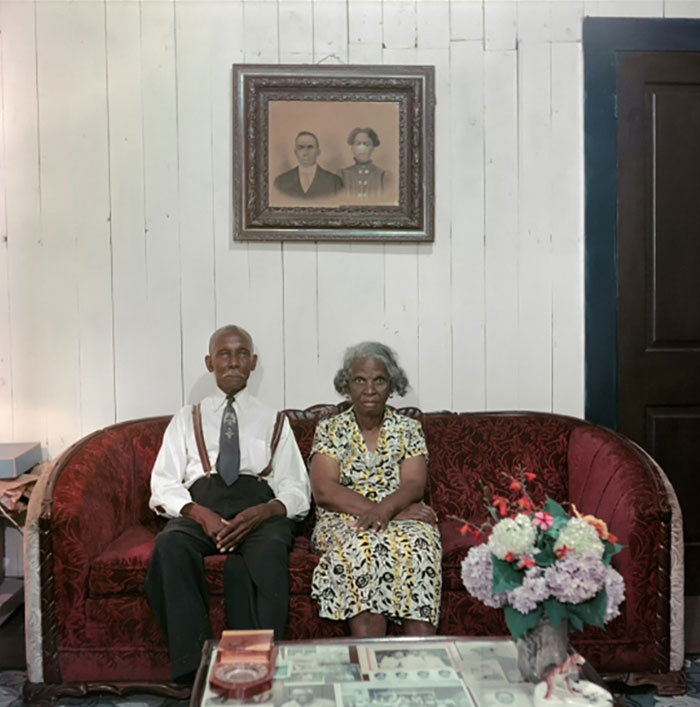
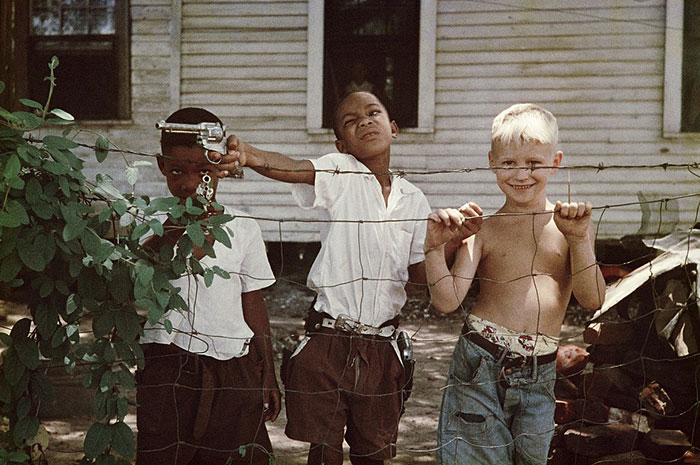
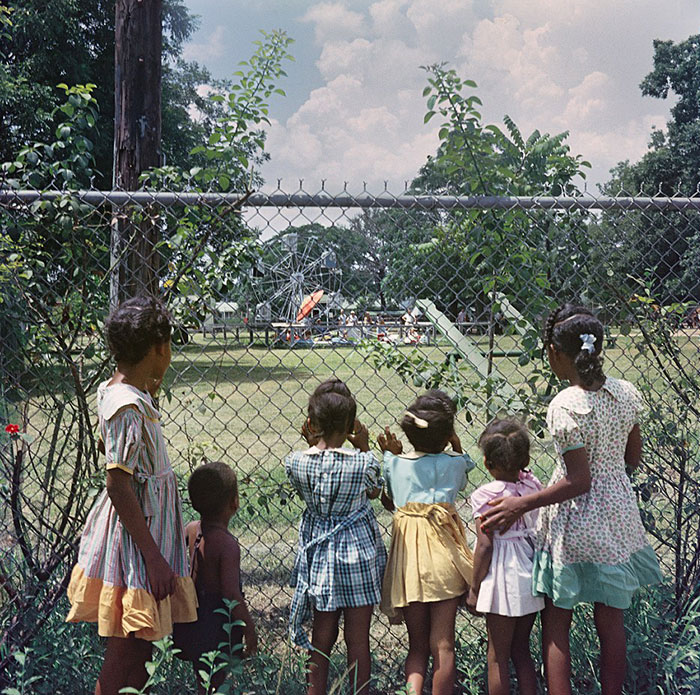
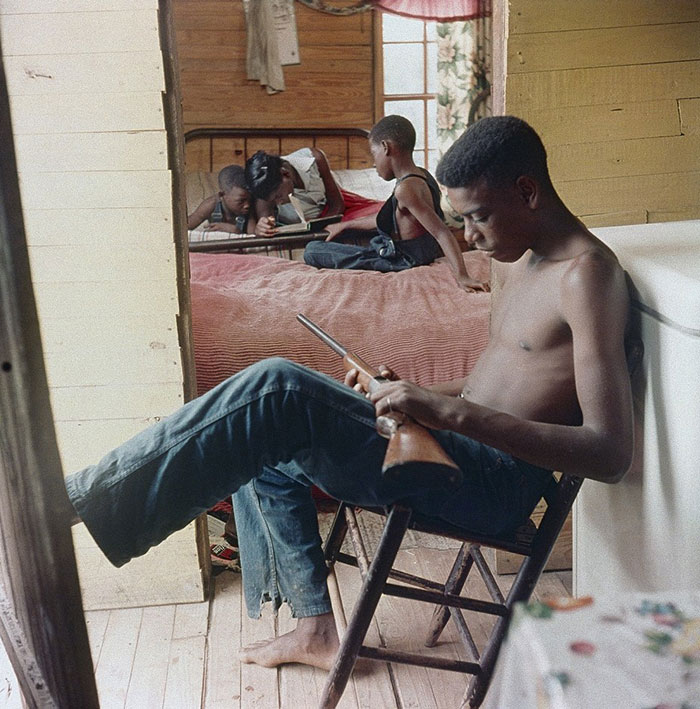
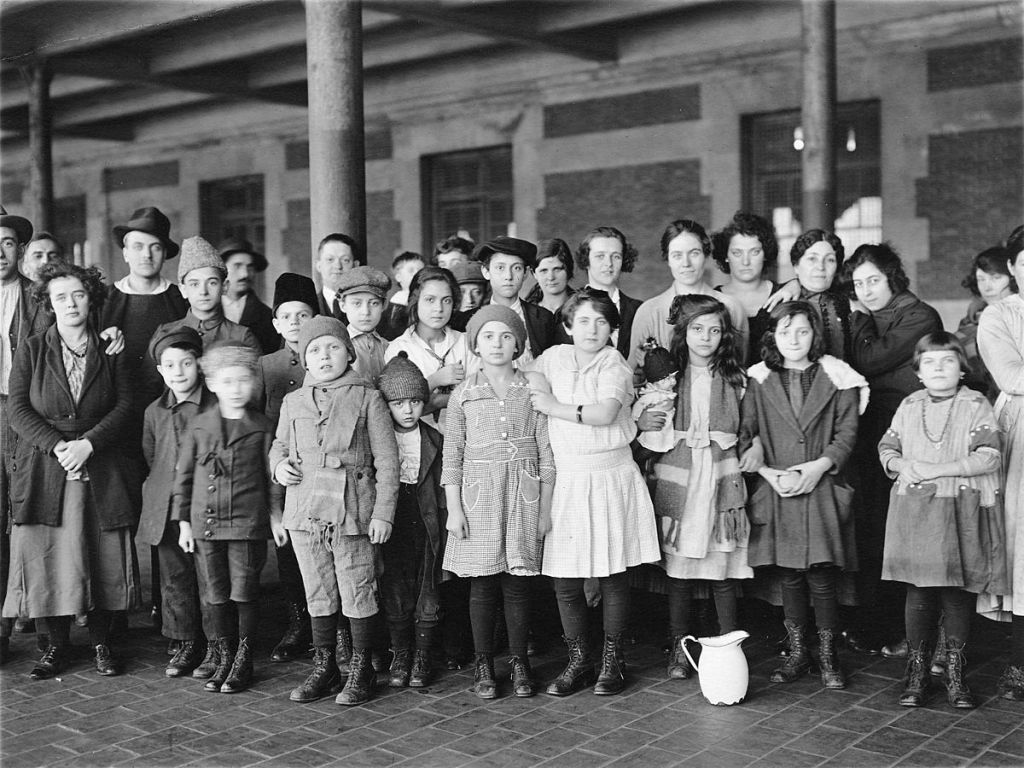
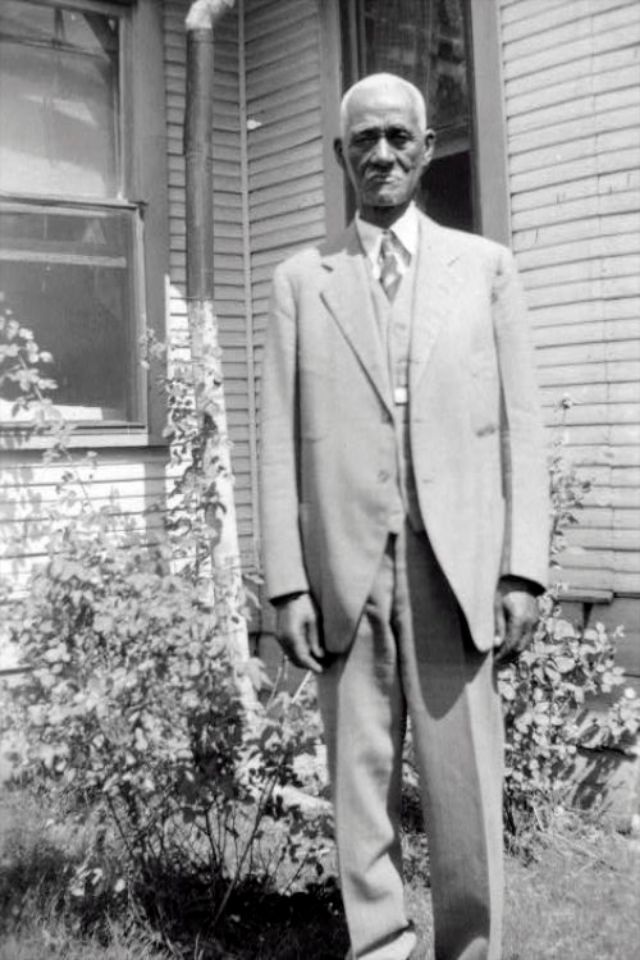
These portraits of African American men and women from locations in Texas were taken in the late 1930s as part of the Federal Writers’ Project (FWP) of the Work Progress Administration (WPA). They are part of a group of 500, together with more than 2,000 first-person accounts of the experience of being a slave. People from Alabama, Arkansas, Indiana, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, Ohio, and Rhode Island are also represented.
Most of the photos show individuals standing or sitting outside; a few are posed with or next to personal possessions; several group portraits are included. Some photographs also depict houses in the background or foreground. Additional images depict objects relating to slavery in Alabama, these include, among others, a “bell rack” restraint from the Federal Museum of Mobile and photographs of sales receipts issued to slave owners.
Federal Writers’ Project interviews with former slaves began as early as 1936 with initial efforts concentrated primarily in Florida. In 1937 an official project was organized and placed under the direction of folklorist John A. Lomax who coordinated and expanded data collecting activities throughout the South. The program continued up through the Spring of 1939. Photographs of former slaves were often taken at the time of the interviews.
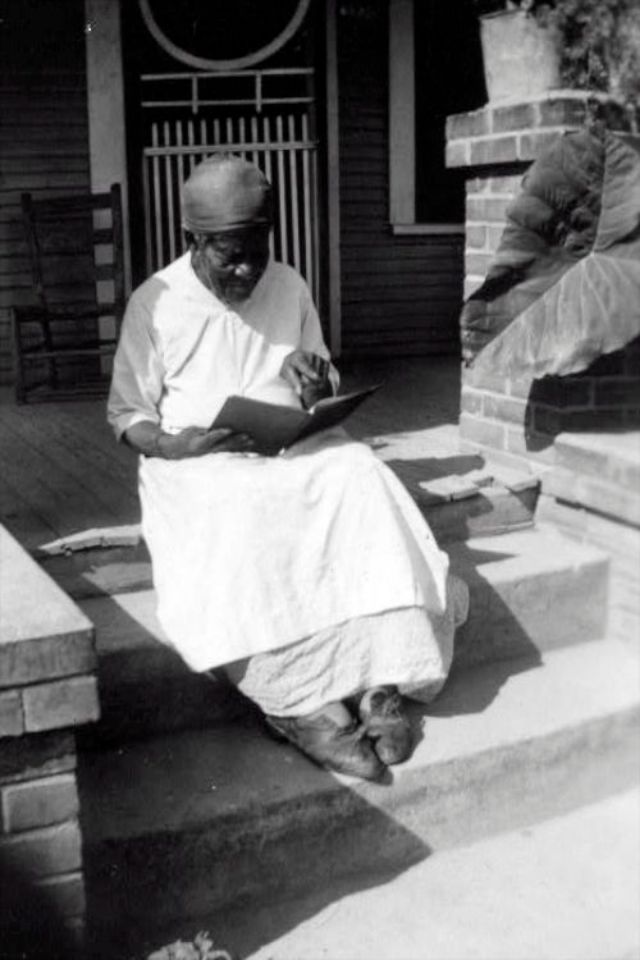
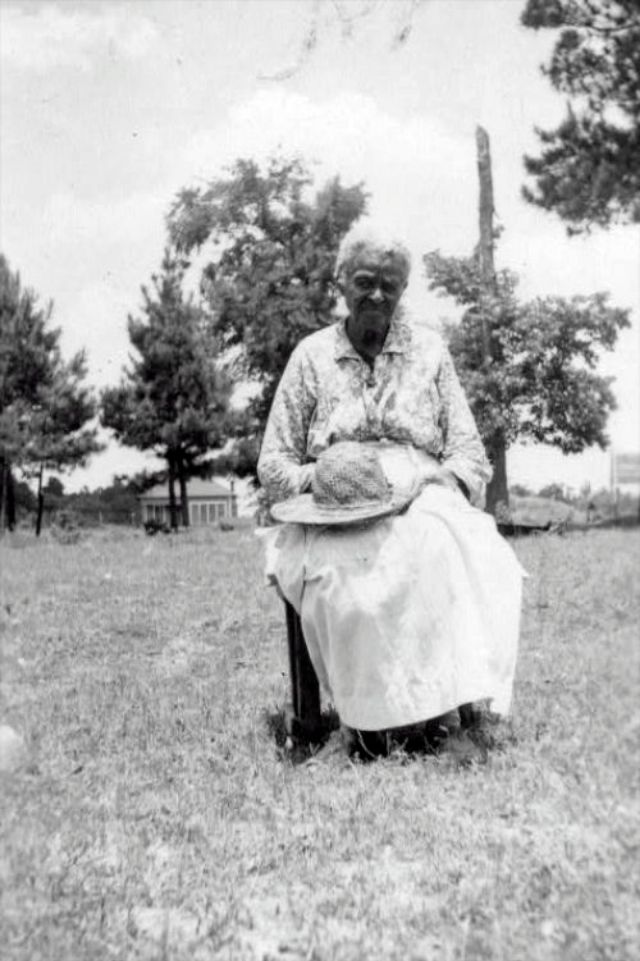
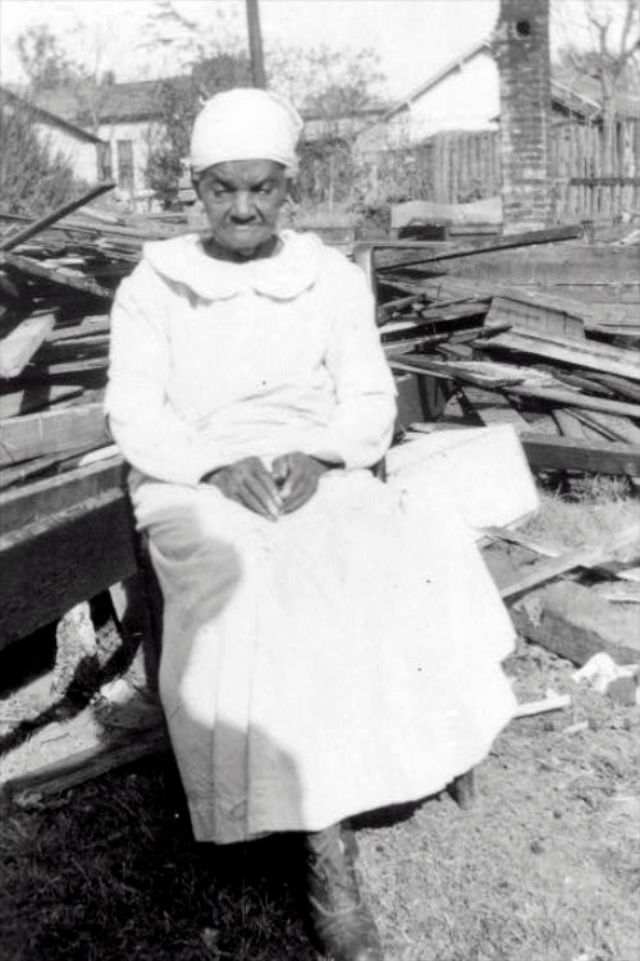
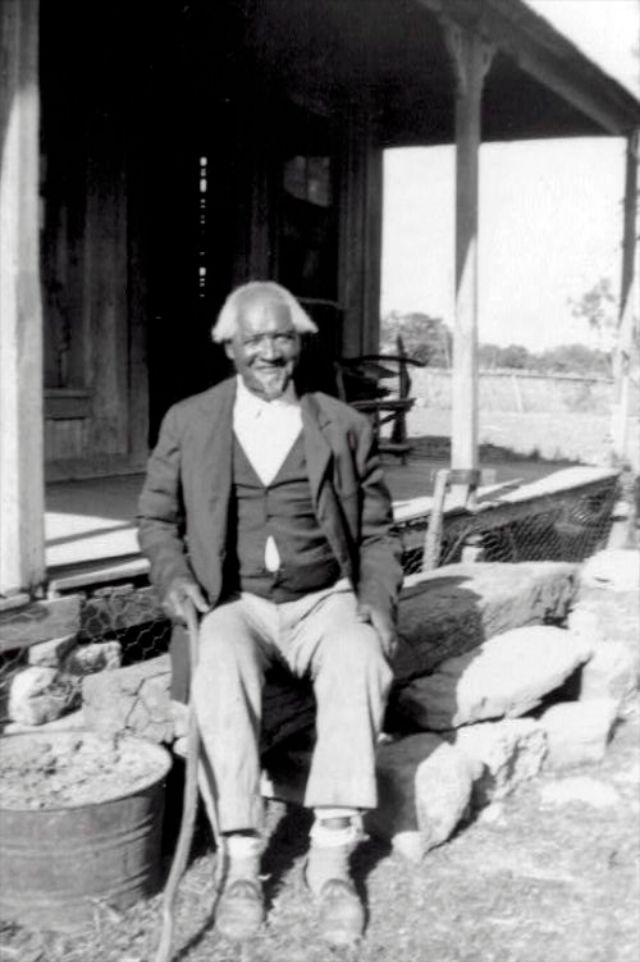
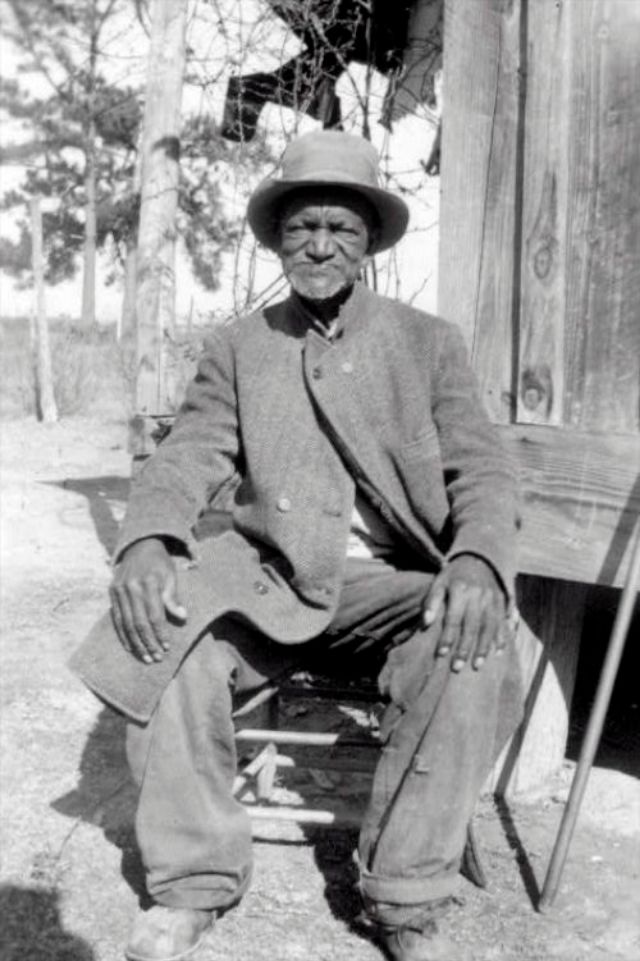
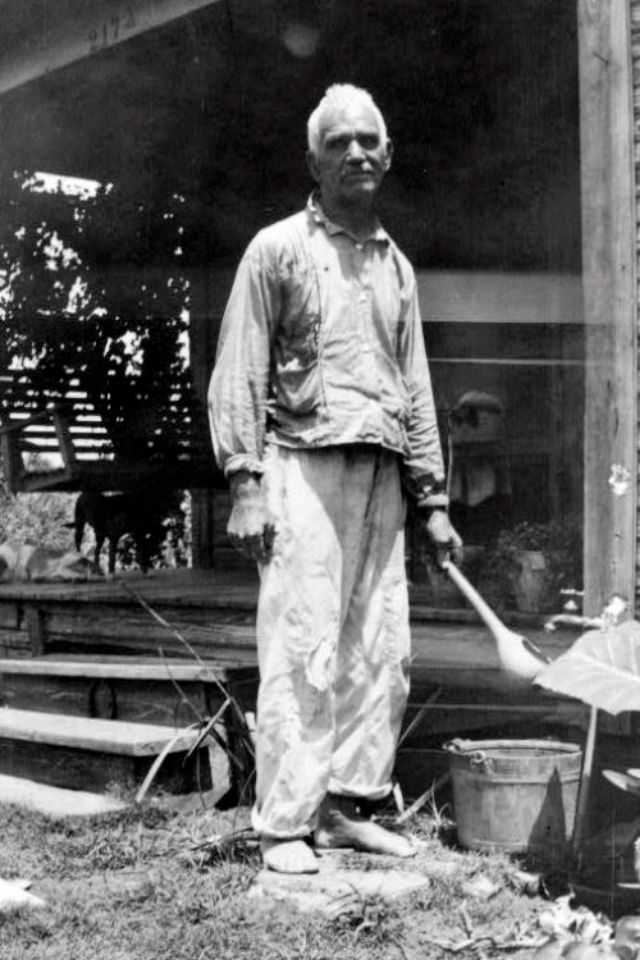
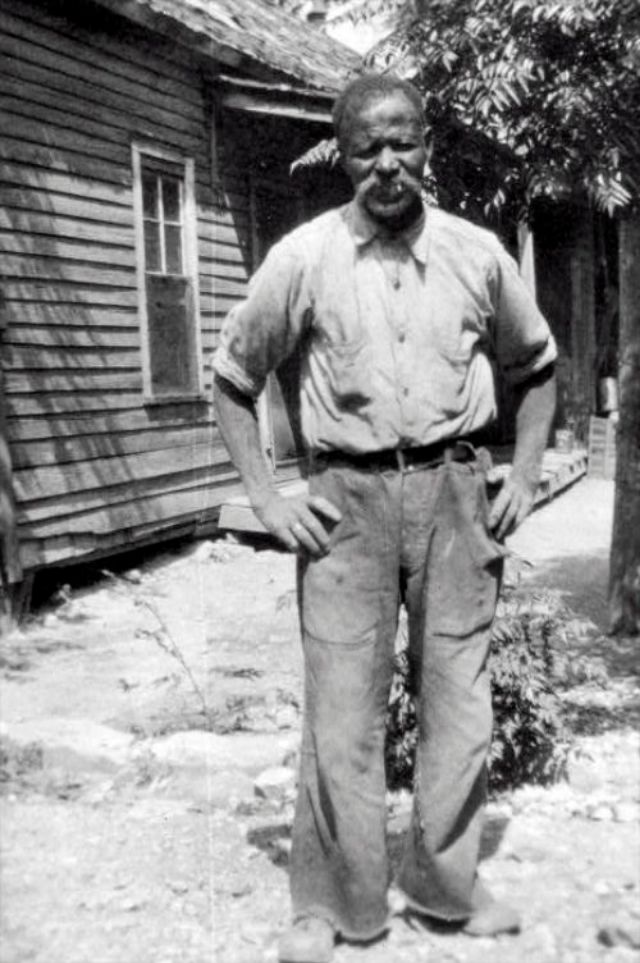
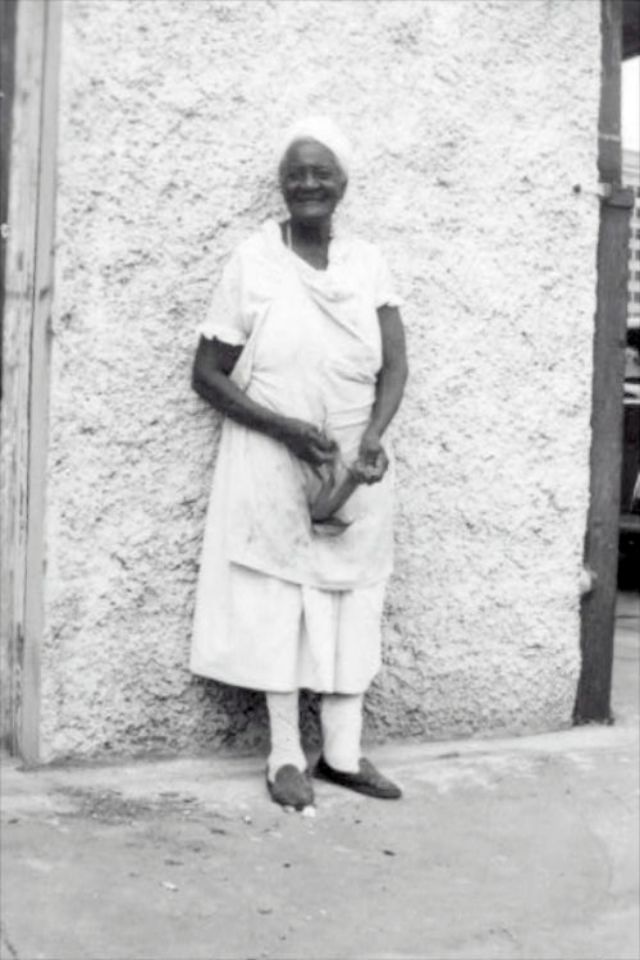
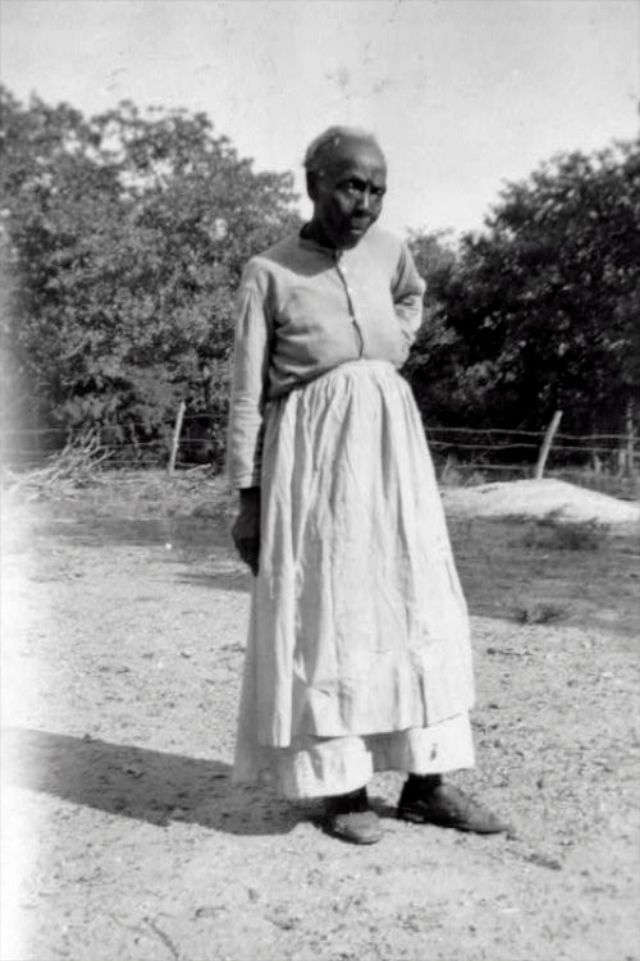
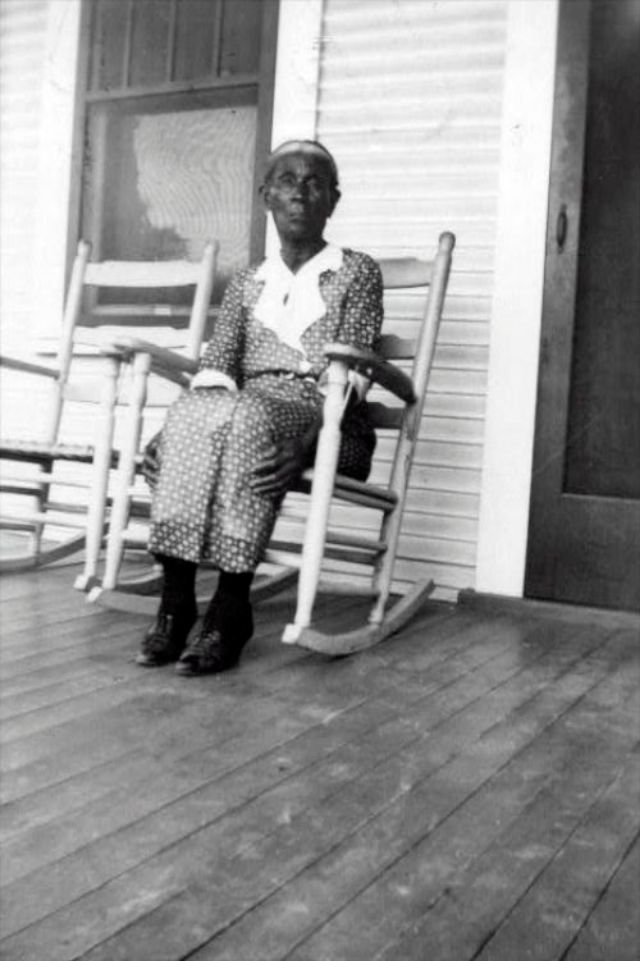
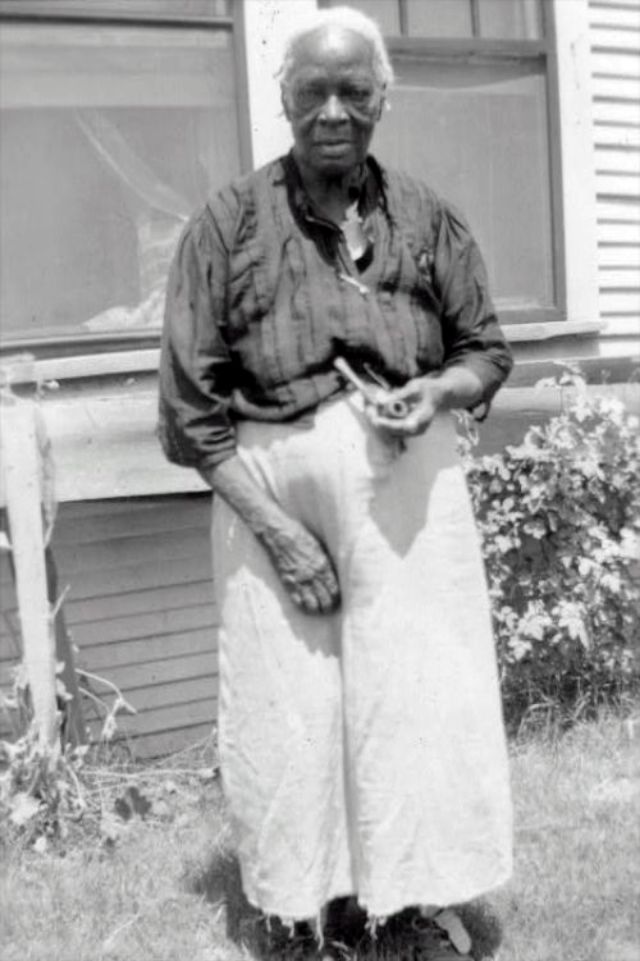
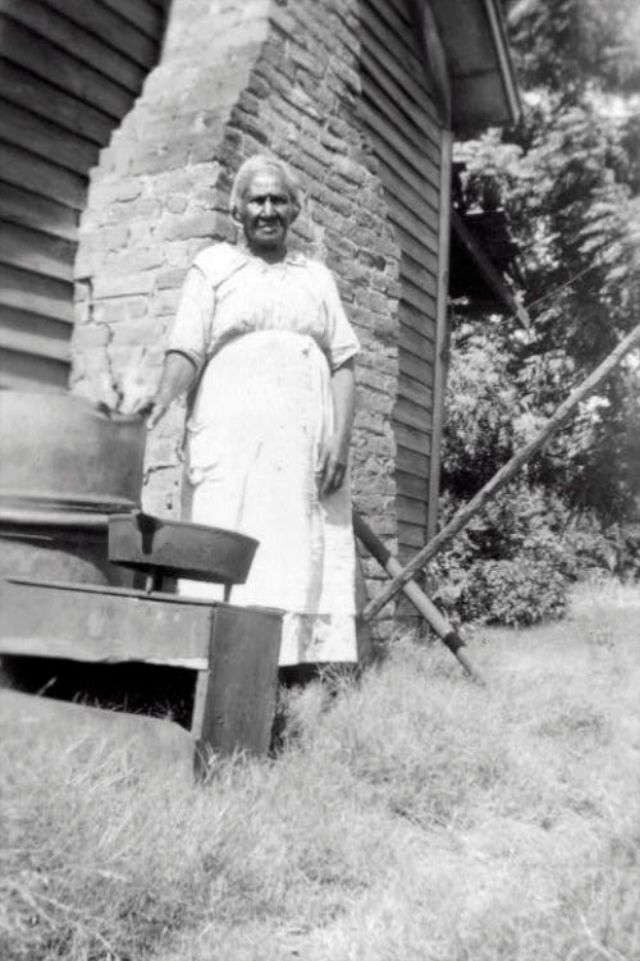
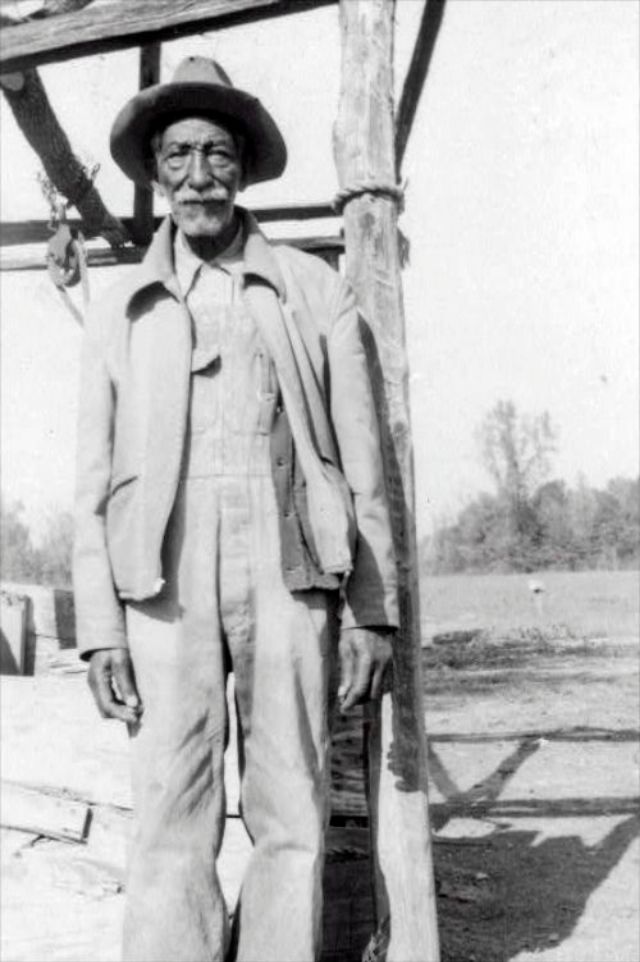
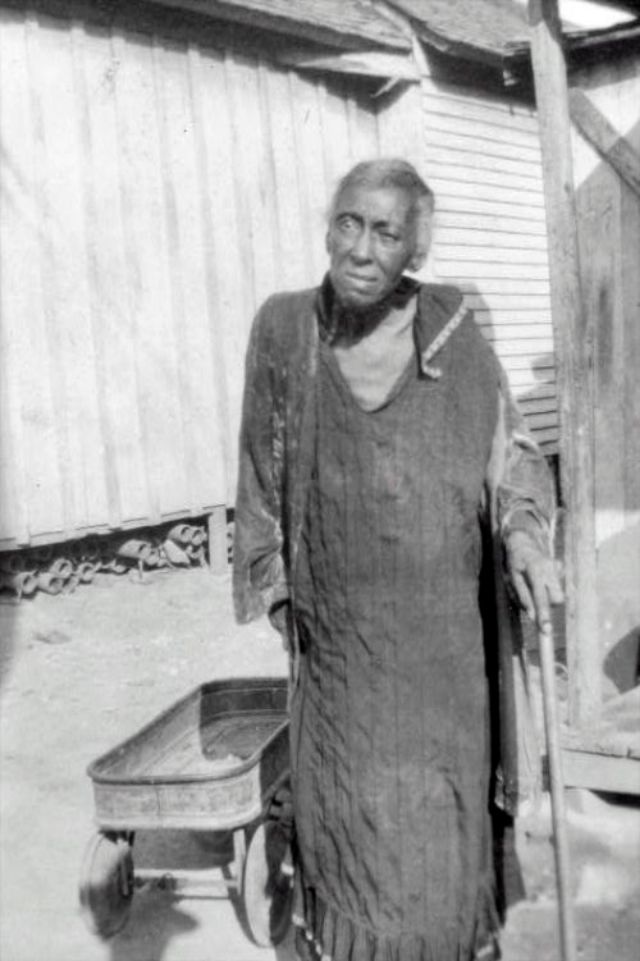
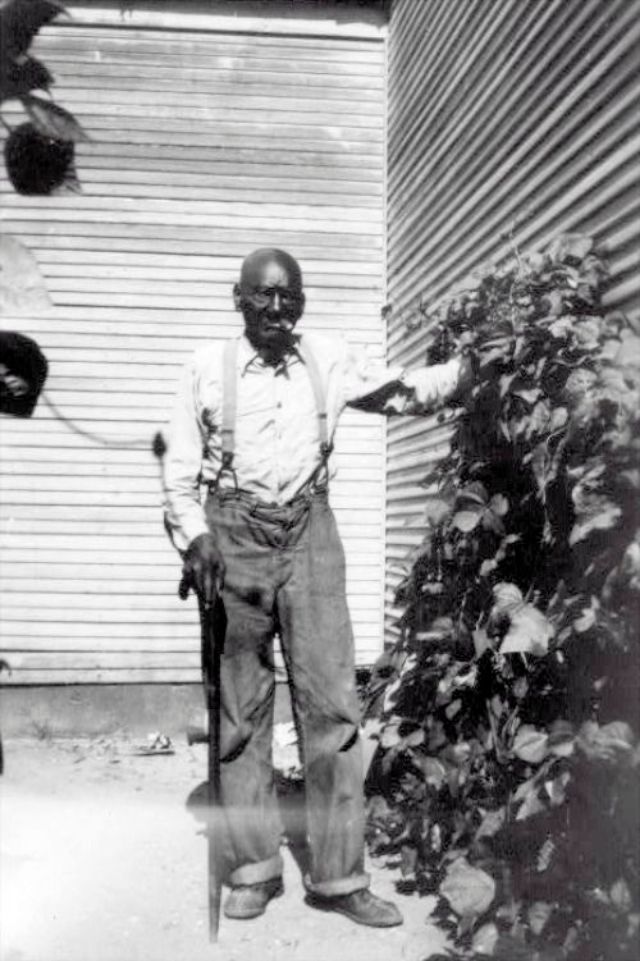
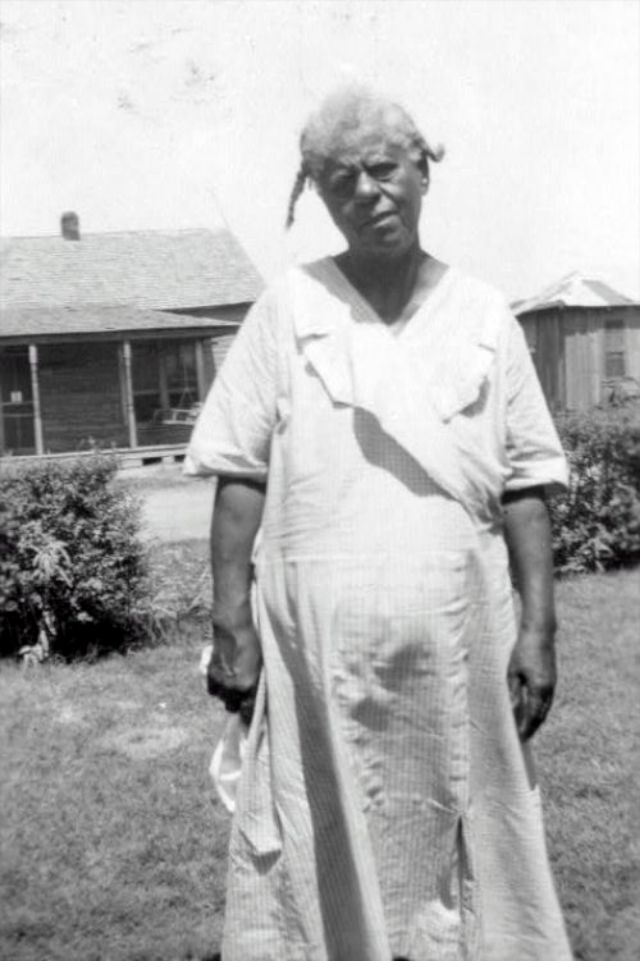
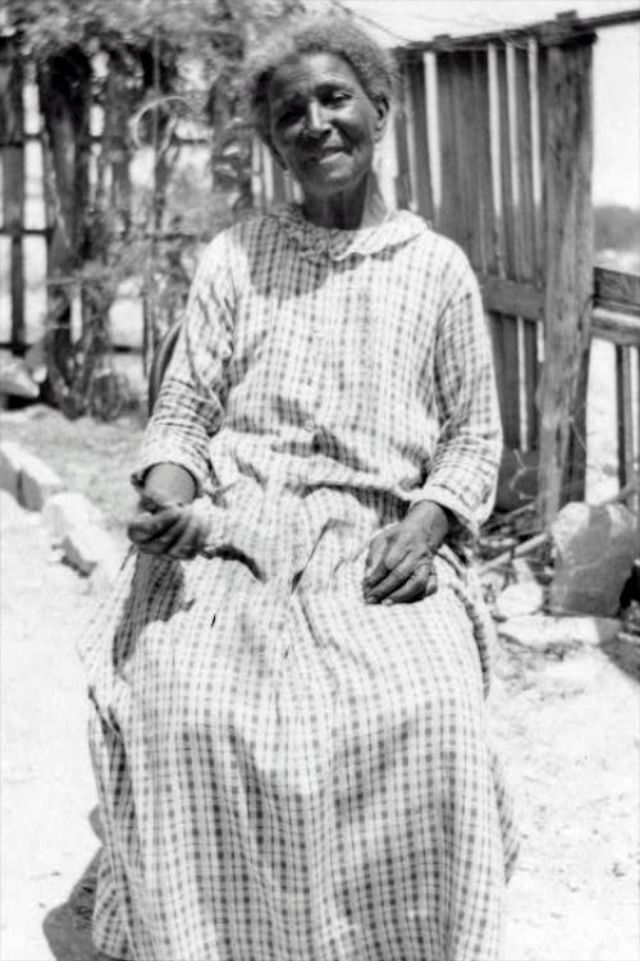
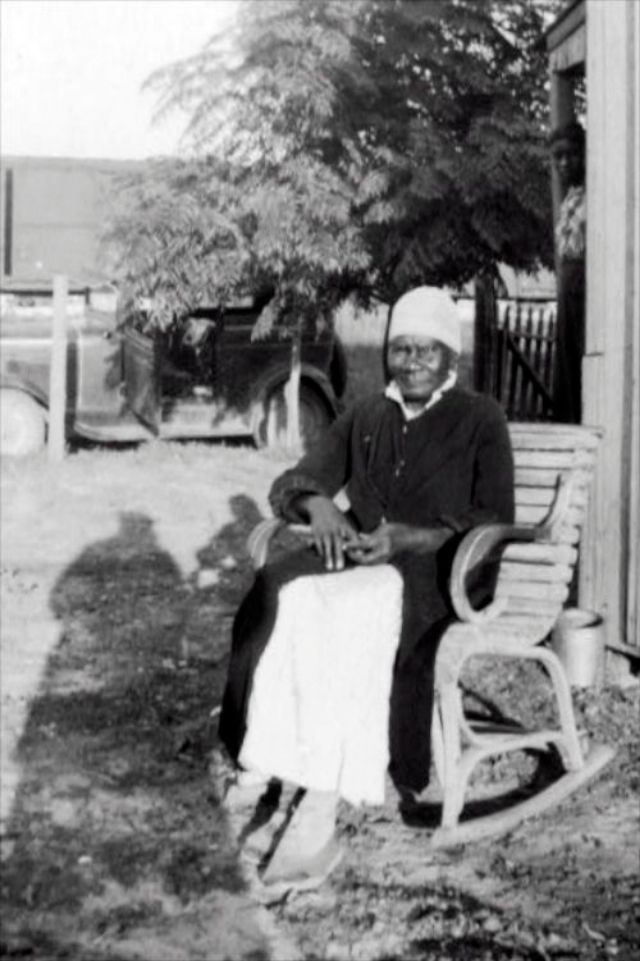
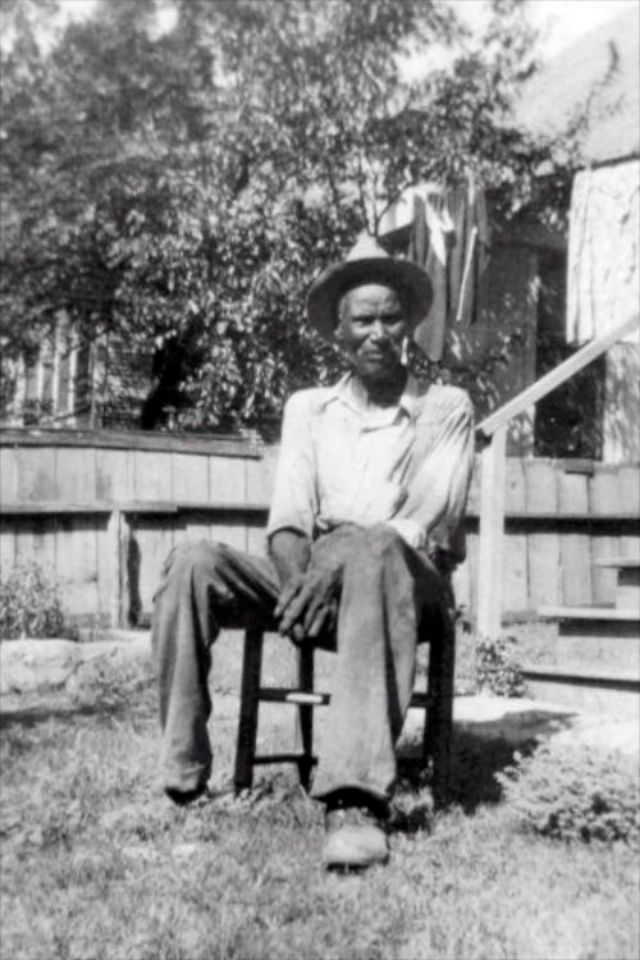
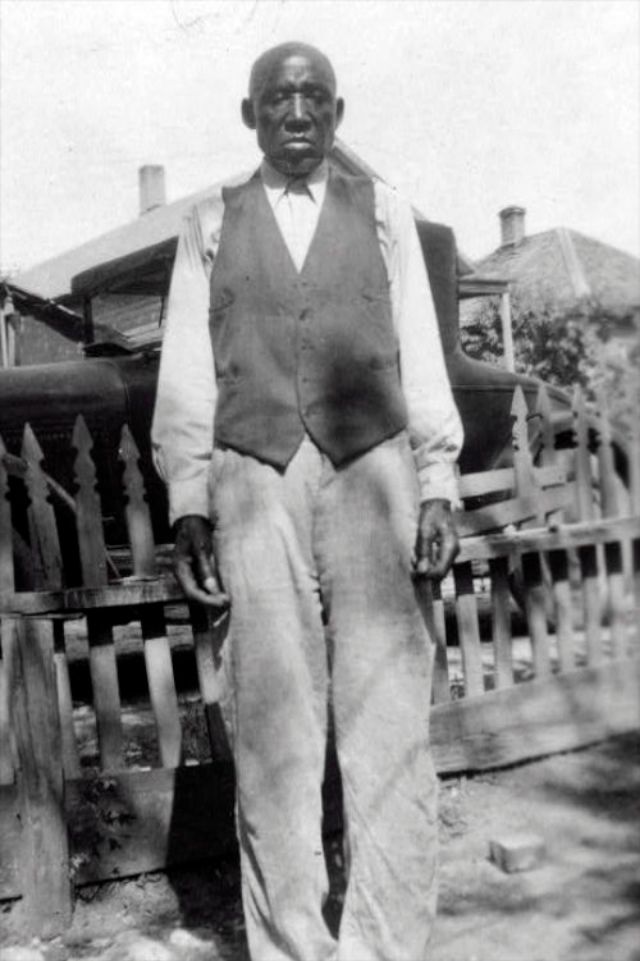
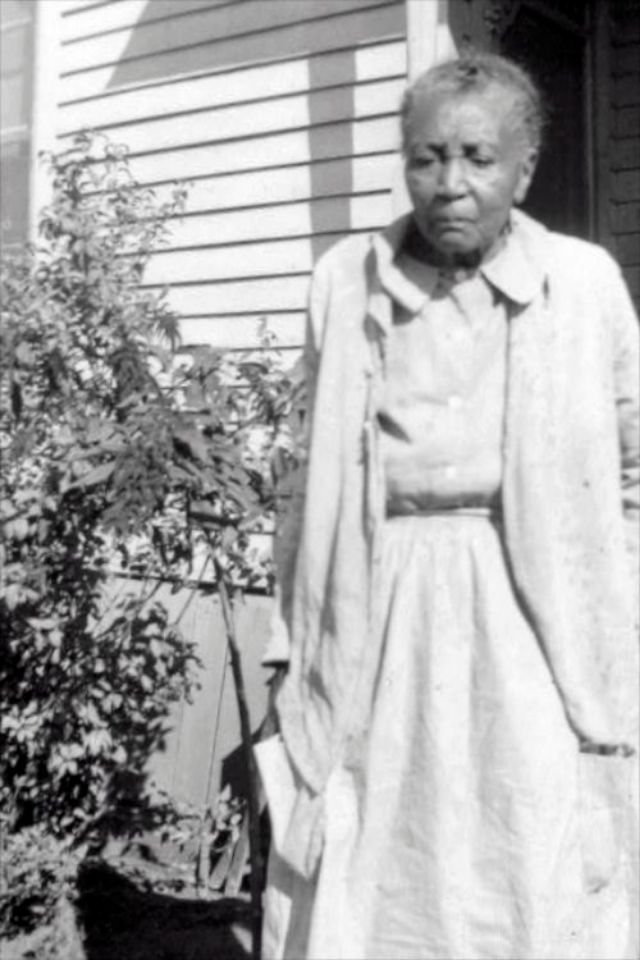
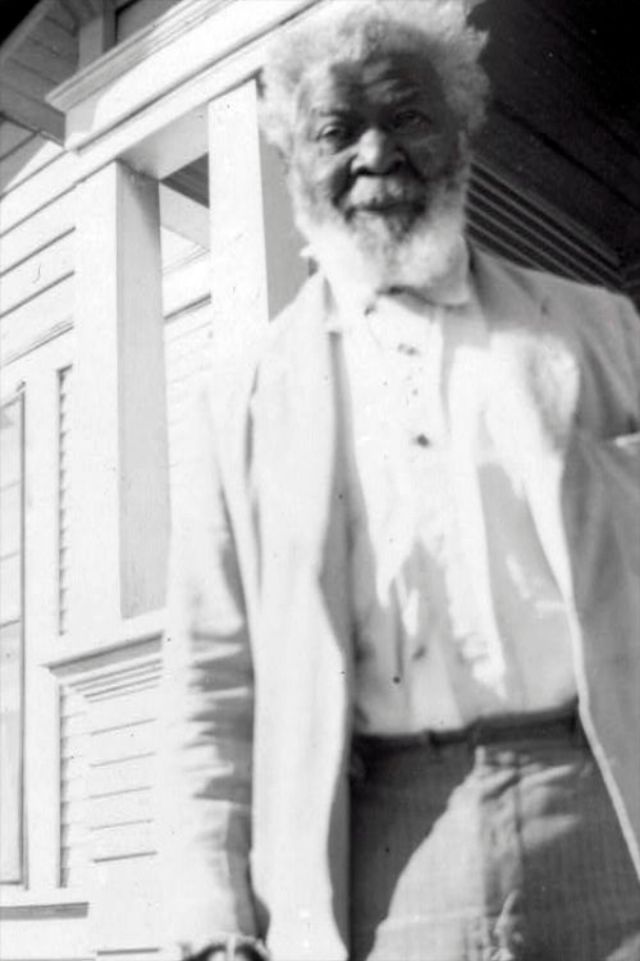
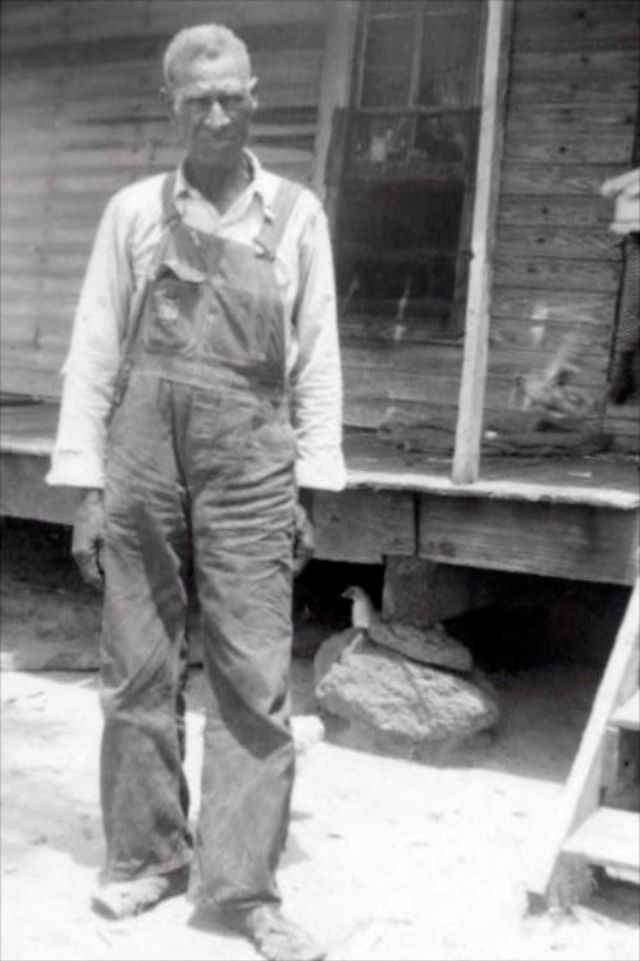
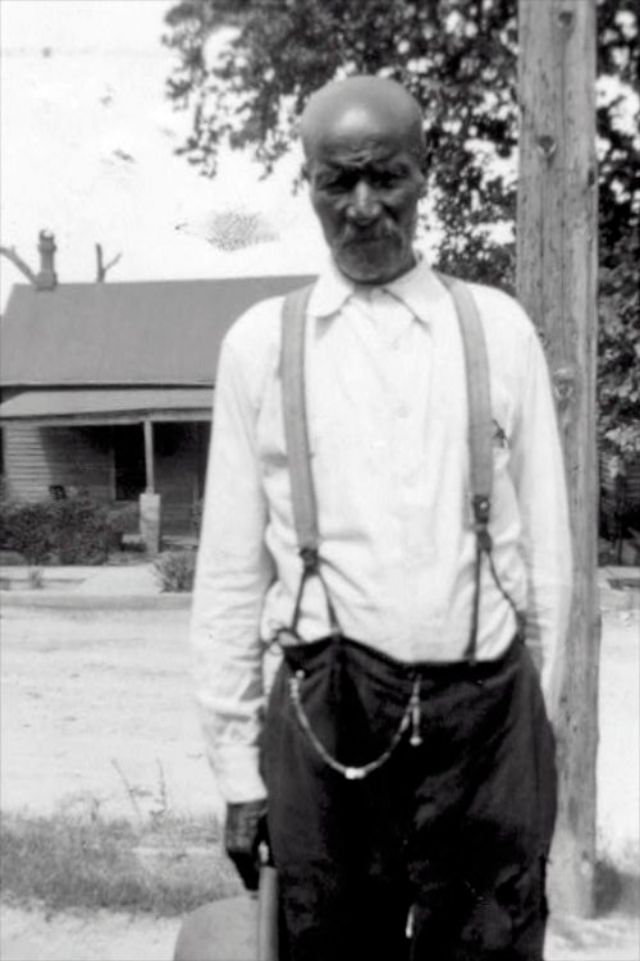
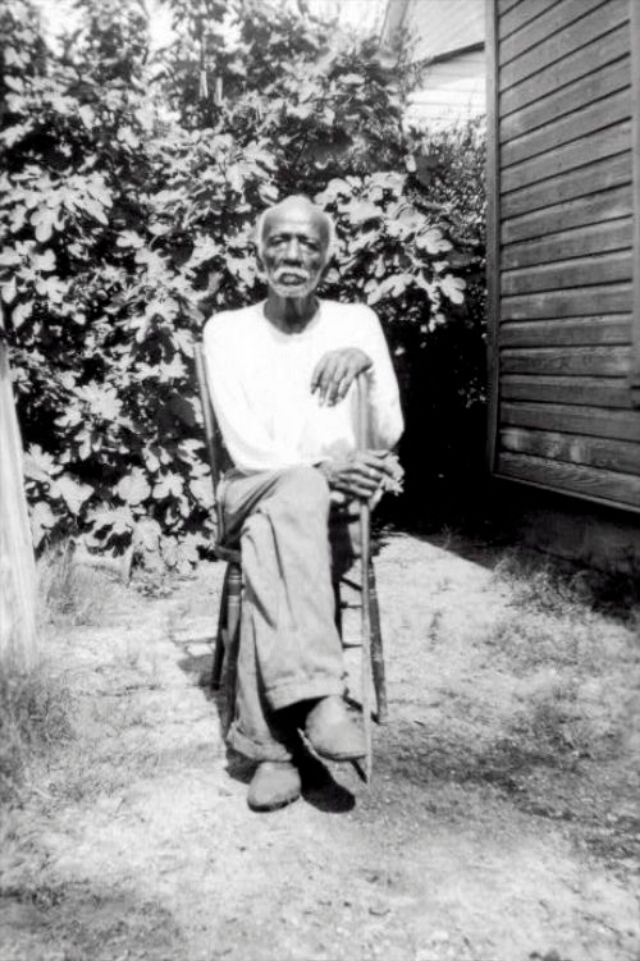
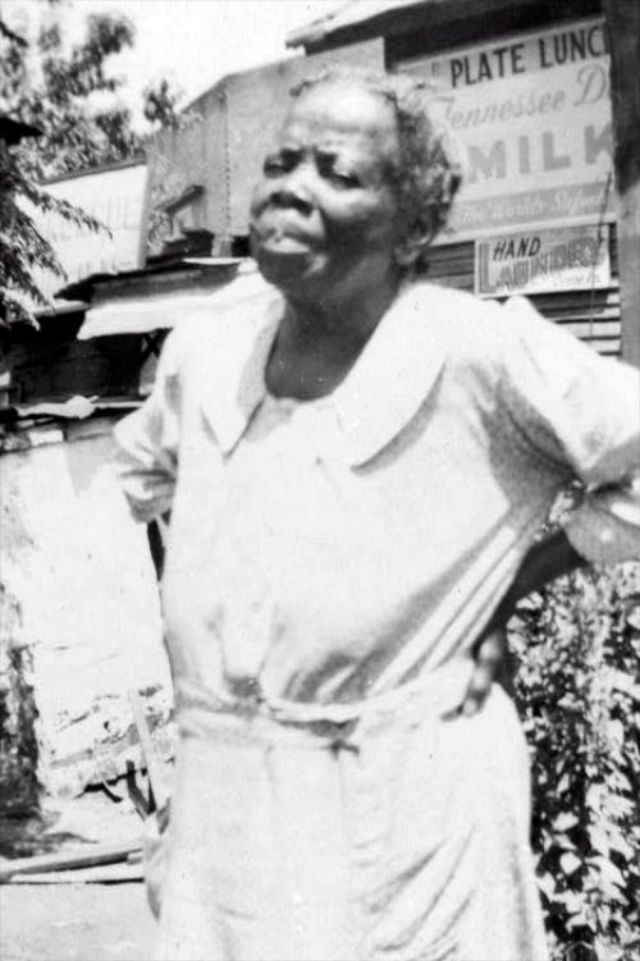
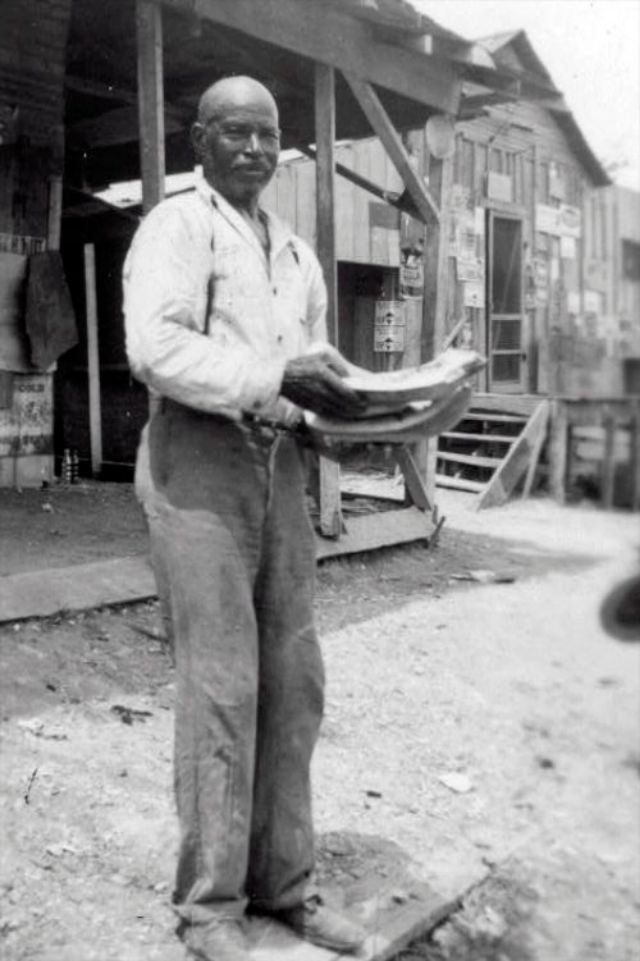
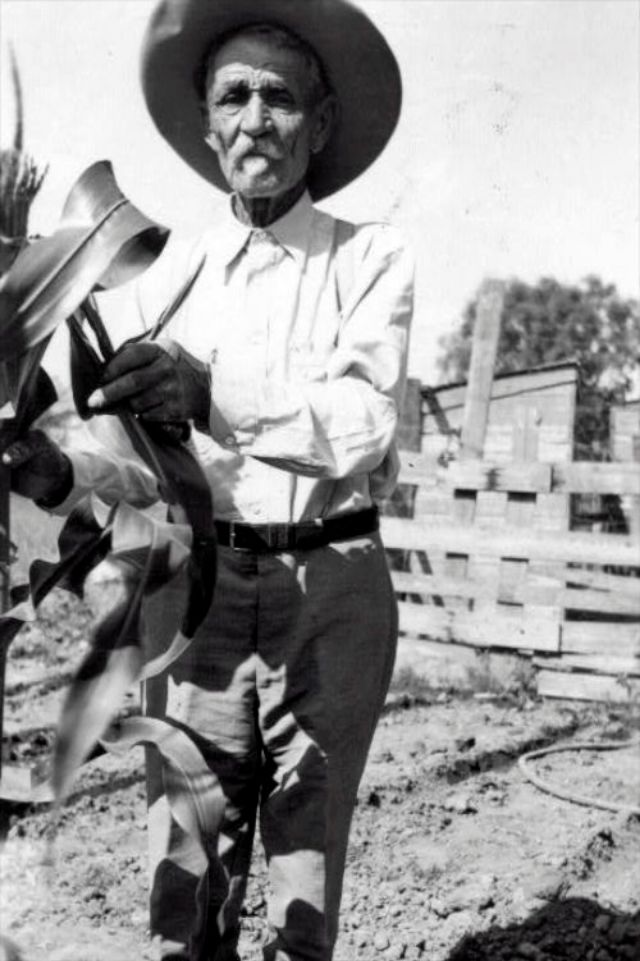
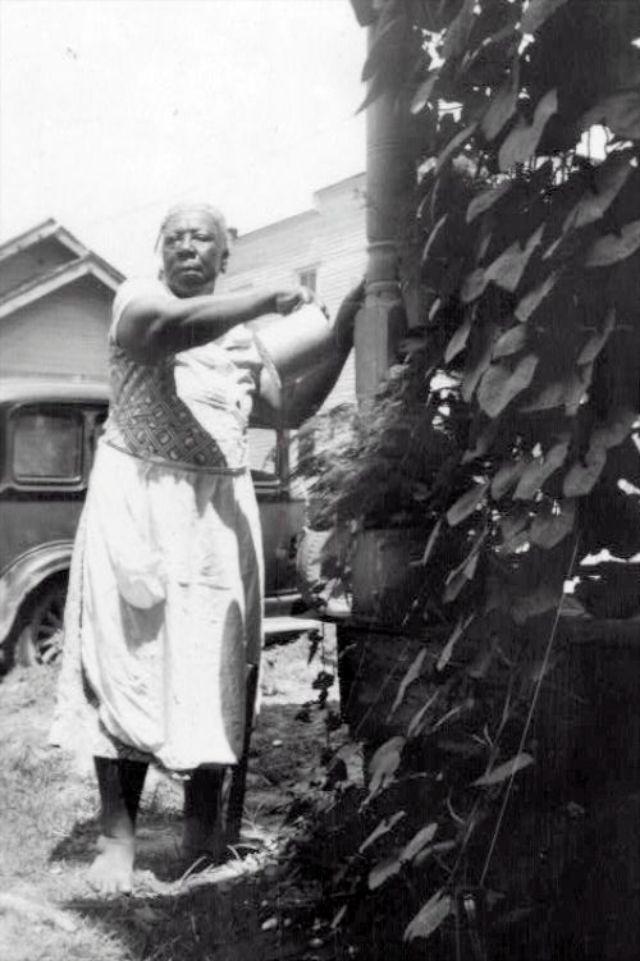
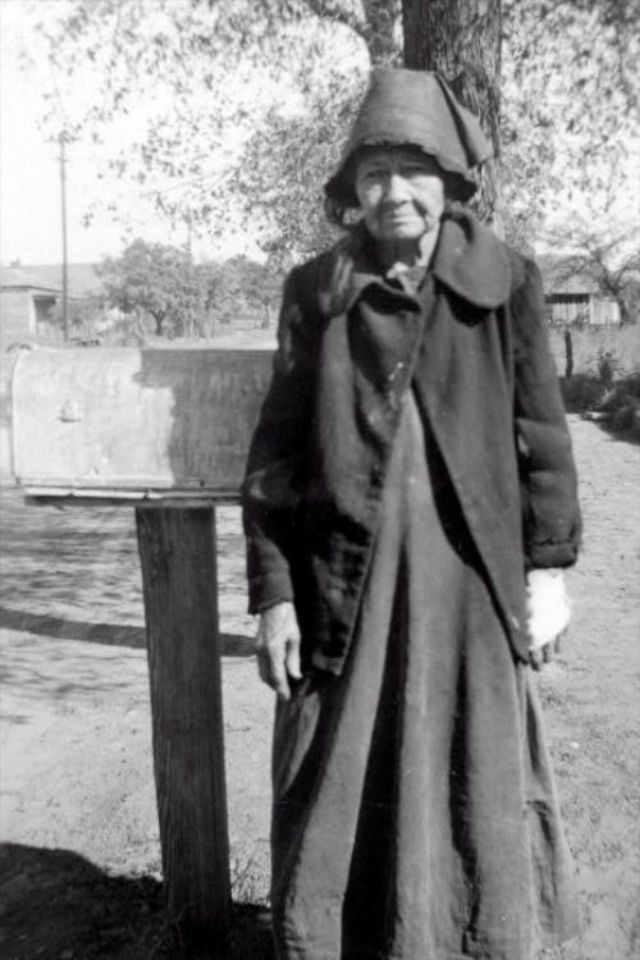
