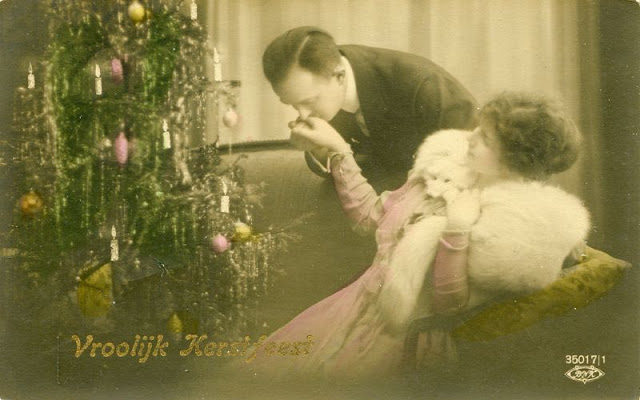
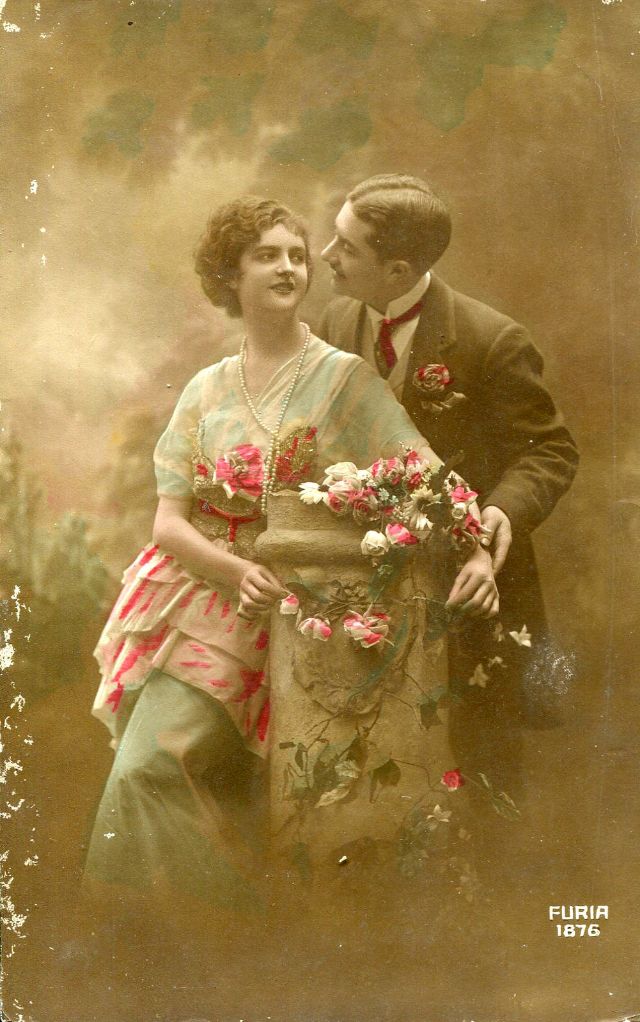
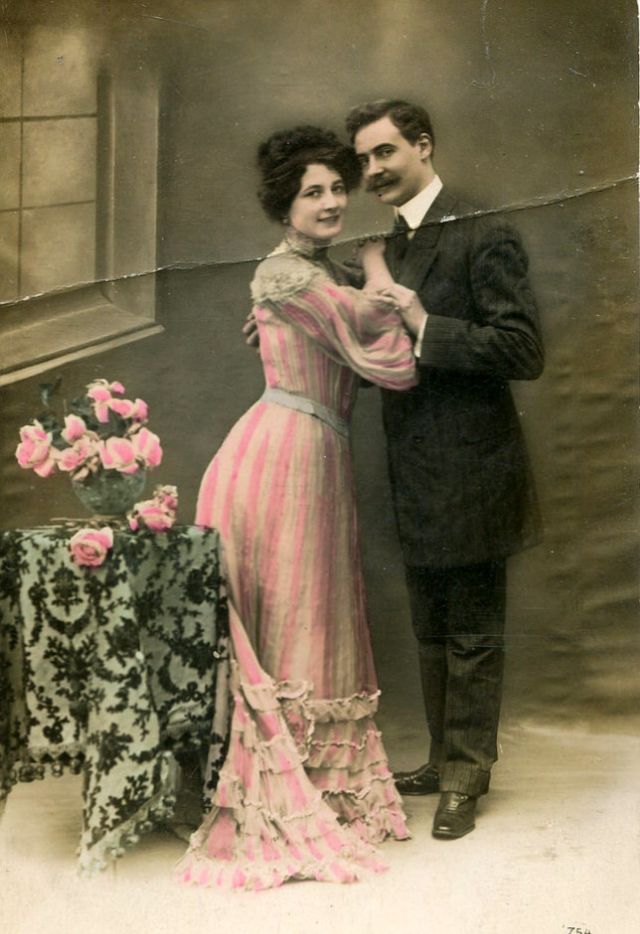
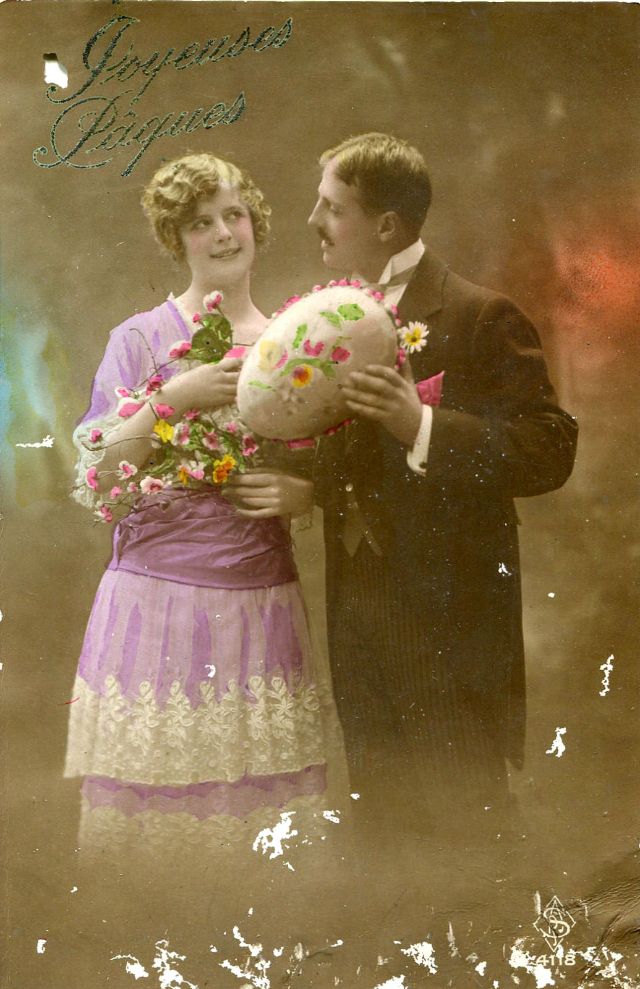
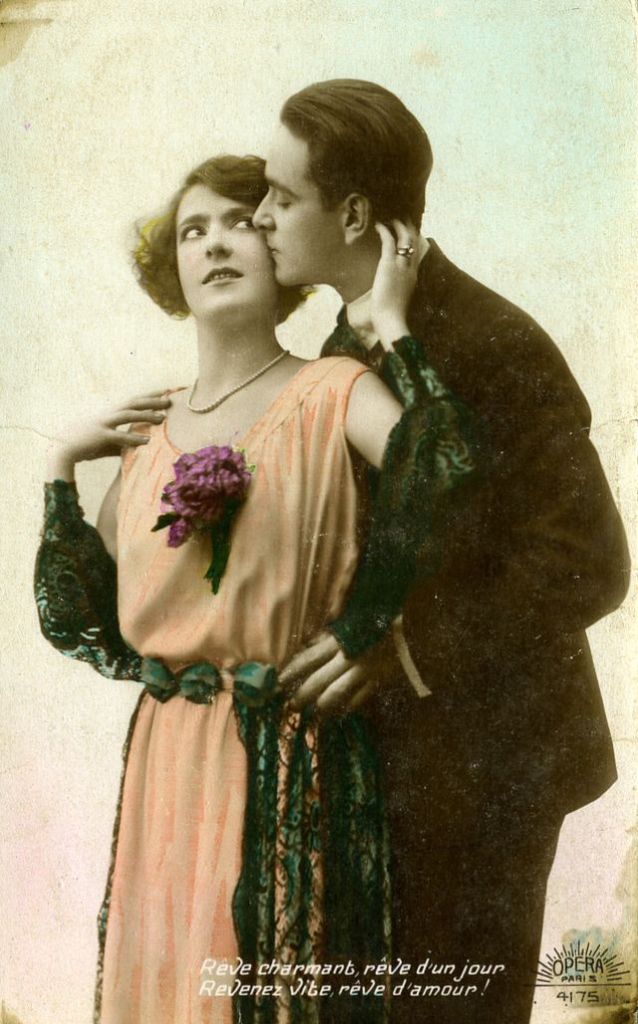
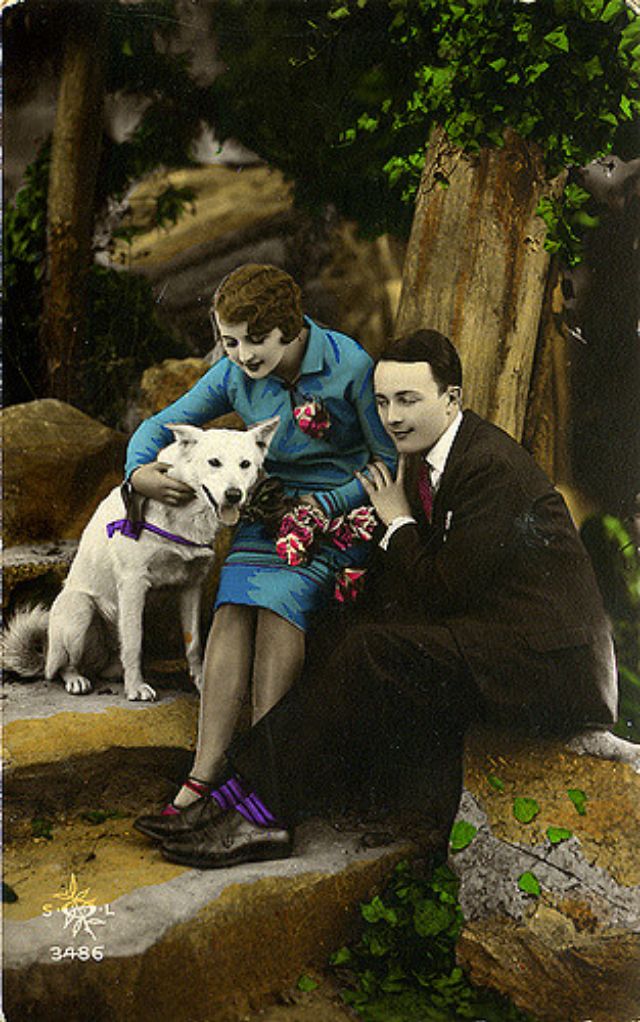
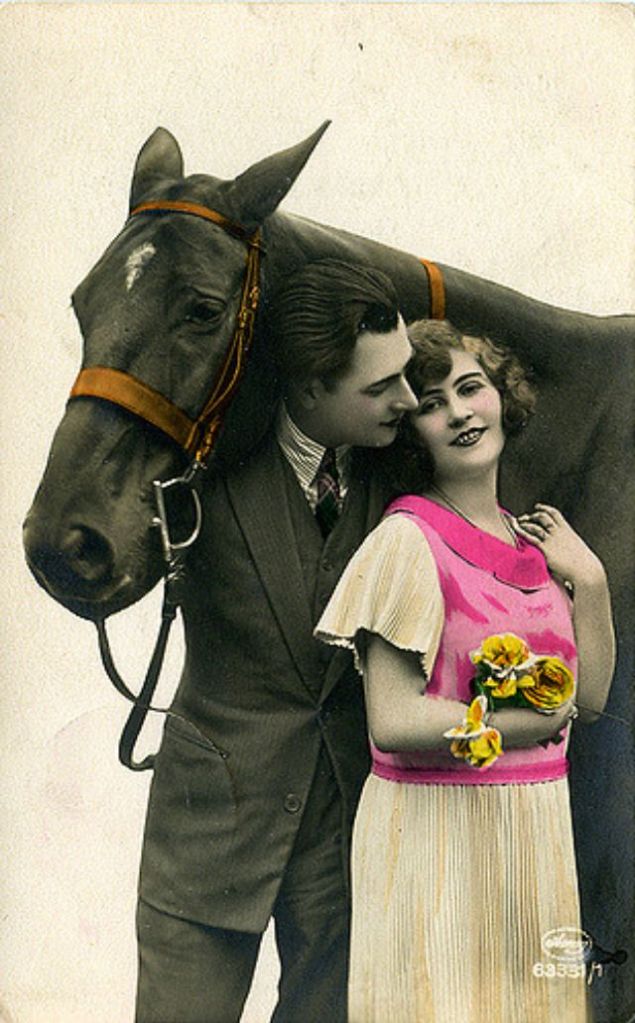
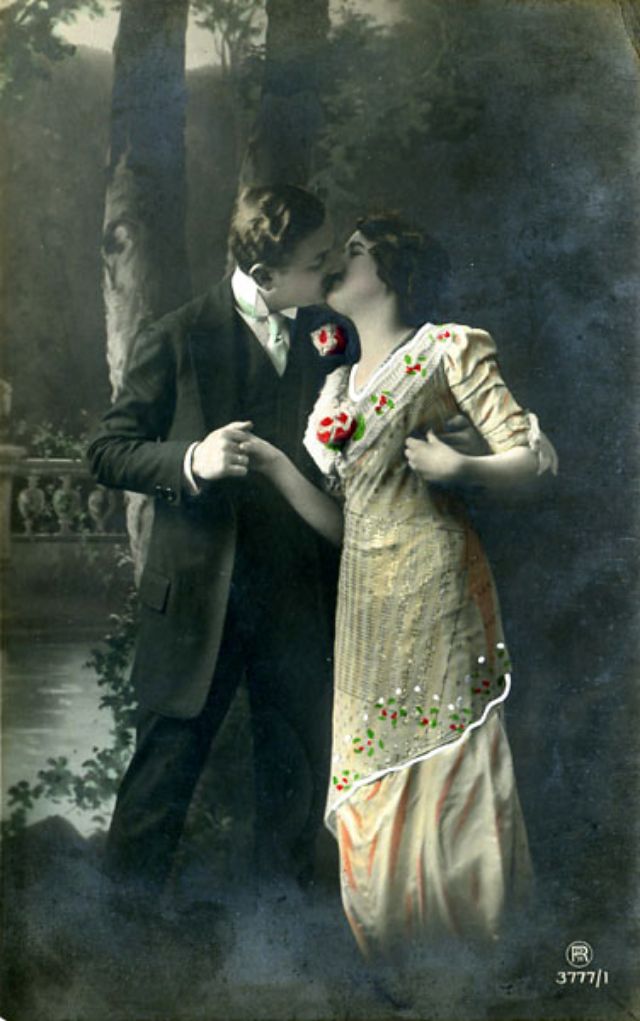
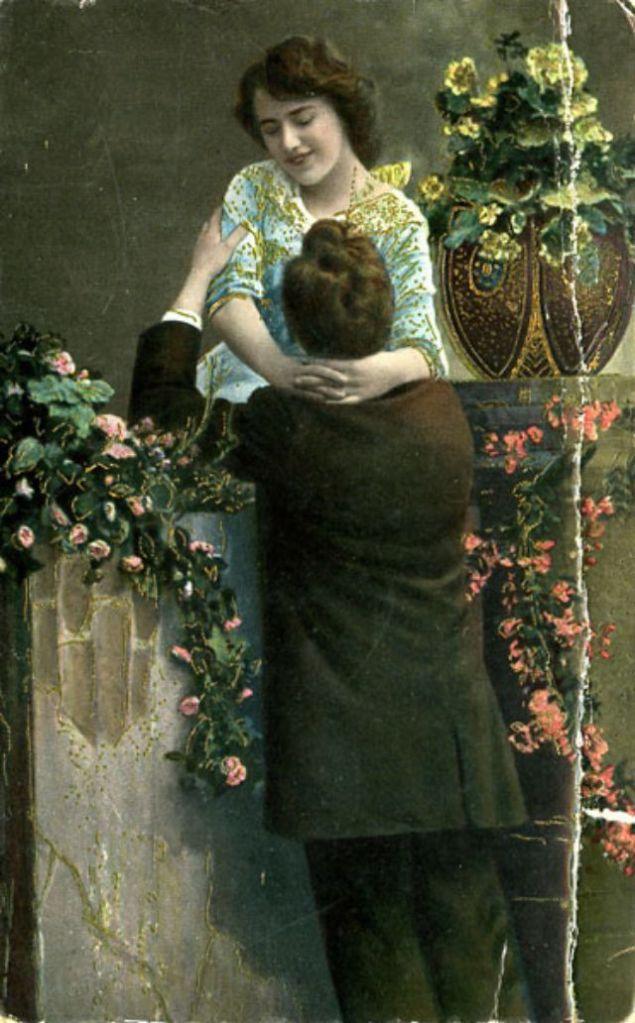
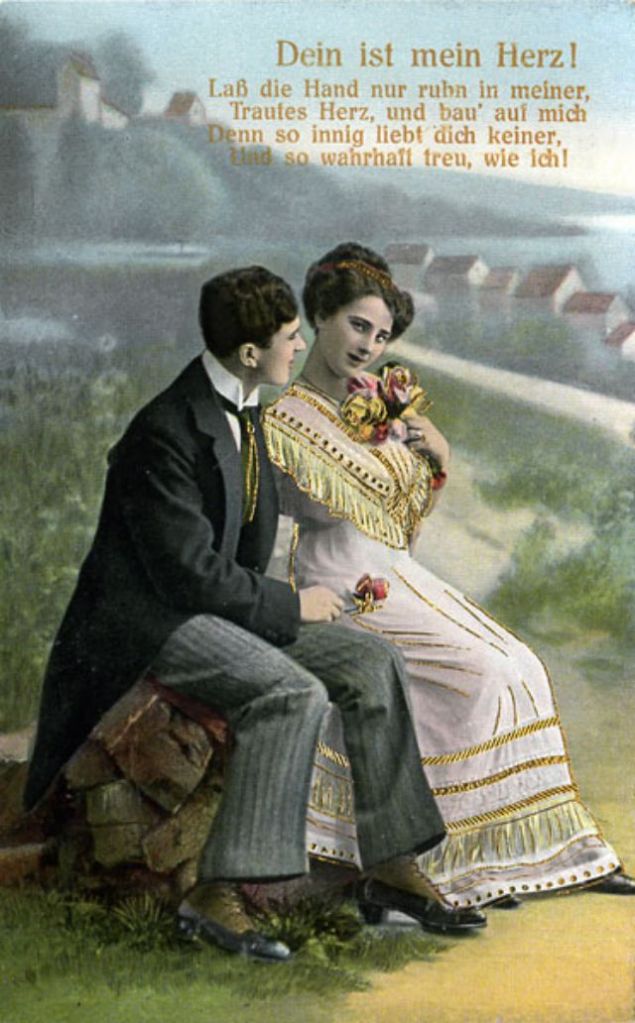
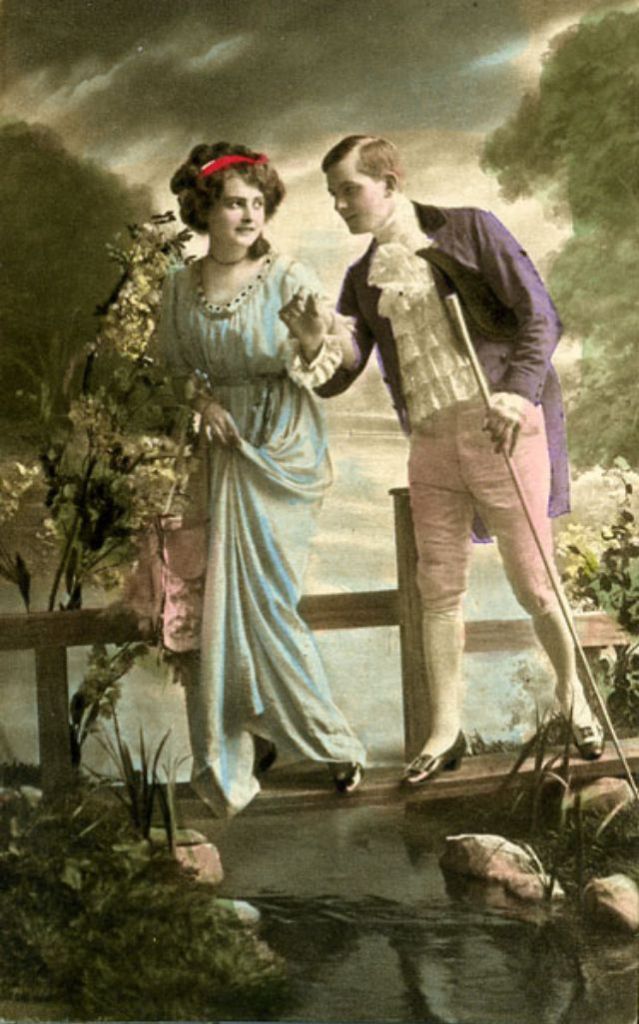
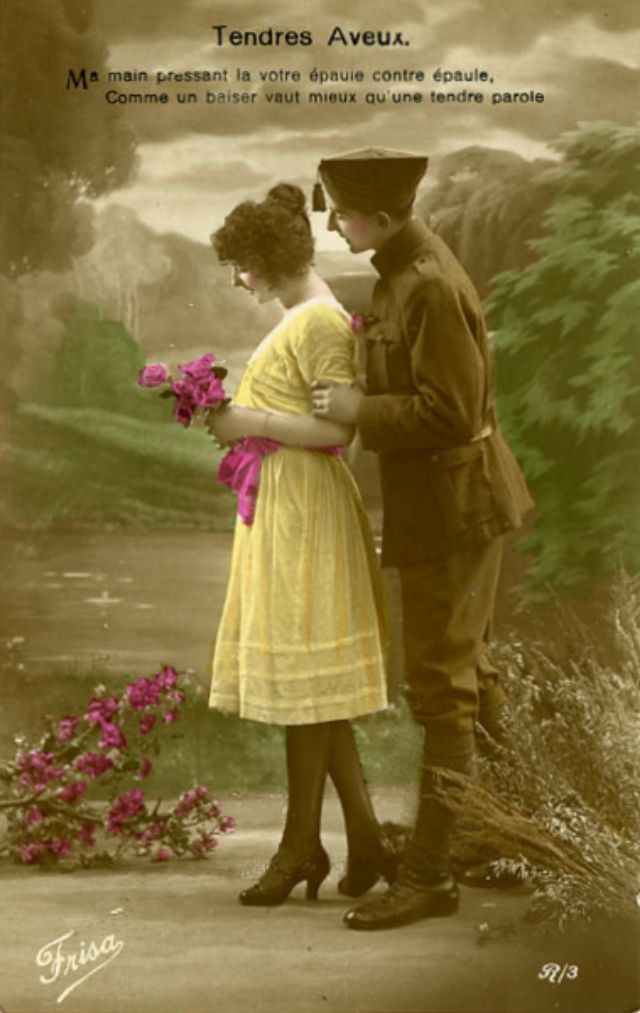
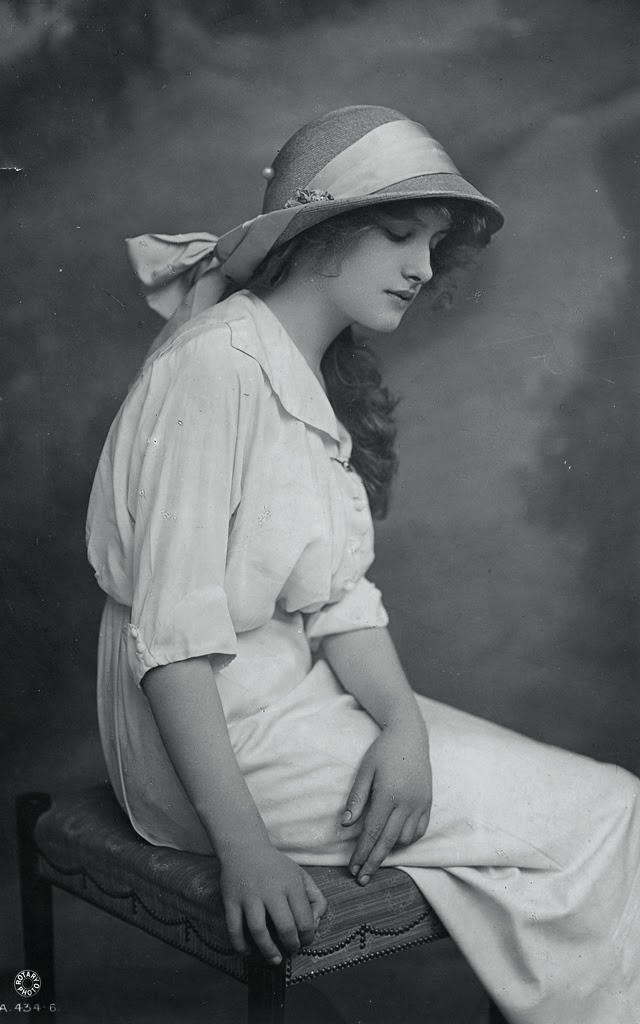
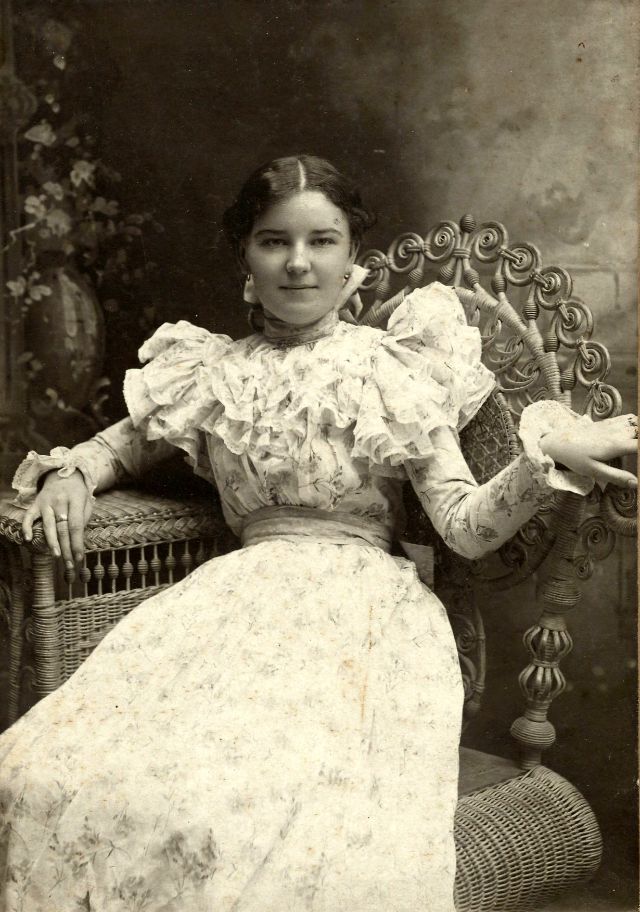
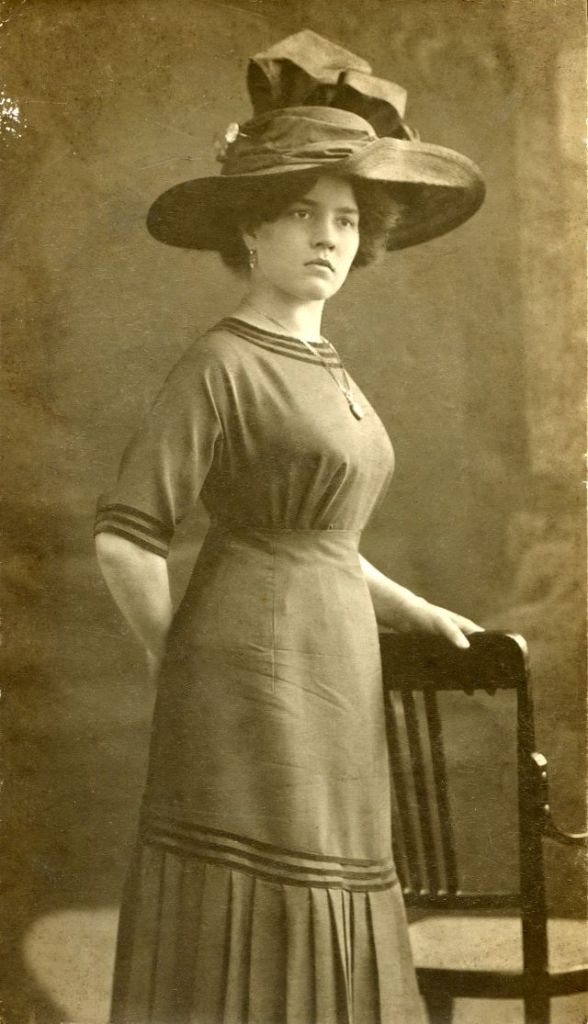