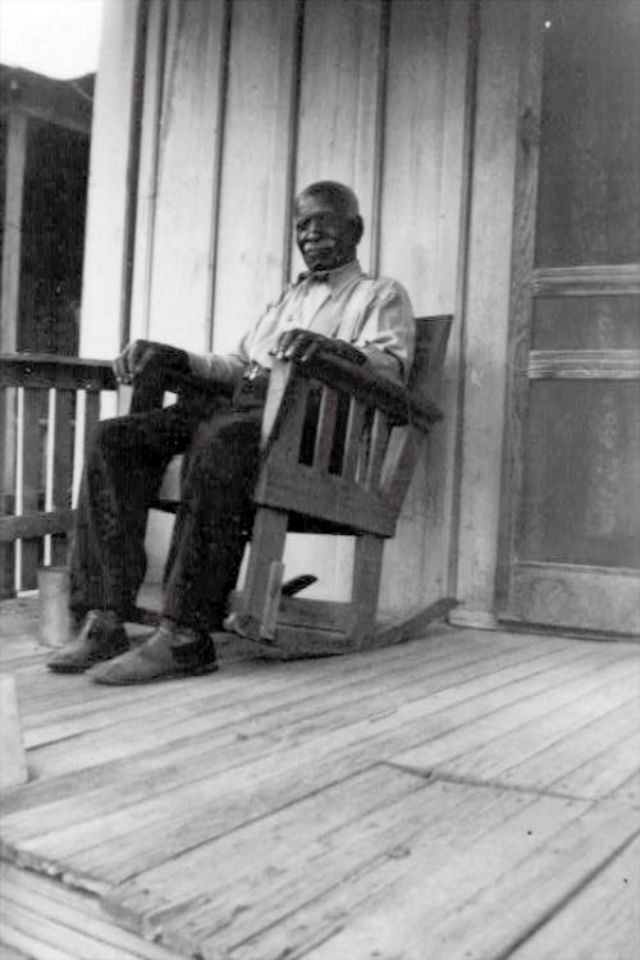
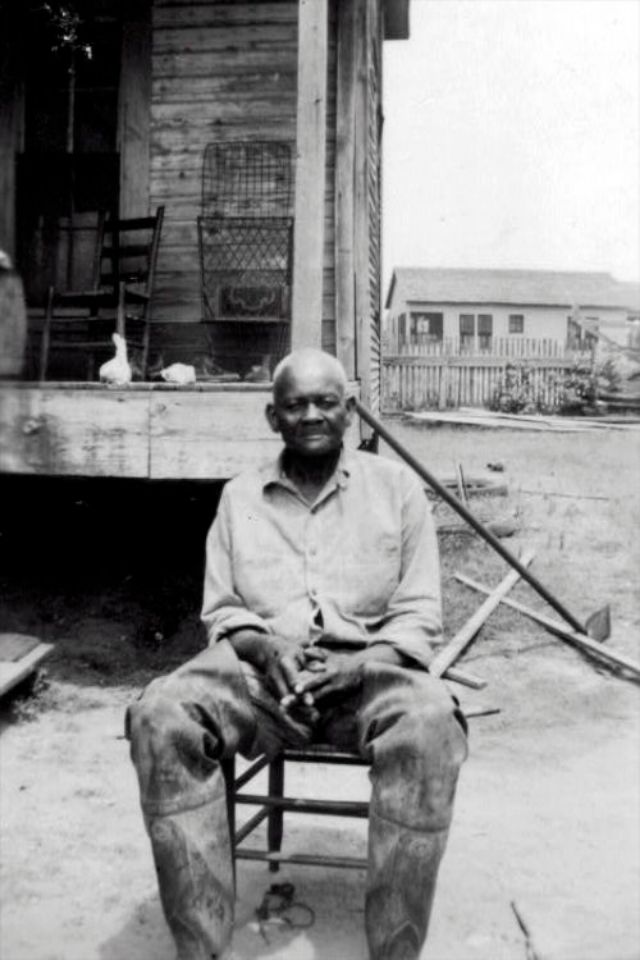




























































(Photos: Library of Congress)

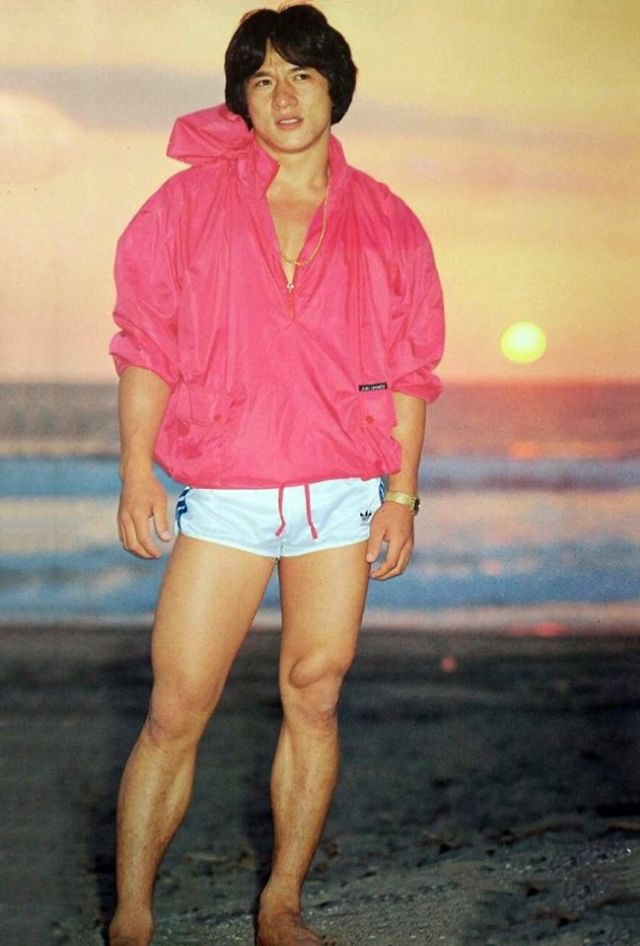
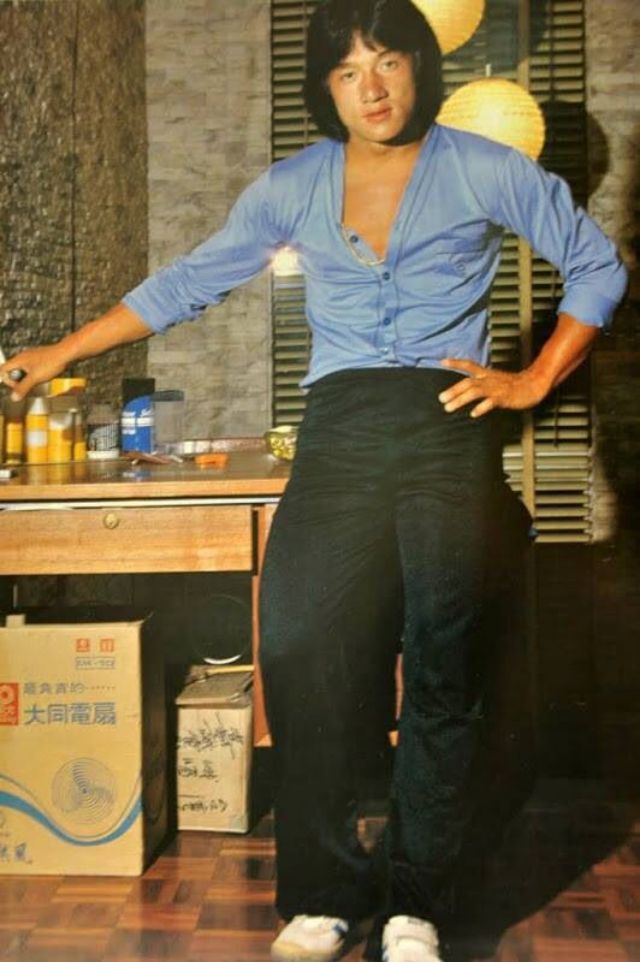
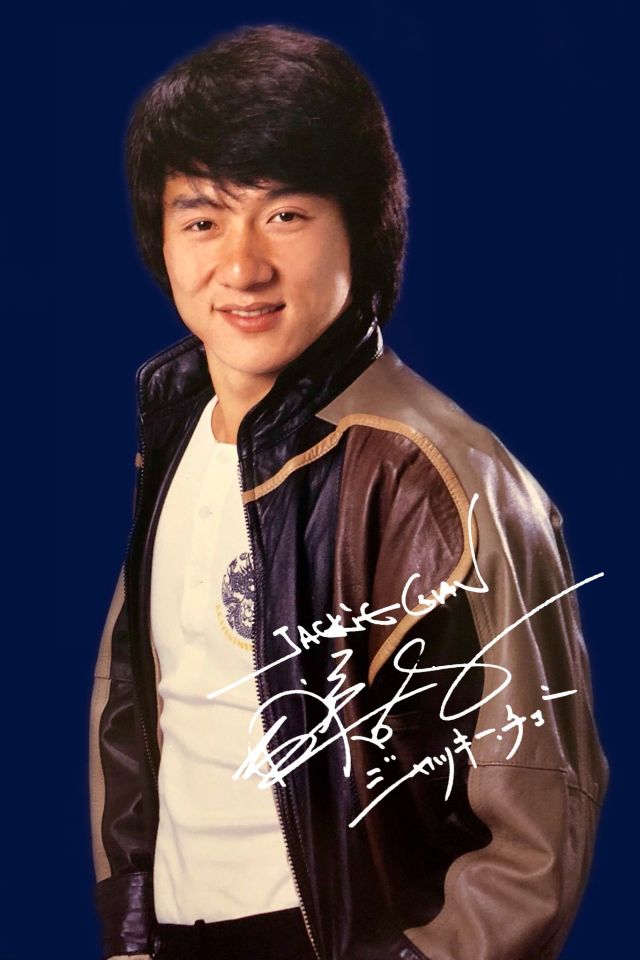
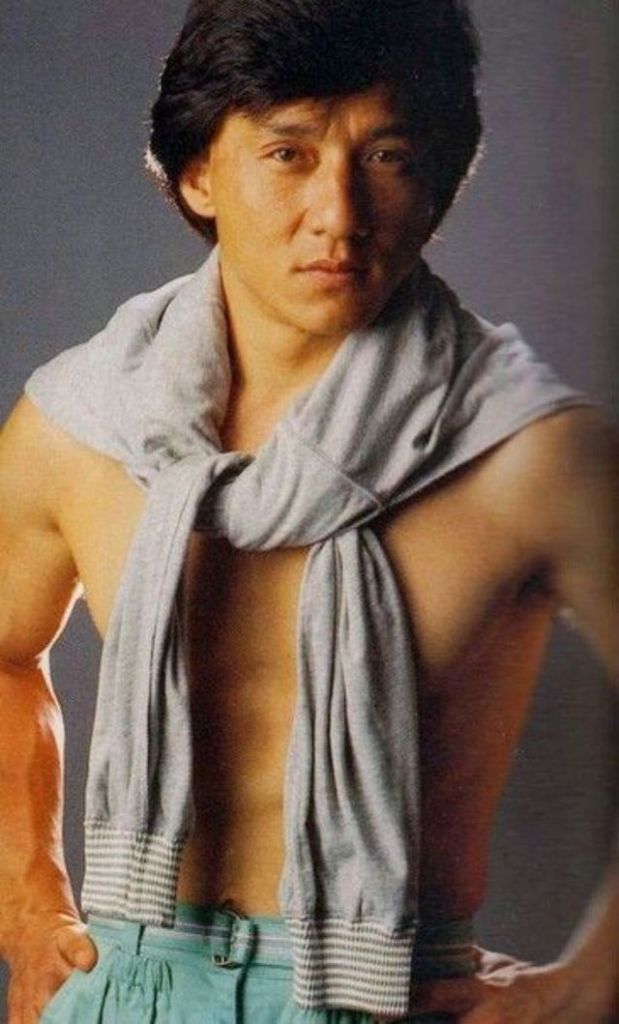
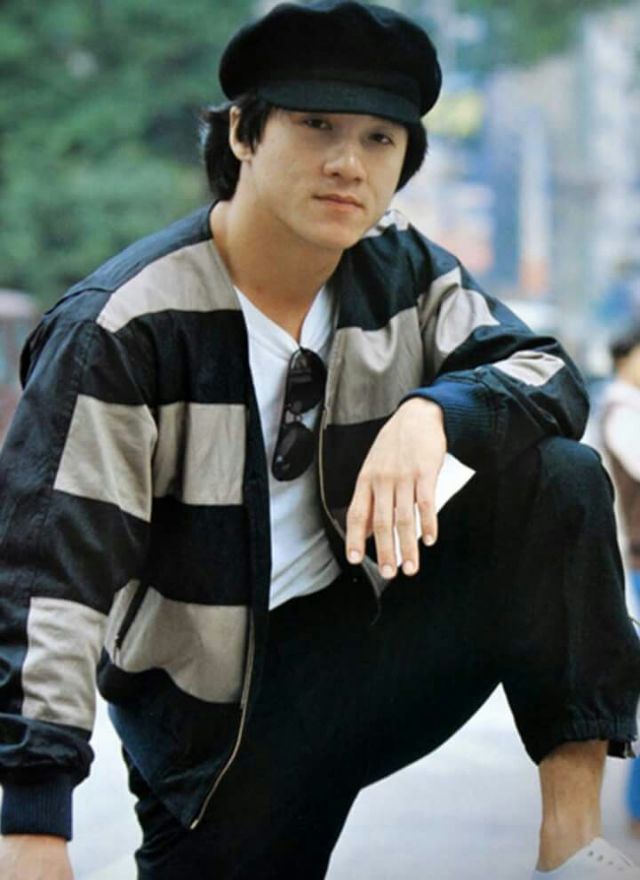
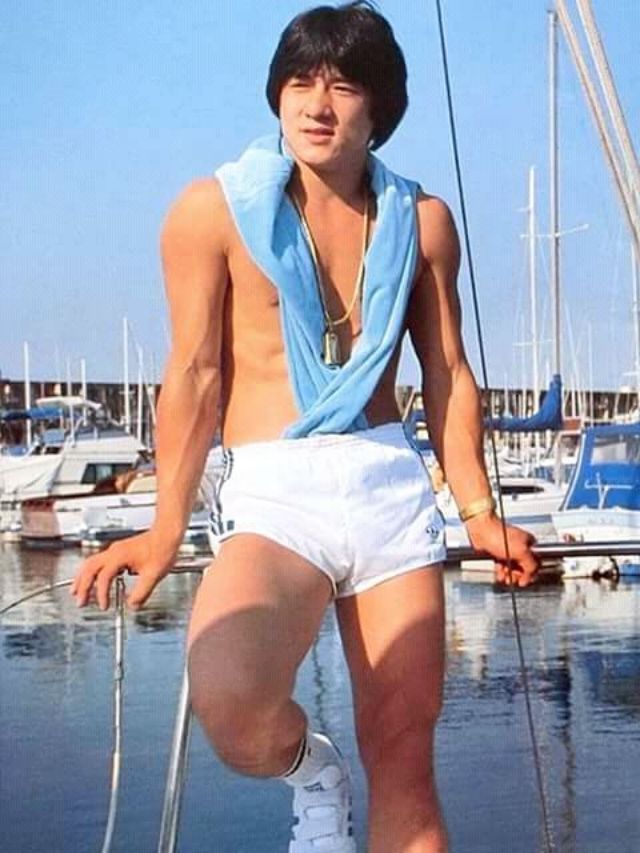
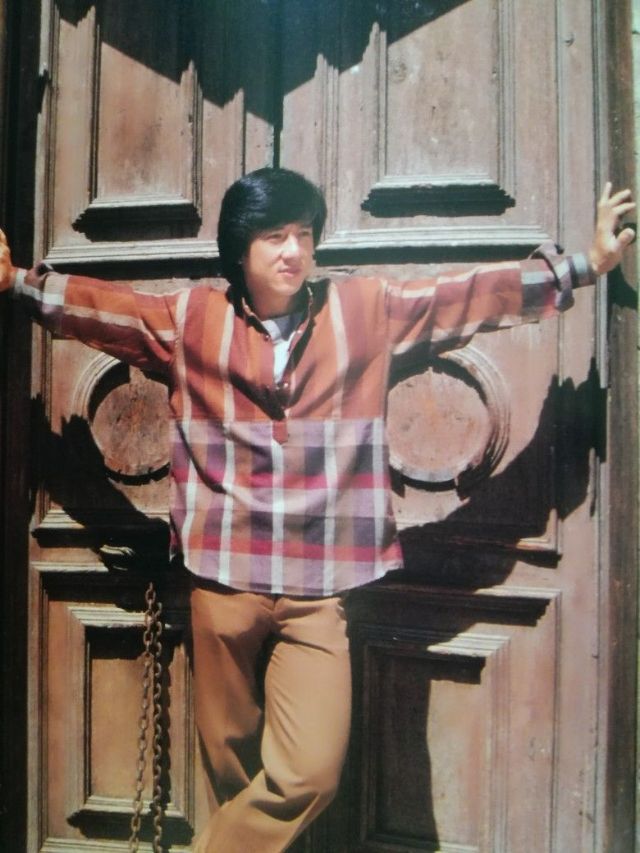
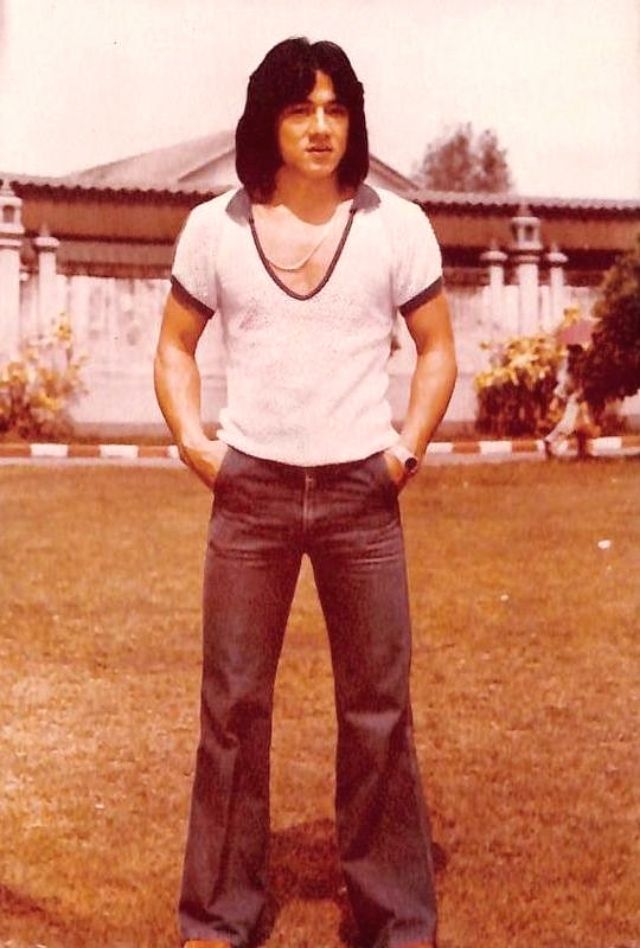
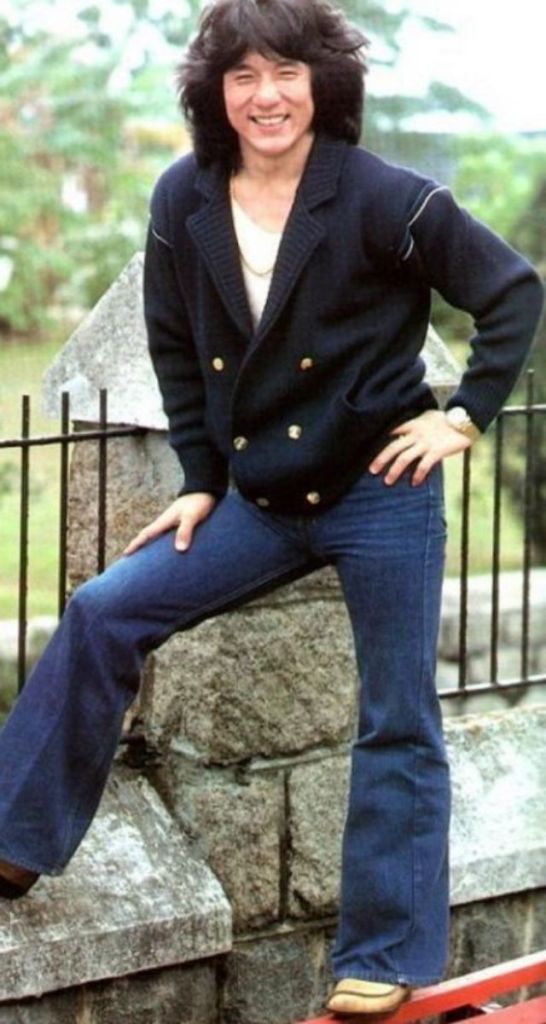
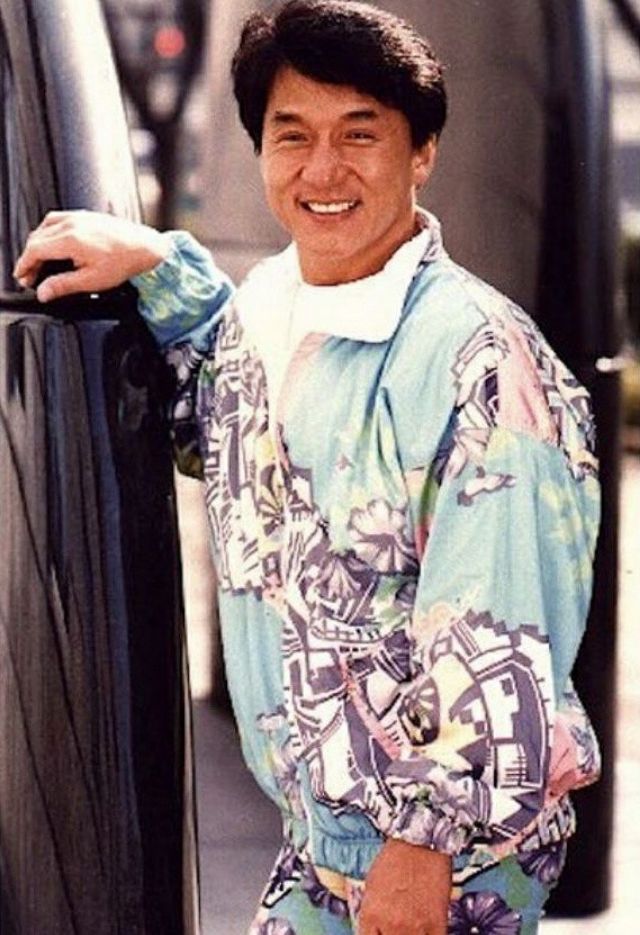
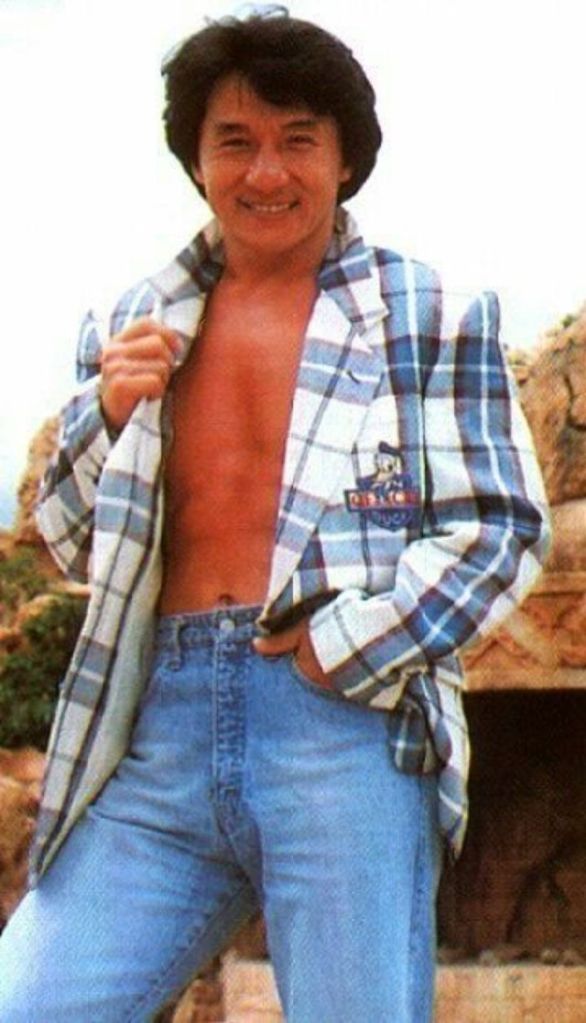
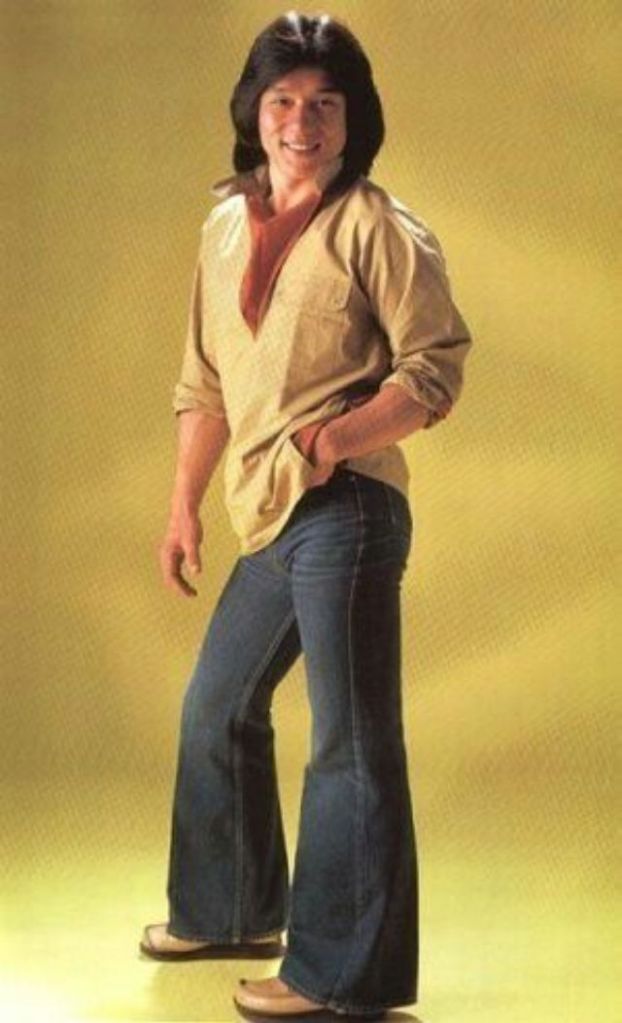
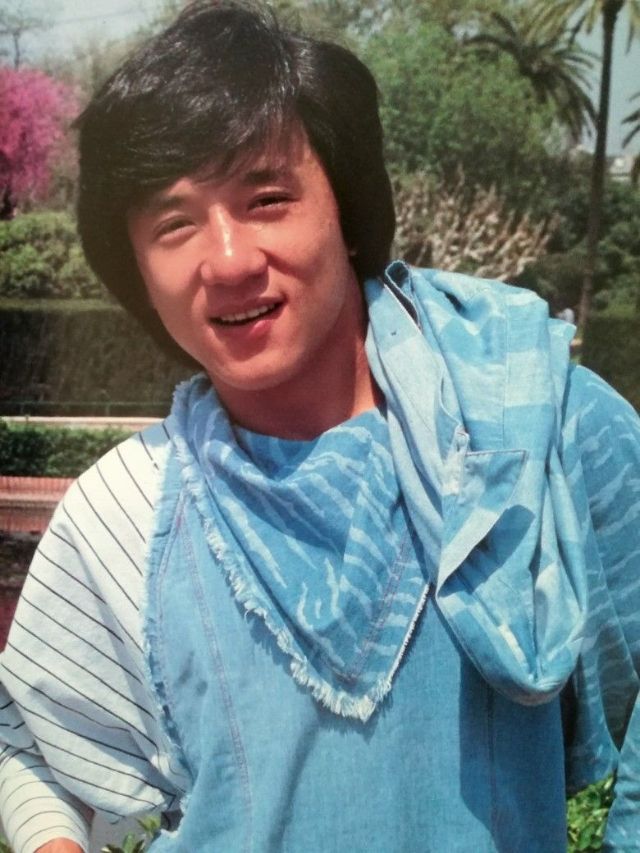
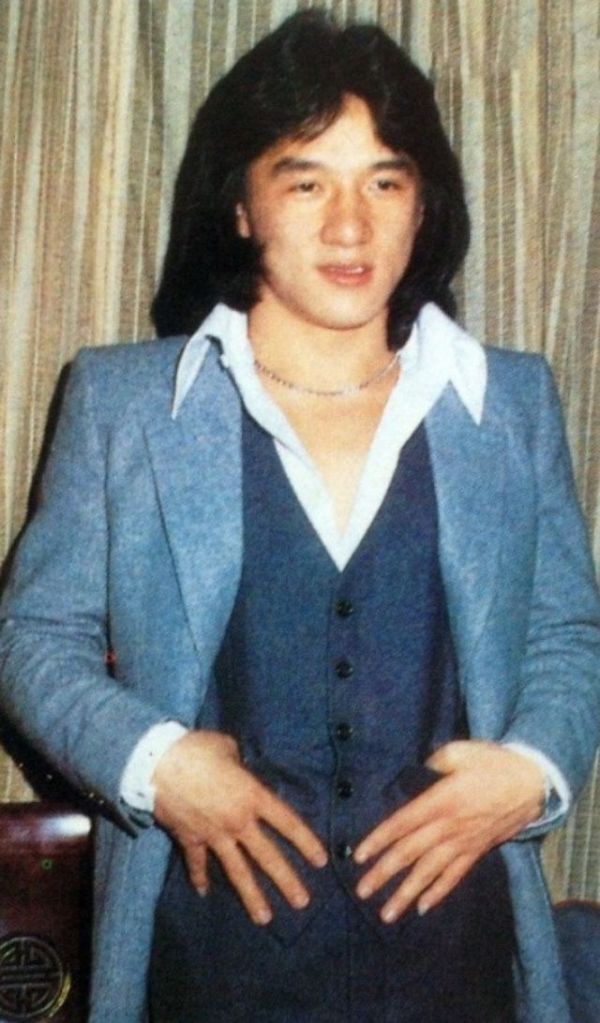
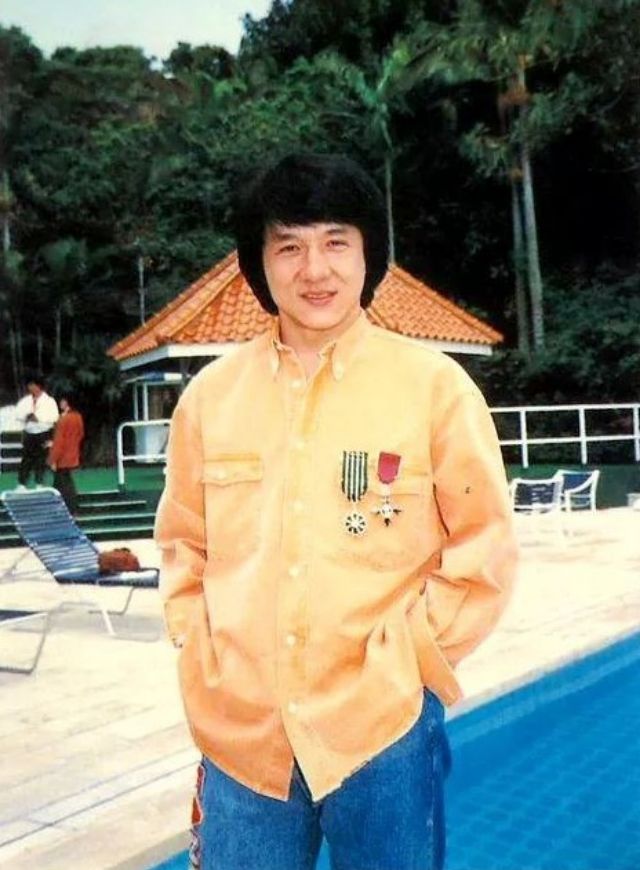
Datuk Fang Shilong (born 7 April 1954) SBS, MBE, PMW, born Chan Kong-sang and known professionally as Jackie Chan, is a Hong Kong actor, director, martial artist and stuntman known for his slapstick acrobatic fighting style, comic timing, and innovative stunts, which he typically performs himself. Chan has been acting since the 1960s, performing in more than 150 films. He is one of the most popular action film stars of all time.
Chan is one of the most recognisable and influential film personalities in the world, and he gained a widespread global following in both the Eastern and Western hemispheres. He has received fame stars on the Hong Kong Avenue of Stars and the Hollywood Walk of Fame. He has been referenced in various pop songs, cartoons, films and video games. He is an operatically trained vocalist and is also a Cantopop and Mandopop star, having released a number of music albums and sung many of the theme songs for the films in which he has starred. He is also a globally known philanthropist and has been named as one of the top 10 most charitable celebrities by Forbes magazine. In 2004, film scholar Andrew Willis stated that Chan was perhaps the “most recognised film star in the world”. In 2015, Forbes estimated his net worth to be $350 million, and as of 2016, he was the second-highest-paid actor in the world.
Since 2013, Chan has been a pro-Communist politician, serving in the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference. After the Hong Kong electoral reform in 2021, Chan became an Election Committee member and could vote for the Chief Executive. (Wikipedia)
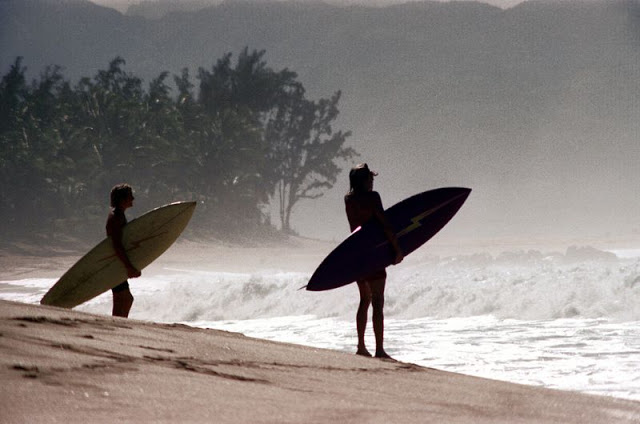































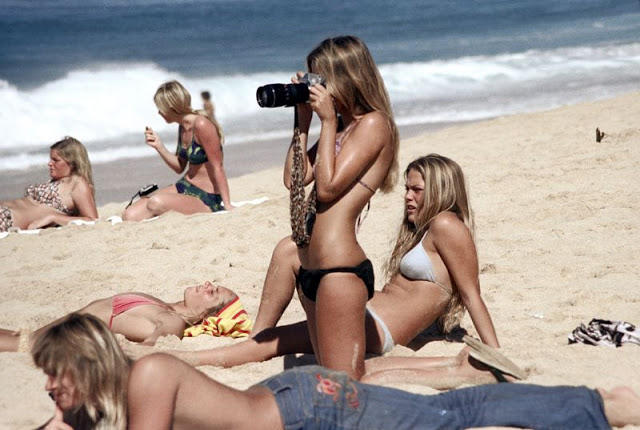
Oahu, also known as “The Gathering Place”, is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island is within Honolulu County and the state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu’s southeast coast.
Including small associated islands such as Ford Island plus those in Kane?ohe Bay and off the eastern (windward) coast, its area is 596.7 square miles (1,545.4 km2), making it the 20th-largest island in the United States.
Oahu is 44 miles (71 km) long and 30 miles (48 km) across. Its shoreline is 227 miles (365 km) long. The island is composed of two separate shield volcanoes: the Wai?anae and Ko?olau Ranges, with a broad valley or saddle (the central Oahu Plain) between them. The highest point is Ka?ala in the Wai?anae Range, rising to 4,003 feet (1,220 m) above sea level.
The island, which constitutes the bulk of Honolulu County, had a population of 1,016,508 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, up from 953,207 people in 2010 (approximately 70% of the total 1,455,271 population of Hawaii, with approximately 81% of those living in or near the Honolulu urban area). Oahu has for a long time been known as the “Gathering Place”. The term O?ahu has no confirmed meaning in Hawaiian, other than that of the place itself. Ancient Hawaiian tradition attributes the name’s origin in the legend of Hawai?iloa, the Polynesian navigator credited with discovery of the Hawaiian Islands. The story relates that he named the island after his daughter.
Oahu has a well-developed transportation network that resembles that of many other U.S. cities. There are four Interstate Highways on Oahu: H-1, H-2, H-3, and H-201. H-1 runs from Kapolei (Leeward side) to Honolulu, where it turns into Kalaniana?ole Highway. H-2 serves as a spur route towards the suburbs of Mililani and Waipio, the town of Wahiawa, the North Shore, and Schofield Barracks. H-3 connects central Oahu to Windward Oahu and Marine Corps Base Hawaii via the Tetsuo Harano Tunnels. H-201, the only auxilliary Interstate Highway outside of the contiguous United States, serves as a bypass of H-1. Other areas are predominantly served by state highways. The City and County of Honolulu operates a bus system known as TheBus and is currently building a new elevated rail system.
The city of Honolulu—largest city, state capital, and main deepwater marine port for the State of Hawai?i—is located here. As a jurisdictional unit, the entire island of Oahu is in Honolulu County, although as a place name, Honolulu occupies only a portion of the southeast end of the island.
Well-known features found on Oahu include Waikiki, Pearl Harbor, Diamond Head, Hanauma, Kane?ohe Bay, Kailua Bay, North Shore, and the resort destination, Ko Olina.