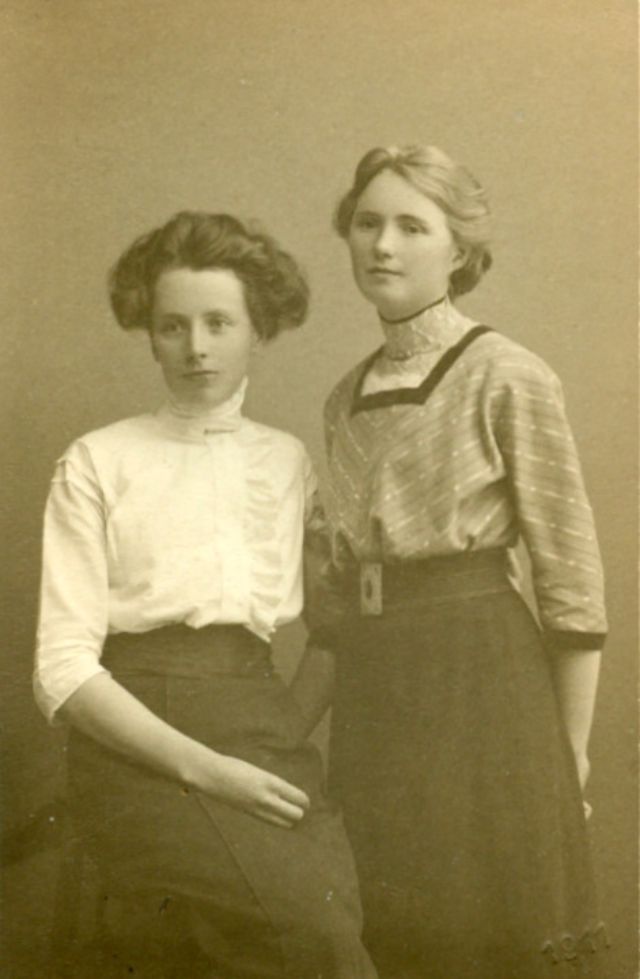
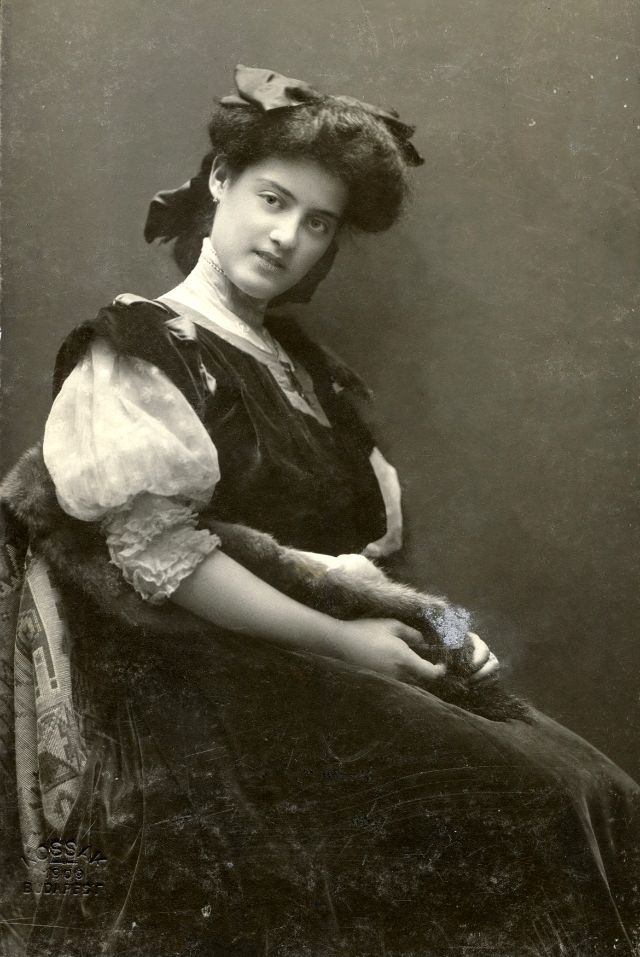
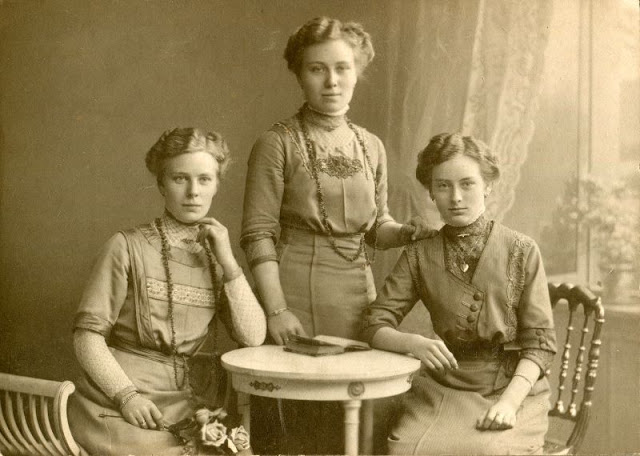
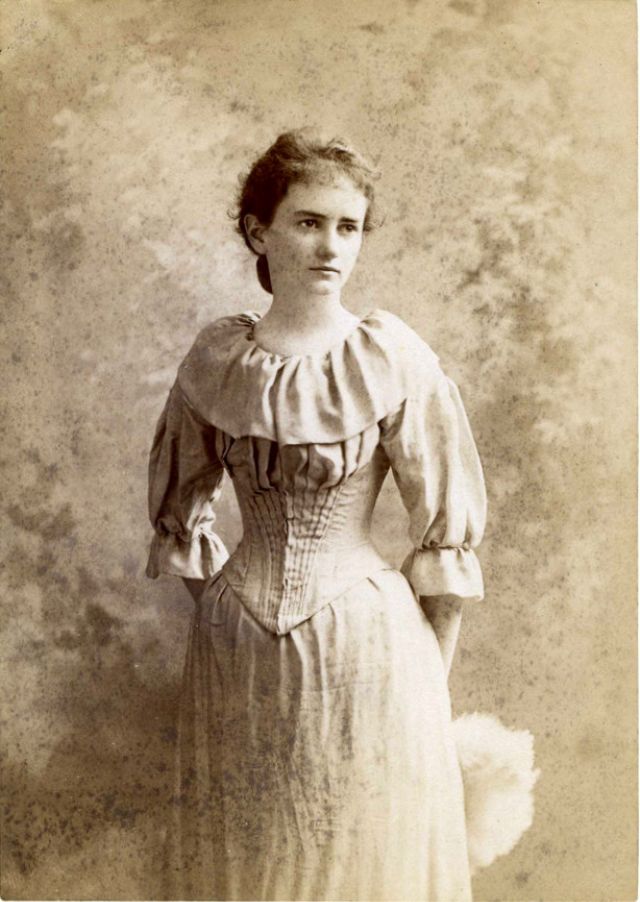
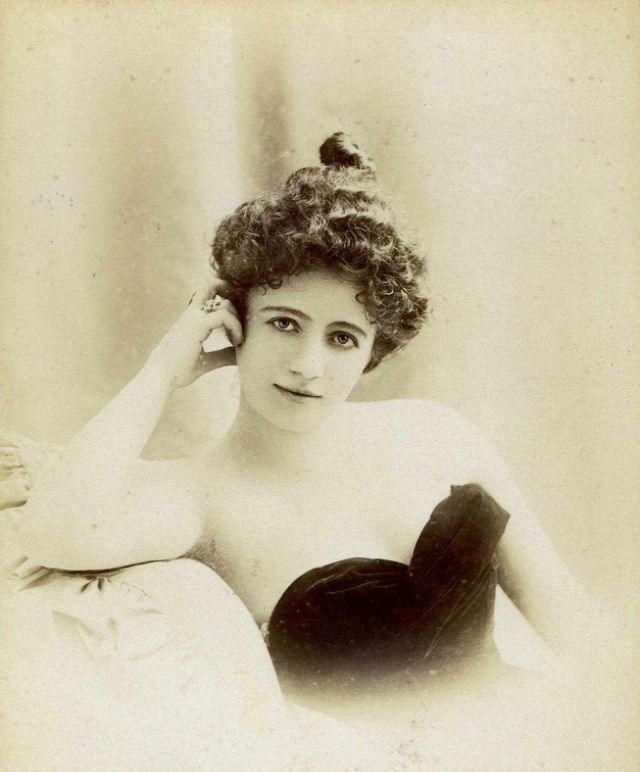
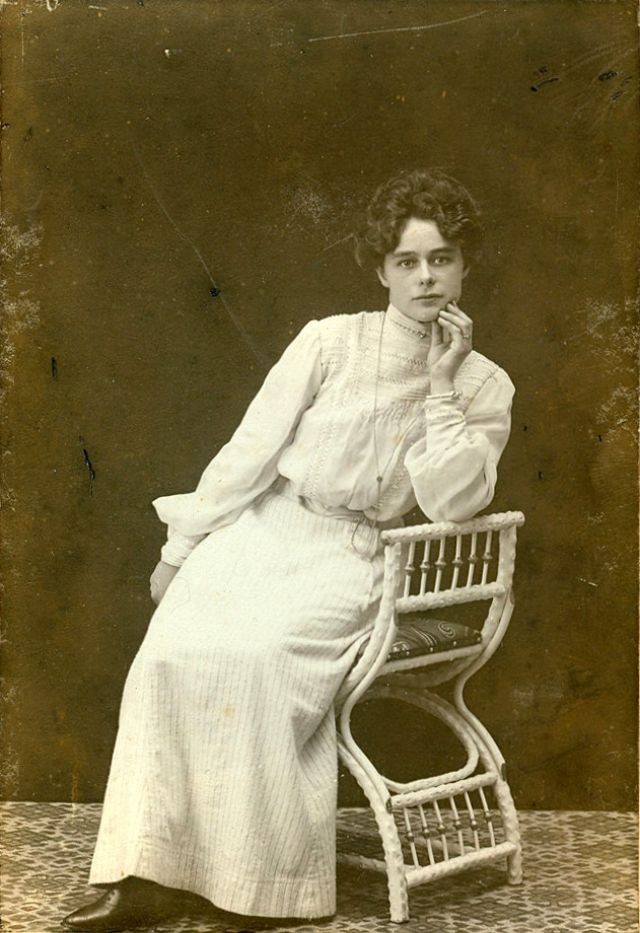
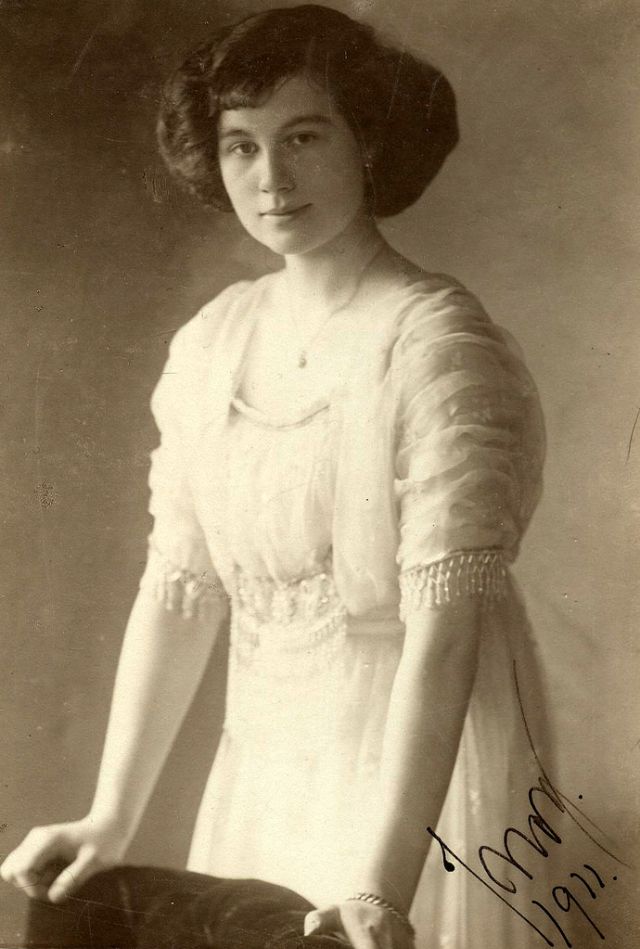
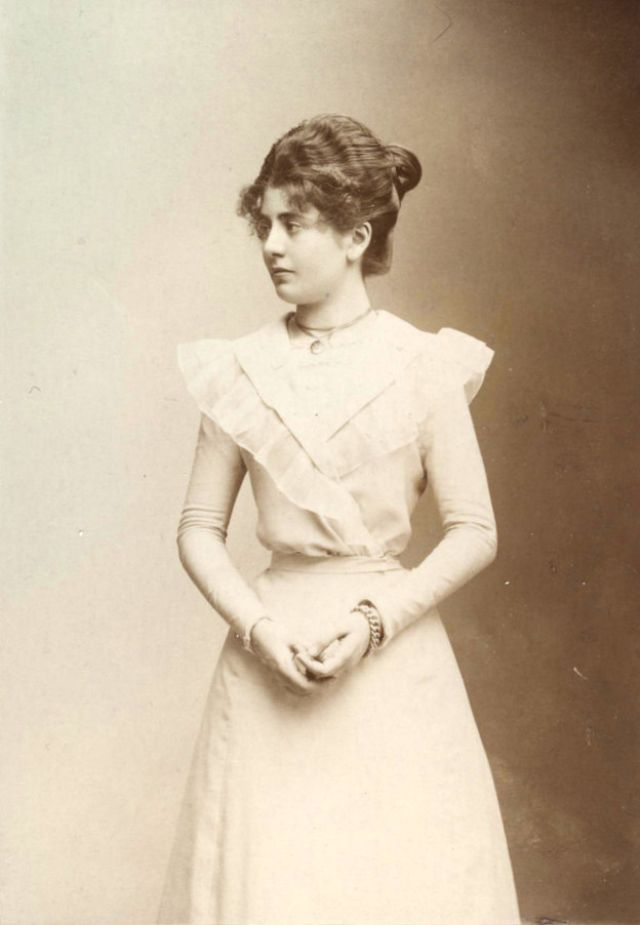
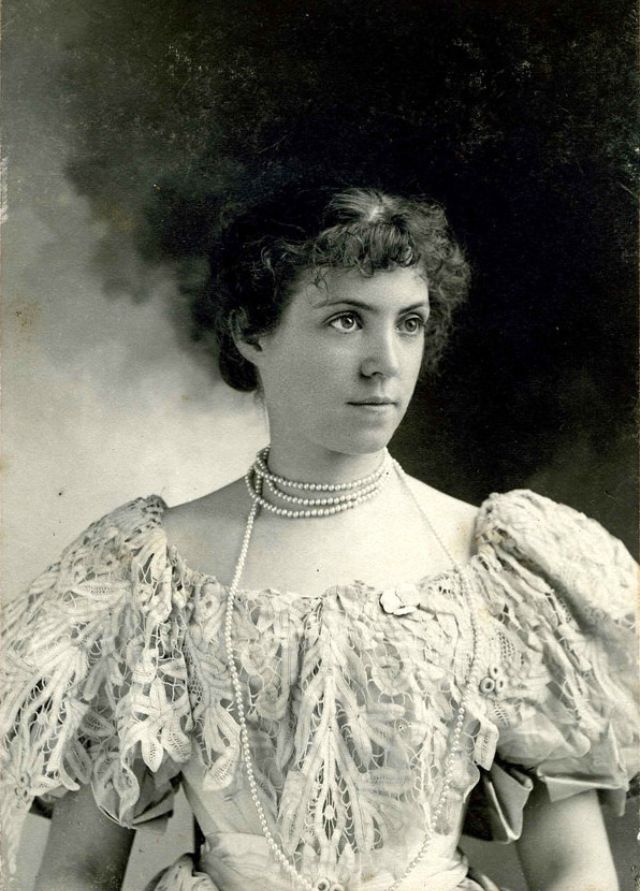
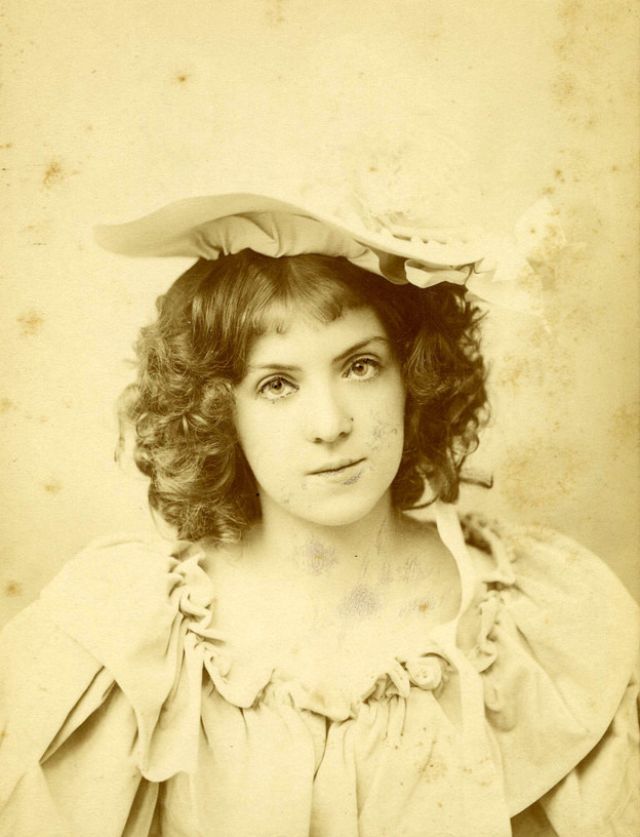
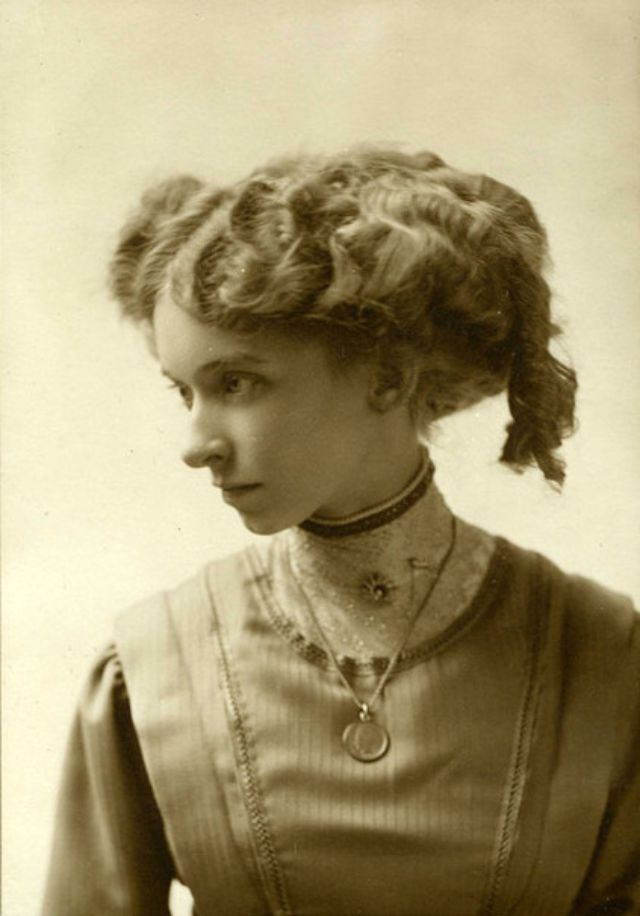
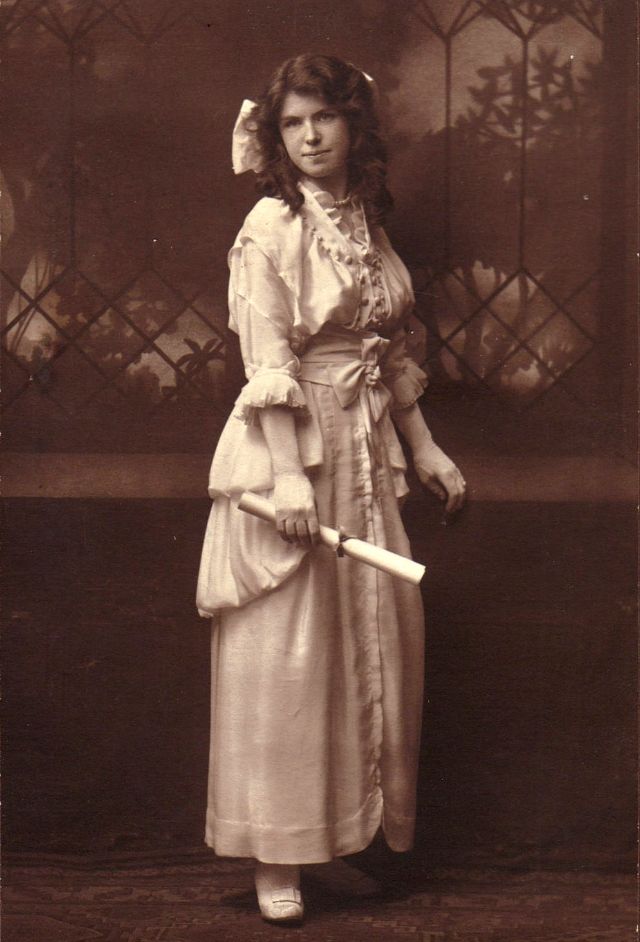
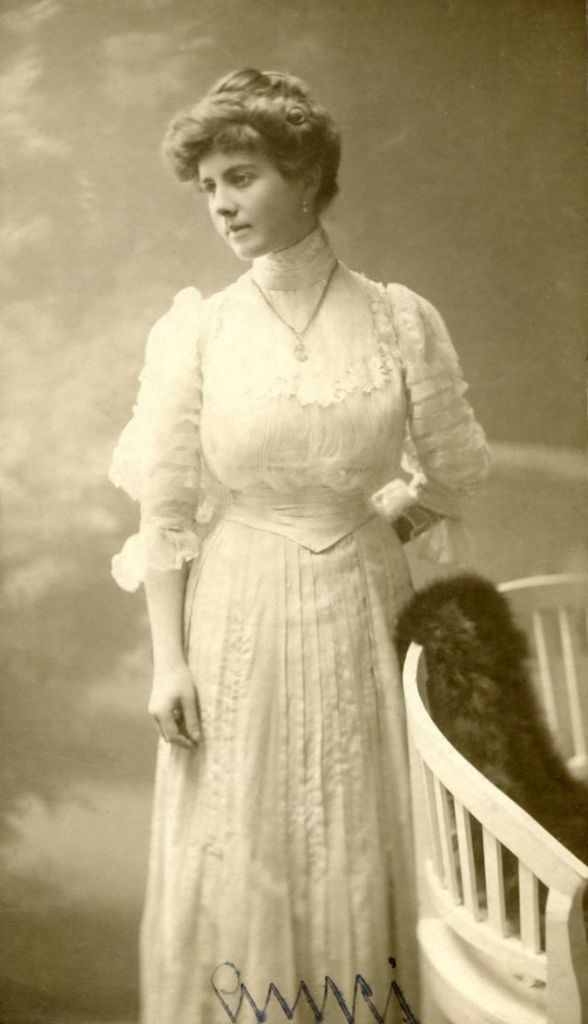
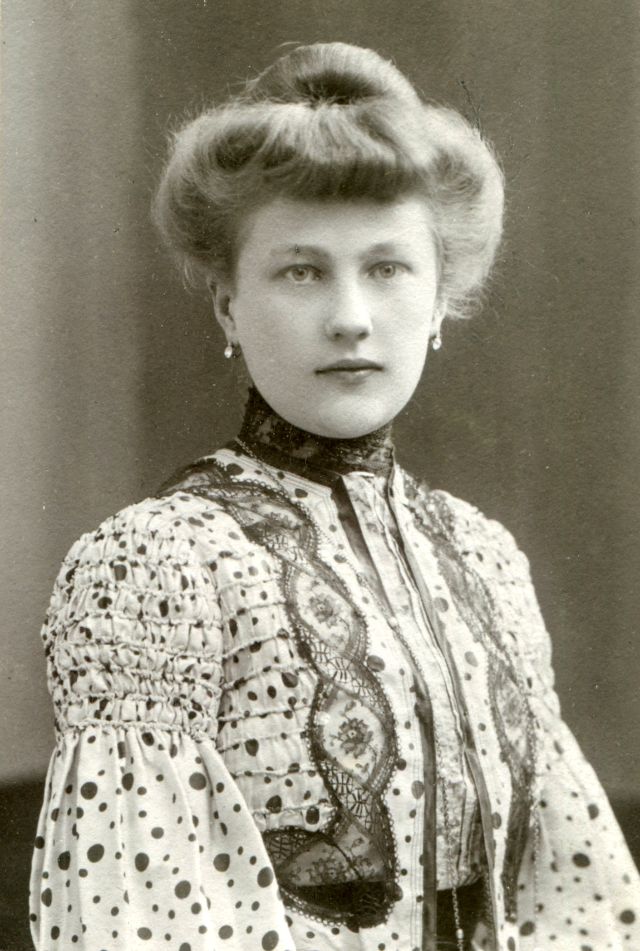
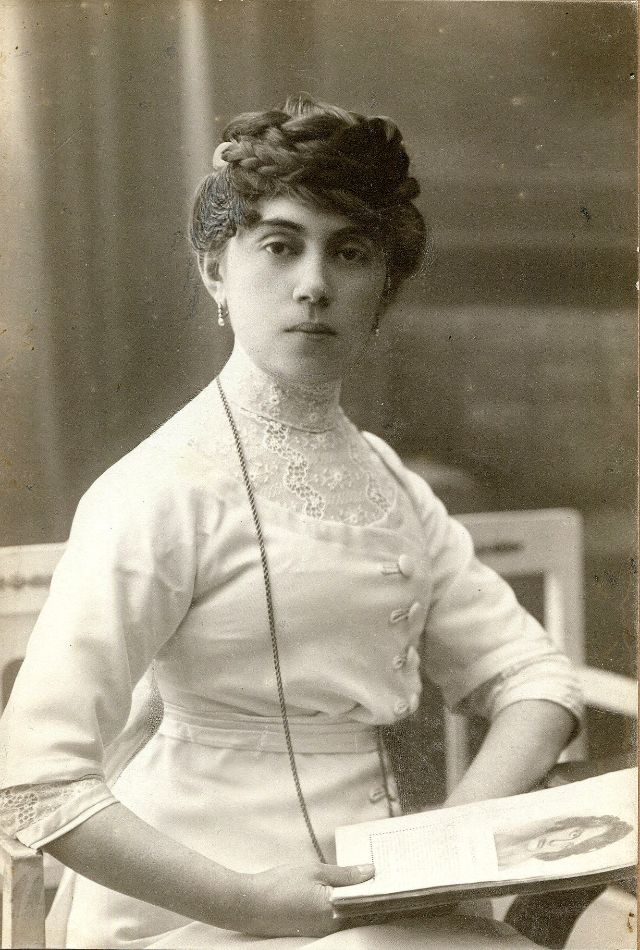