While the island is designated the City and County of Honolulu, excluding the minor Northwestern Hawaiian Islands, residents identify settlements using town names (generally those of the census-designated places), and consider the island to be divided into various areas which may overlap. The most commonly accepted areas are the “City”, “Town” or “Town side”, which is the urbanized area from Halawa to the area below Diamond Head (residents of the island north of the Ko?olau Mountains consider the Town Side to be the entire southern half), “West Oahu”, which goes from Pearl Harbor to Kapolei, ?Ewa and may include the Makaha and Wai?anae areas; the “North Shore” (northwestern coast); the “Windward Side” (northeastern coast from Kahuku to Kane?ohe); the “East Side” or “East Coast” (the eastern portion of the island, from Kane?ohe on the northeast, around the tip of the island to include much of the area east of Diamond Head); and “The Valley” or “Central Oahu” which runs northwest from Pearl Harbor toward Hale?iwa. These terms are somewhat flexible, depending on the area in which the user lives, and are used in a mostly general way, but residents of each area identify strongly with their part of the island, especially those outside of widely-known towns. For instance, if locals are asked where they live, they would usually reply “Windward Oahu” rather than “Laie”.
Being roughly diamond-shaped, surrounded by ocean and divided by mountain ranges, directions on Oahu are not generally described with the compass directions found throughout the world. Locals instead use directions originally using Honolulu as the central point. To go ?ewa means traveling toward the western tip of the island, “Diamond Head” is toward the eastern tip, mauka is inland (toward the central Ko?olau Mountain range, north of Honolulu) and makai toward the sea. When these directions became common, Diamond Head was the eastern edge of the primary populated area. Today, with a much larger populace and extensive development, the mountain itself is often not actually to the east when directions are given, and is not to be used as a literal point of reference—to go “Diamond Head” is to go to the east from anywhere on the island.
Oahu is also known for having the longest rain shower in history, which lasted for 200 consecutive days. Kane?ohe Ranch reported 247 straight days with rain from August 27, 1993 to April 30, 1994. The average temperature in Oahu is around 70–85 °F (21–29 °C) and the island is the warmest in June through October. The weather during the winter is cooler, but still warm with an average temperature of 68–78 °F (20–26 °C).
The windward side is known for some of the most beautiful beaches in the world. Lanikai Beach on the windward coast of Oahu has been consistently ranked among the best beaches in the world. (Wikipedia)
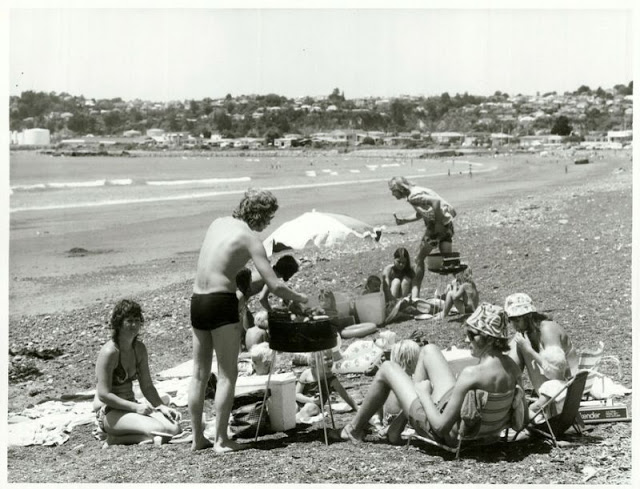
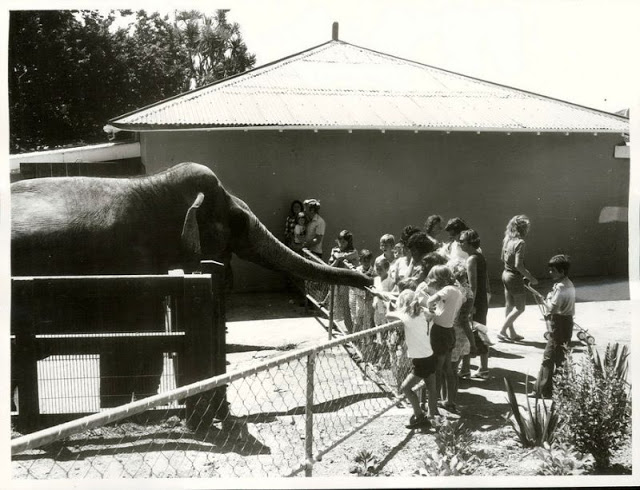
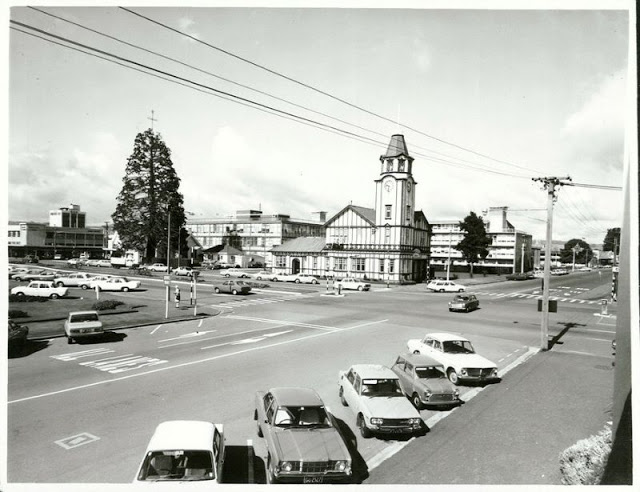
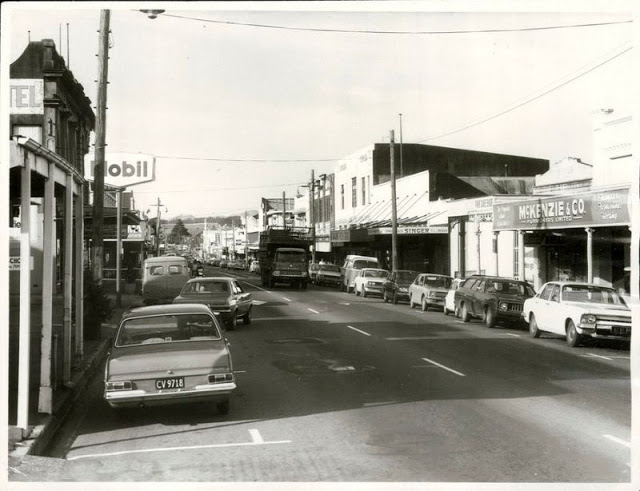
These fascinating photos were taken by Nick DeWolf that show daily life of Oahu beaches, Hawaii in 1973.
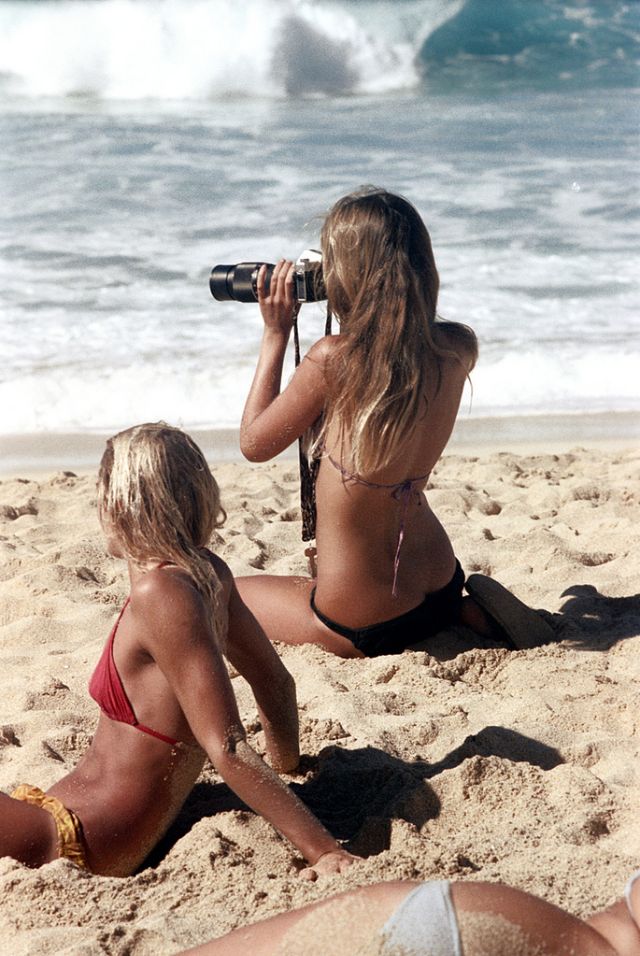
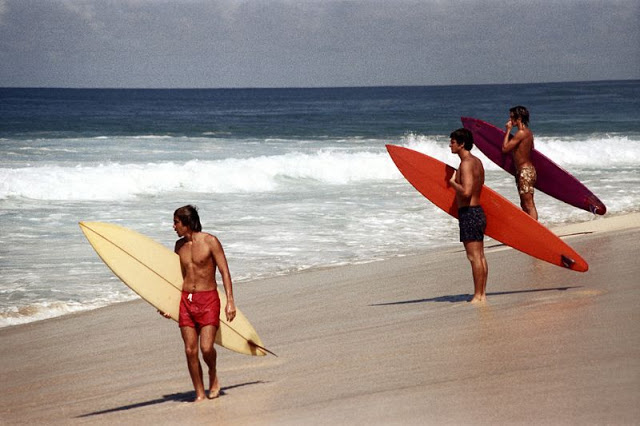
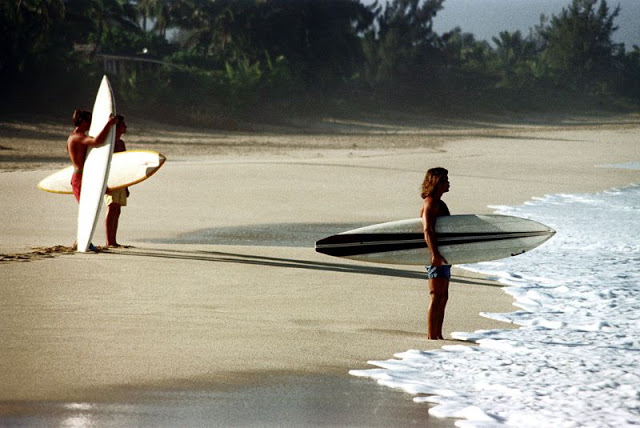
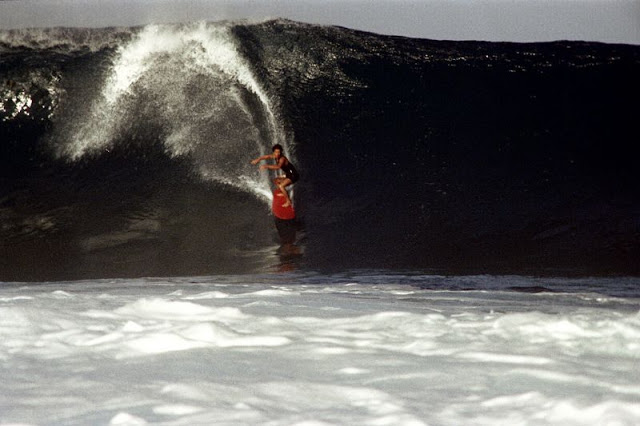
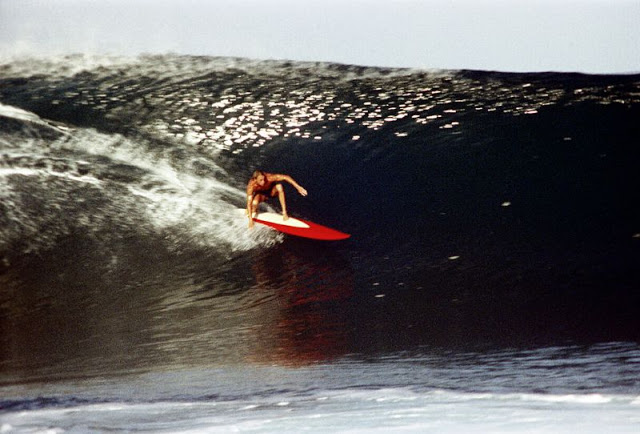
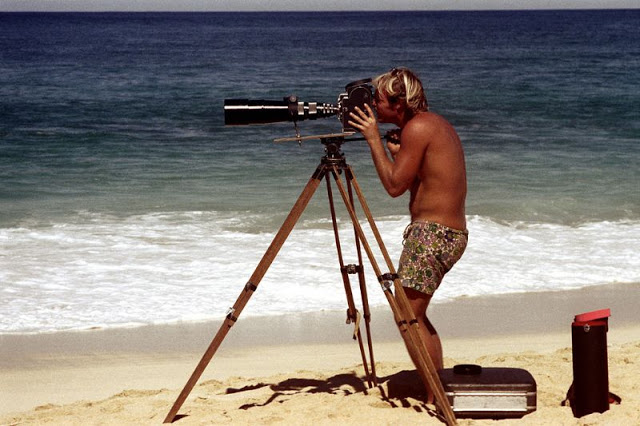
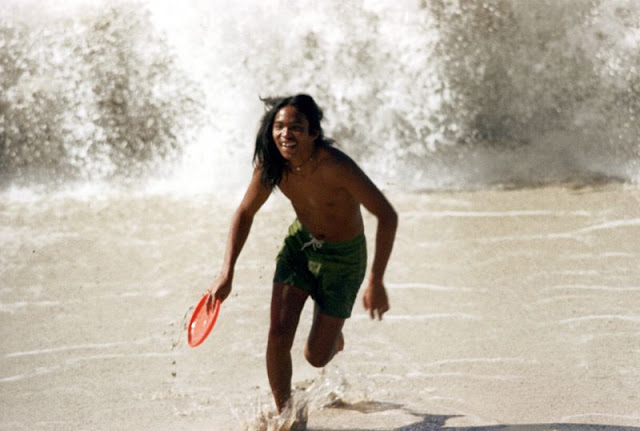
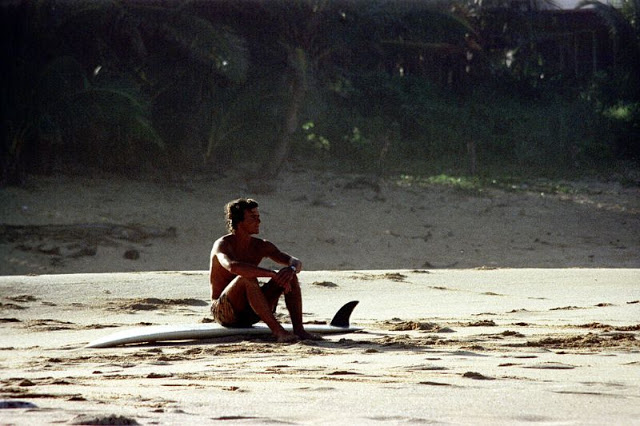
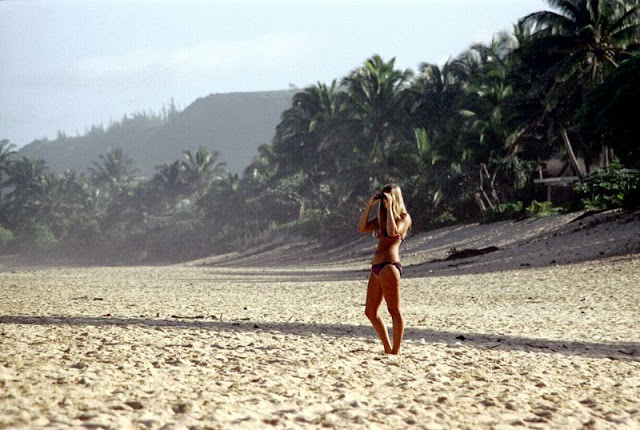
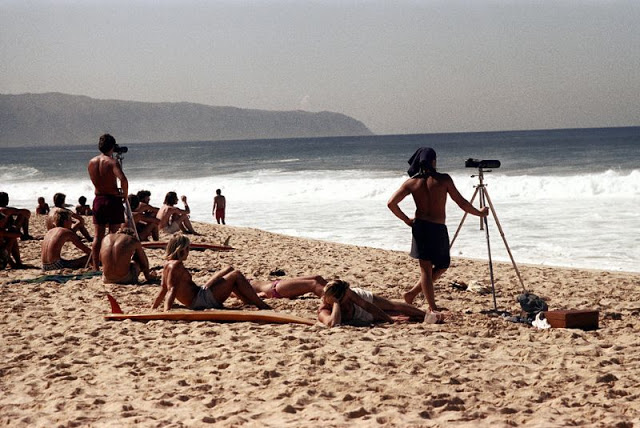
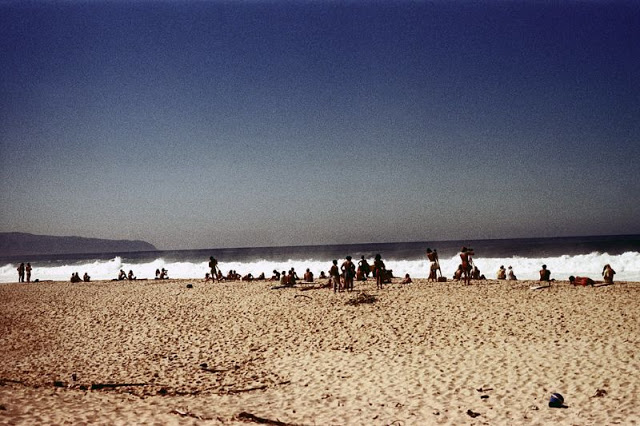
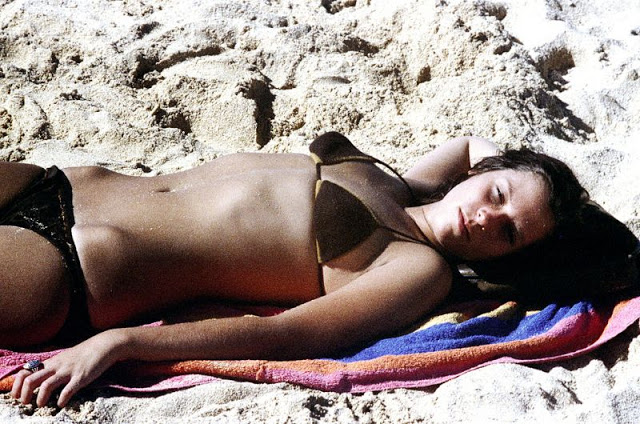
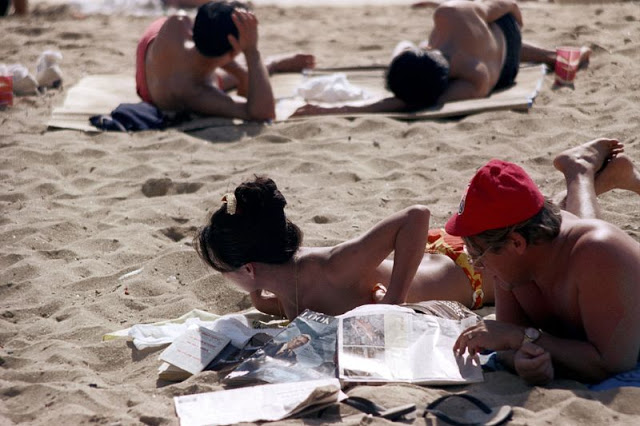
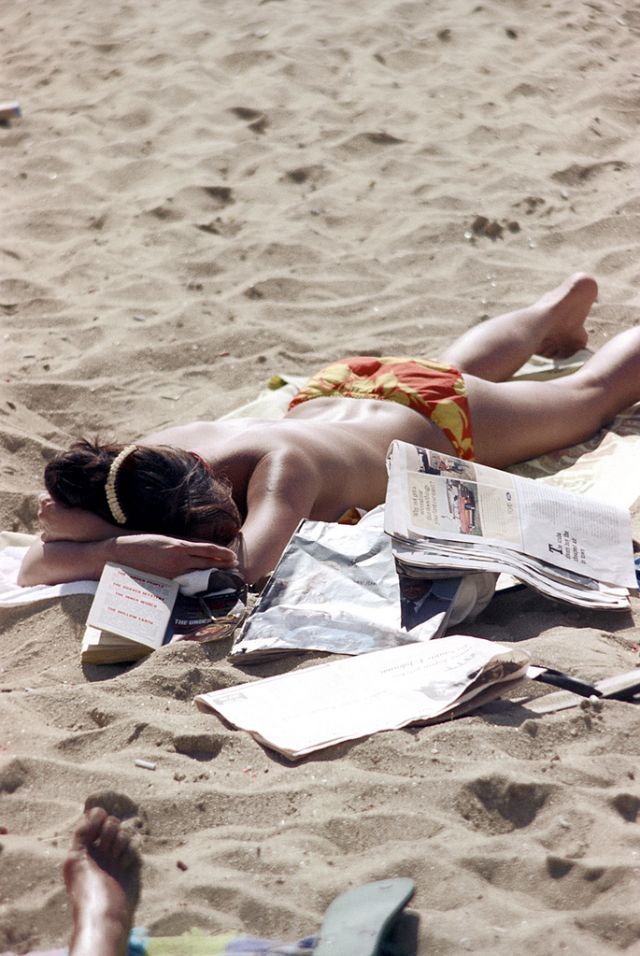
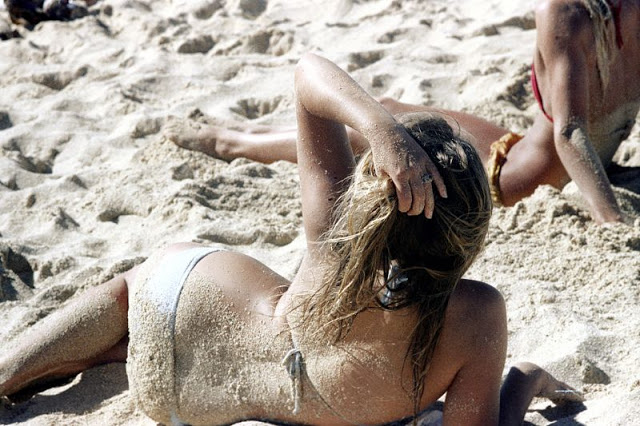
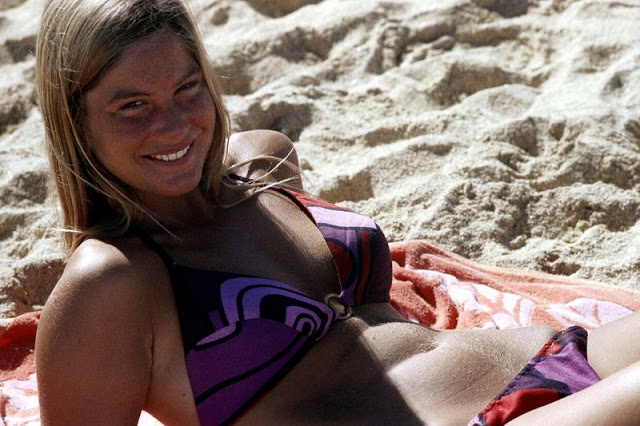
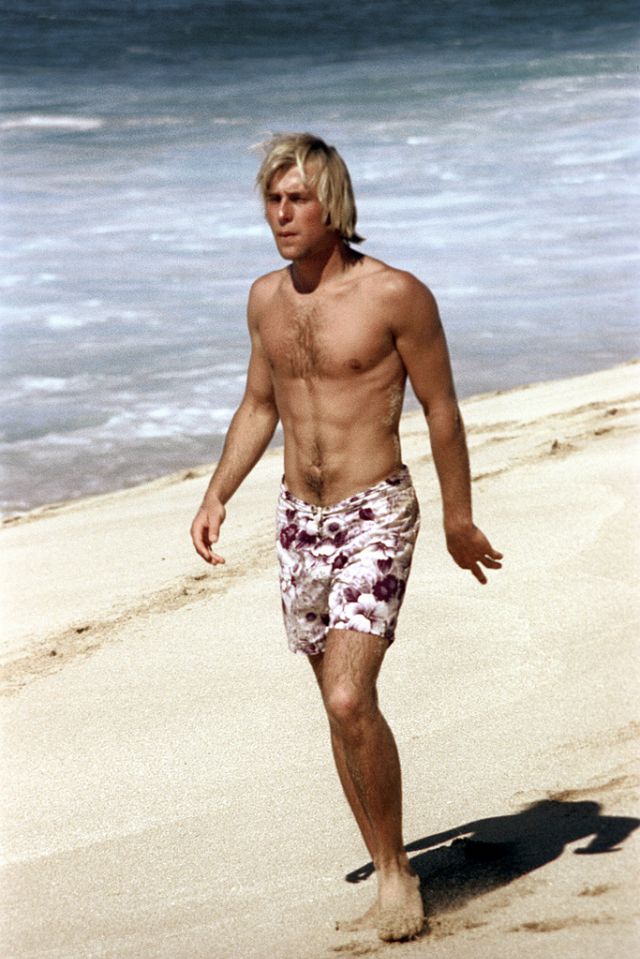
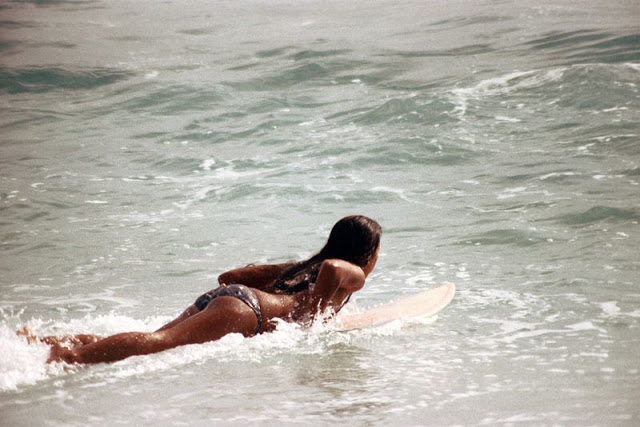
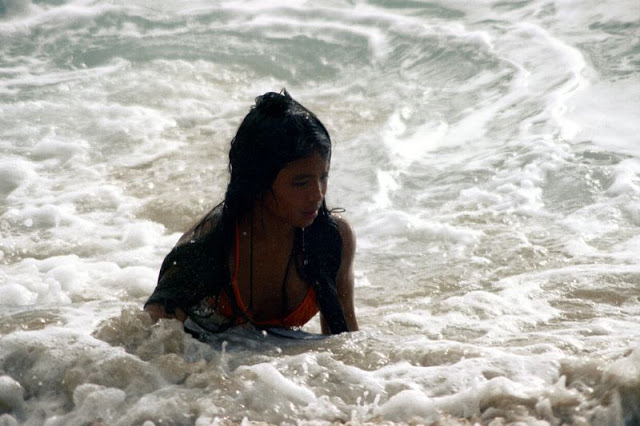
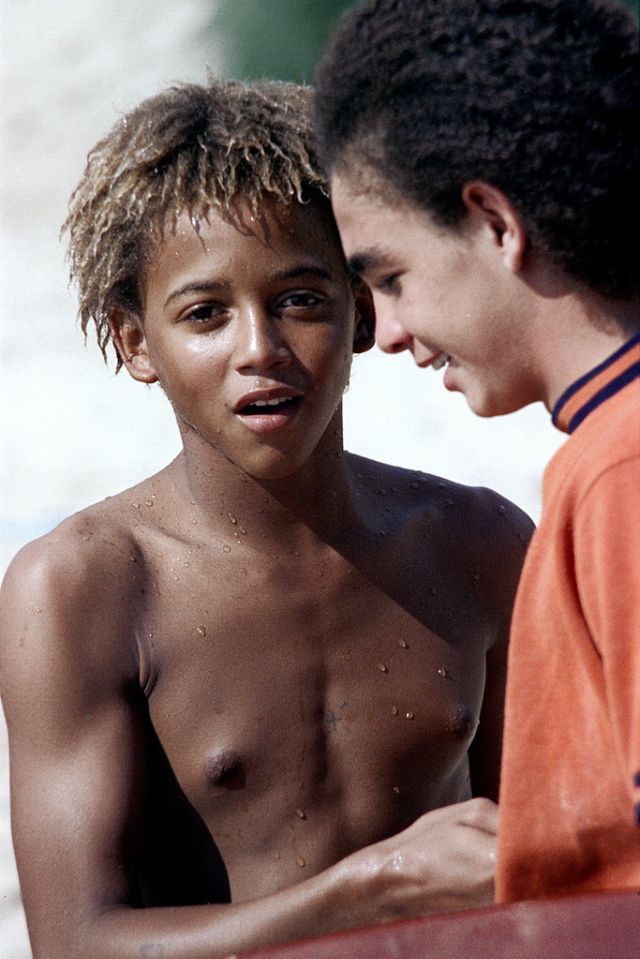
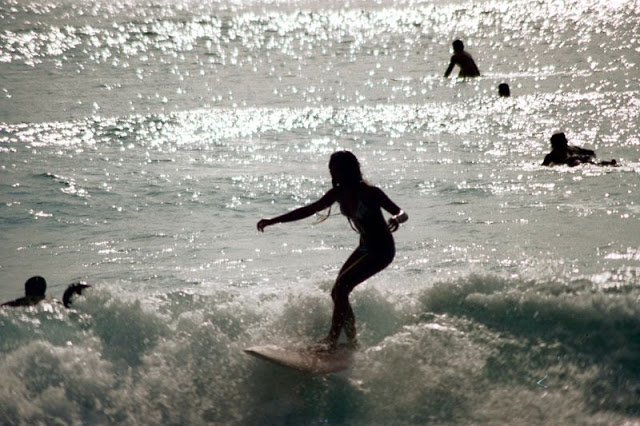
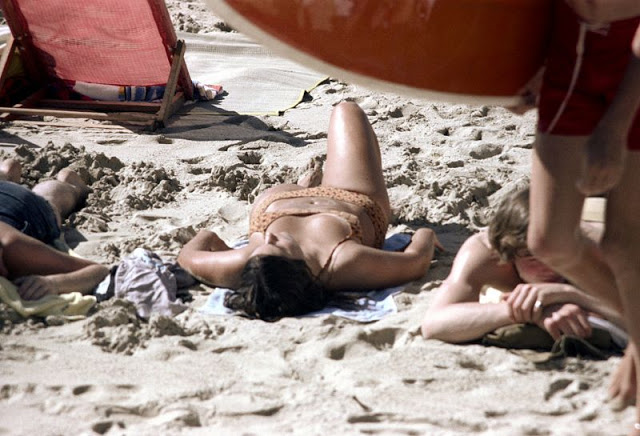
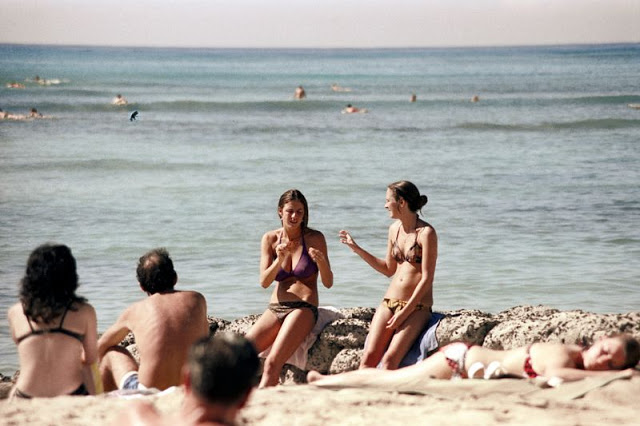
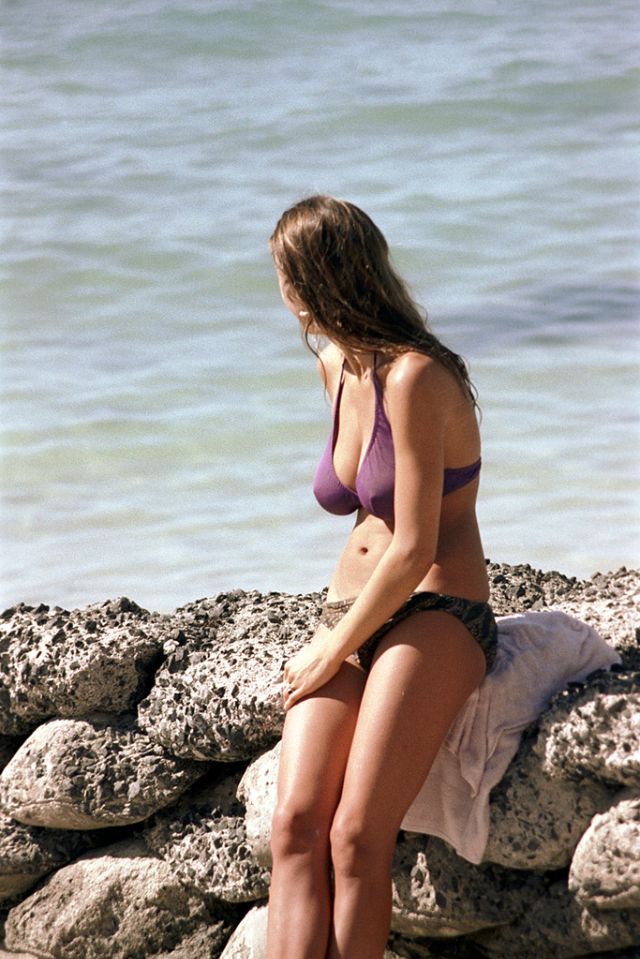
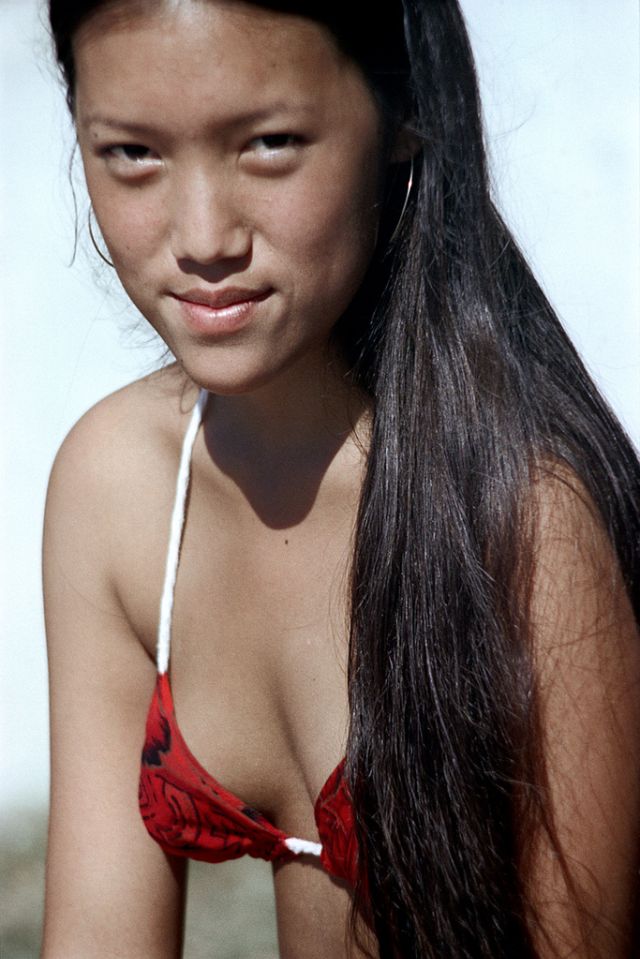
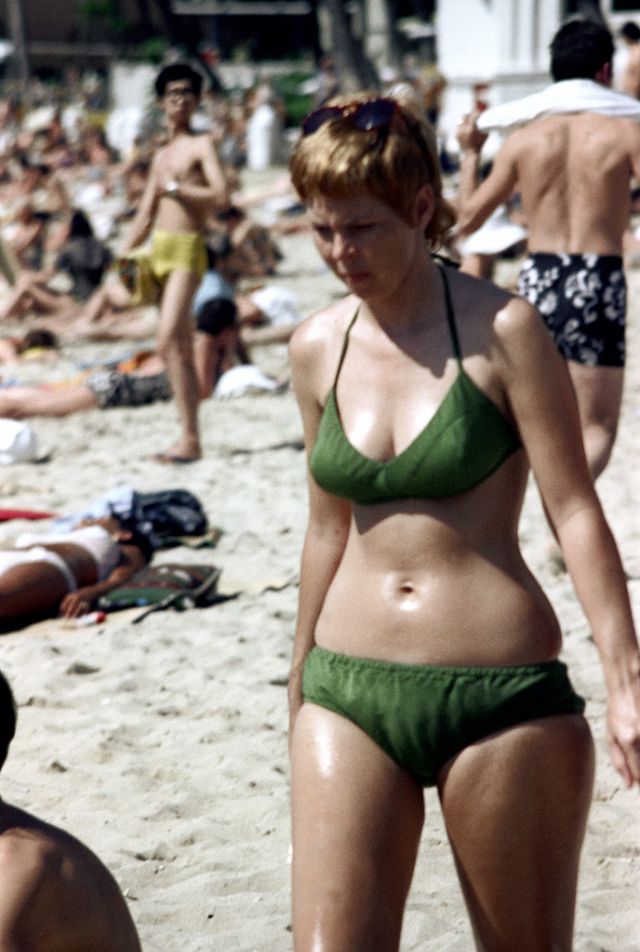
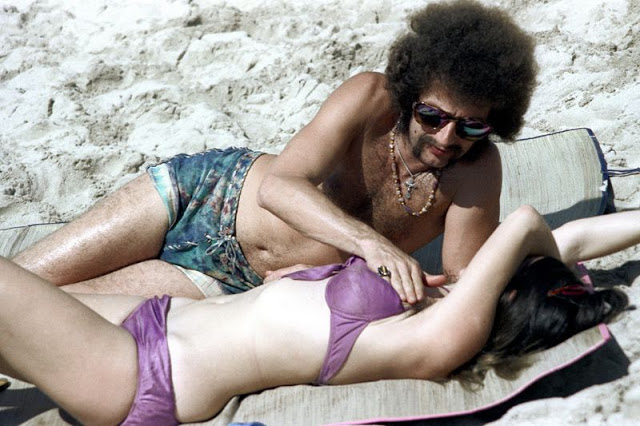
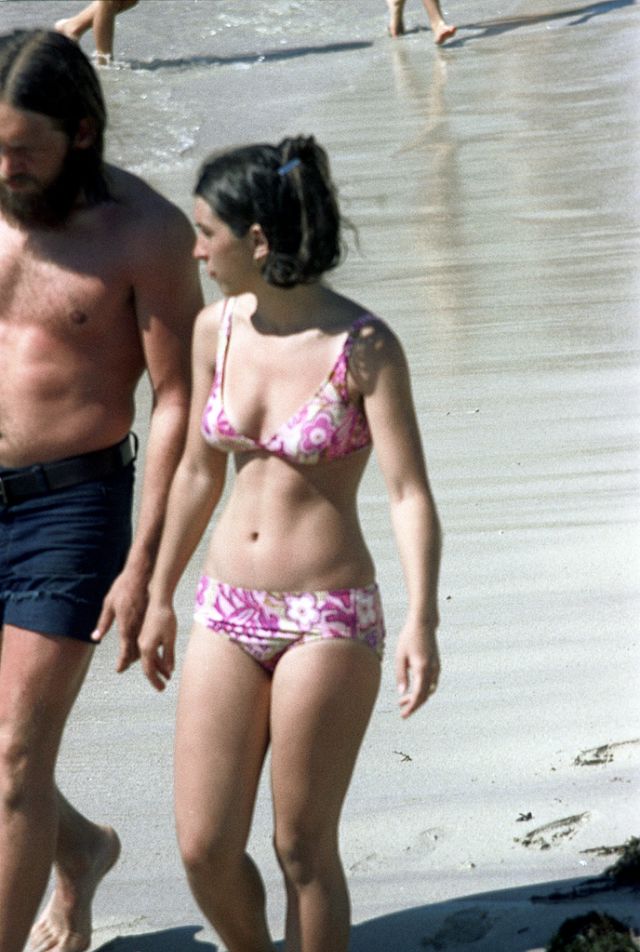
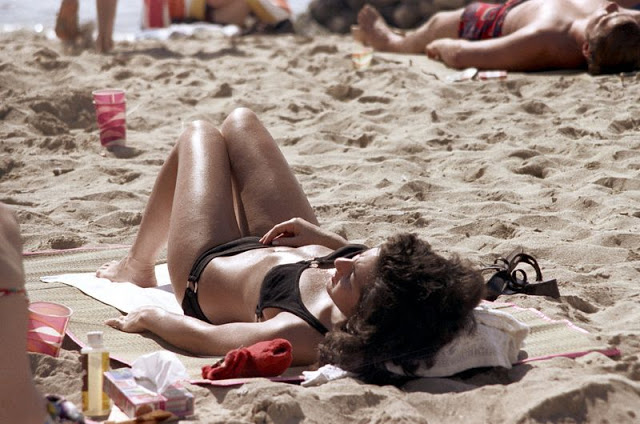
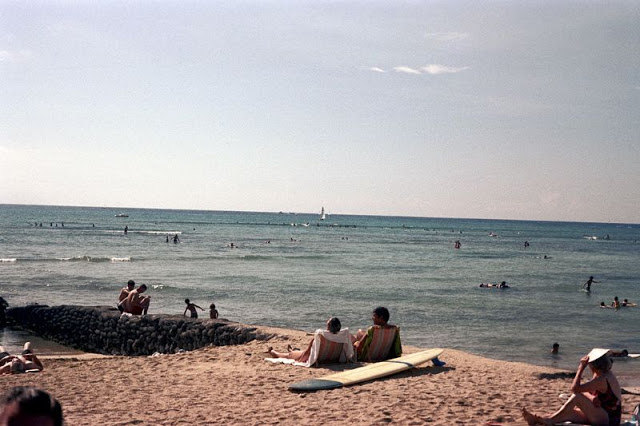
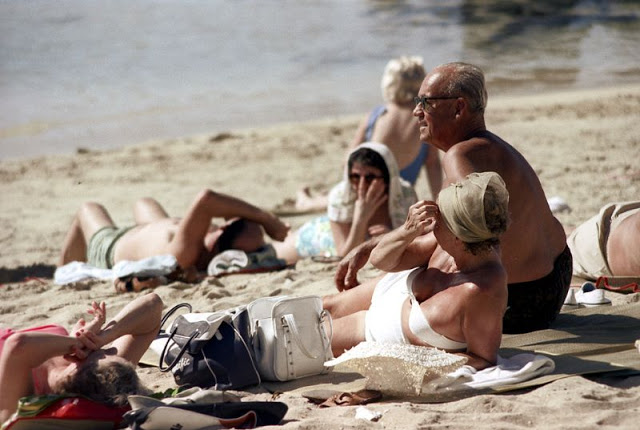
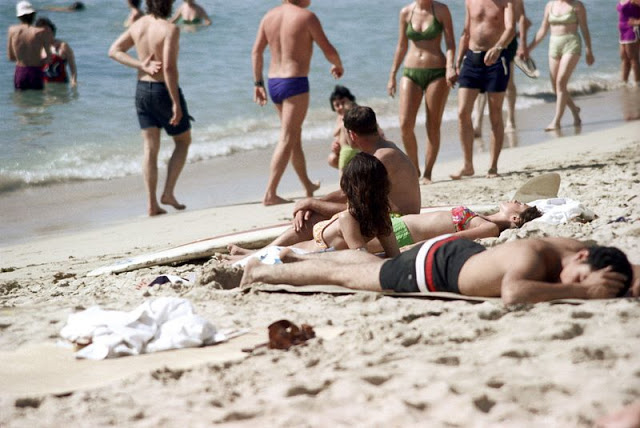
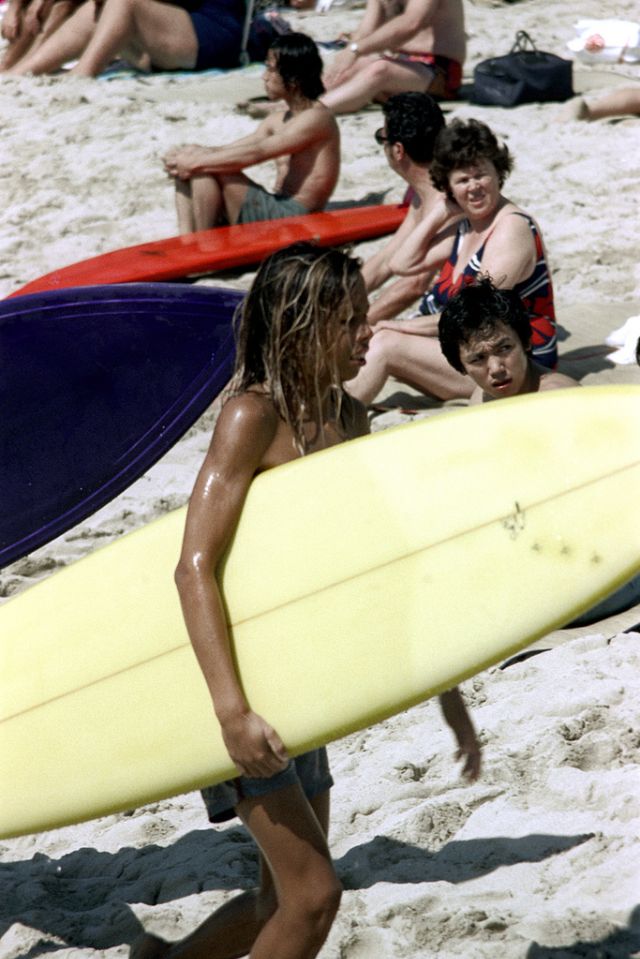
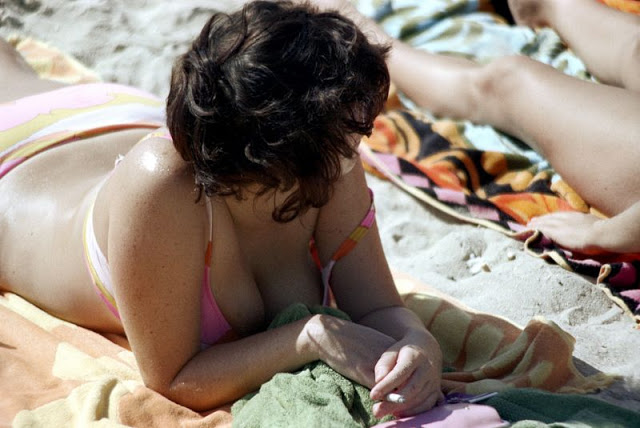
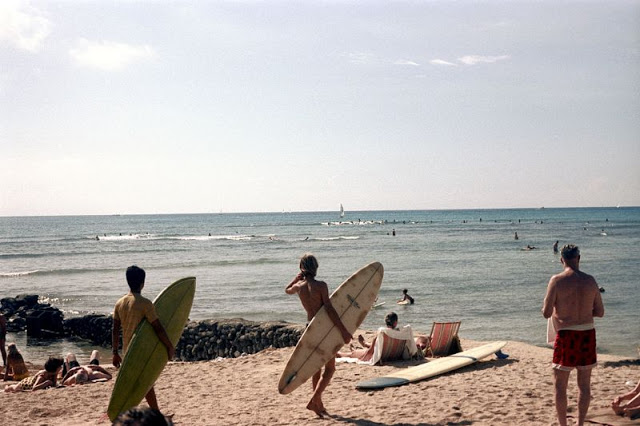
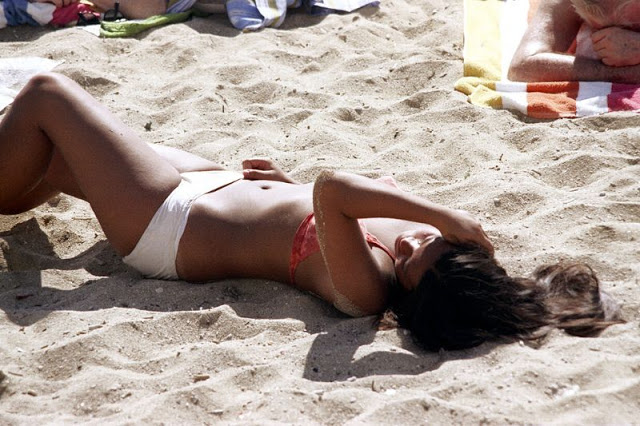
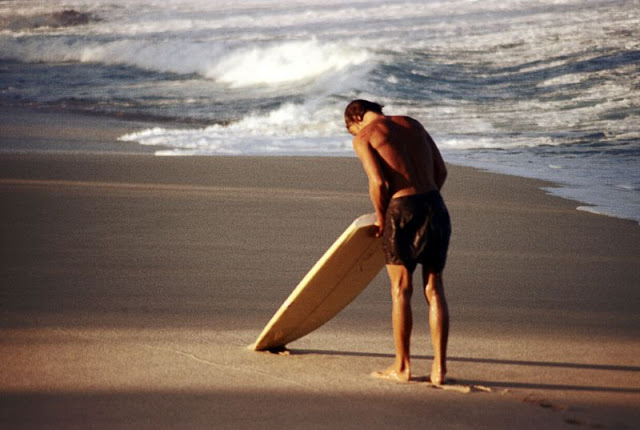
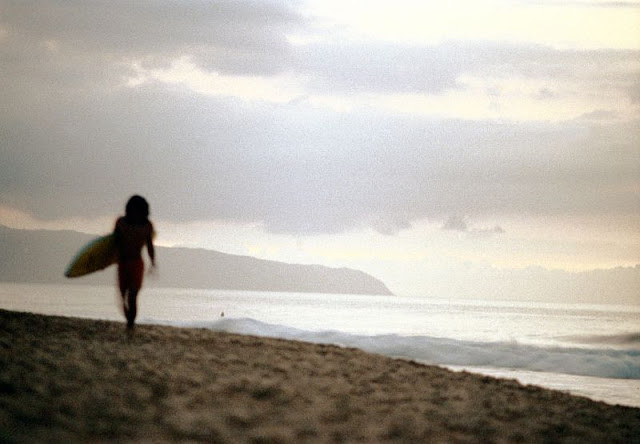
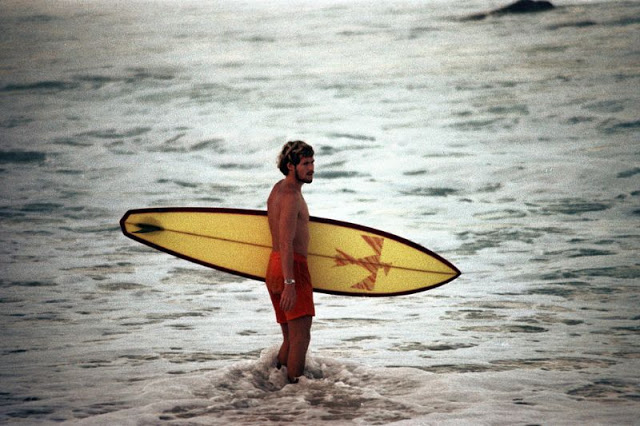