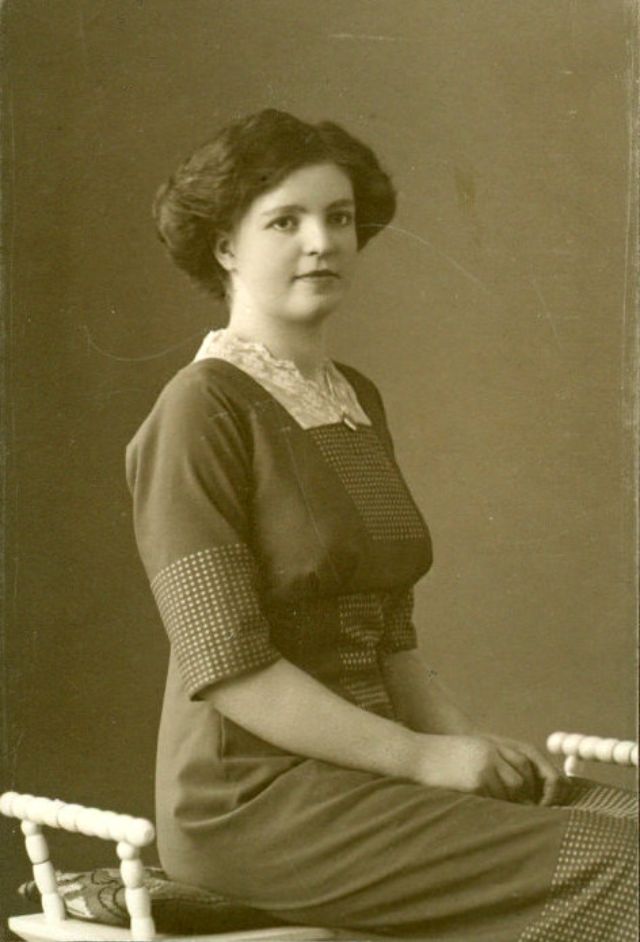
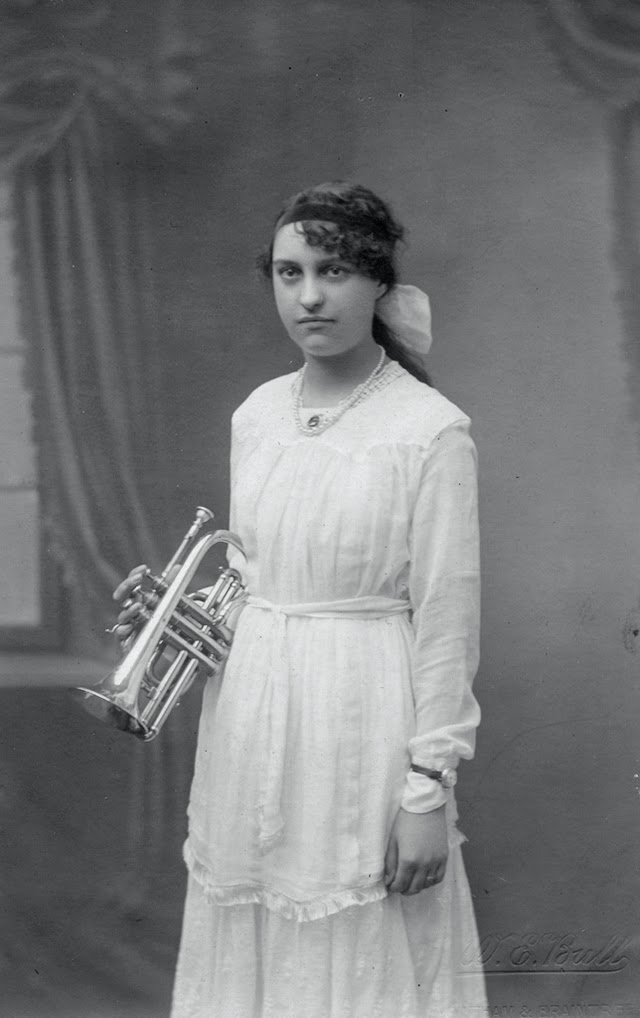
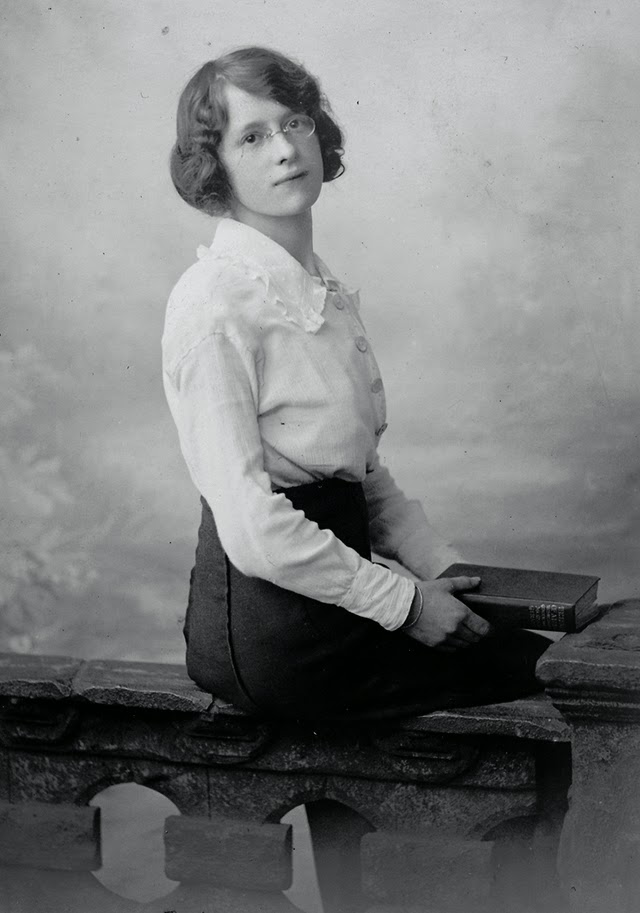
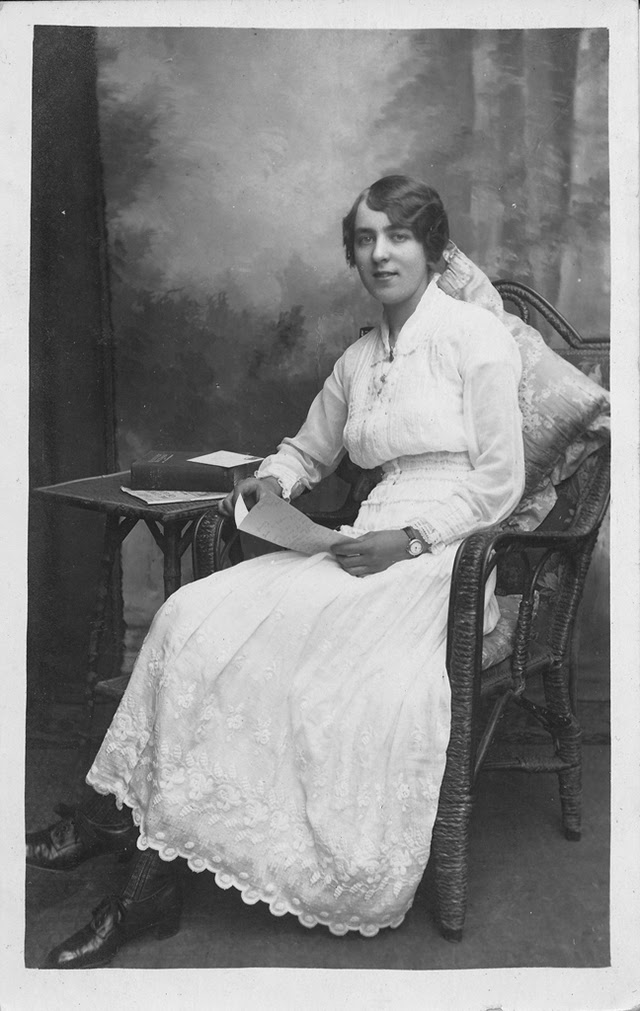
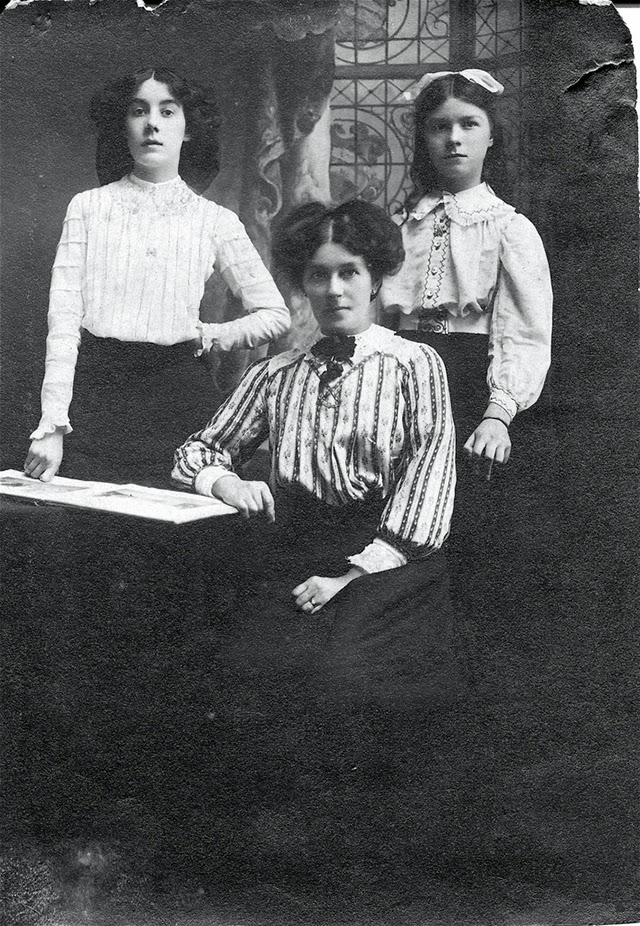
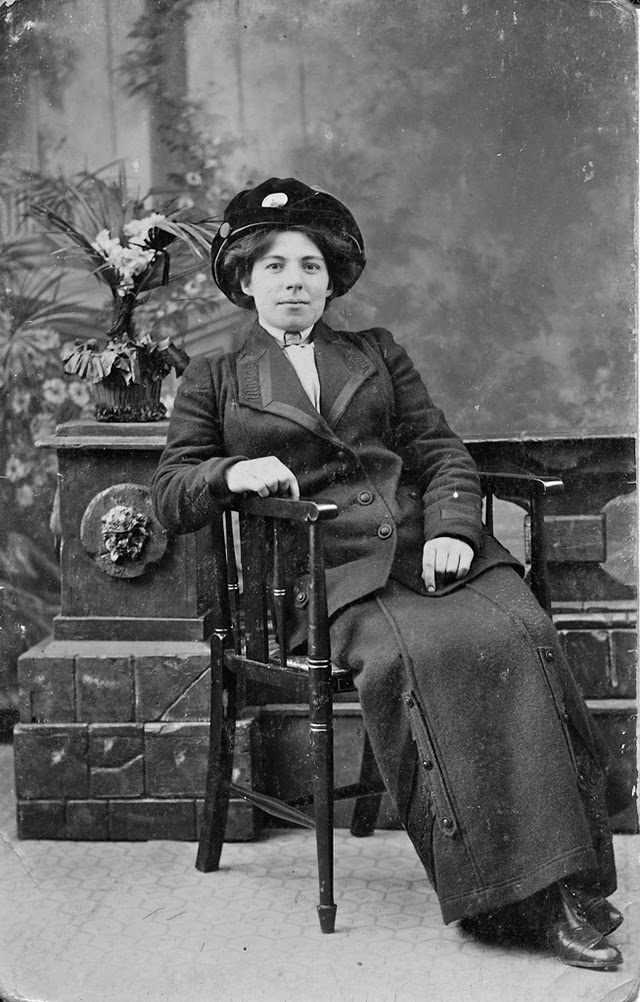
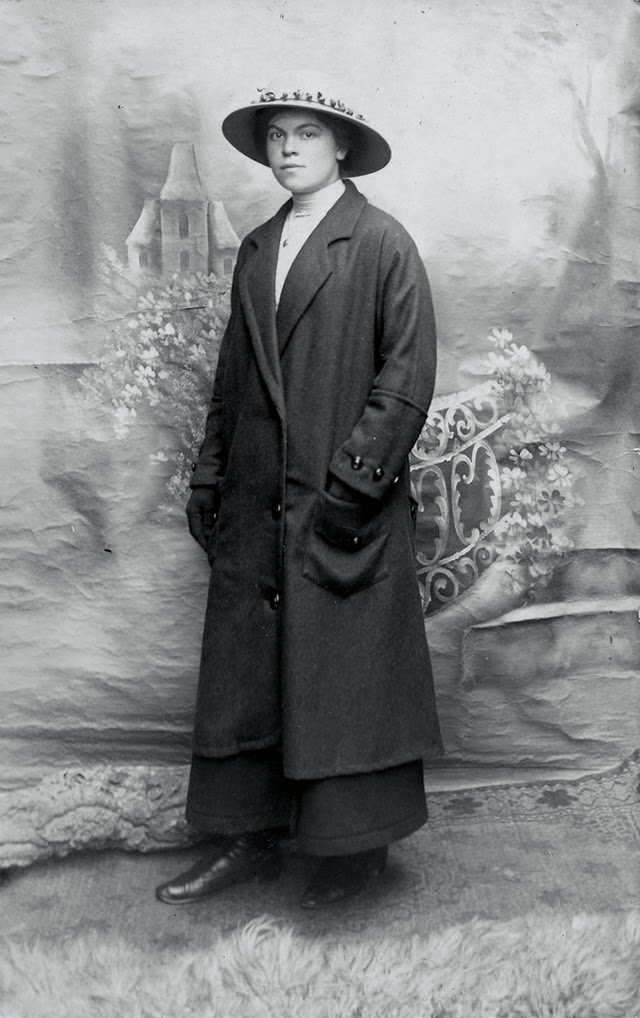
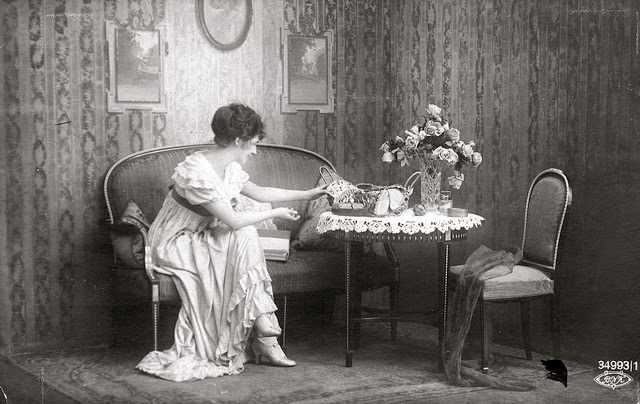
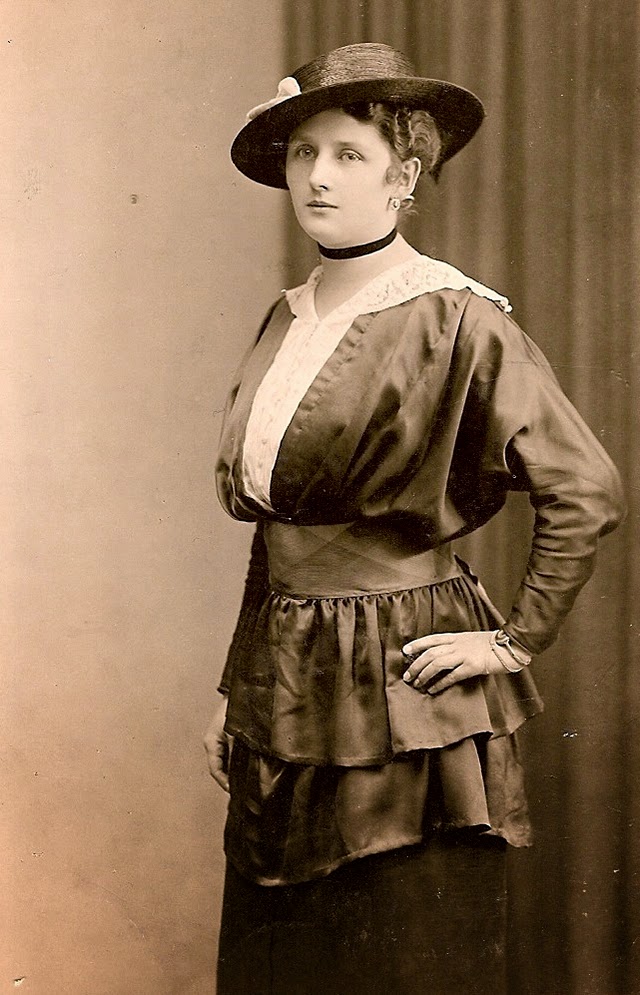
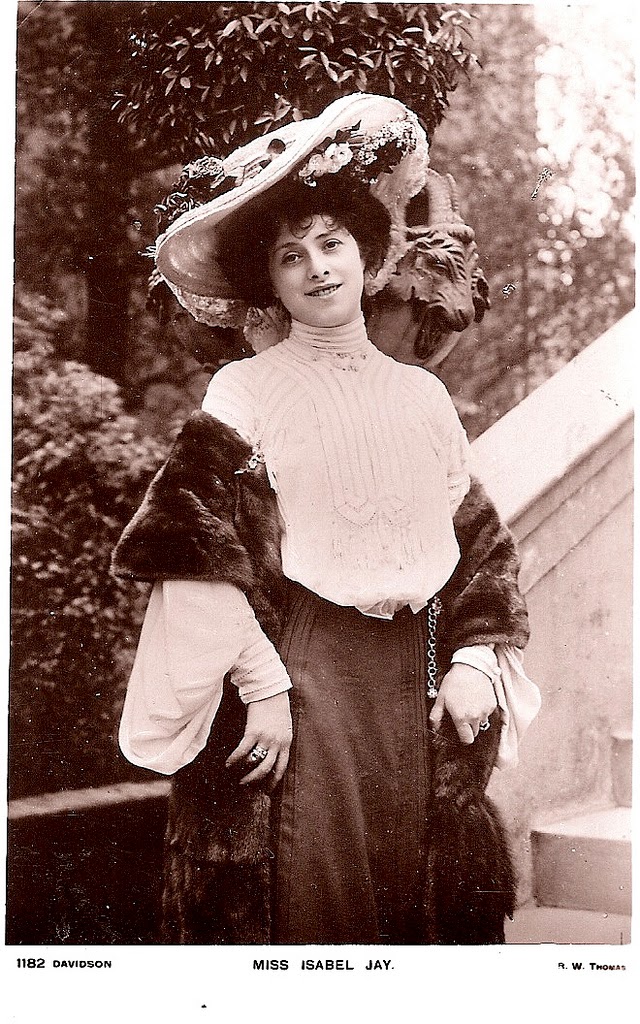
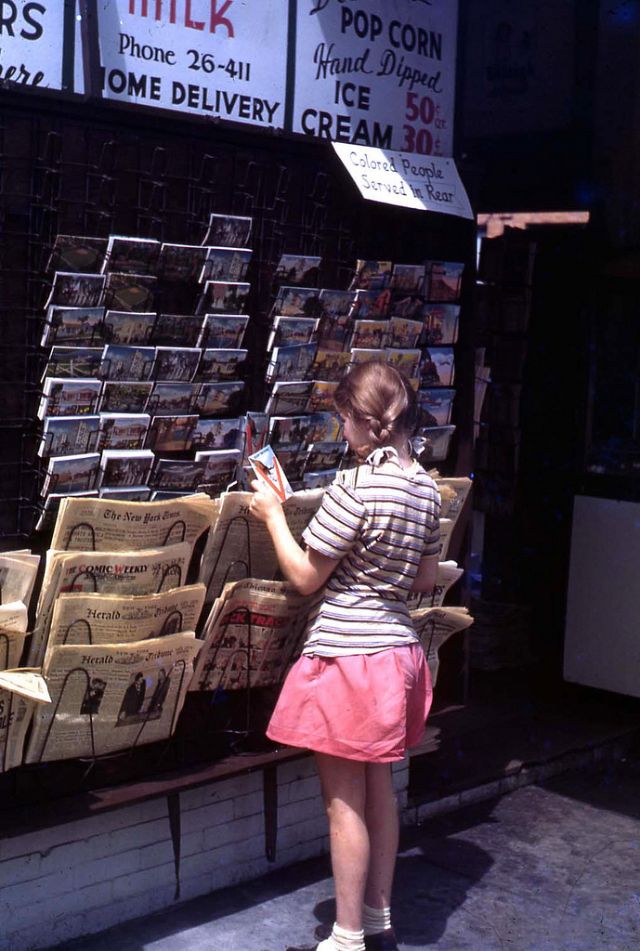
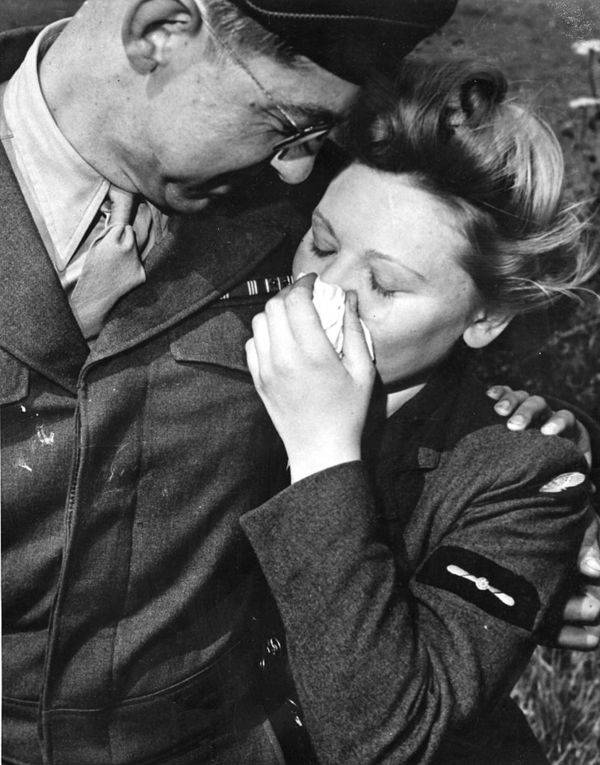
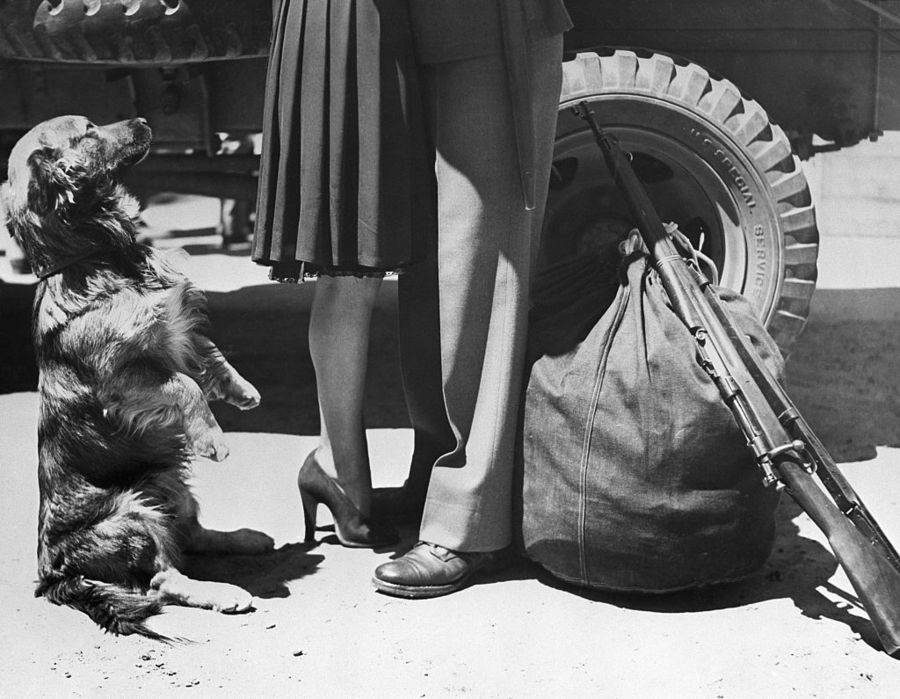
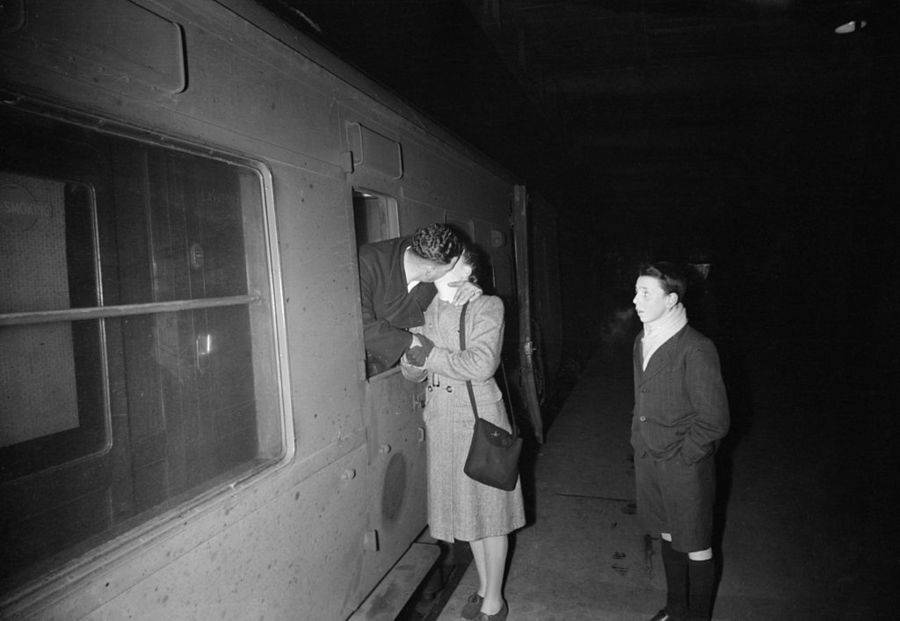
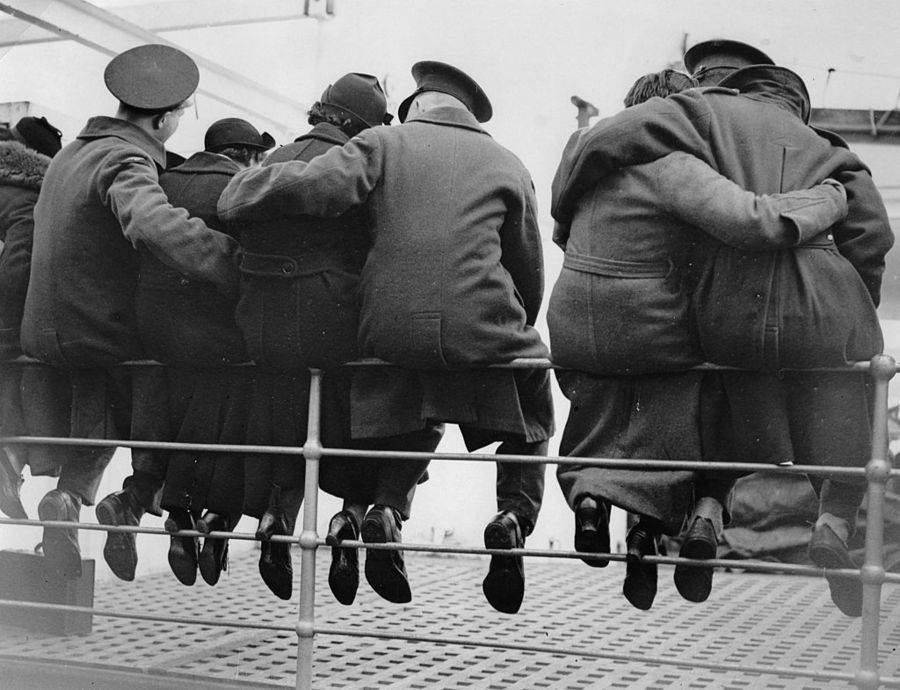
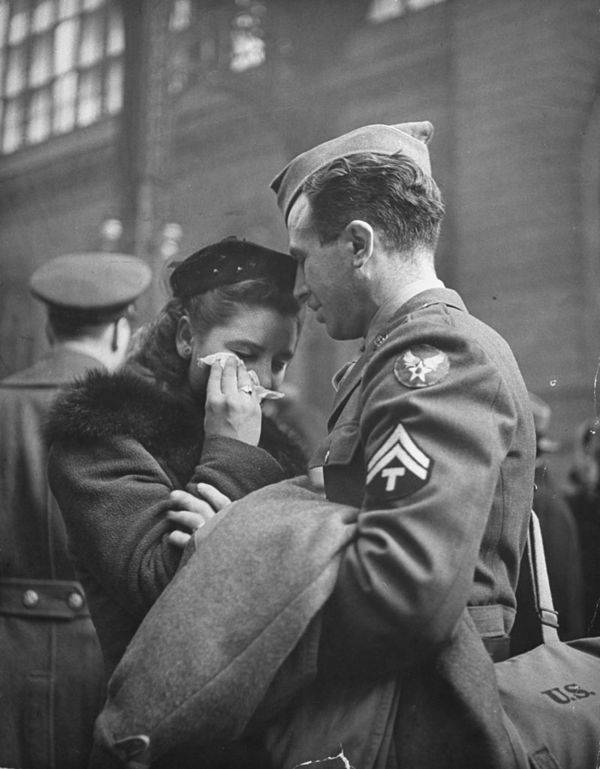