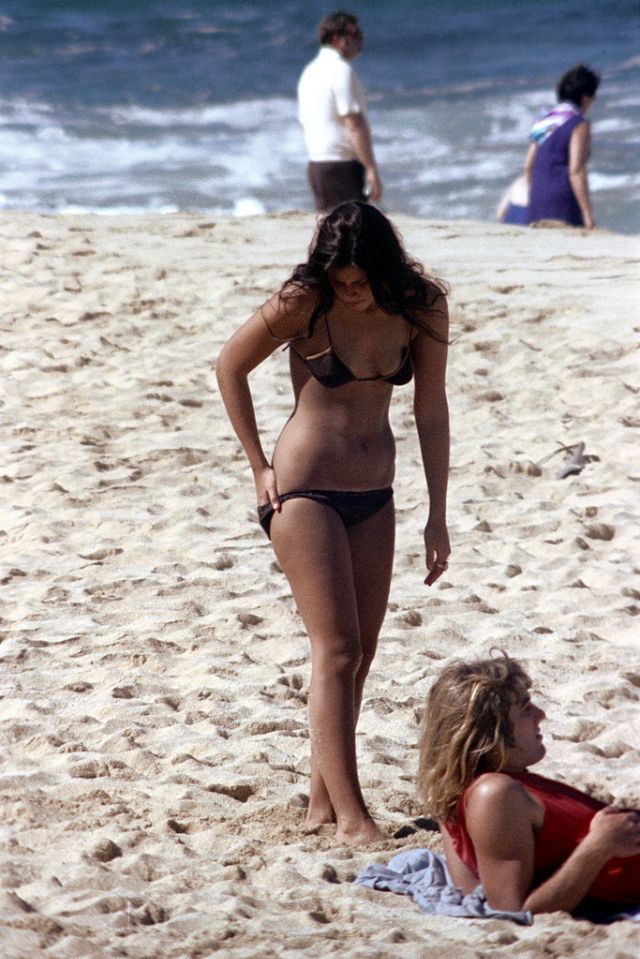
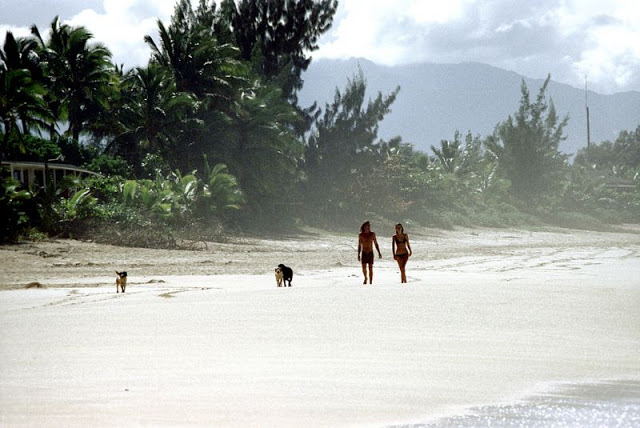
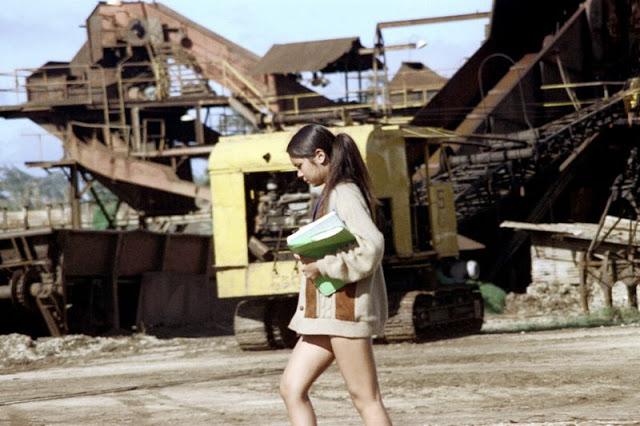
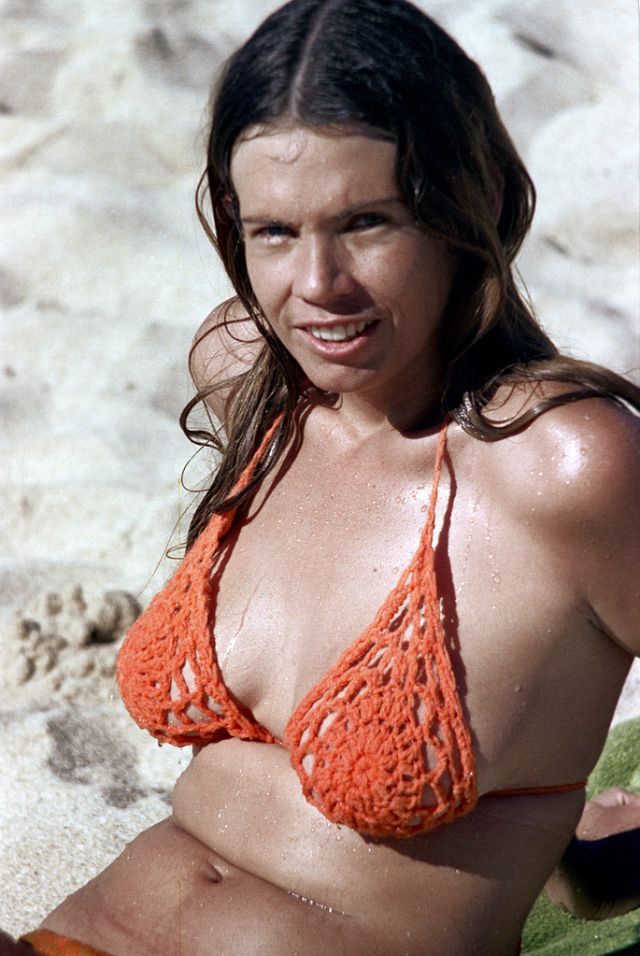
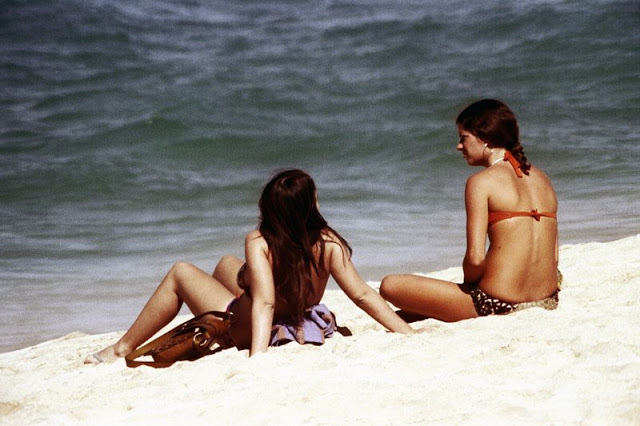


































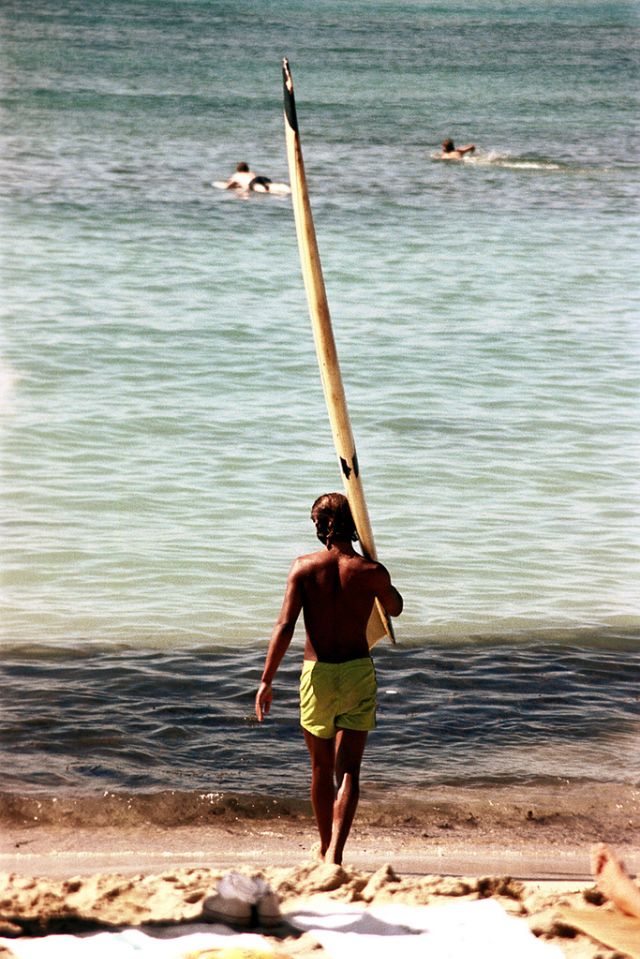


















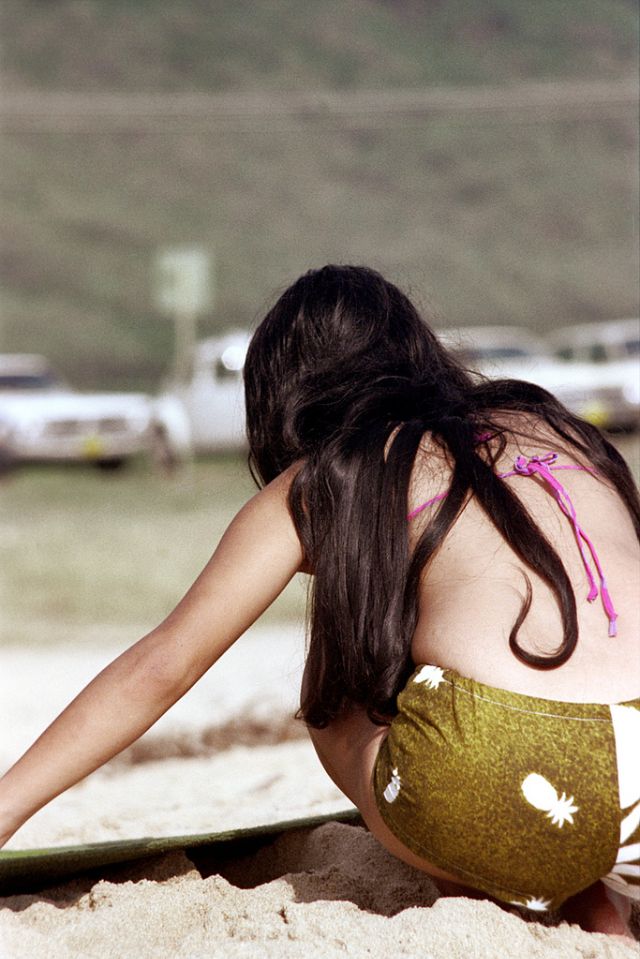
(Photos © Nick DeWolf)

Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, covering over 17,125,191 square kilometres (6,612,073 sq mi), and encompassing one-eighth of Earth’s inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has the most borders of any country in the world, with sixteen sovereign nations. It has a population of 146.2 million; and is the most populous country in Europe, and the ninth-most populous country in the world. Moscow, the capital, is the largest city entirely within Europe; while Saint Petersburg is the country’s second-largest city and cultural centre.
The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD. The medieval state of Rus’ arose in the 9th century. In 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire. Rus’ ultimately disintegrated, and the Grand Duchy of Moscow rose during the 15th century. By the 18th century, the nation had vastly expanded through conquest, annexation, and exploration to evolve into the Russian Empire, the third-largest empire in history. Following the Russian Revolution, the Russian SFSR became the largest and leading constituent of the Soviet Union, the world’s first constitutionally socialist state. The Soviet Union played a decisive role in the Allied victory in