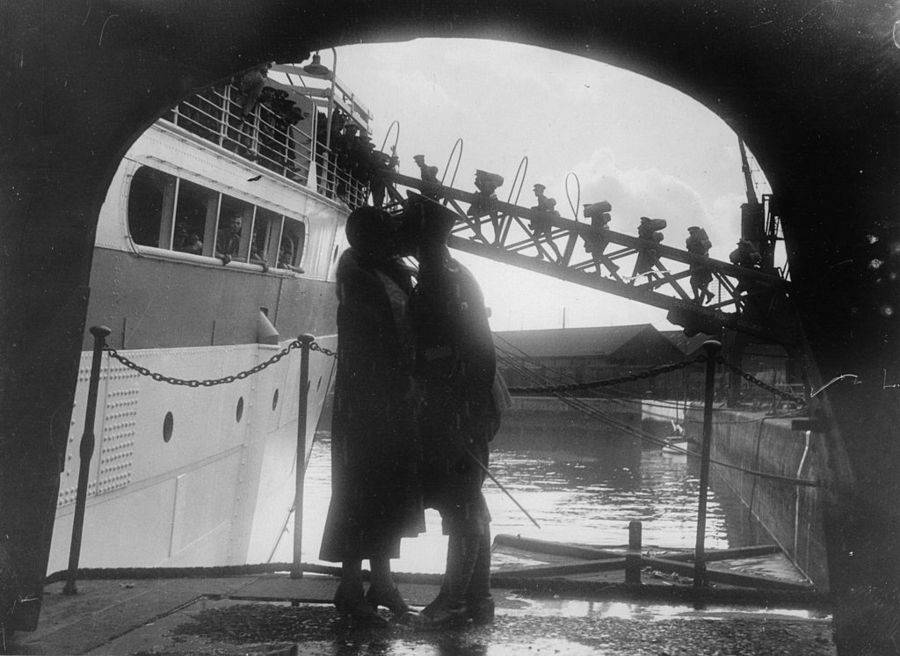
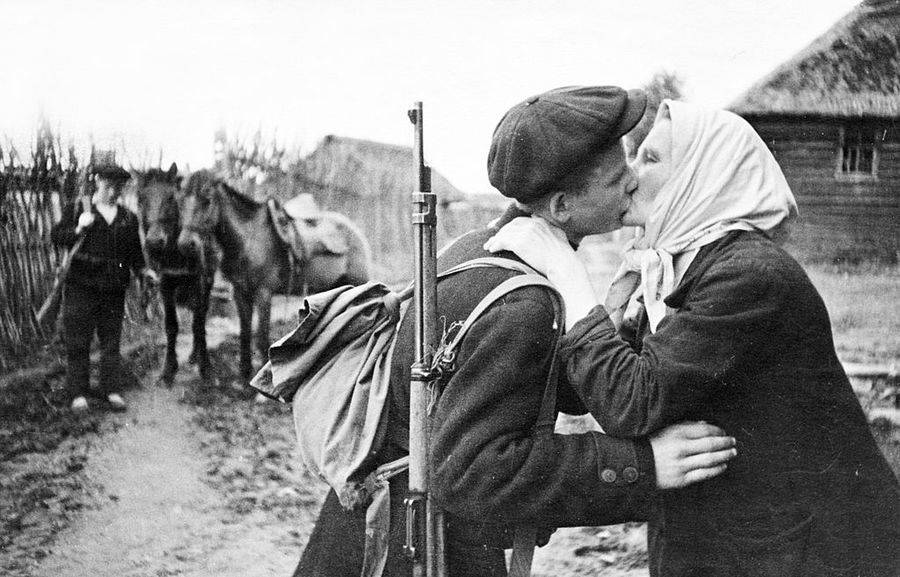
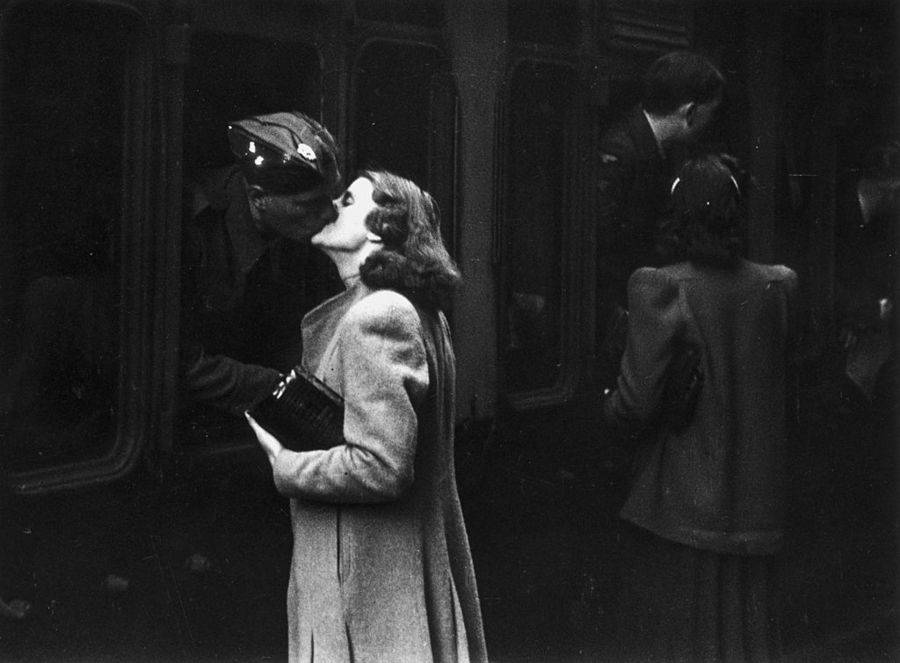
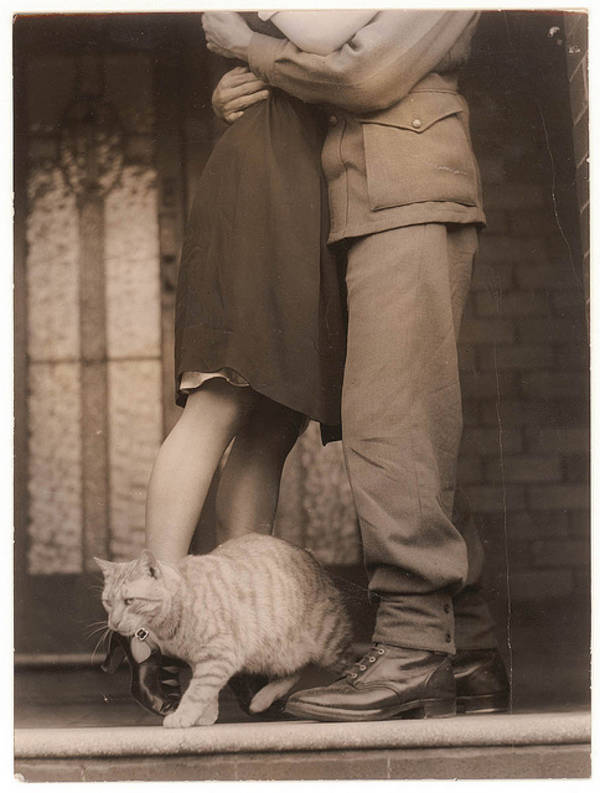
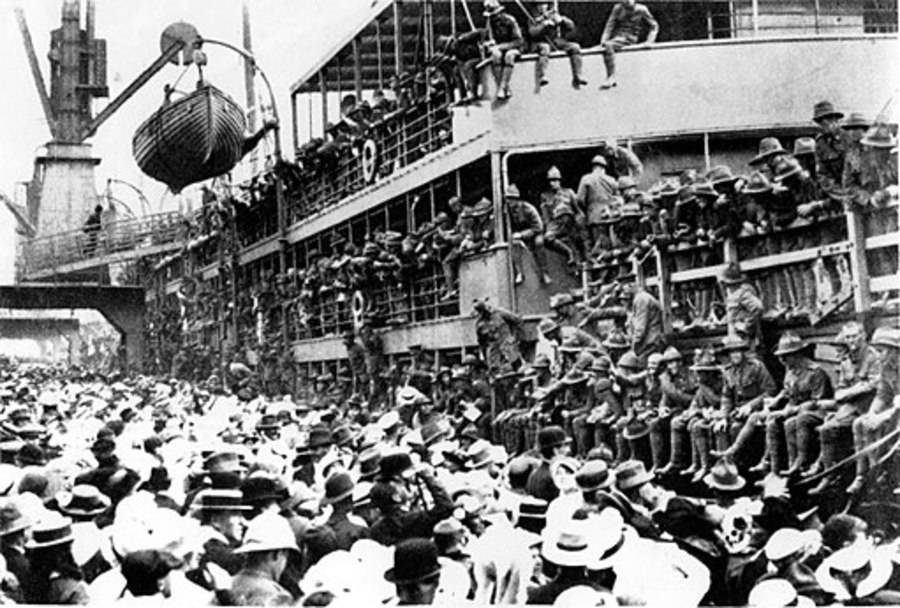
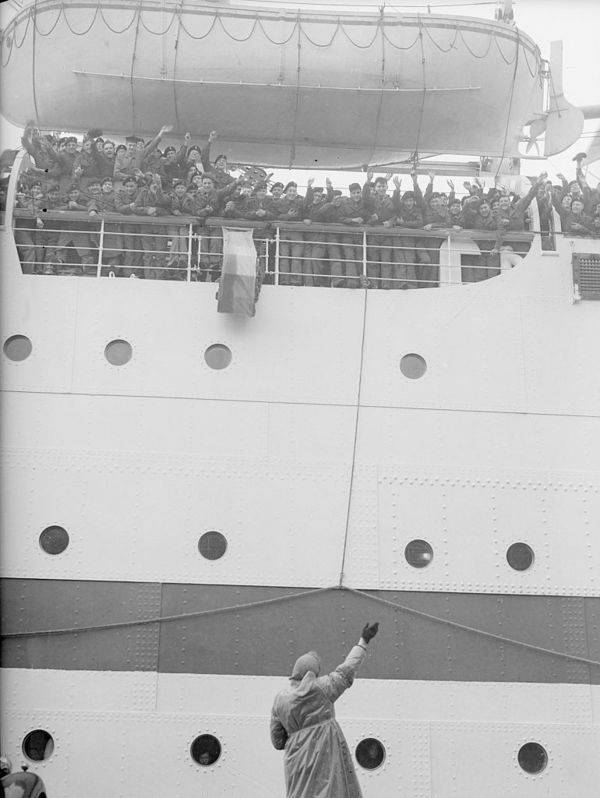
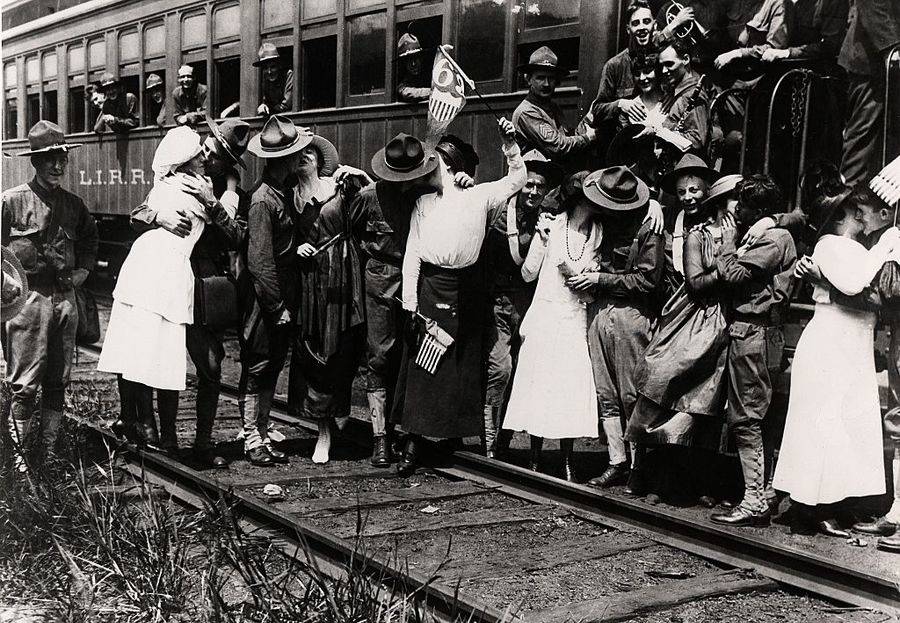
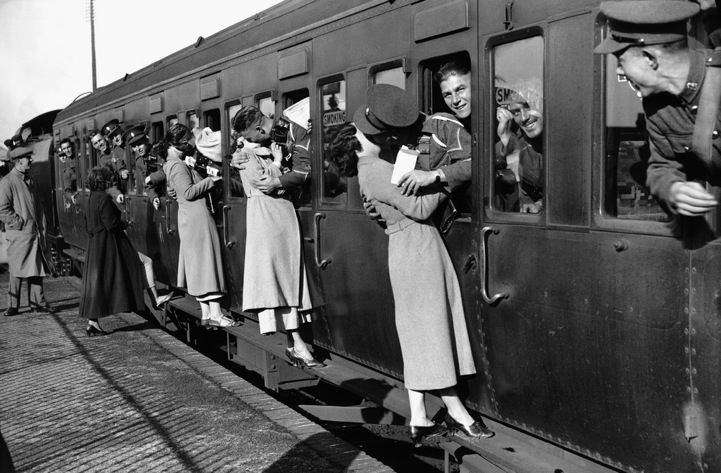
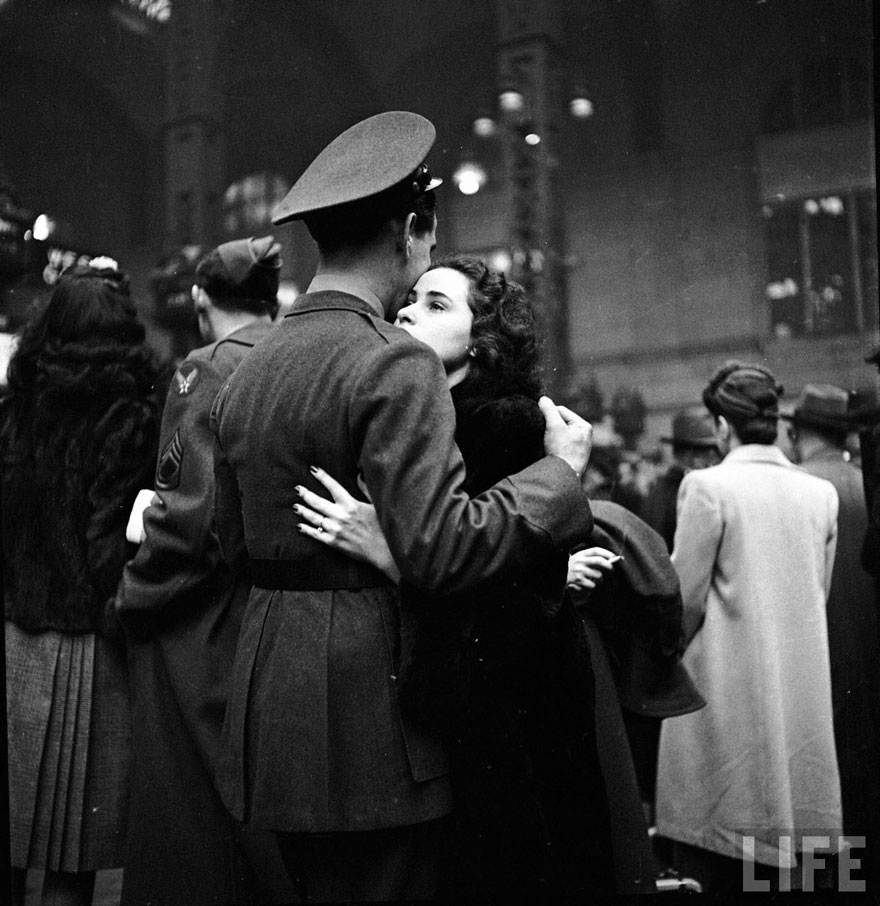
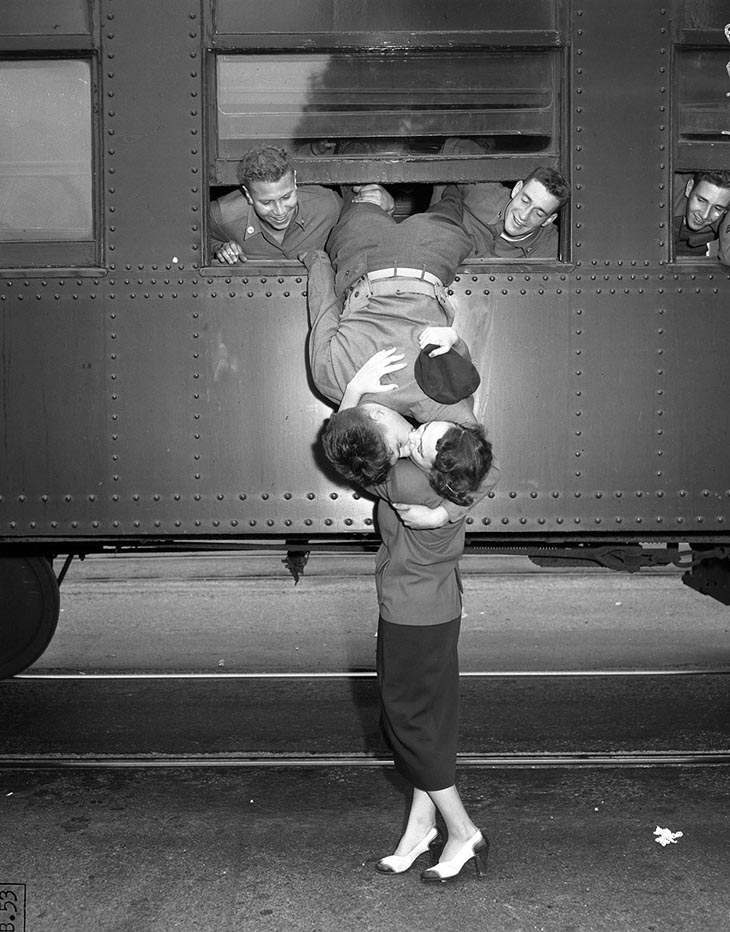
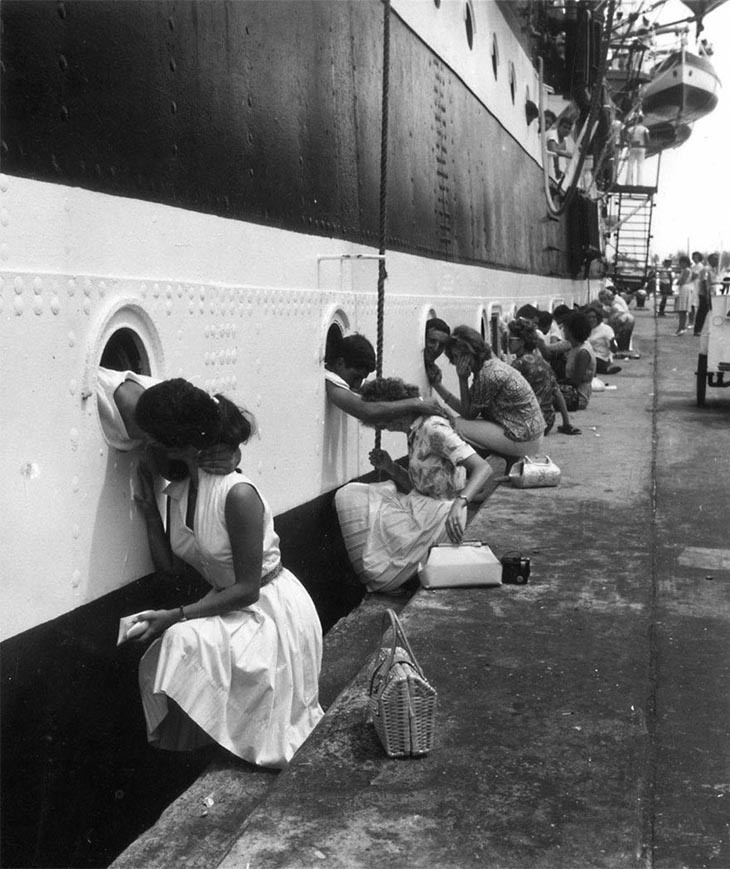
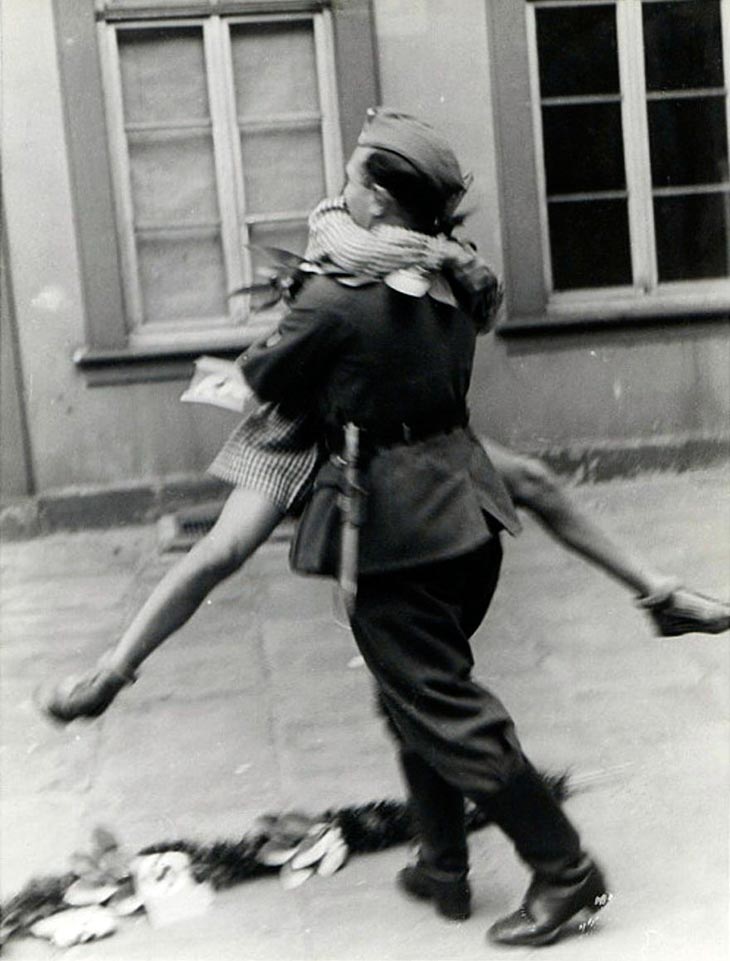
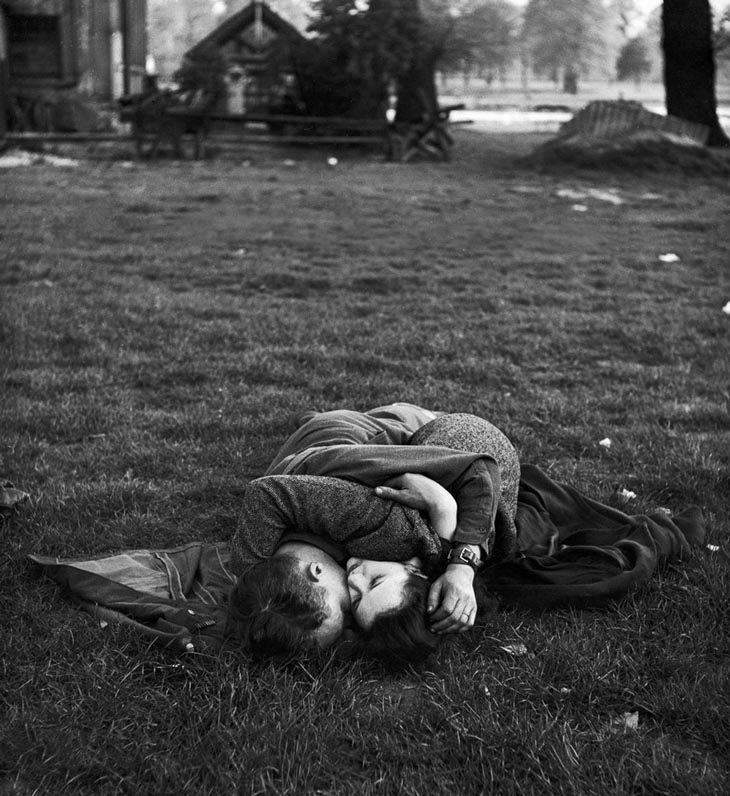
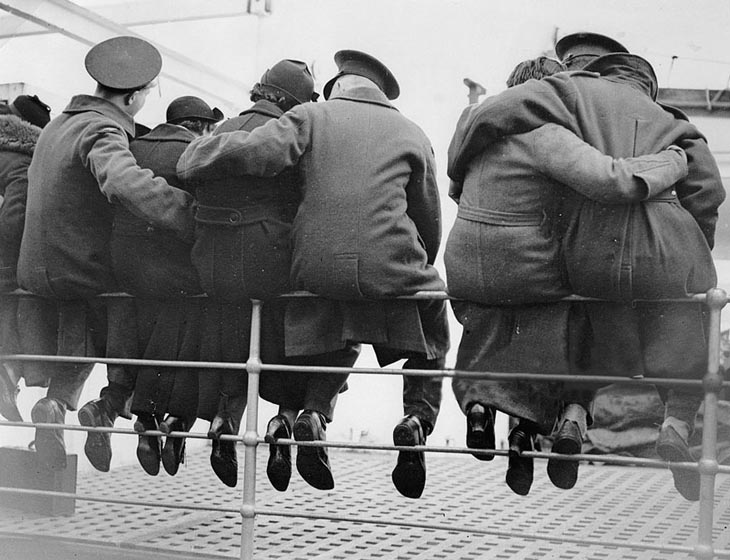
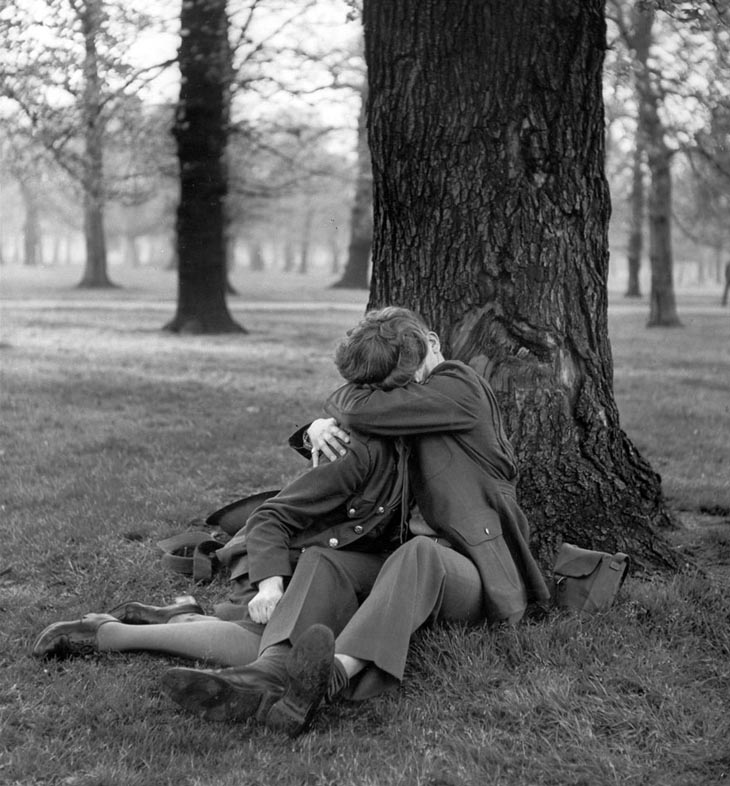