World War II, and emerged as a superpower and rival to the United States during the Cold War. The Soviet era saw some of the most significant technological achievements of the 20th century, including the world’s first human-made satellite and the launching of the first human in space.
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Russian SFSR reconstituted itself as the Russian Federation. In the aftermath of the constitutional crisis of 1993, a new constitution was adopted, and Russia has since been governed as a federal semi-presidential republic. Vladimir Putin has dominated Russia’s political system since 2000; during the period Russia has experienced democratic backsliding, and has shifted to an authoritarian state.
Russia is a great power, and a potential superpower. It is ranked 52nd in the Human Development Index, with a universal healthcare system, and a free university education. Russia’s economy is the world’s eleventh-largest by nominal GDP and the sixth-largest by PPP. It is a recognized nuclear-weapons state, possessing the world’s largest stockpile of nuclear weapons; with the second-most powerful military, and the fourth-highest military expenditure. Russia’s extensive mineral and energy resources are the world’s largest, and it is among the leading producers of oil and natural gas globally. It is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, a member of the G20, the SCO, the Council of Europe, BRICS, the APEC, the OSCE, the IIB and the WTO, as well as the leading member of the CIS, the CSTO, and the EAEU. Russia is also home to 30 UNESCO World Heritage Sites. (Wikipedia)