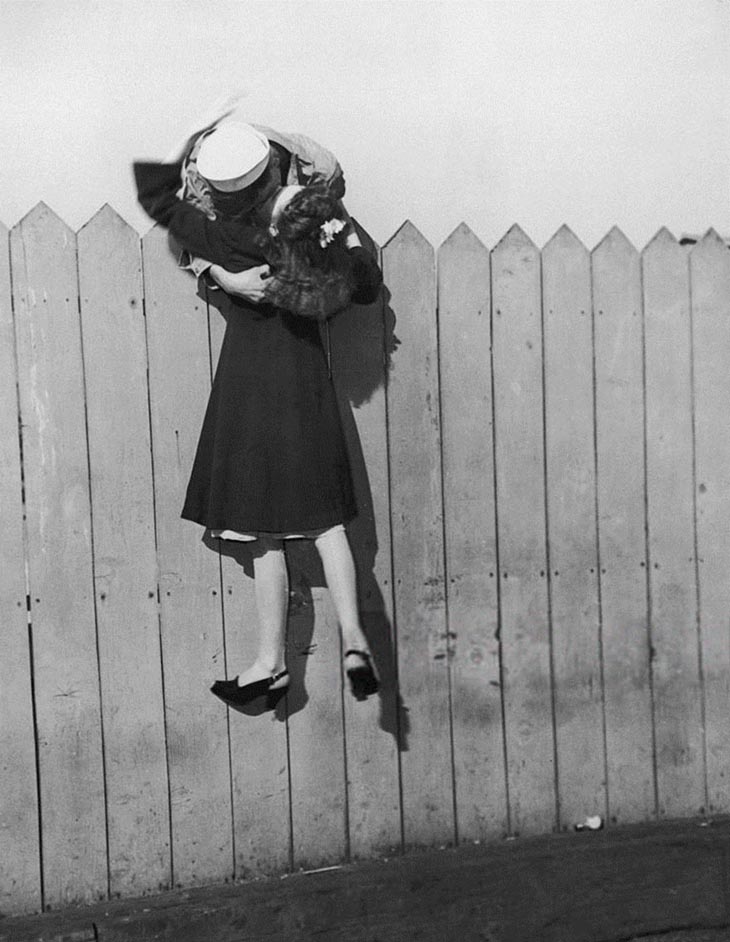
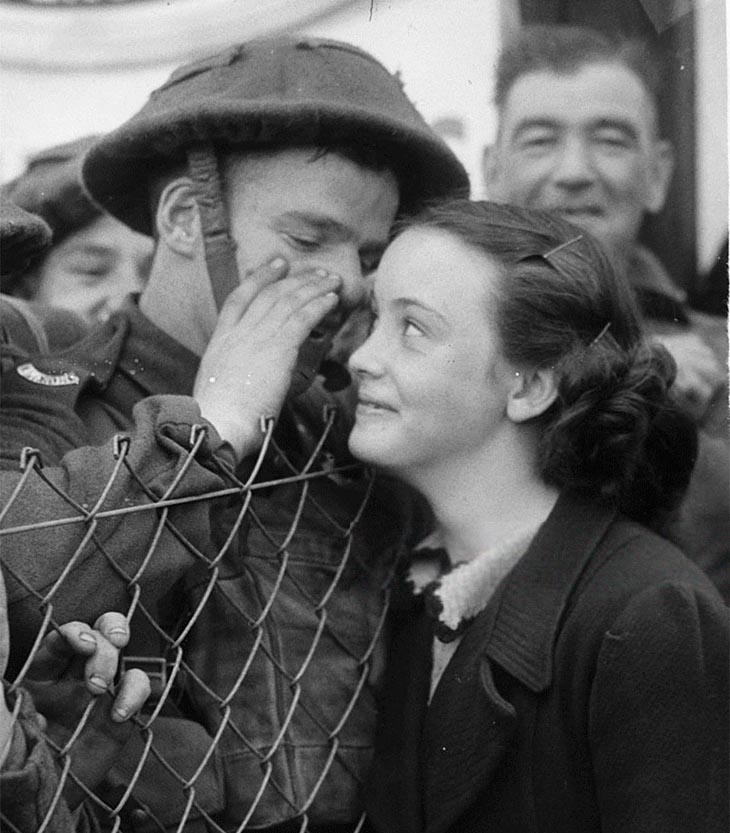
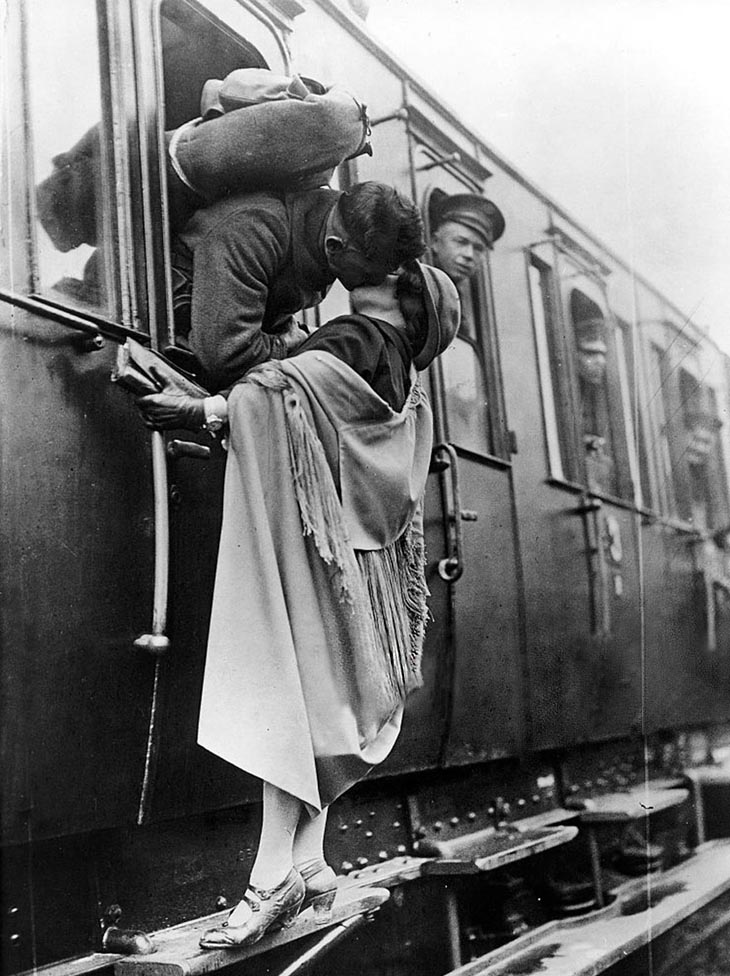
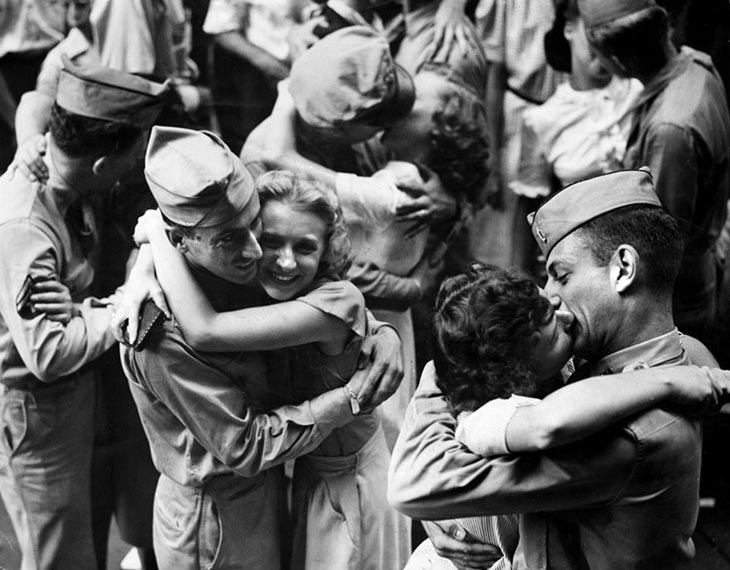
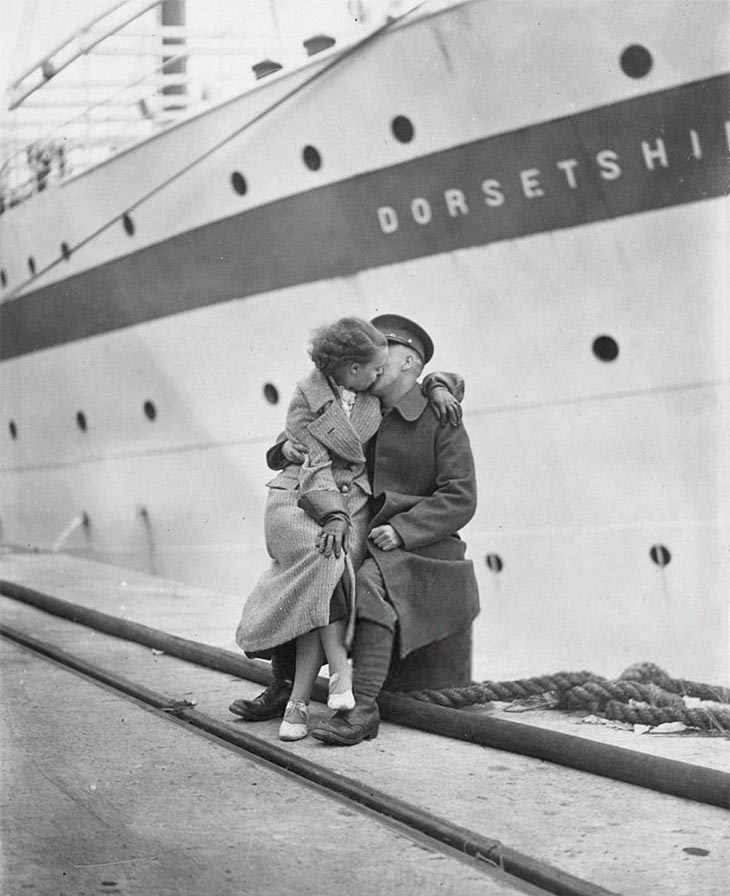
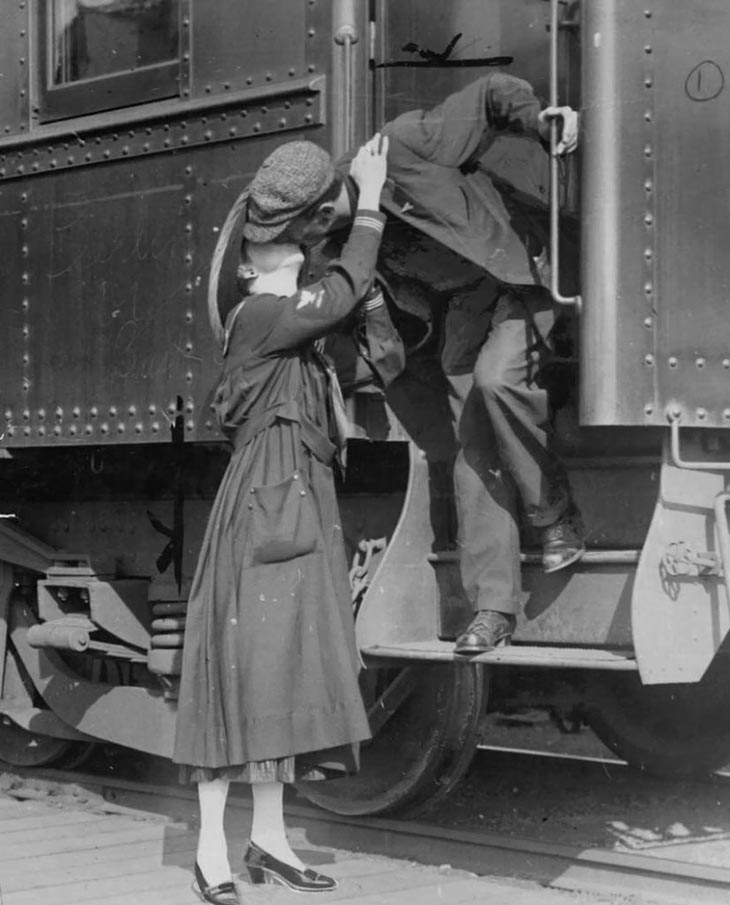
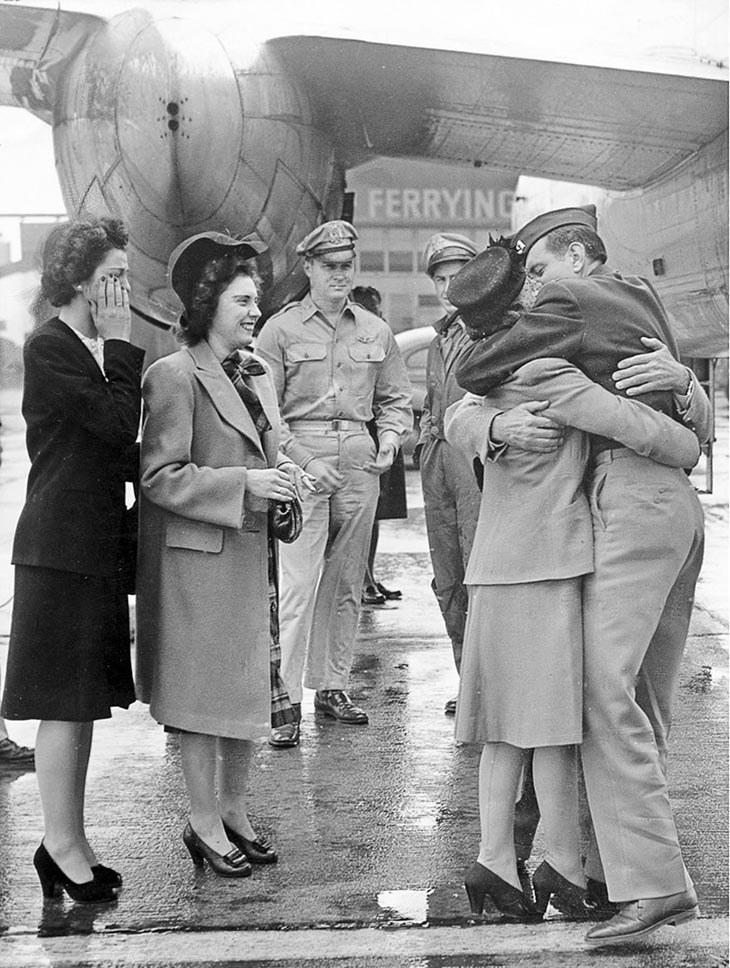
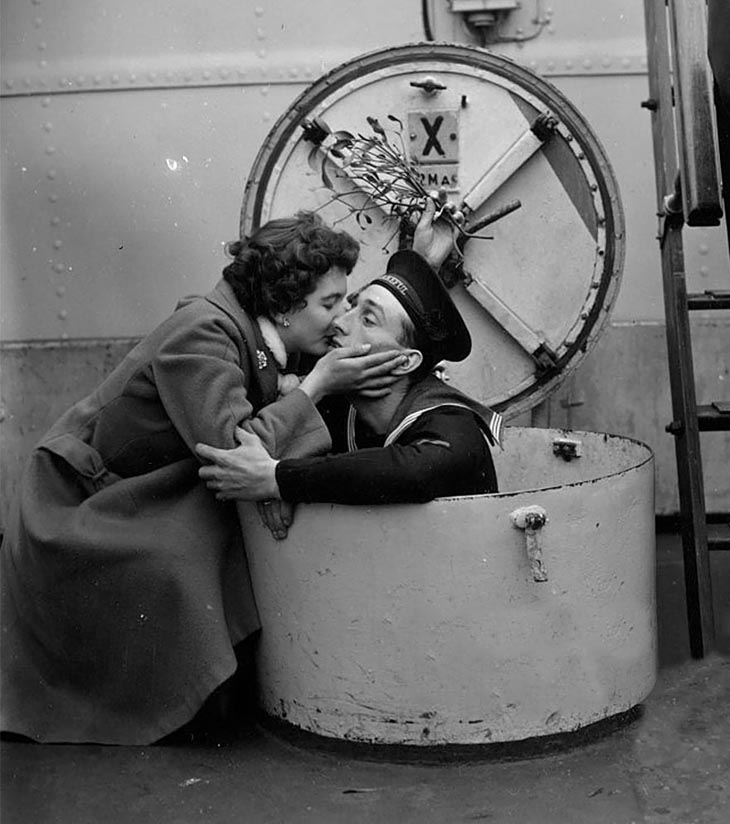
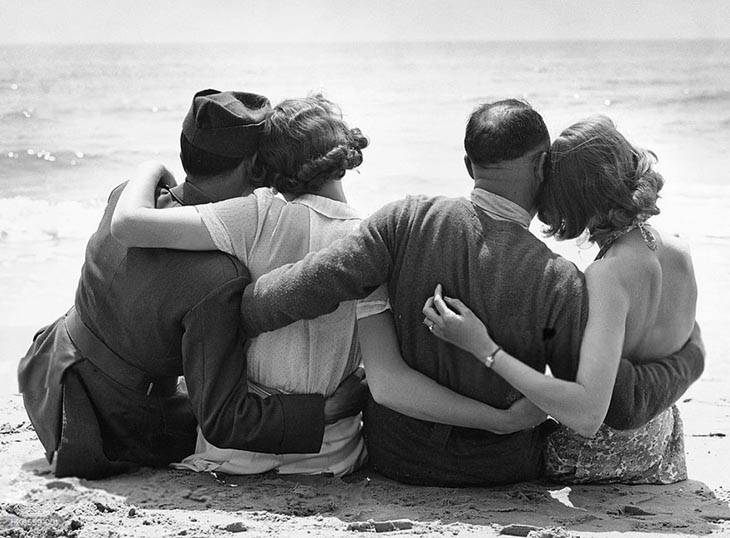
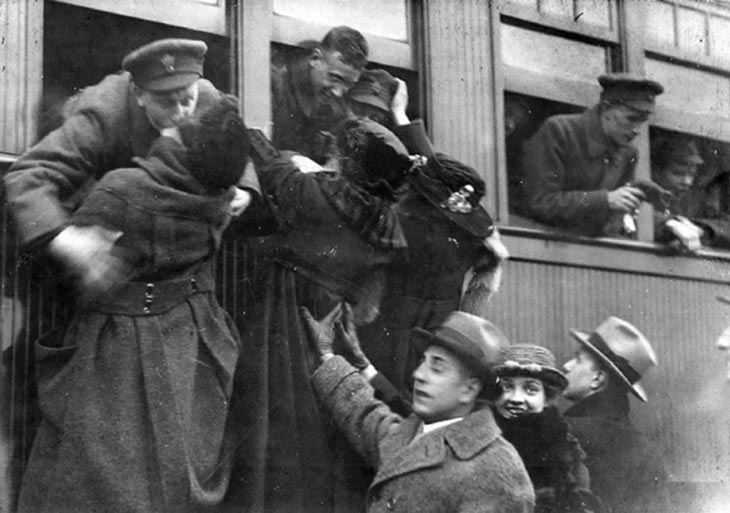
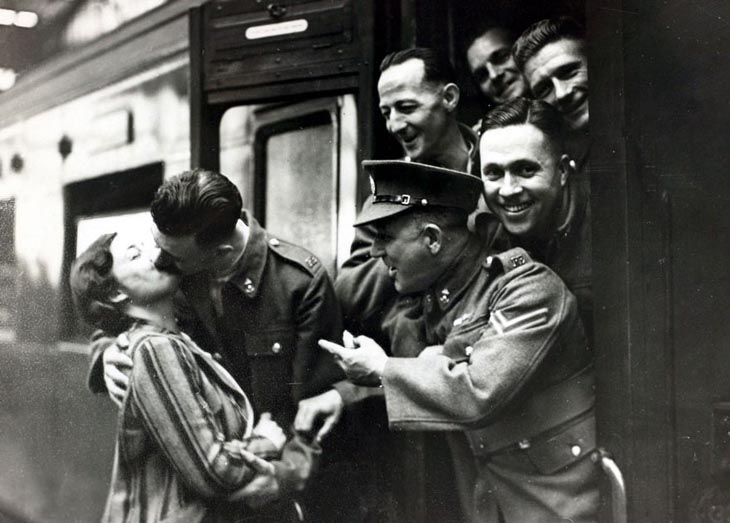
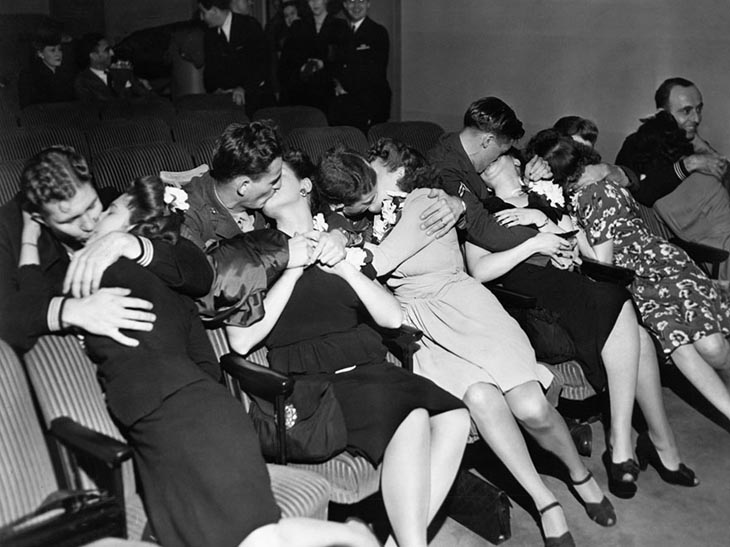
These fascinating postcards show how men expressed romantic gestures with their lovers from between the 1900s and 1920s.

















































Bringing You the Wonder of Yesterday – Today

These fascinating postcards show how men expressed romantic gestures with their lovers from between the 1900s and 1920s.


















































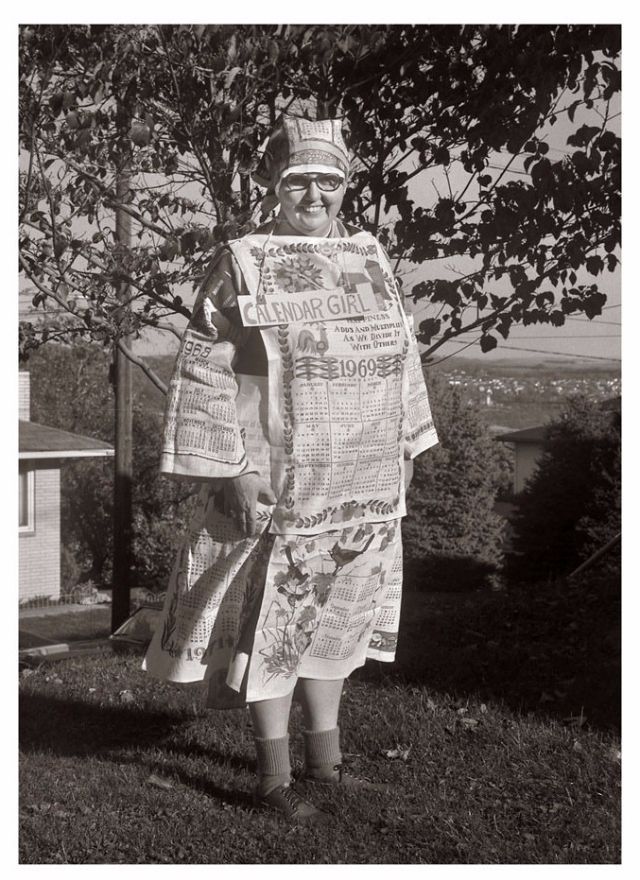
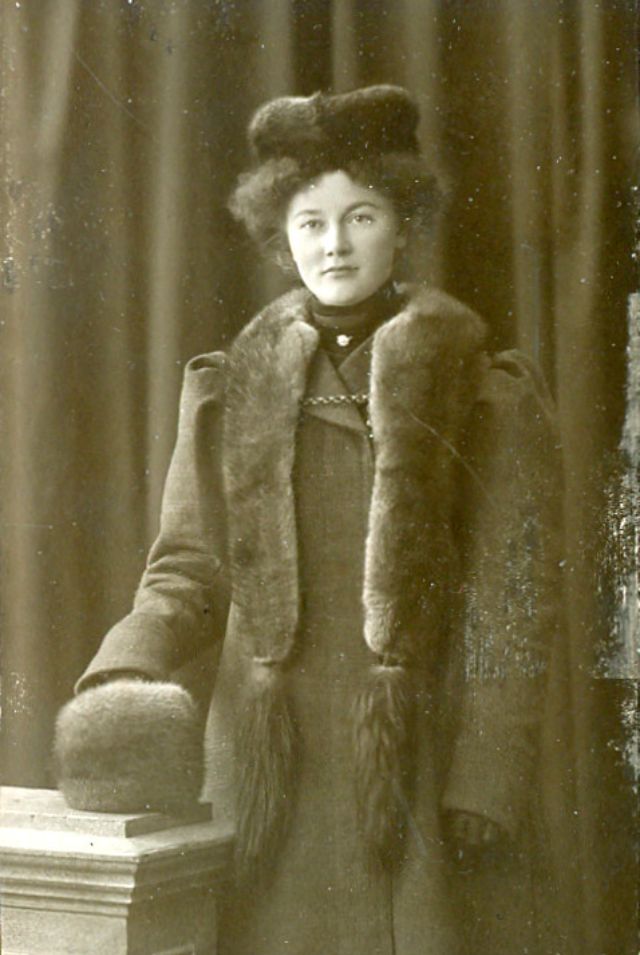
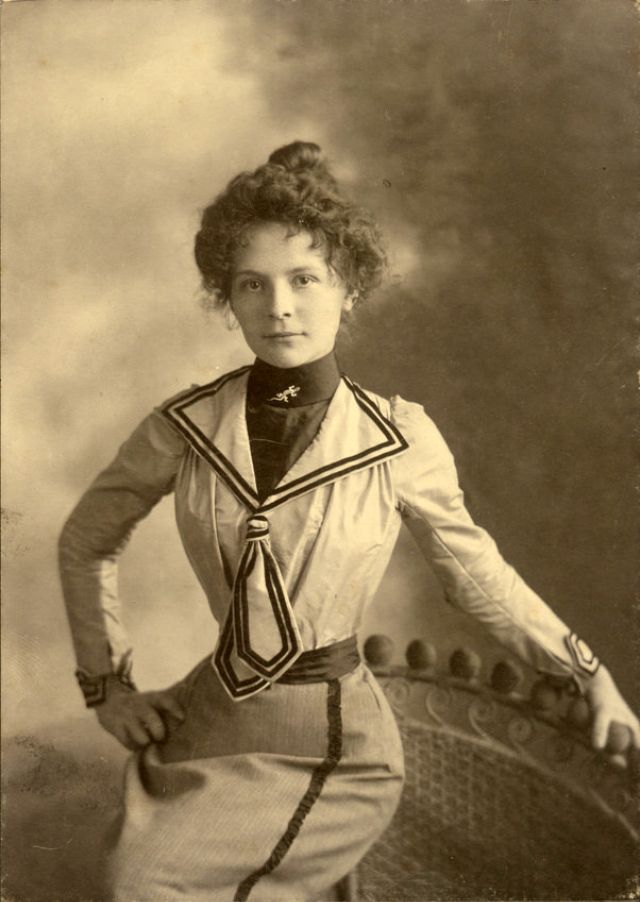
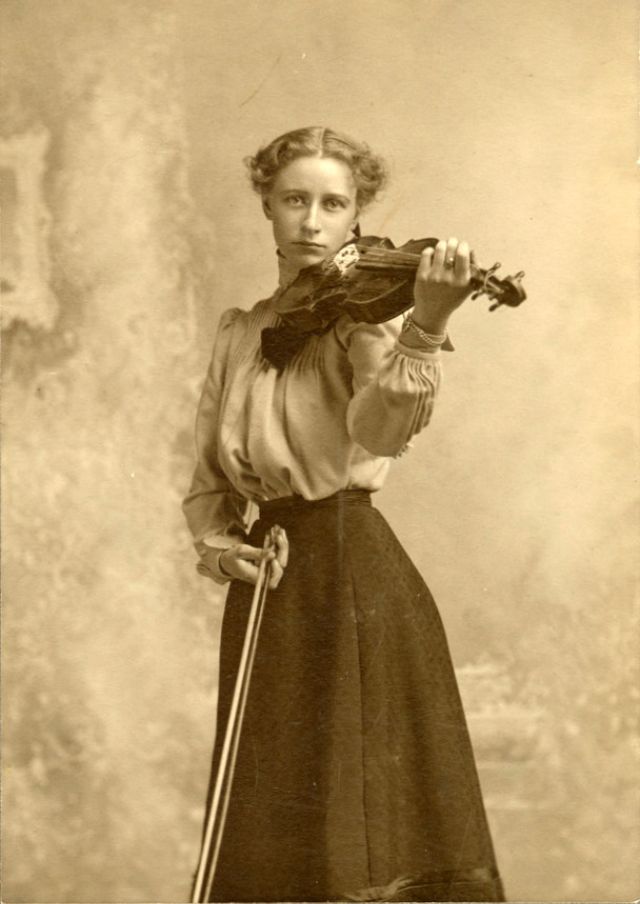
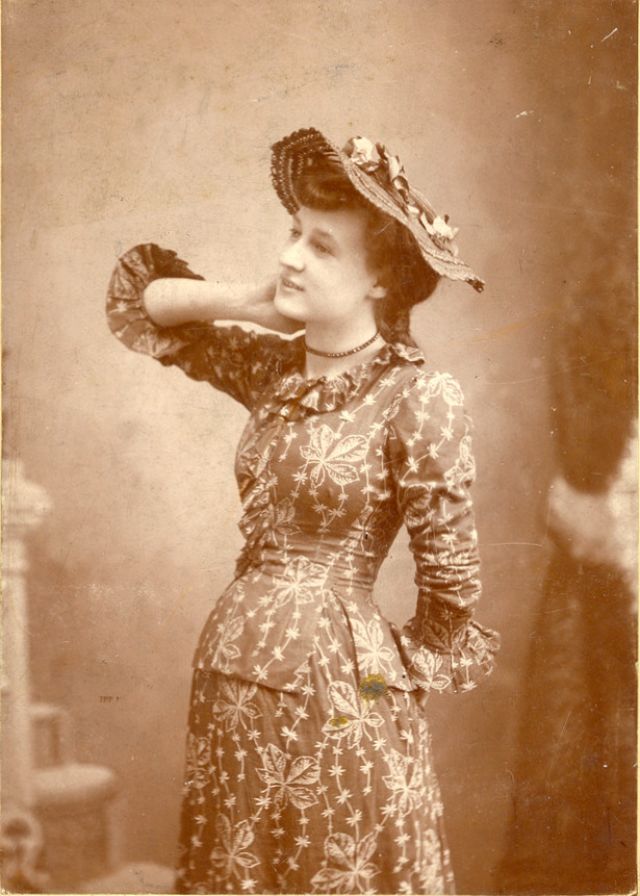
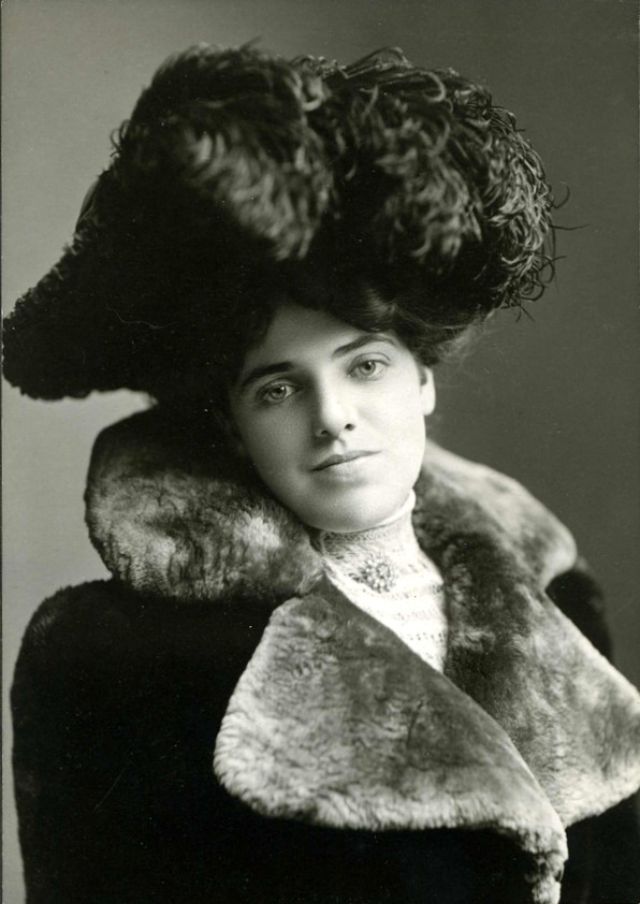
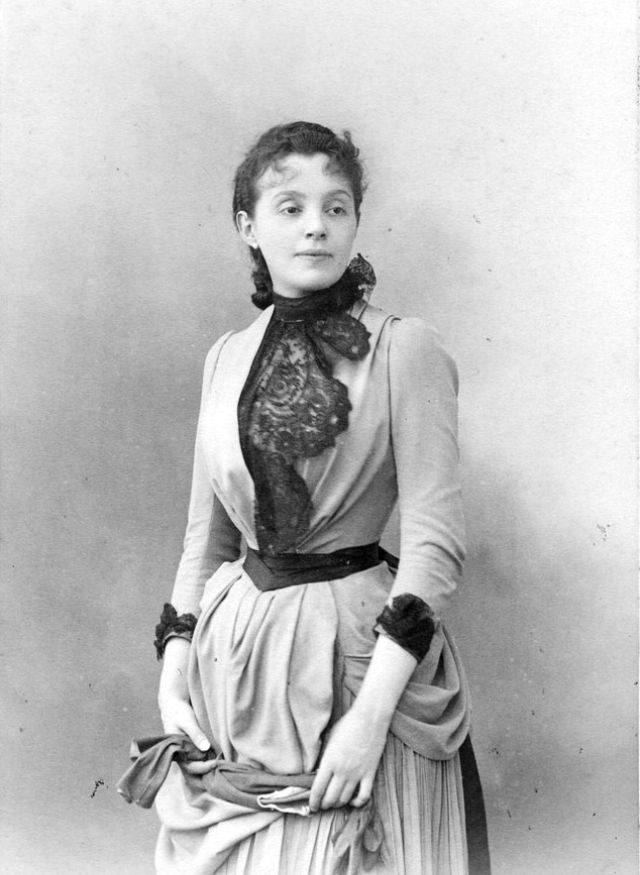
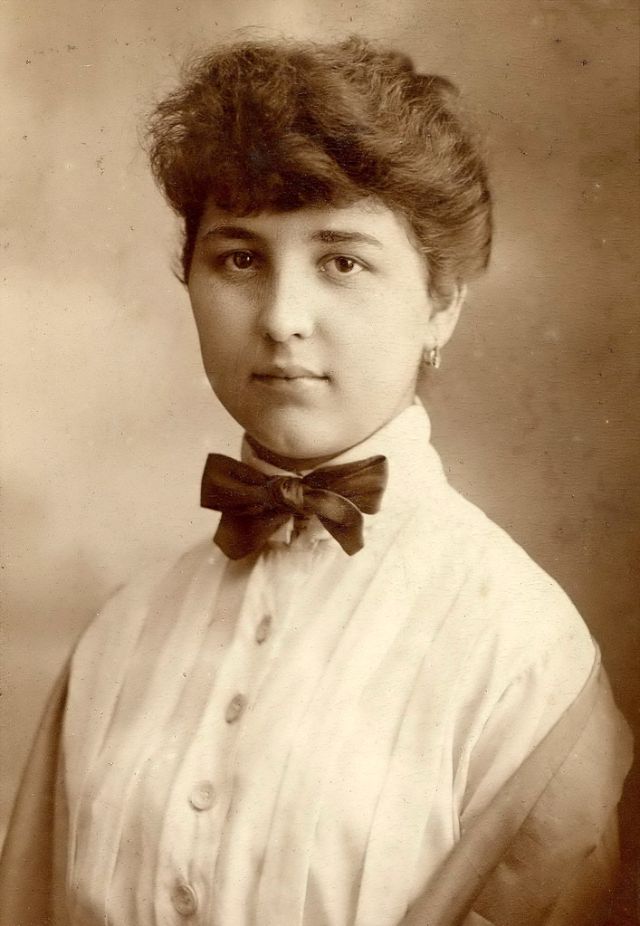
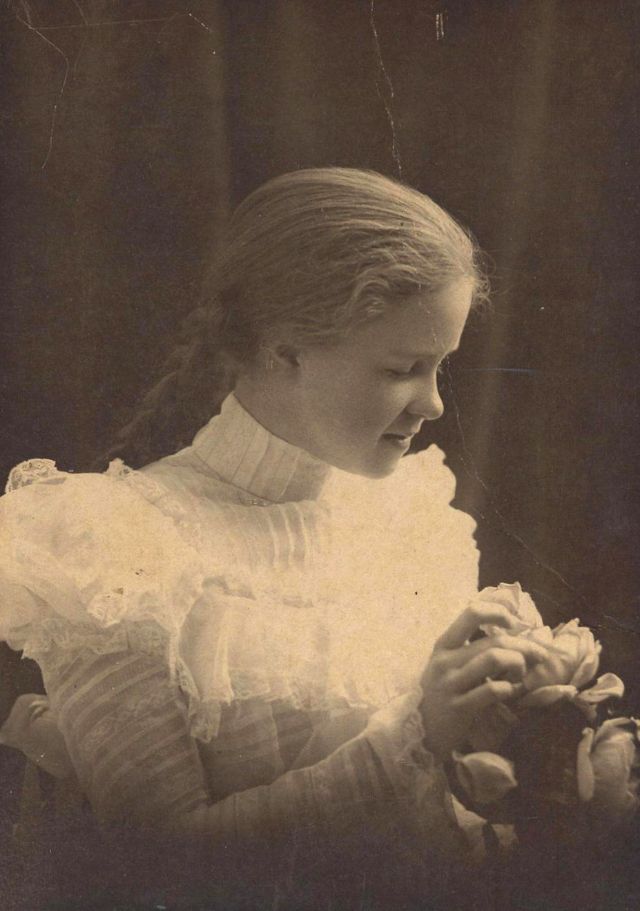
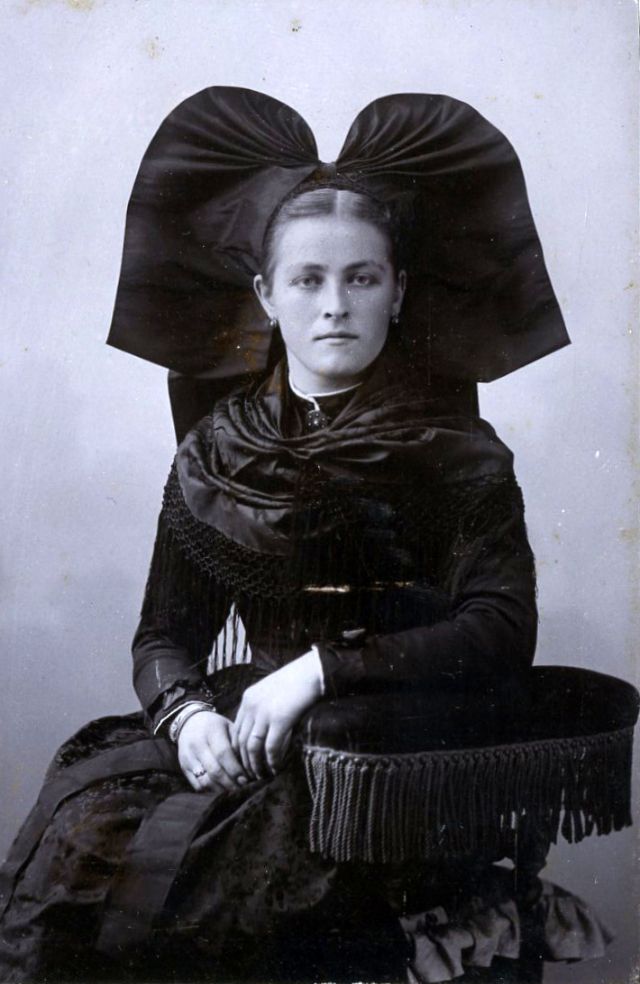
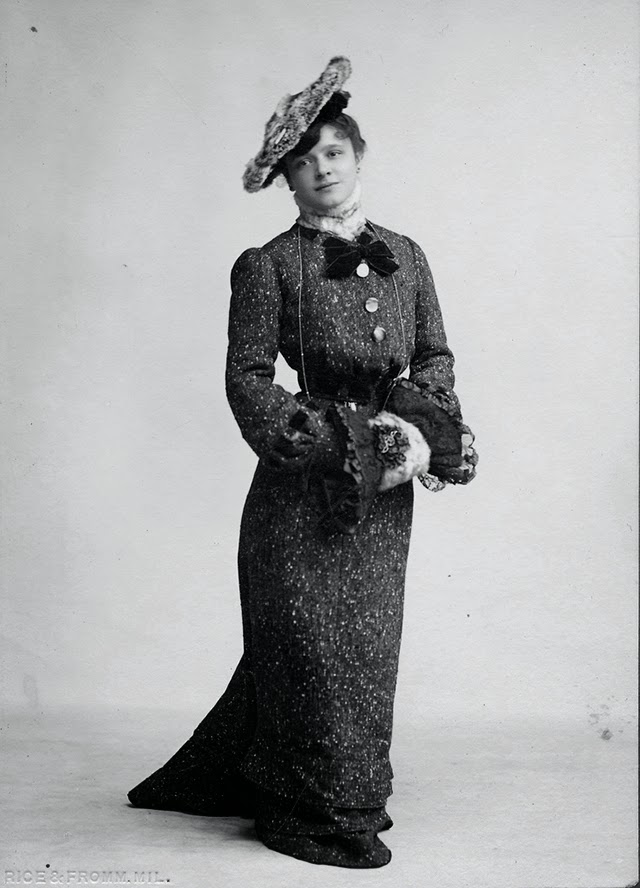
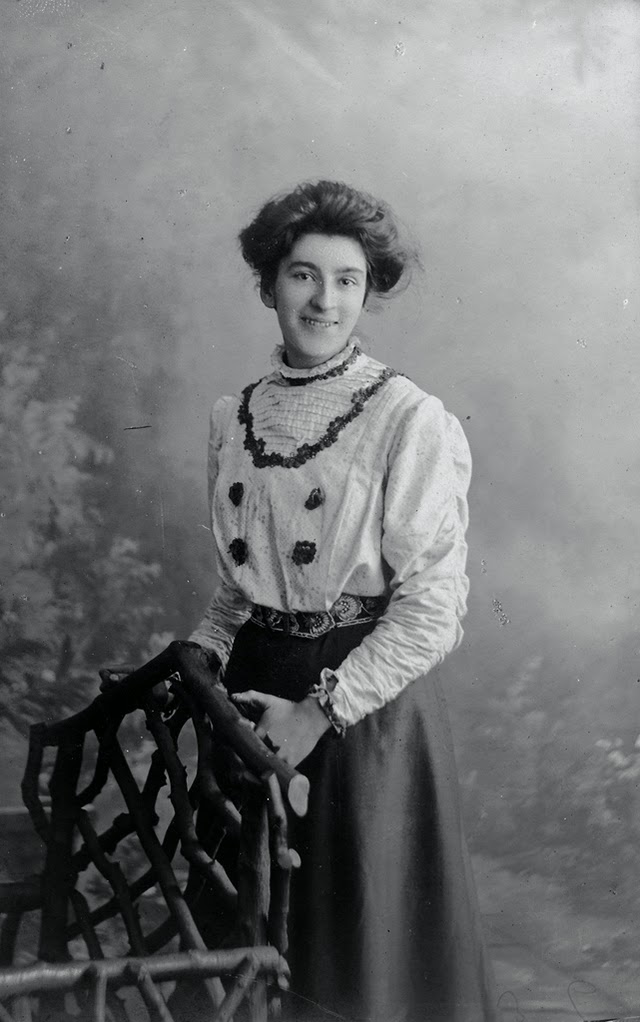
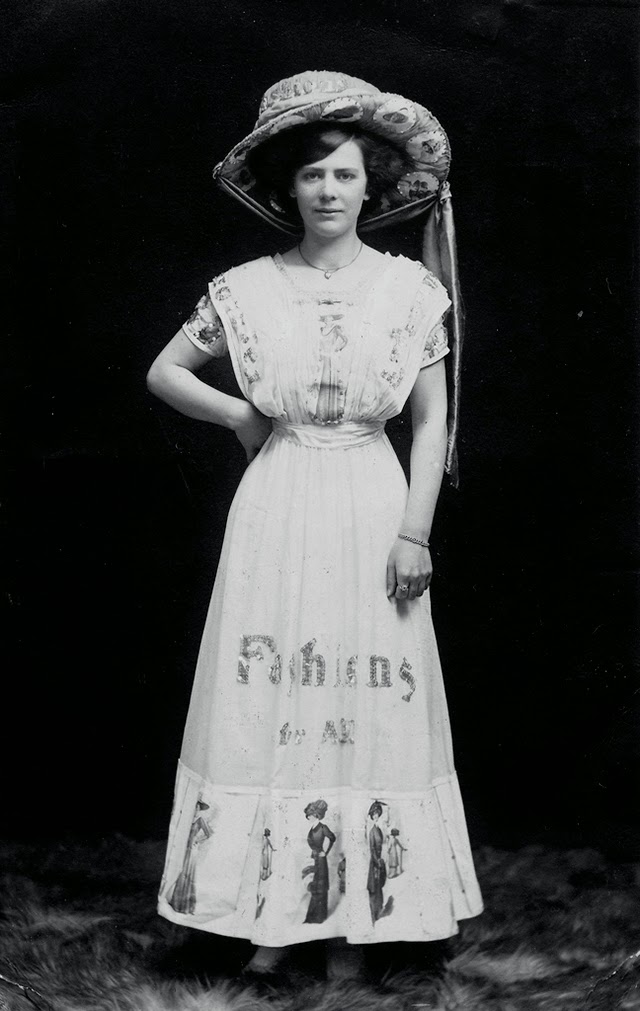
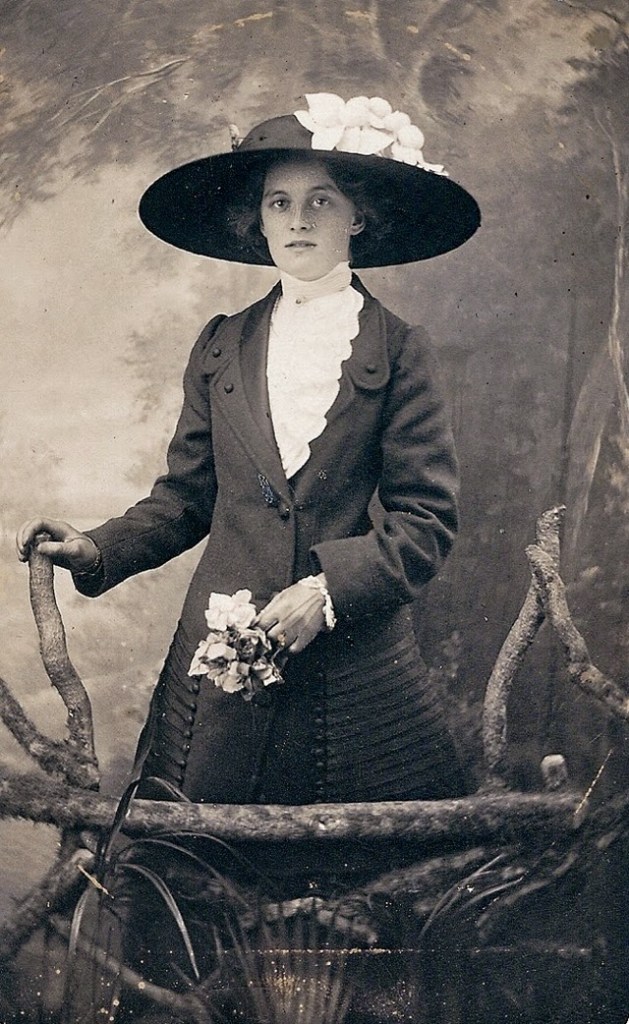
There are many ways to express ourselves, and these people wore some weird costumes to make more impressive.