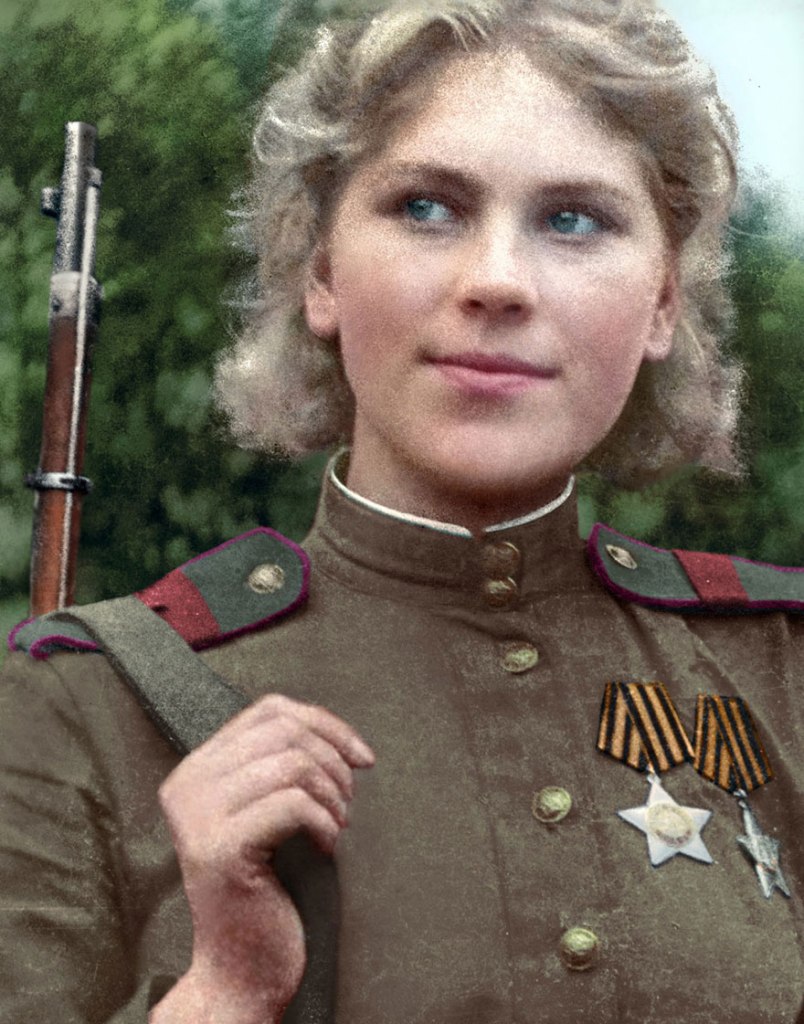
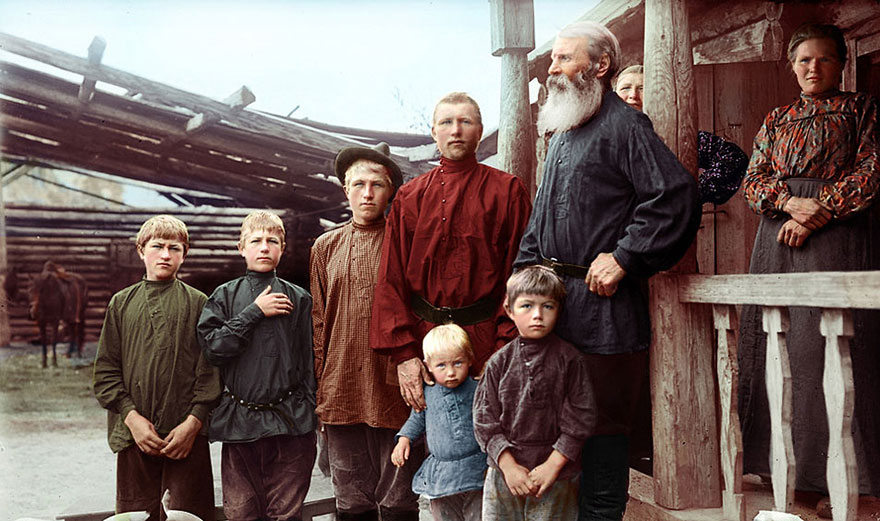
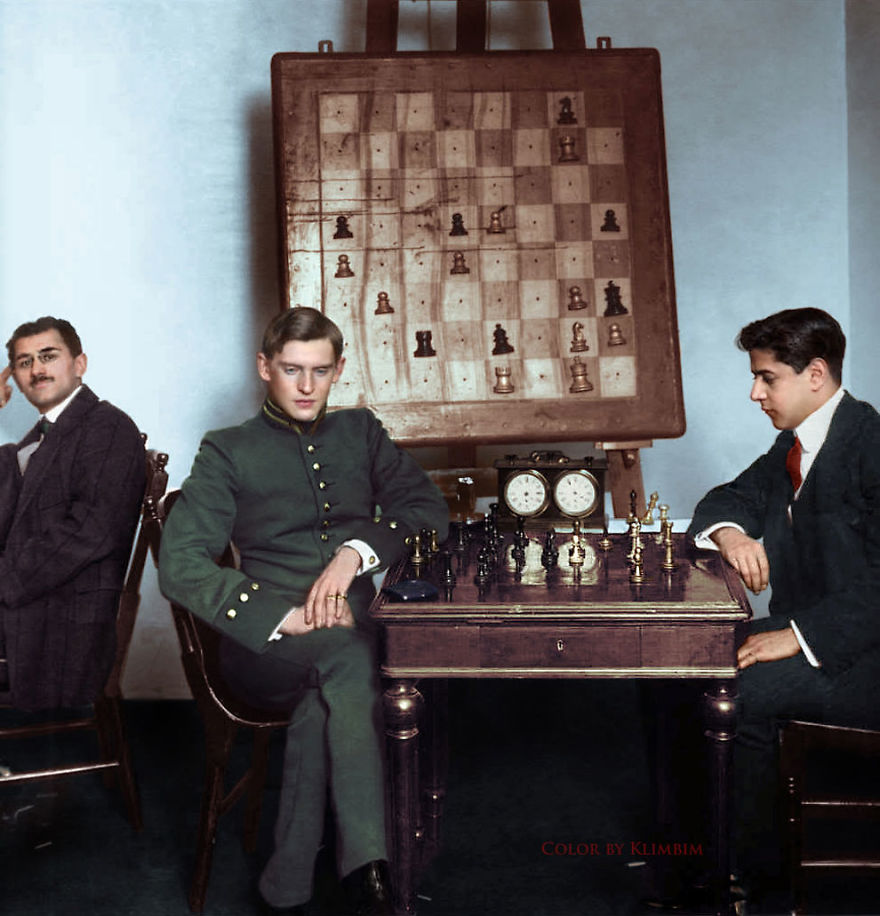
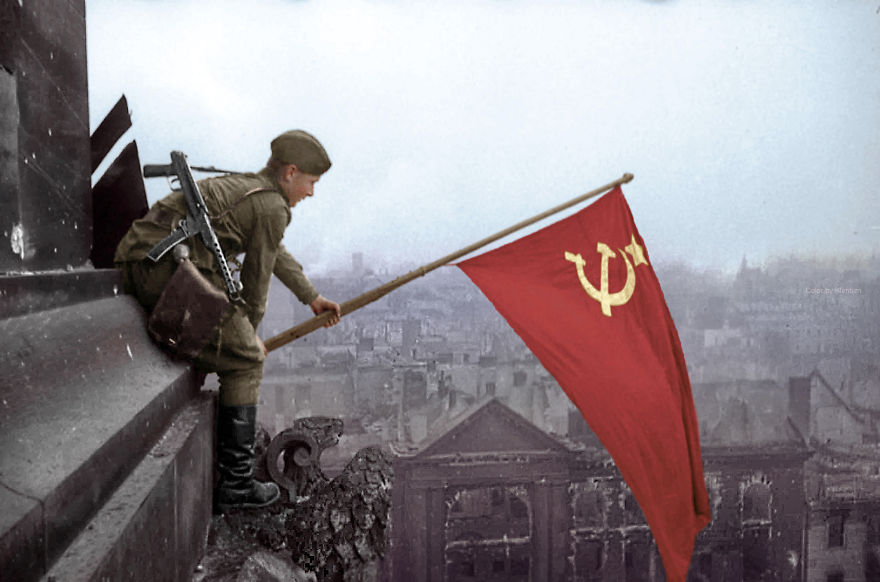
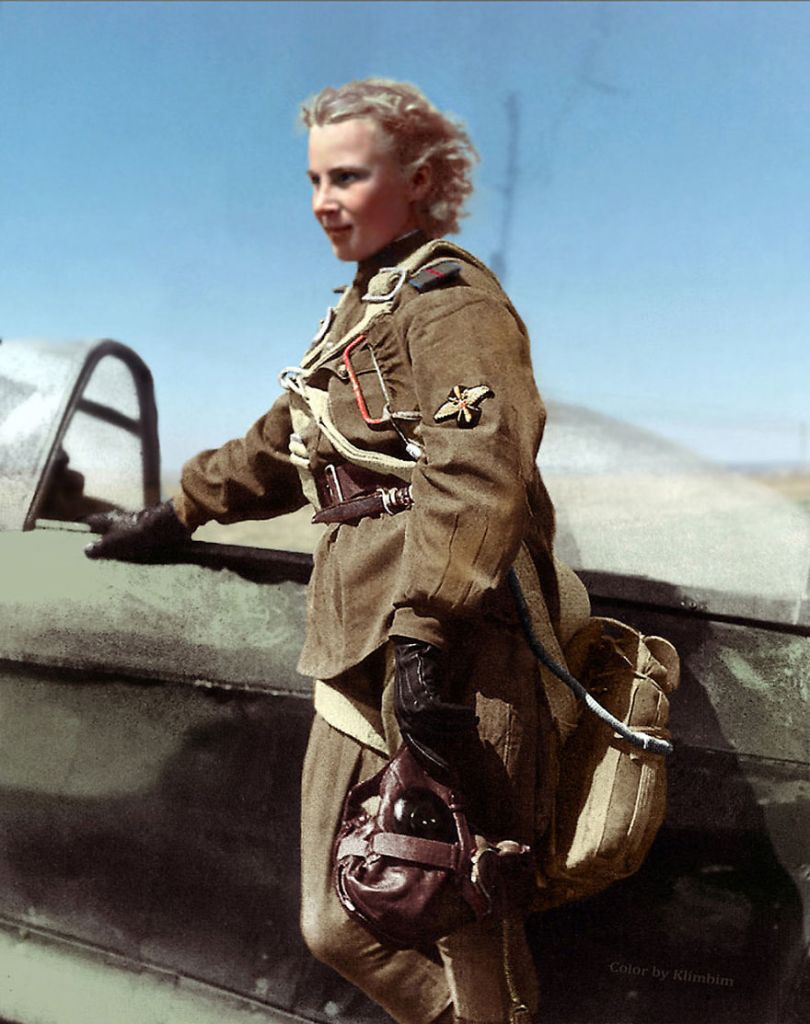
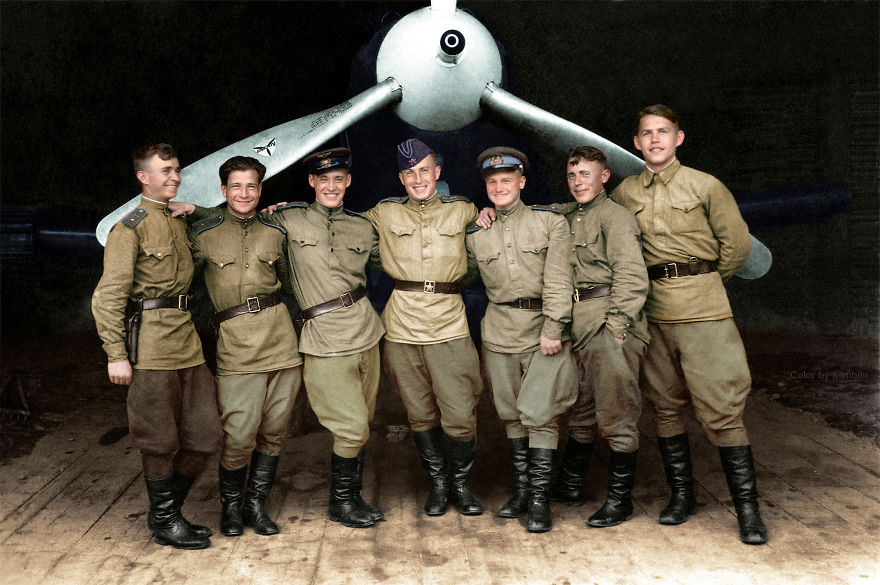
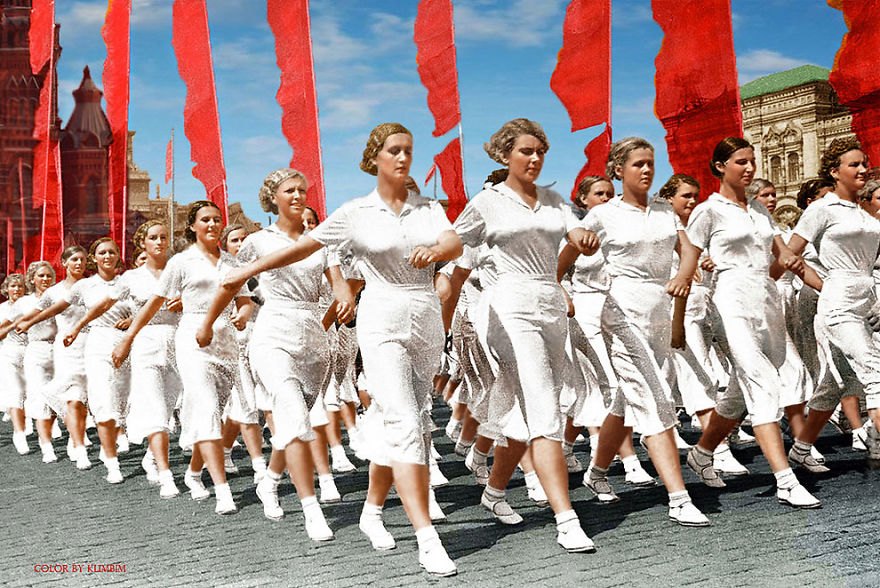
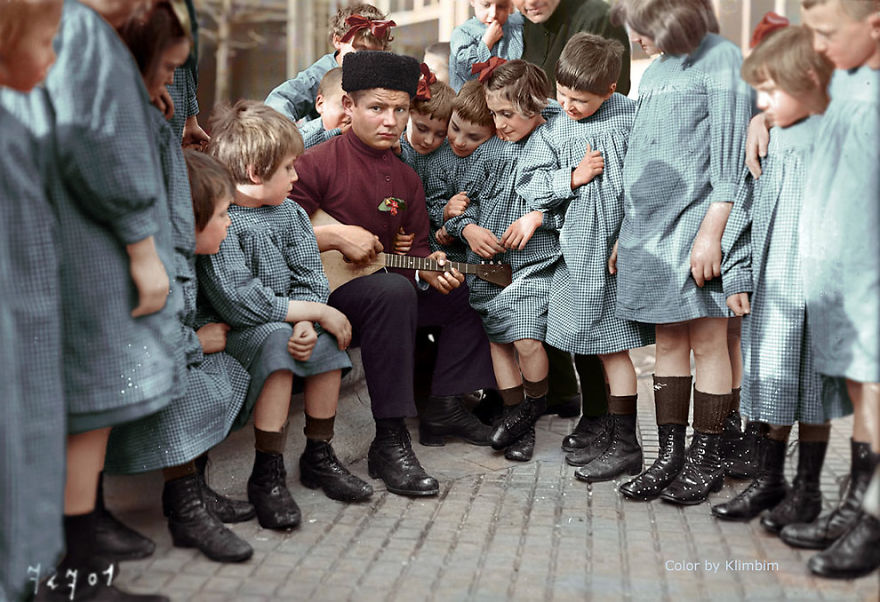
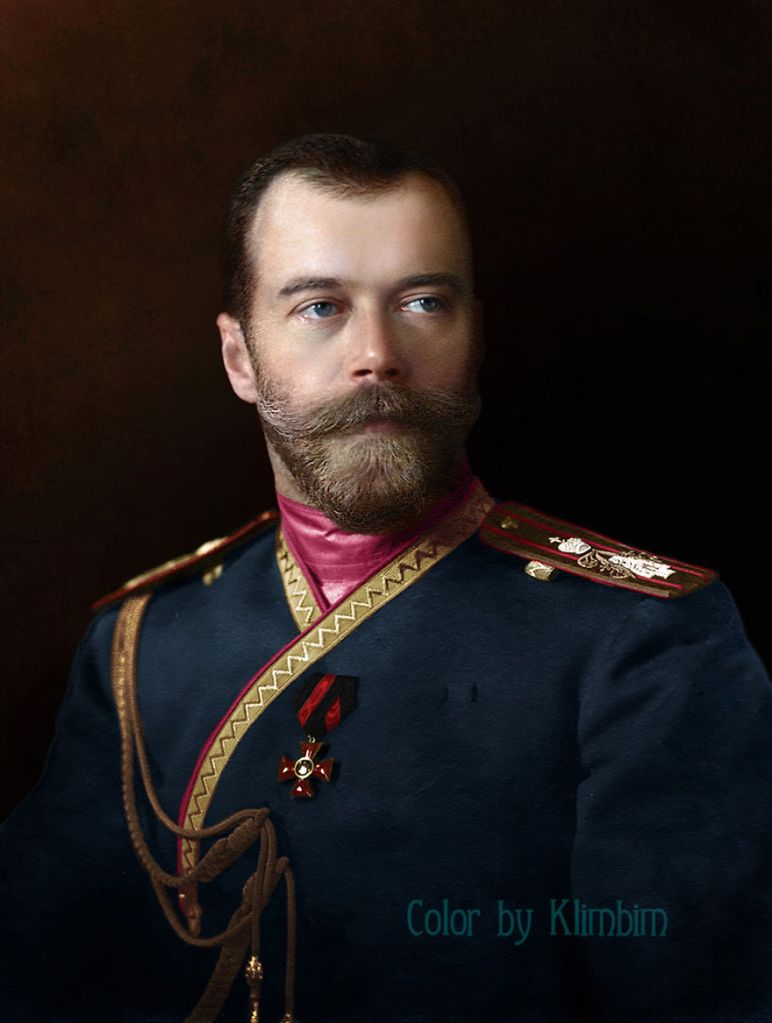
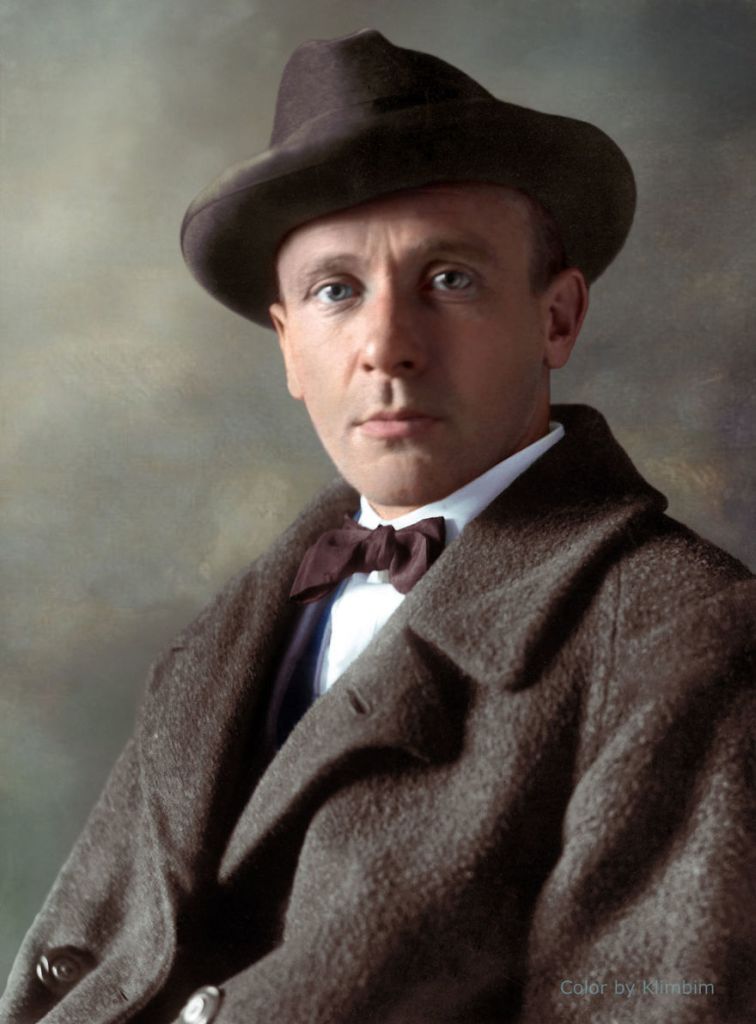
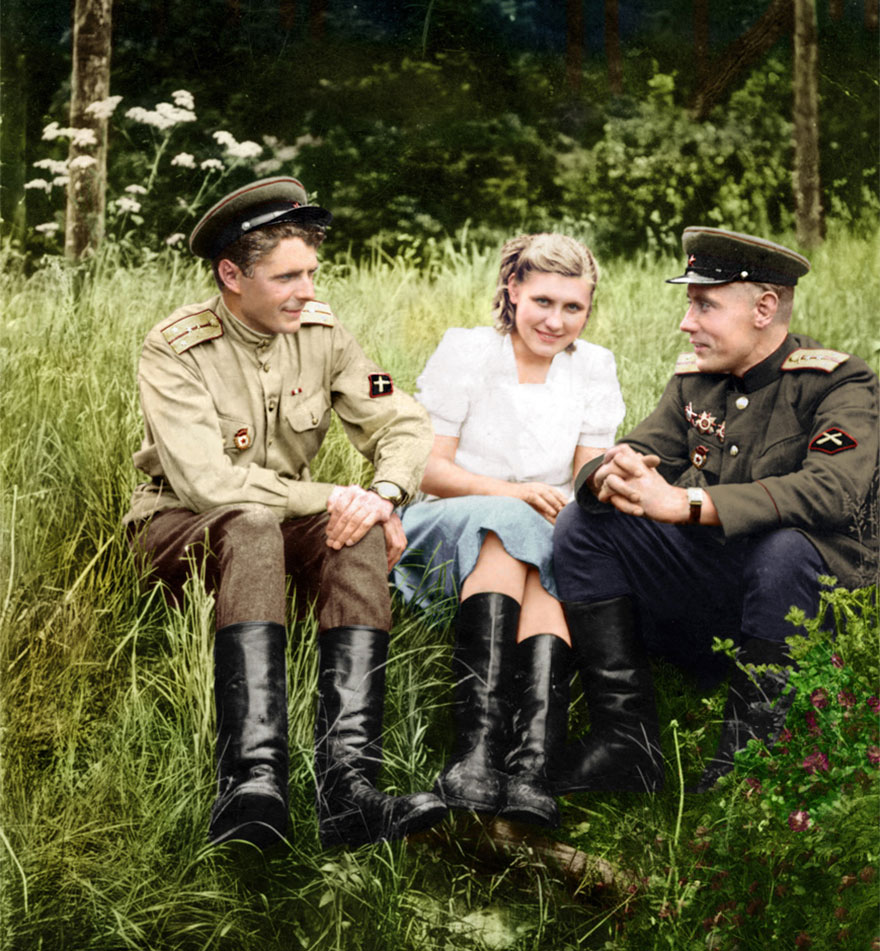
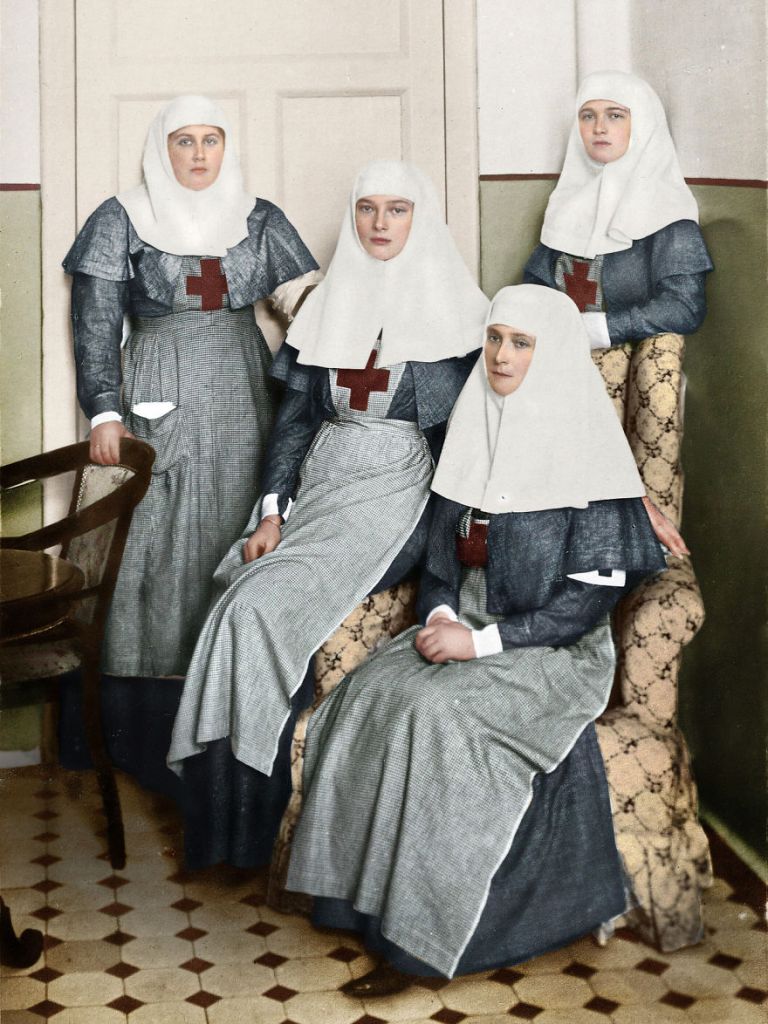
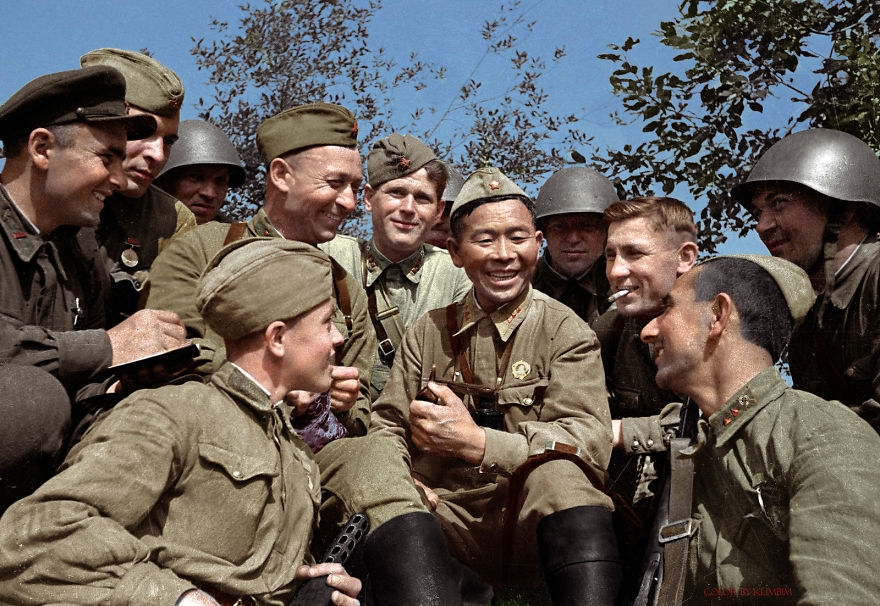
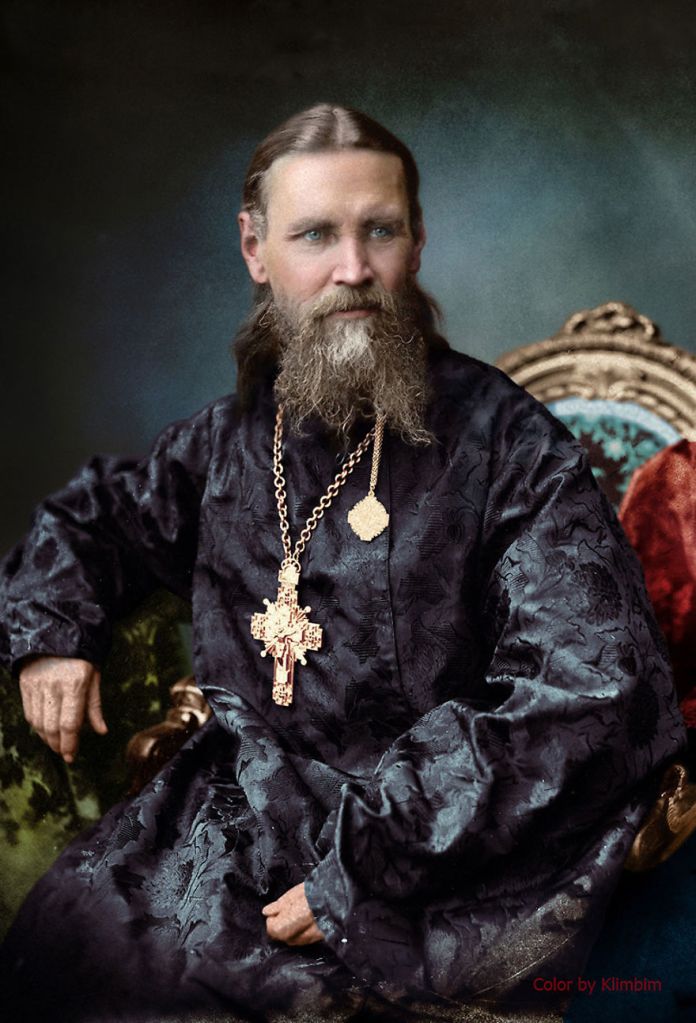
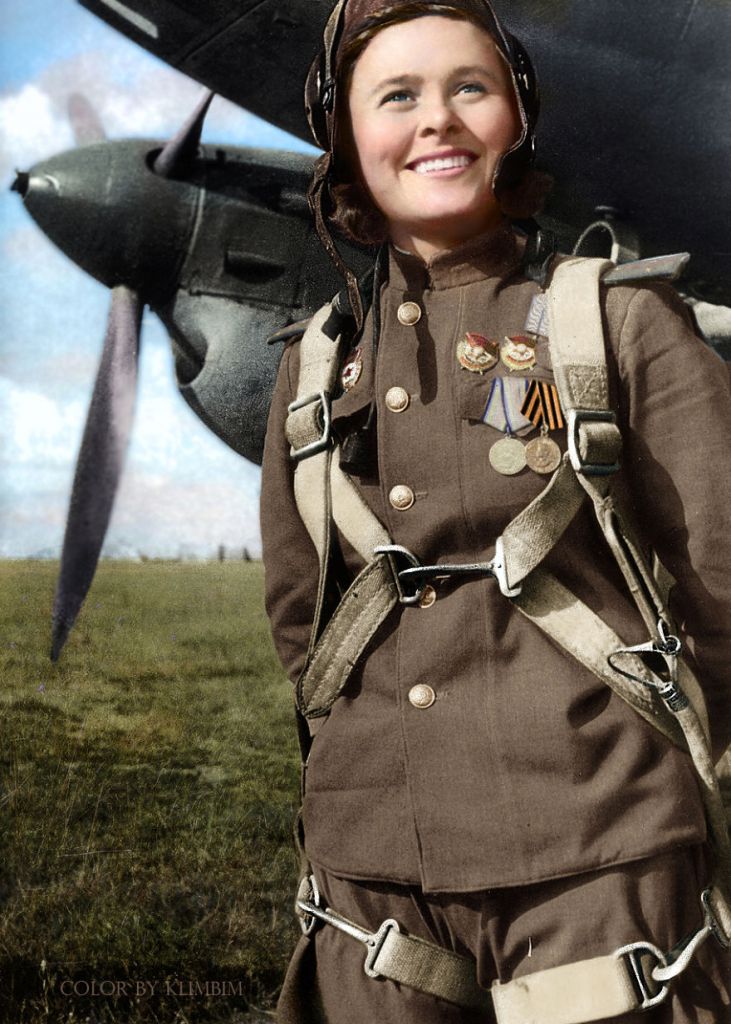
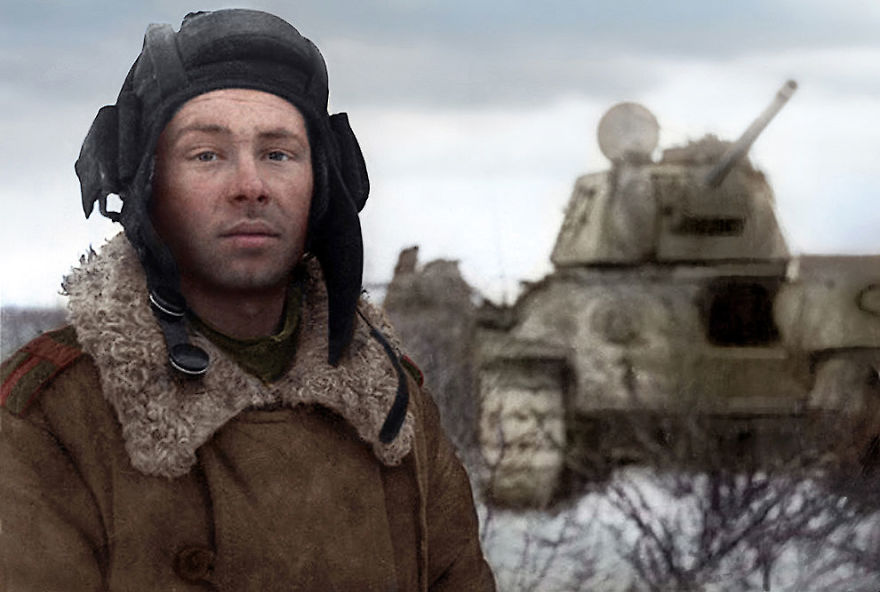
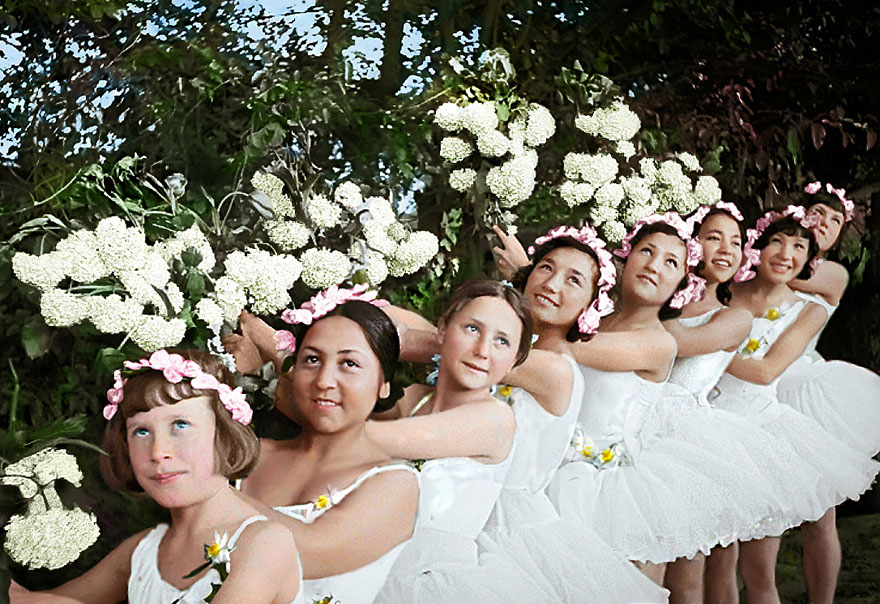
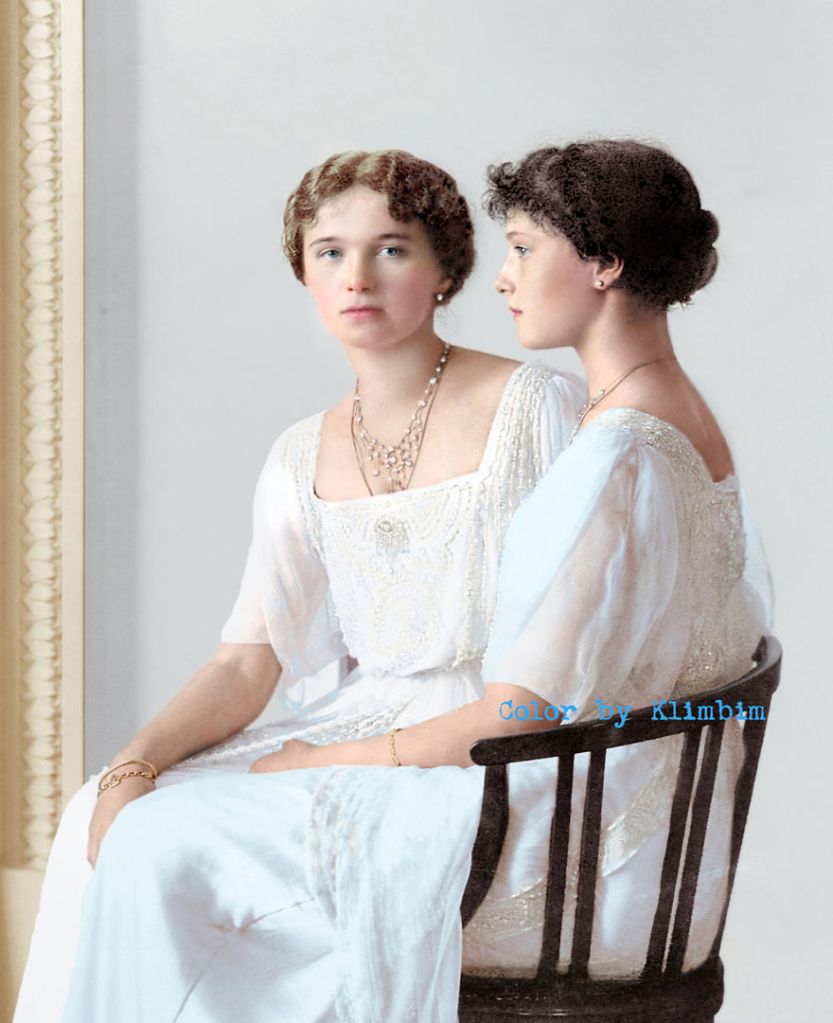
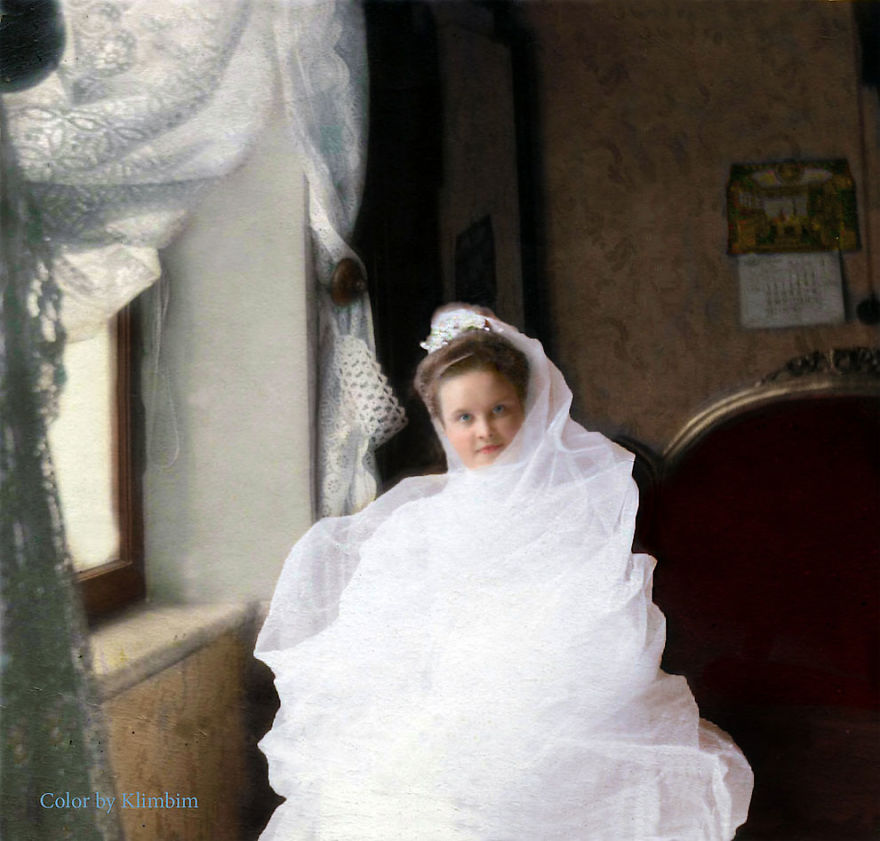
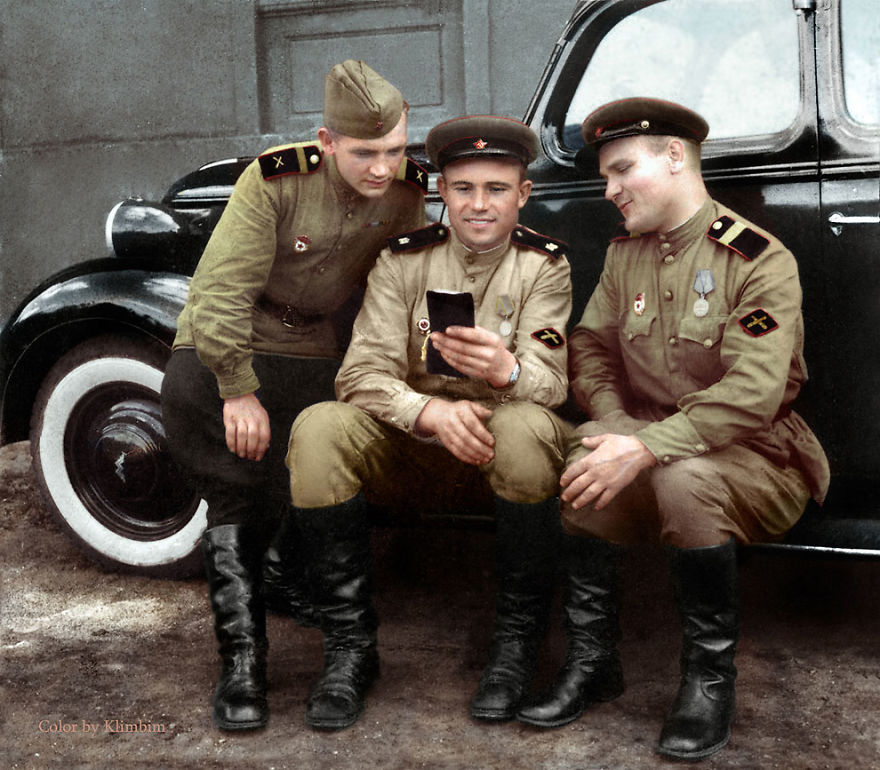
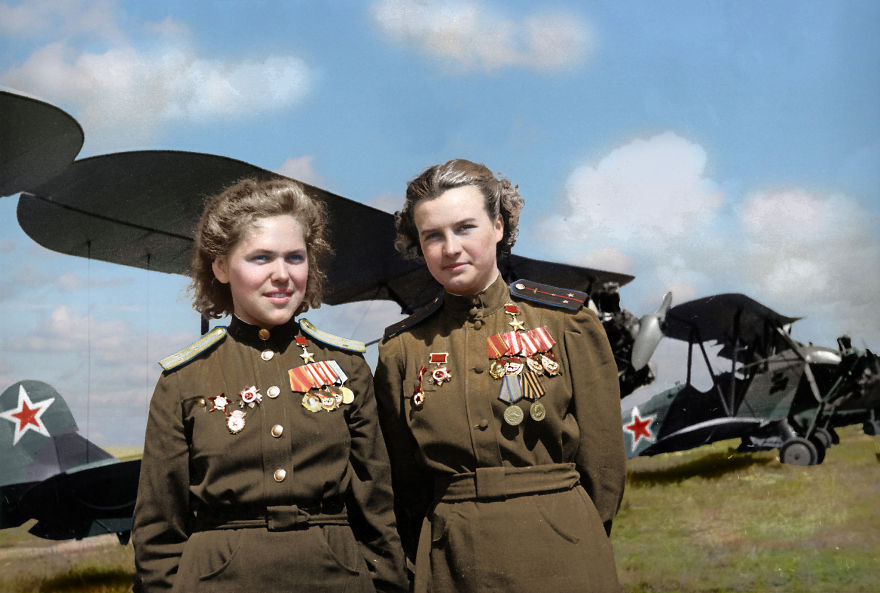
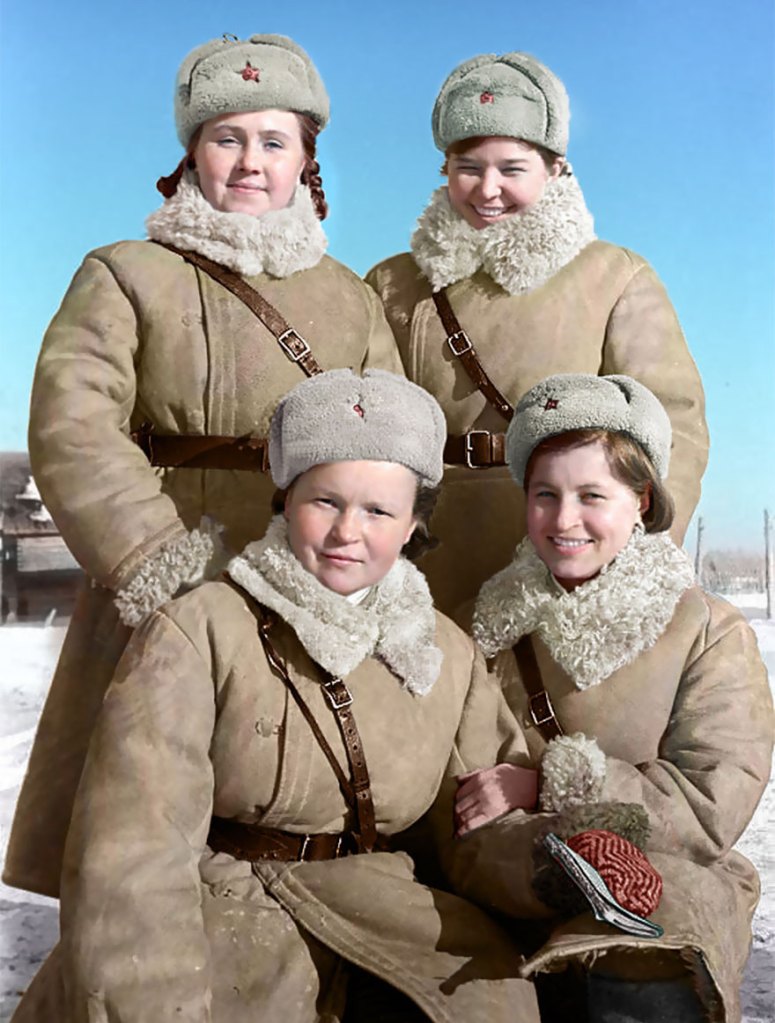
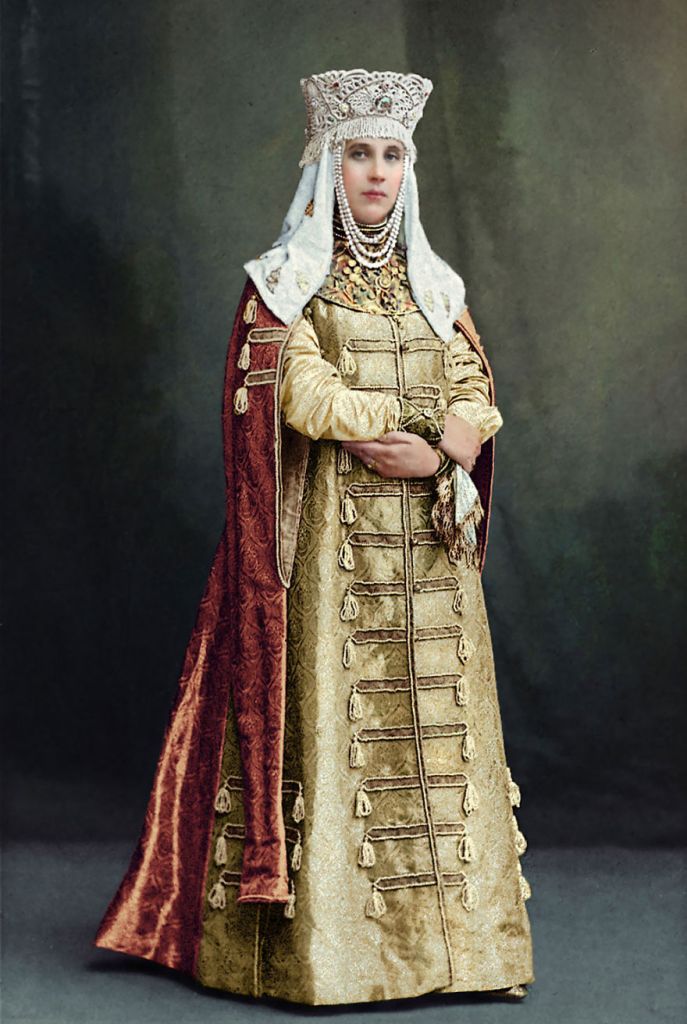
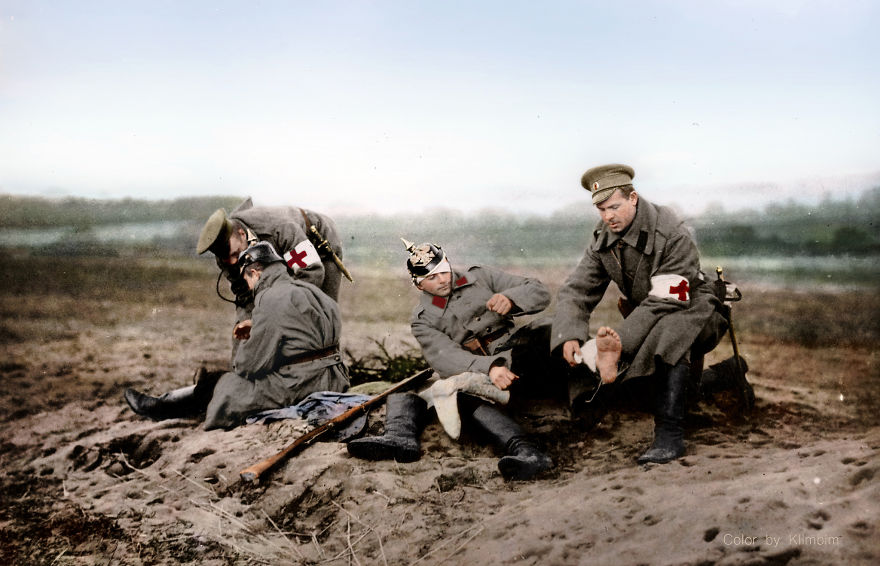
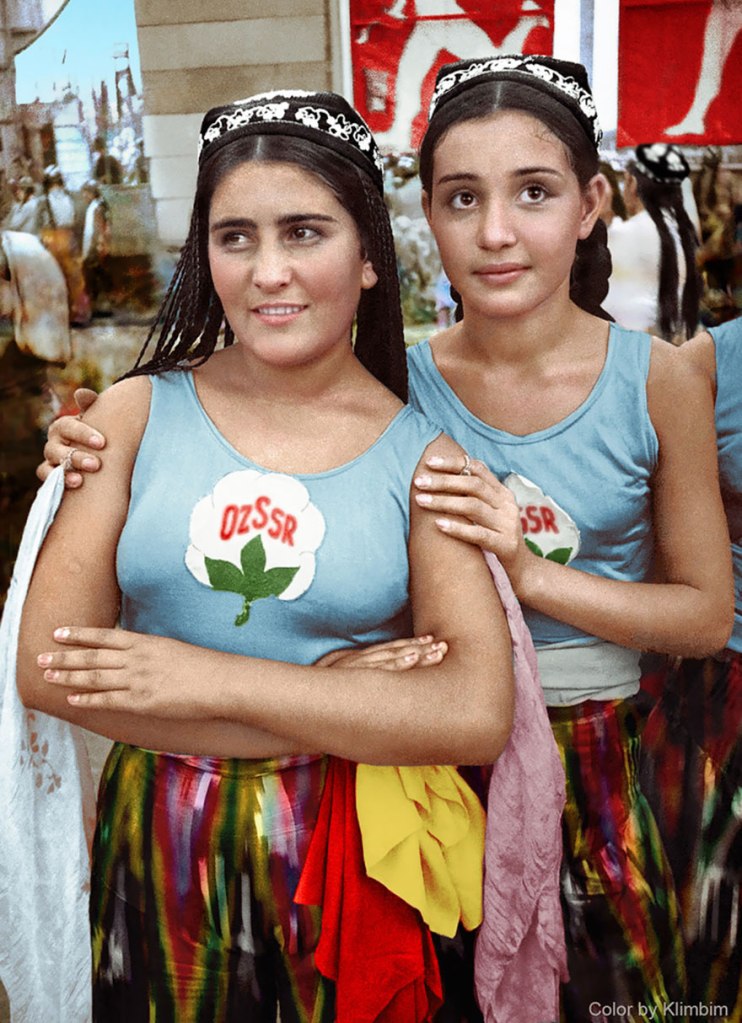
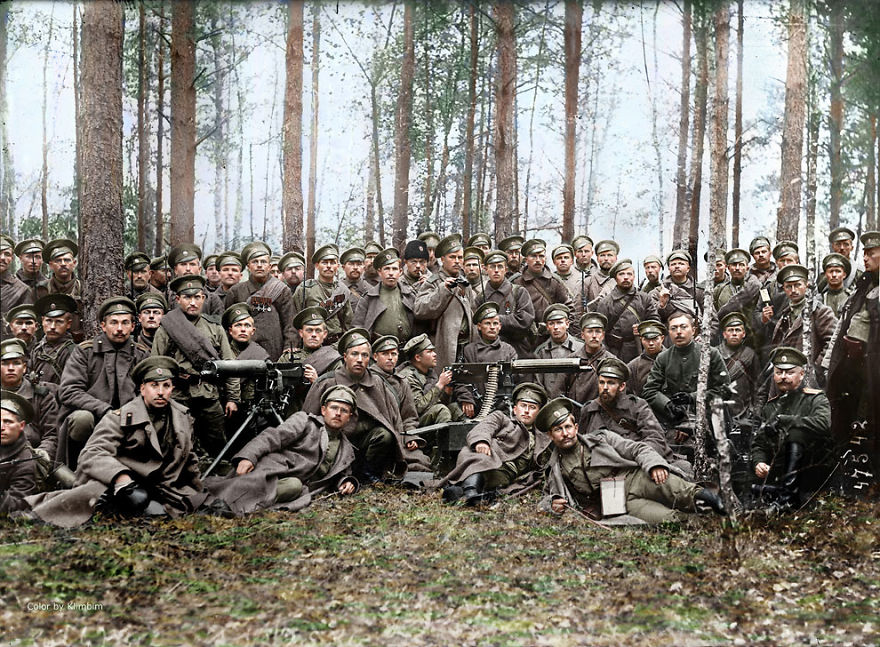
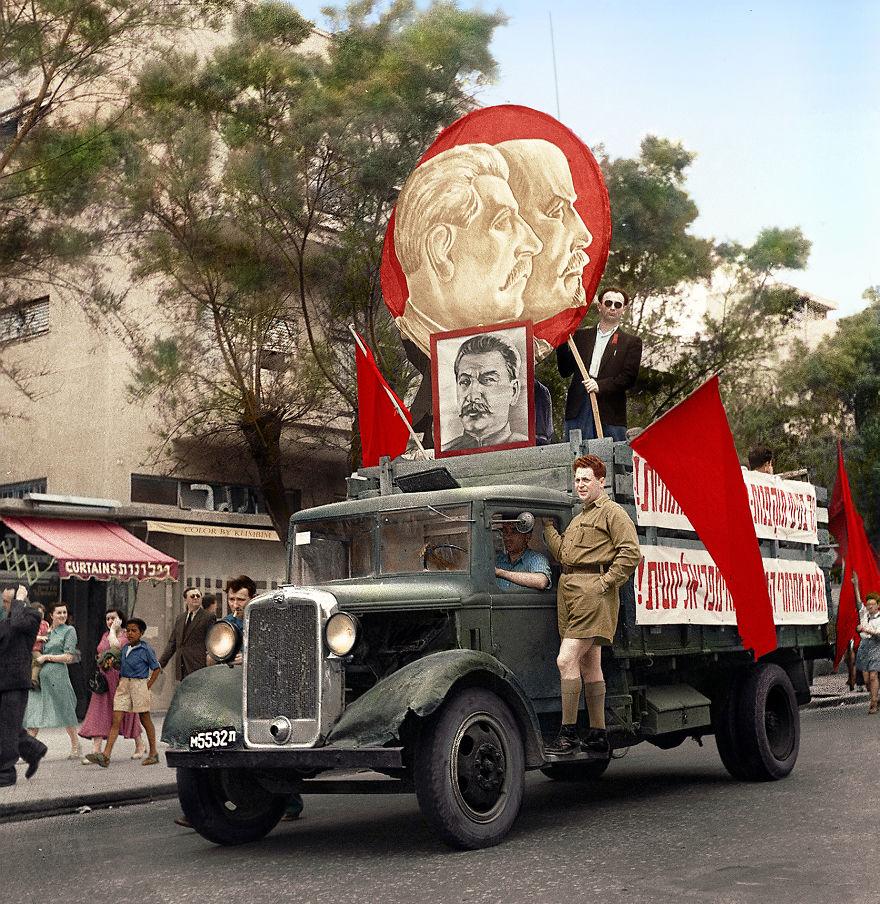
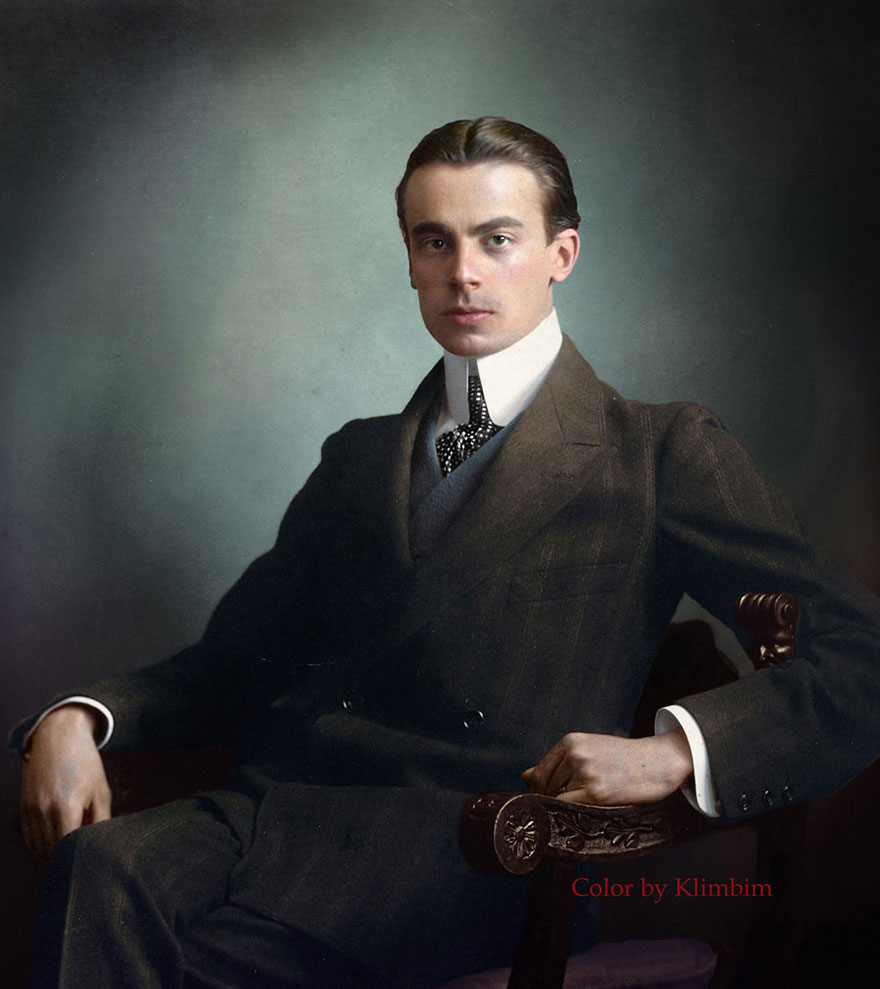
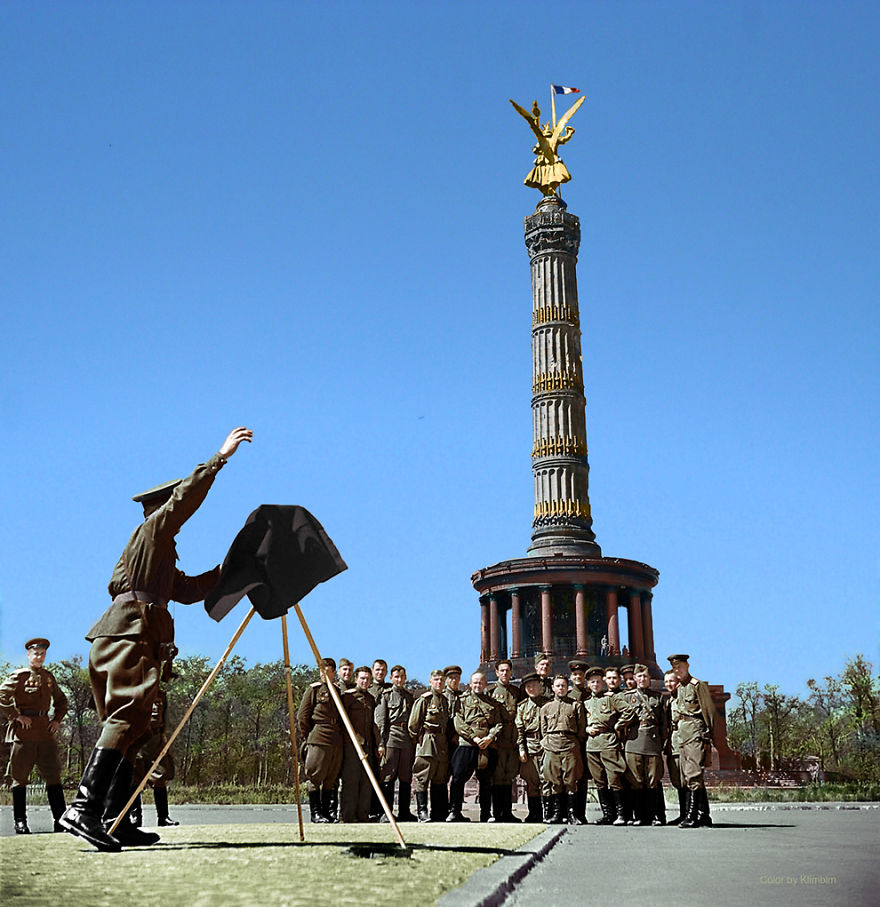
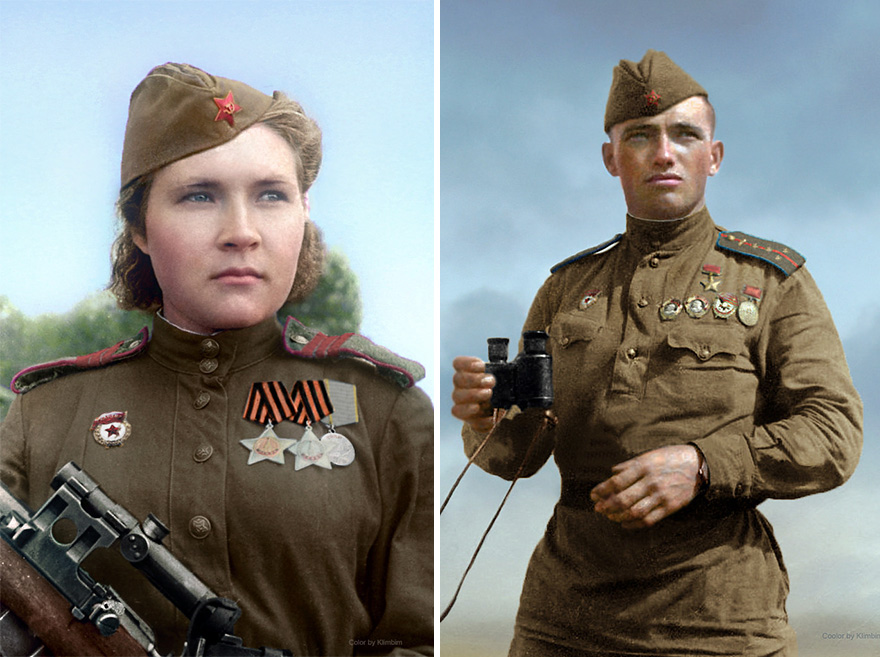
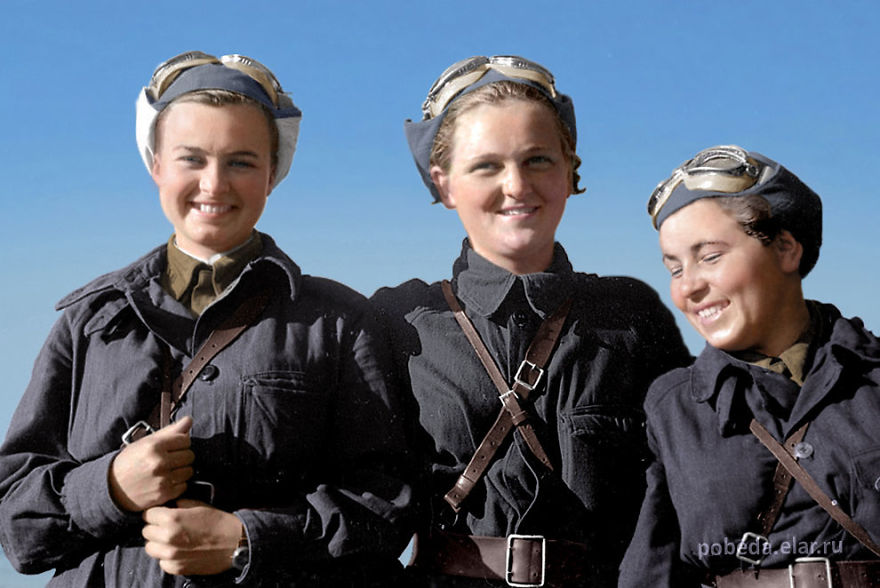
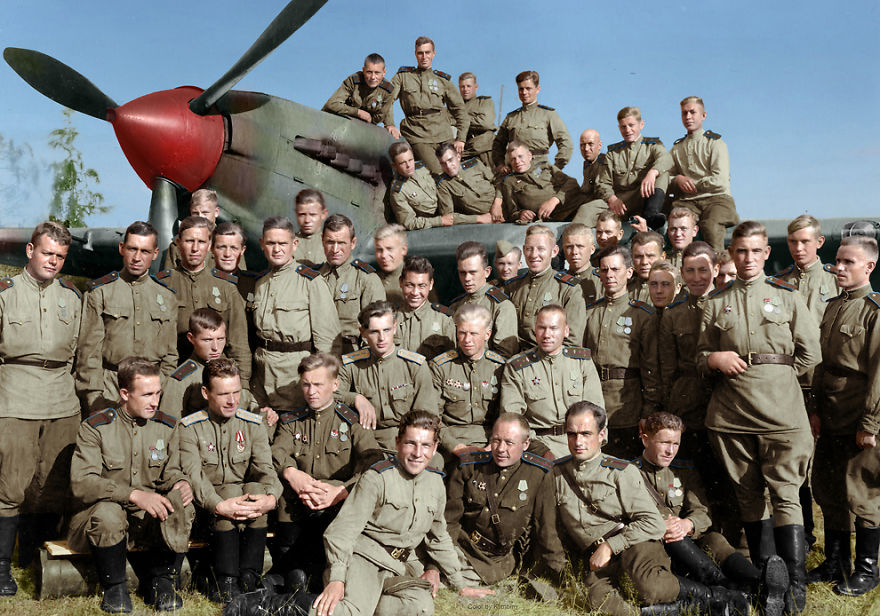
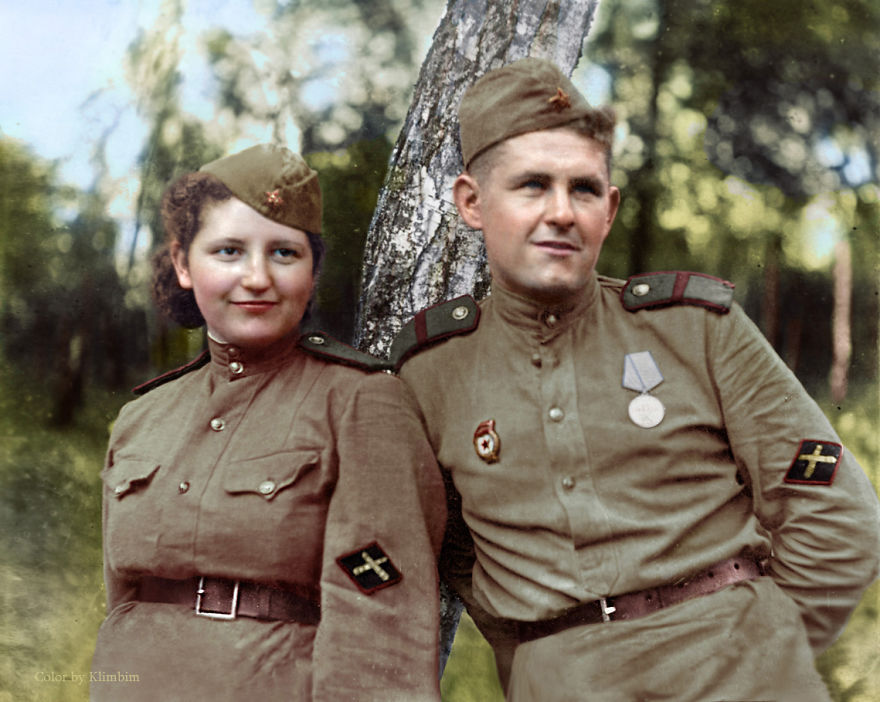
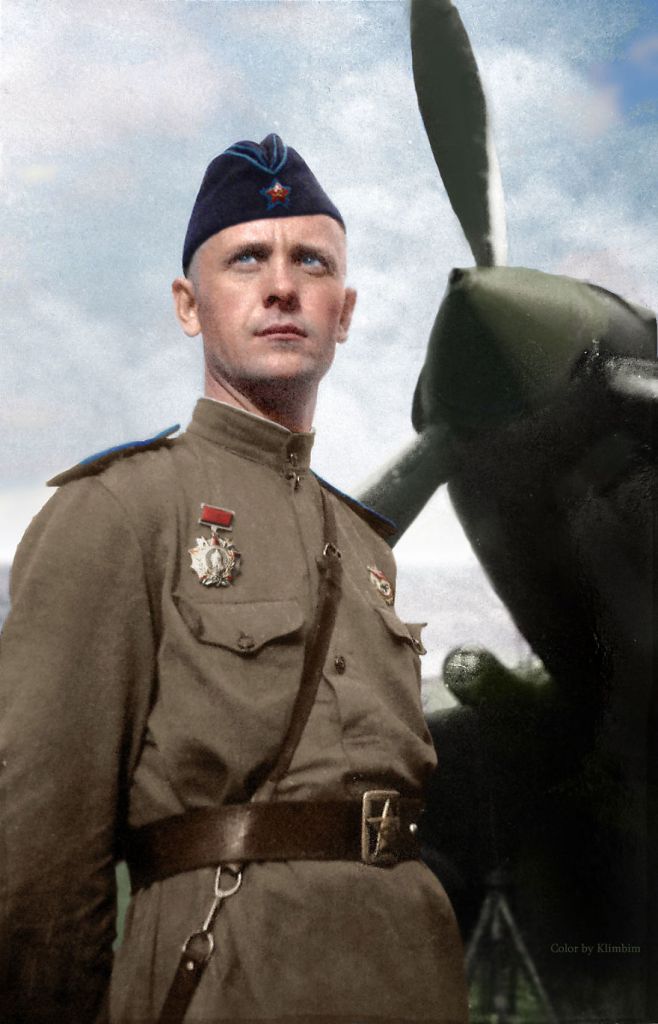





























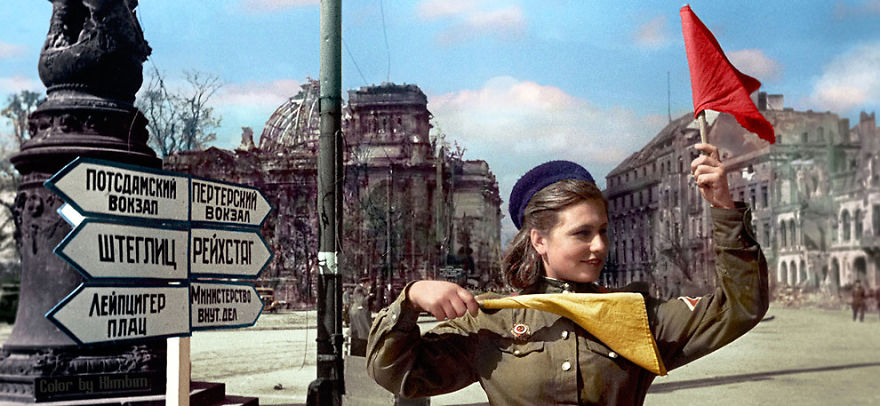





































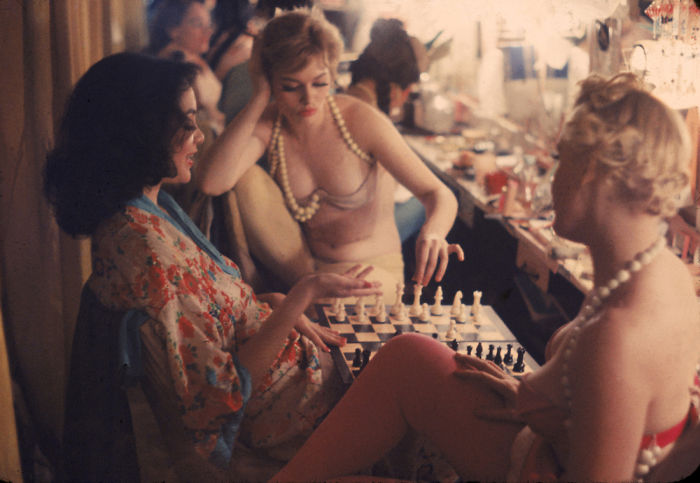
(Photos colorized by Klimbim)