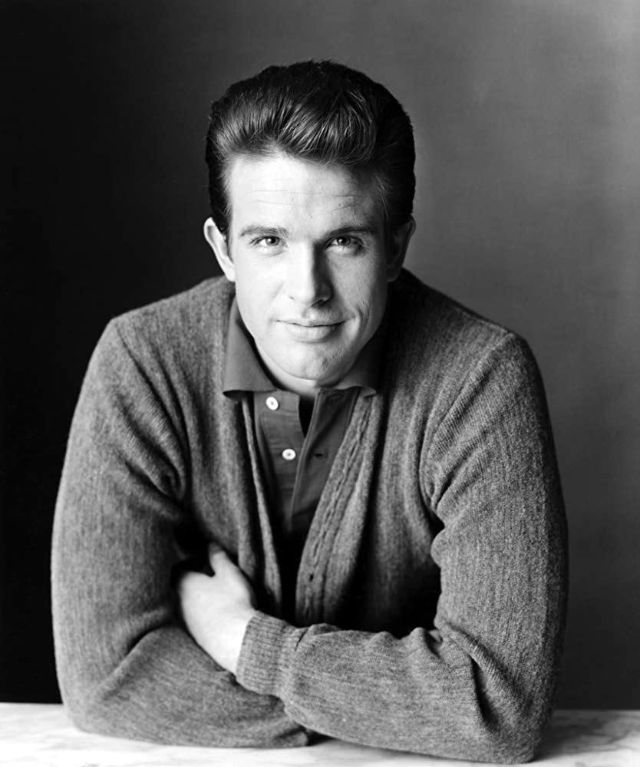








































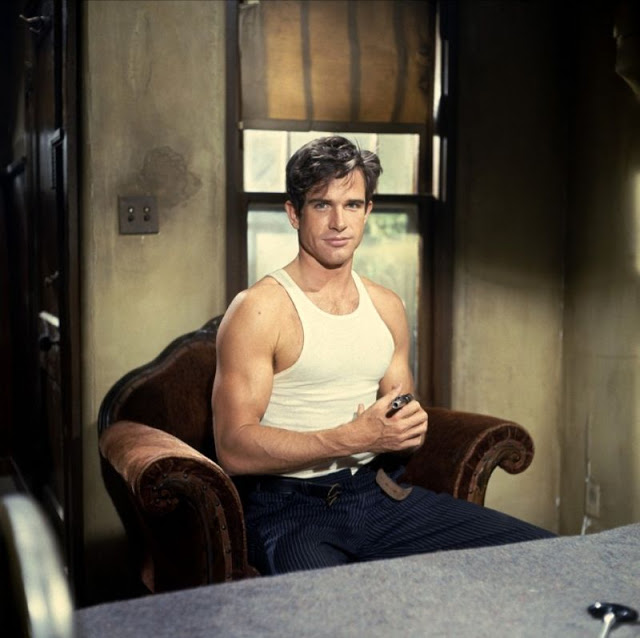
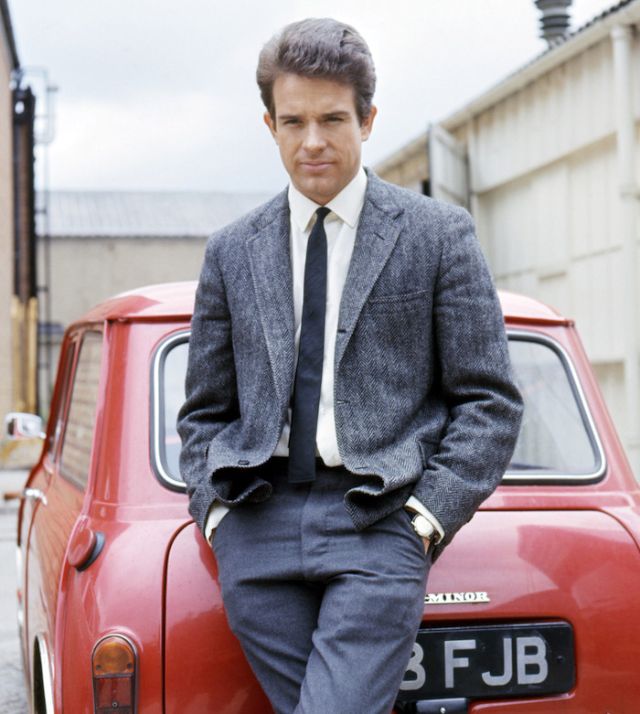
Henry Warren Beatty (né Beaty; born March 30, 1937) is an American actor, director, producer, and screenwriter, whose career spans over six decades. He has been nominated for 15 Academy Awards, including four for Best Actor, four for Best Picture, two for Best Director, three for Original Screenplay, and one for Adapted Screenplay – winning Best Director for Reds (1981). Beatty is the only person to have been nominated for acting in, directing, writing, and producing the same film, and he did so twice: first for Heaven Can Wait (with Buck Henry as co-director), and again with Reds.
Eight of the films he has produced have earned 53 Academy nominations, and in 1999, he was awarded the academy’s highest honor, the Irving G. Thalberg Award. Beatty has been nominated for 18 Golden Globe Awards, winning six, including the Golden Globe Cecil B. DeMille Award, with which he was honored in 2007. Among his Golden Globe–nominated films are Splendor in the Grass (1961), his screen debut, and Bonnie and Clyde (1967), Shampoo (1975), Heaven Can Wait, Reds, Dick Tracy (1990), Bugsy (1991), Bulworth (1998), and Rules Don’t Apply (2016), all of which he also produced.
Director and collaborator Arthur Penn described Beatty as “the perfect producer”, adding, “He makes everyone demand the best of themselves. Warren stays with a picture through editing, mixing, and scoring. He plain works harder than anyone else I have ever seen.” Beatty’s films often have a left-leaning political message. Praising Bulworth, Patricia J. Williams said: “[Beatty] knows power… and this movie is effective precisely because it takes on the issue of power.”
Director and collaborator Arthur Penn described Beatty as “the perfect producer”, adding, “He makes everyone demand the best of themselves. Warren stays with a picture through editing, mixing and scoring. He plain works harder than anyone else I have ever seen.”
With Bonnie and Clyde, Beatty helped to usher in New Hollywood – a movement in American film history from the mid-1960s to the early 1980s, when a new generation of young filmmakers came to prominence in the United States. (Wikipedia)
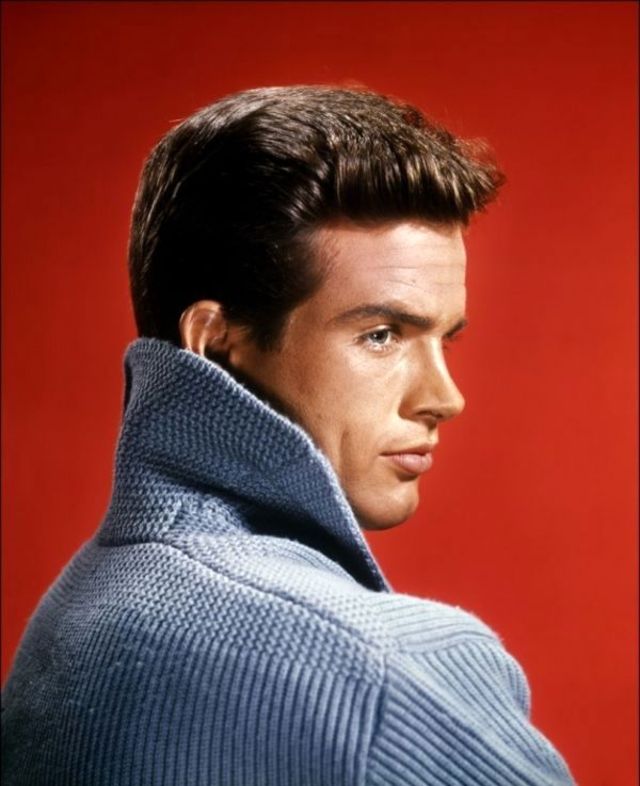
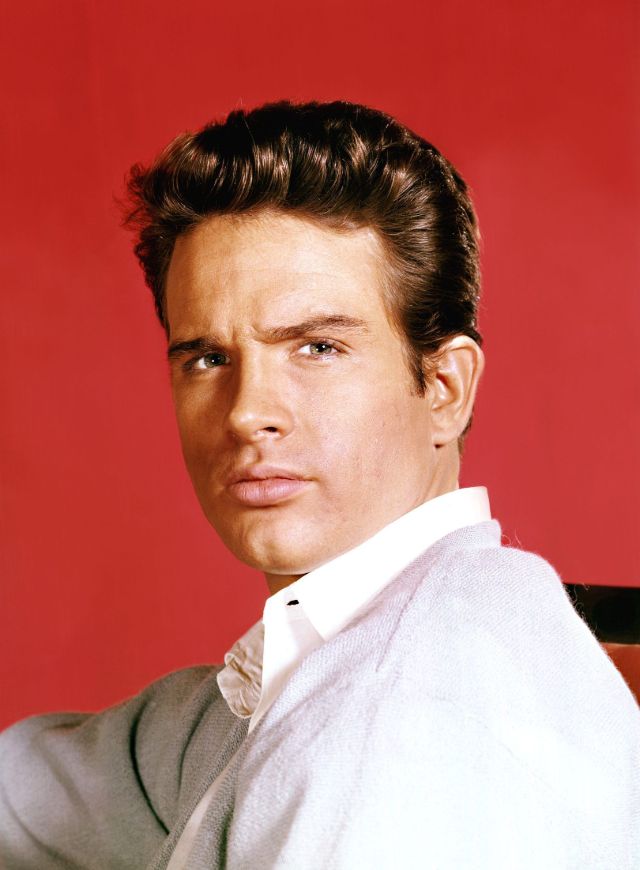
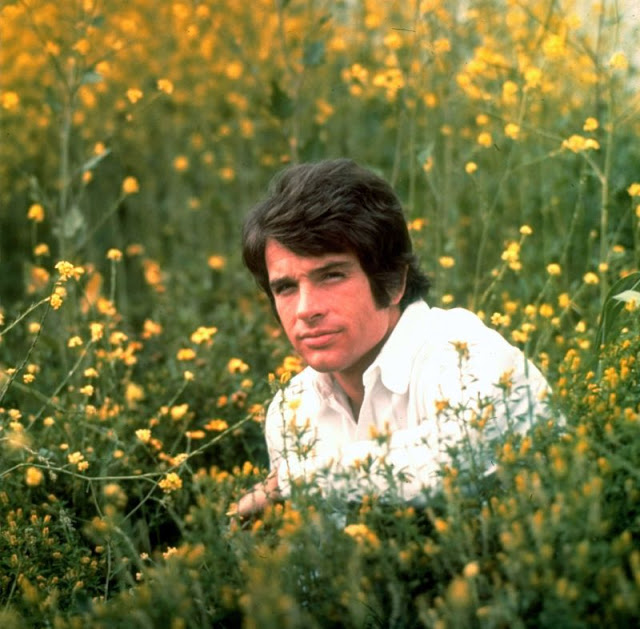
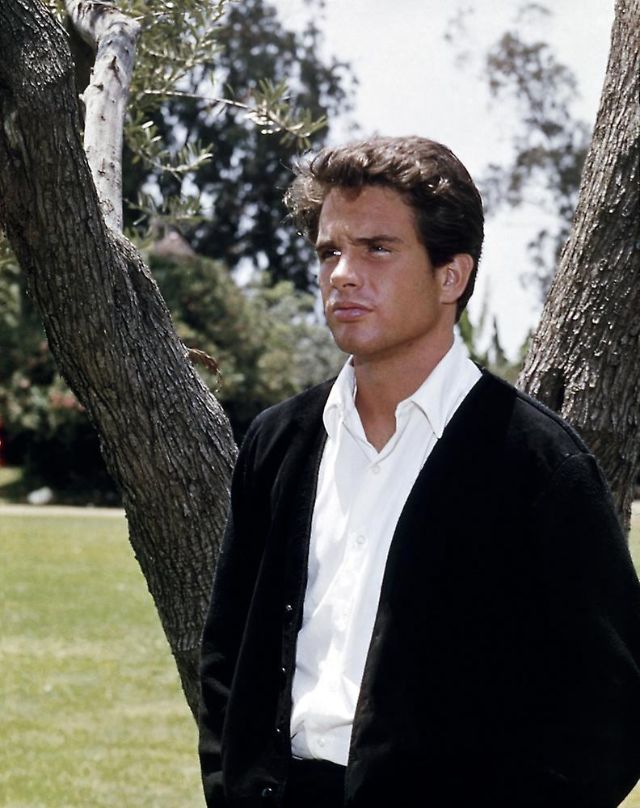
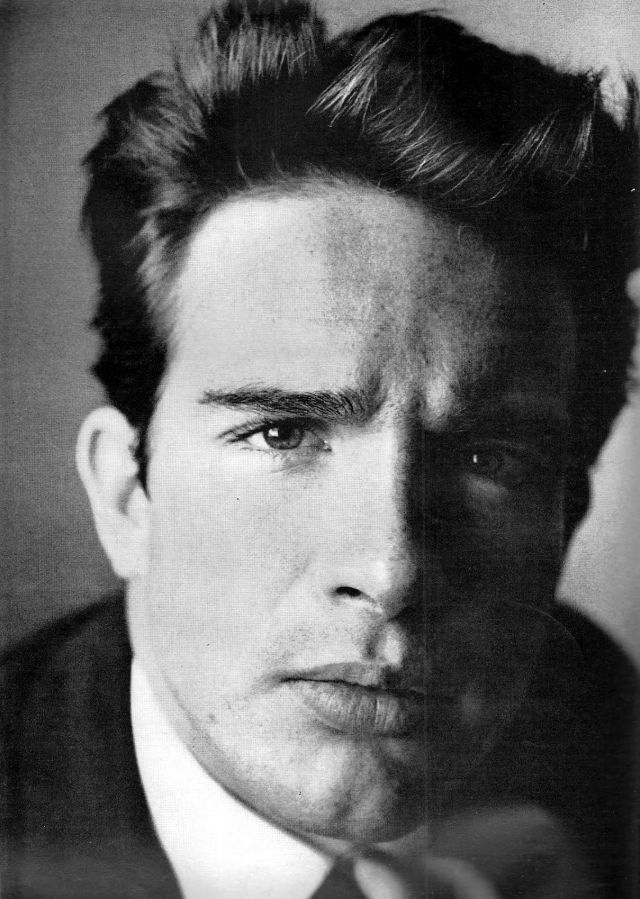
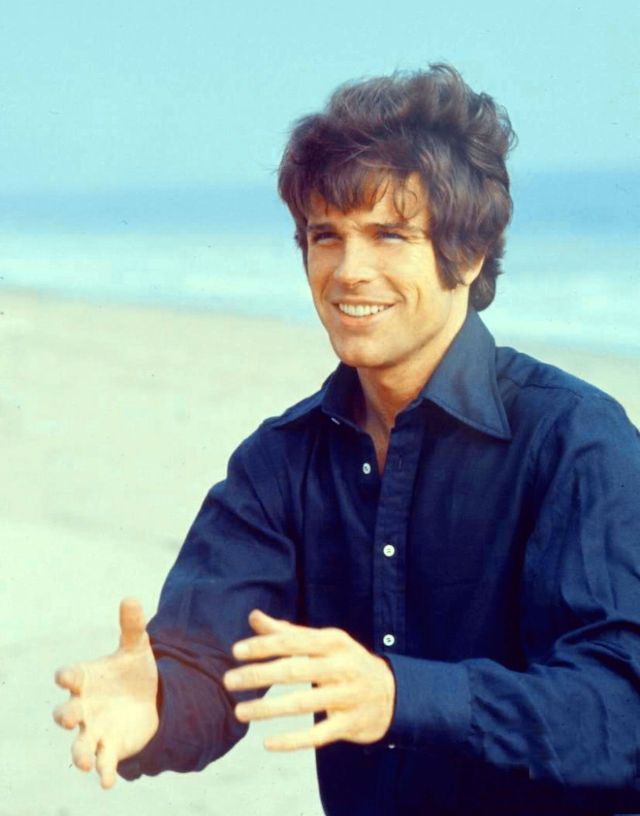
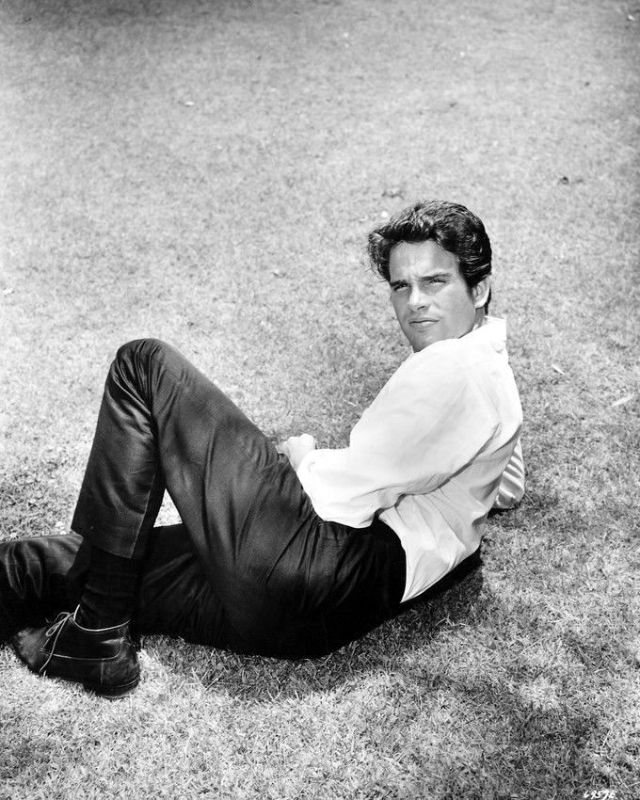
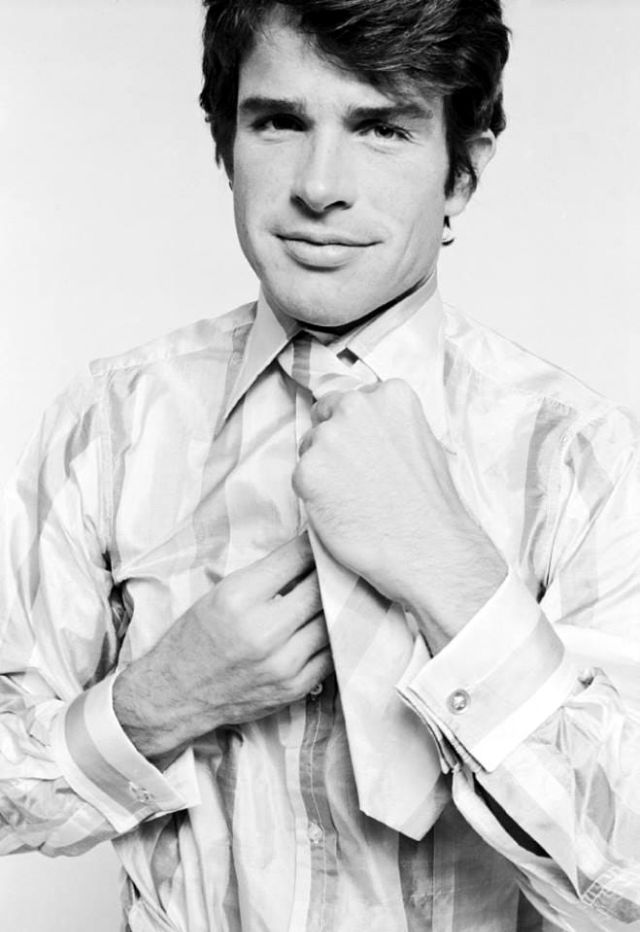
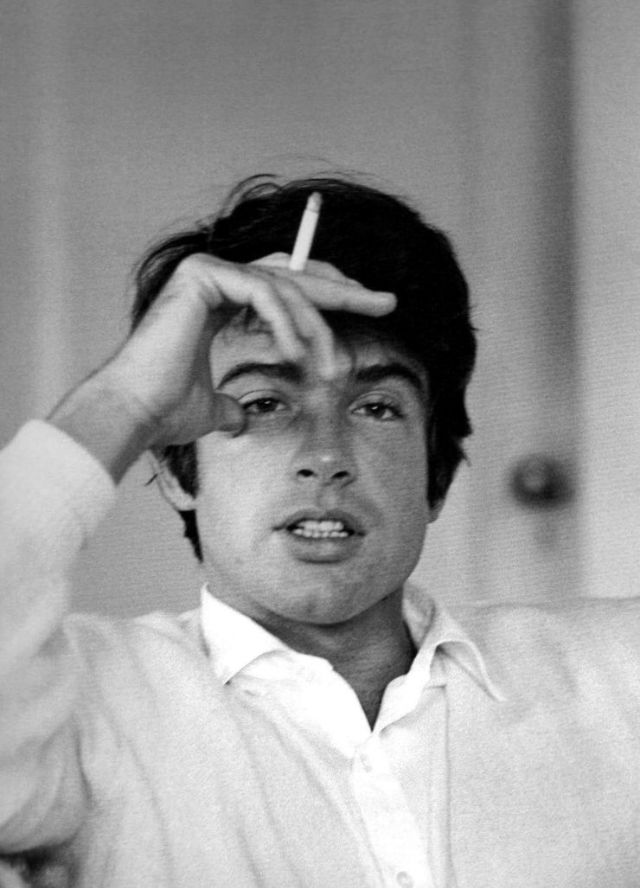
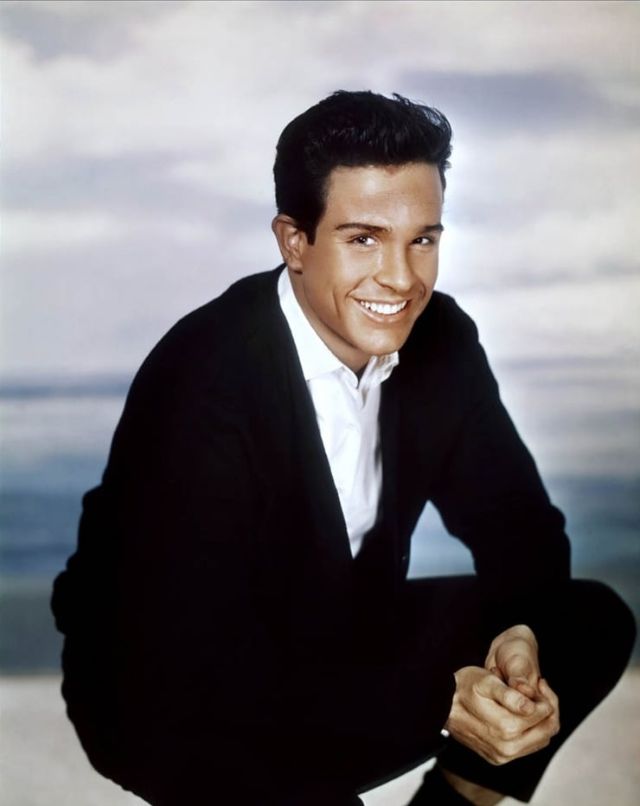
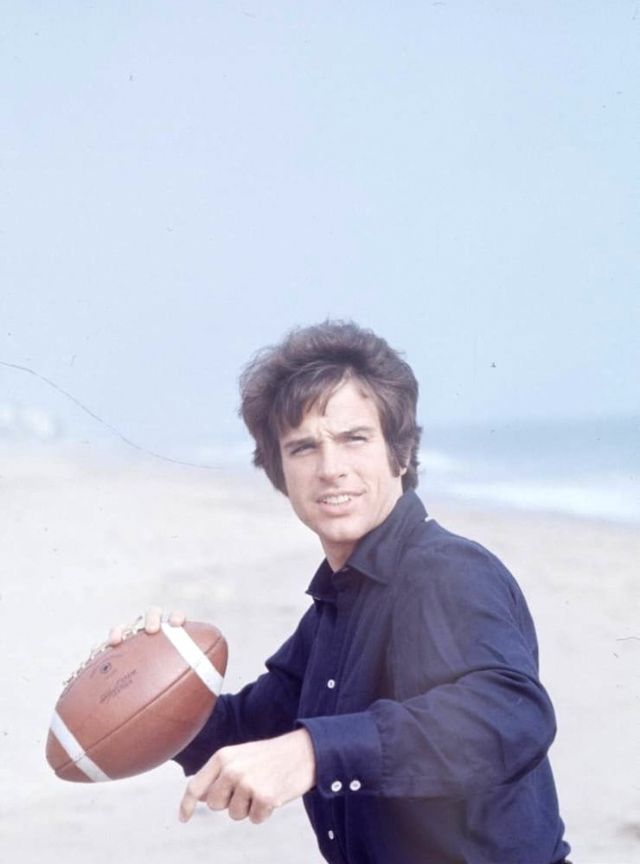
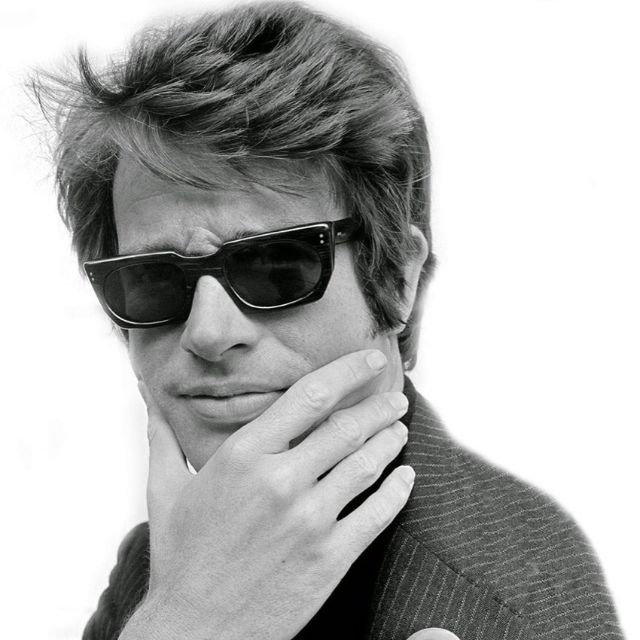
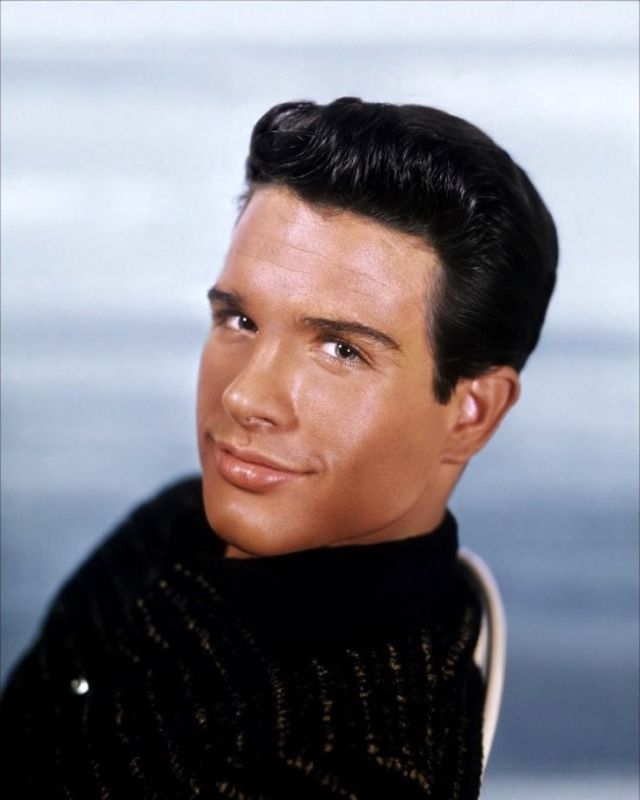
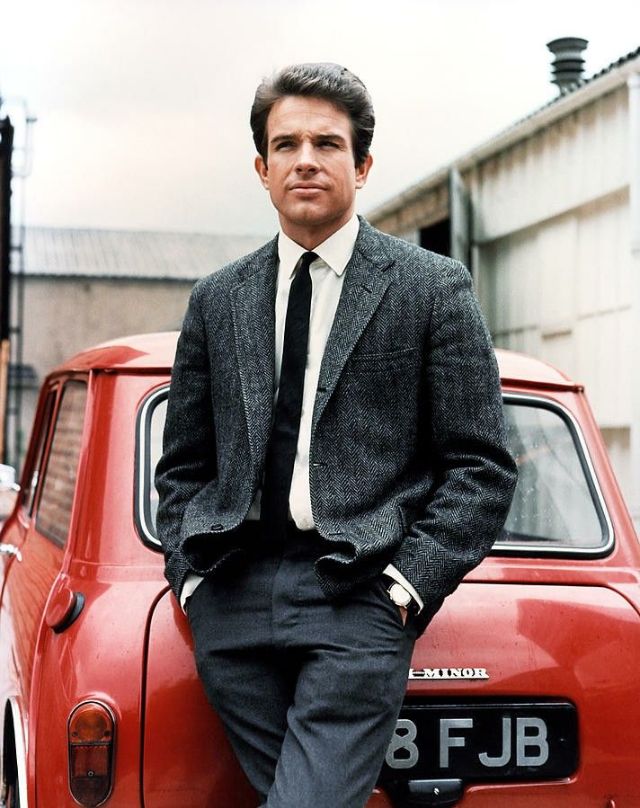
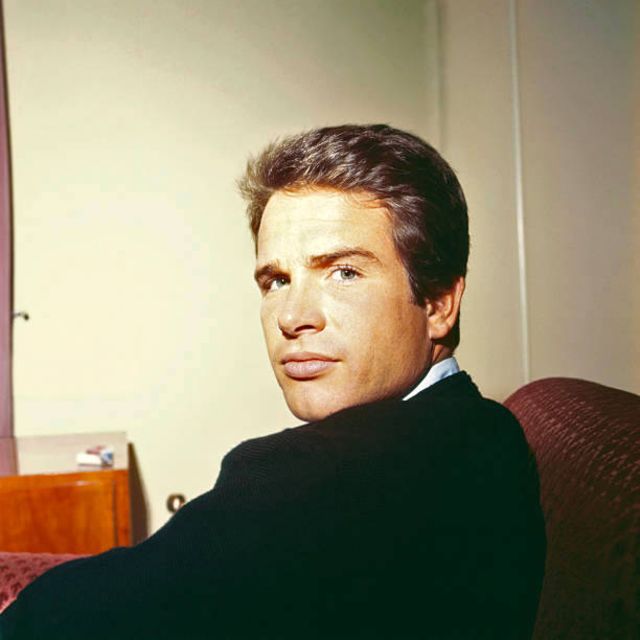
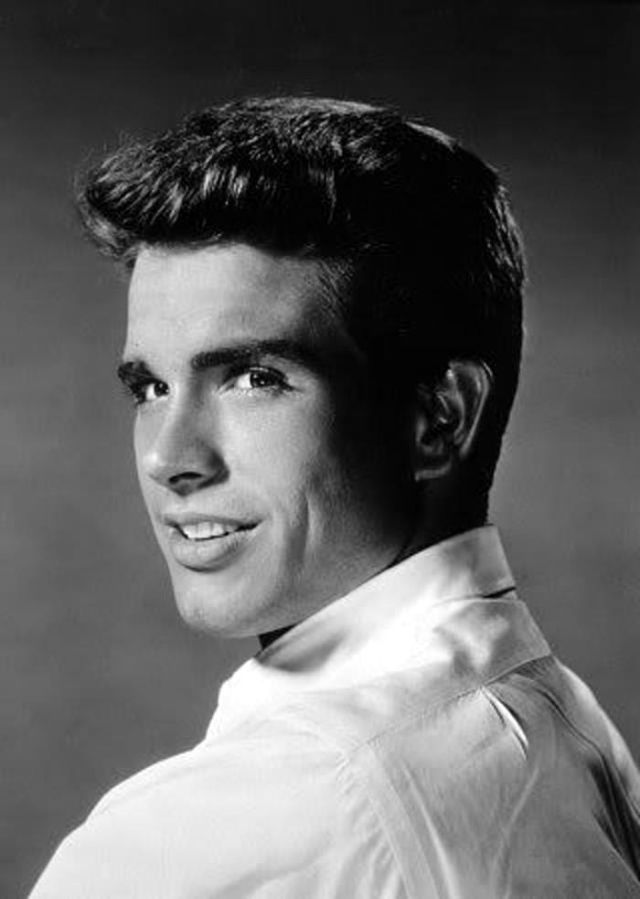
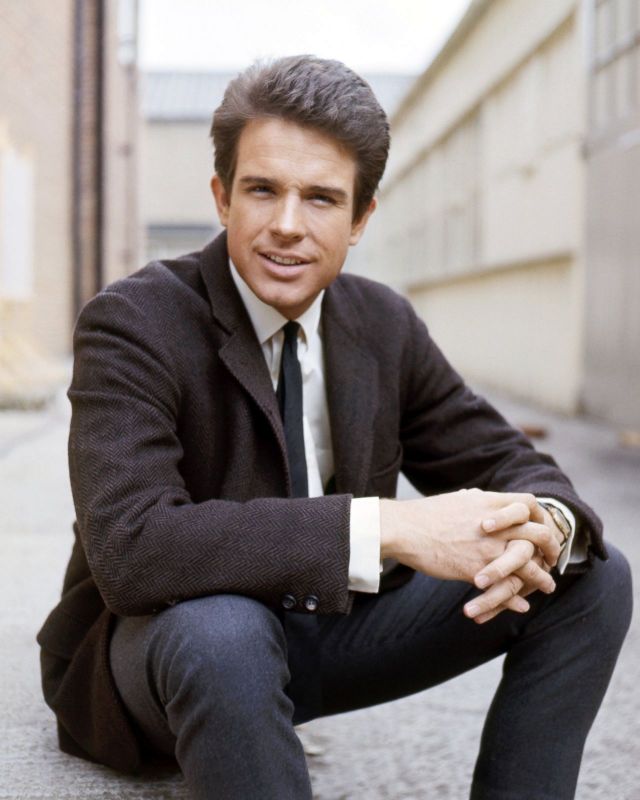
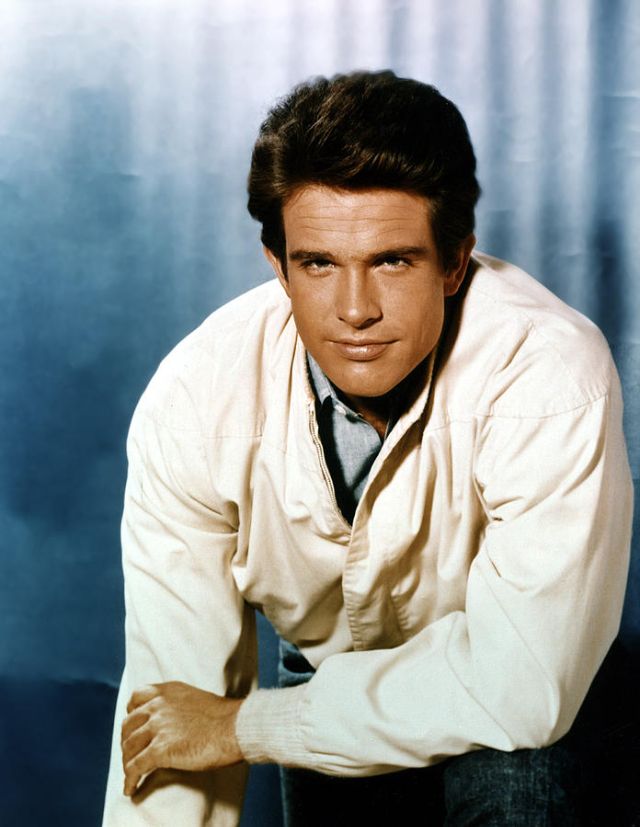
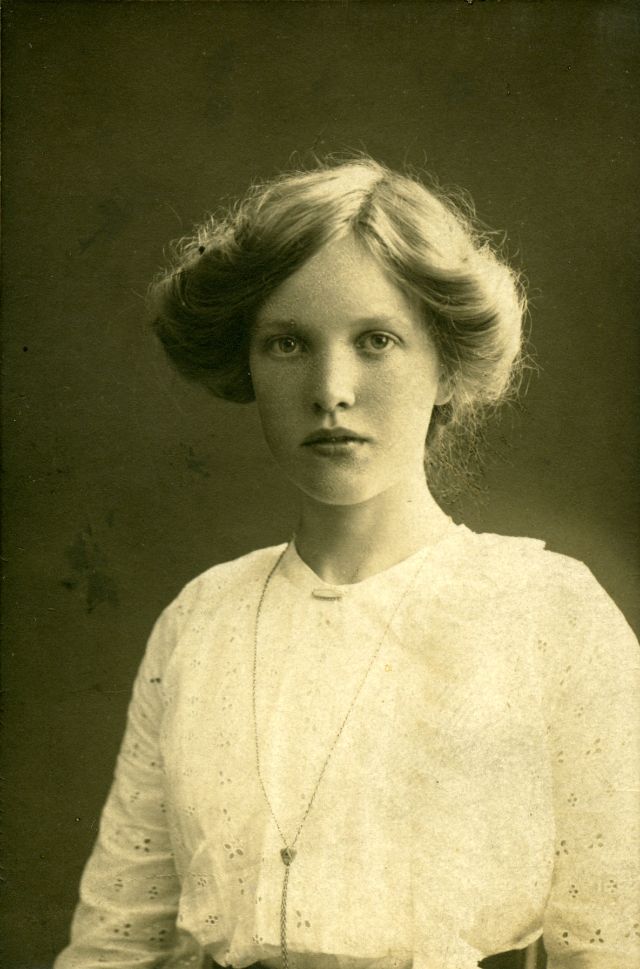
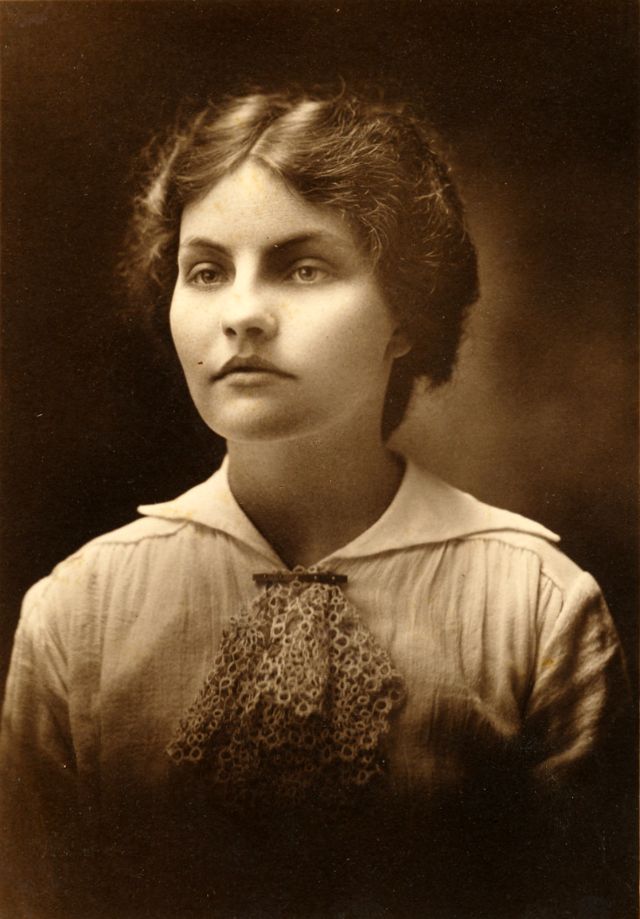
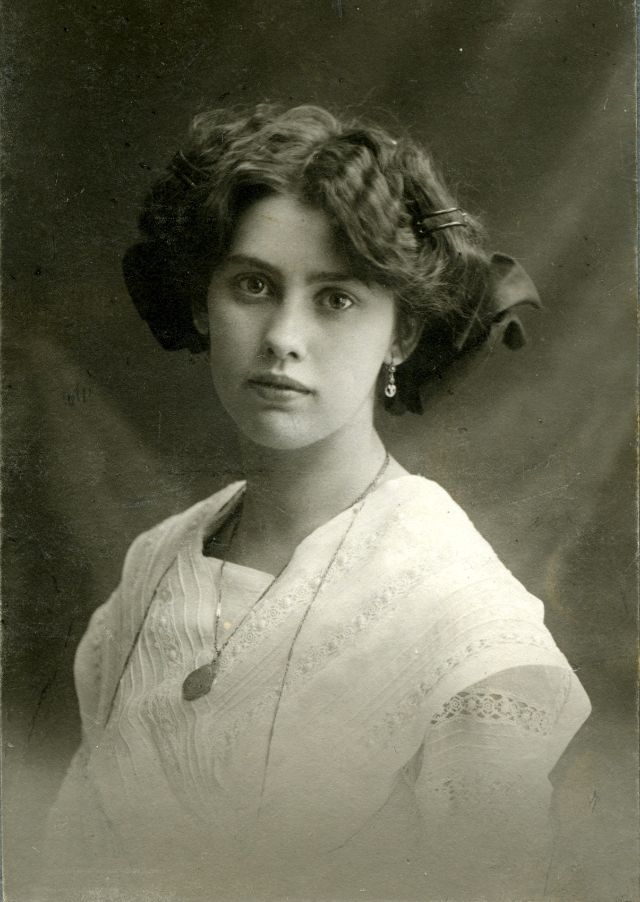
Take alook at these gorgeous photos to see portrait of a young Warren Beatty in the 1950s and 1960s.

































































































The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, 326 Indian reservations, and some minor possessions. At 3.8 million square miles (9.8 million square kilometers), it is the world’s third- or fourth-largest country by geographic area. The United States shares significant land borders with Canada to the north and Mexico to the south as well as limited maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, and Russia. With a population of more than 331 million people, it is the third most populous country in the world. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city is New York City.
Paleo-Indians migrated from Siberia to the North American mainland at least 12,000 years ago, and European colonization began in the 16th century. The United States emerged from the thirteen British colonies established along the East Coast. Disputes with Great Britain over taxation and political representation led to the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), which established the nation’s independence. In the late 18th century, the U.S. began expanding across North America, gradually obtaining new territories, sometimes through war, frequently displacing Native Americans, and admitting new states; by 1848, the United States spanned the continent. Slavery was legal in the southern United States until the second half of the 19th century, when the American Civil War led to its abolition. The Spanish–American War and World War I established the U.S. as a world power, a status confirmed by the outcome of World War II. During the Cold War, the United States fought the Korean War and the Vietnam War but avoided direct military conflict with the Soviet Union. The two superpowers competed in the Space Race, culminating in the 1969 spaceflight that first landed humans on the Moon. The Soviet Union’s dissolution in 1991 ended the Cold War, leaving the United States as the world’s sole superpower.
The United States is a federal presidential-constitutional republic with three separate branches of government, including a bicameral legislature. It is a founding member of the United Nations, World Bank, International Monetary Fund, Organization of American States, NATO, and other international organizations. It is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council. Considered a melting pot of cultures and ethnicities, its population has been profoundly shaped by centuries of immigration. The United States ranks high in international measures of economic freedom, quality of life, education, and human rights; it has low levels of perceived corruption. However, it has been criticized for inequality related to race, wealth, and income; use of capital punishment; high incarceration rates; and lack of universal health care.
The United States is a highly developed country, accounts for approximately a quarter of global GDP, and is the world’s largest economy by GDP at market exchange rates. By value, the United States is the world’s largest importer and second-largest exporter of goods. Although its population is only 4.2% of the world’s total, it holds 29.4% of the total wealth in the world, the largest share held by any country. Making up more than a third of global military spending, it is the foremost military power in the world and internationally a leading political, cultural, and scientific force. (Wikipedia)
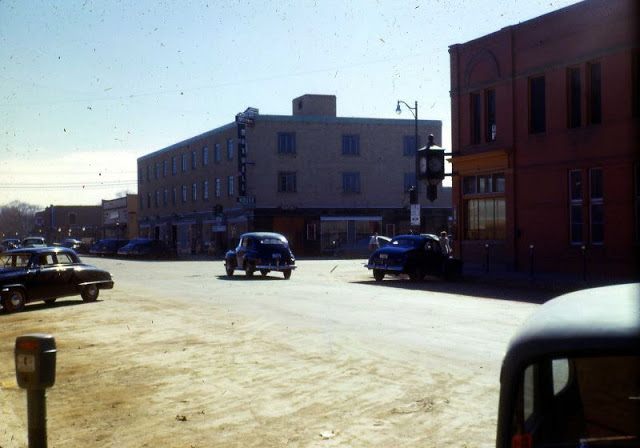
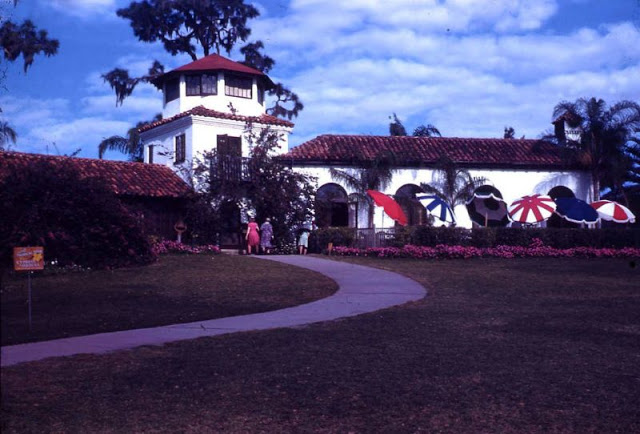
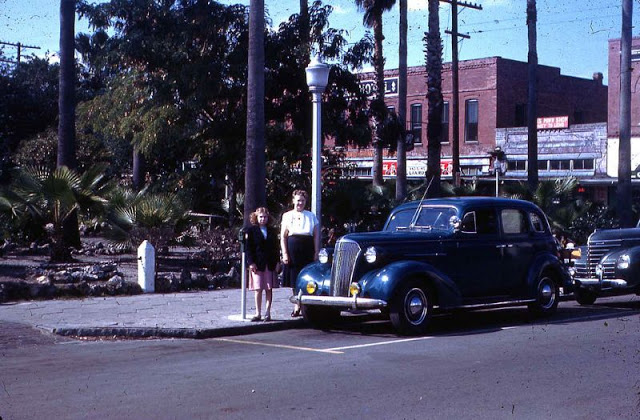
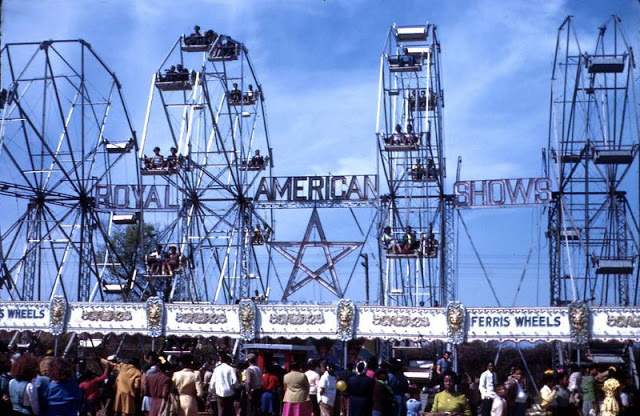
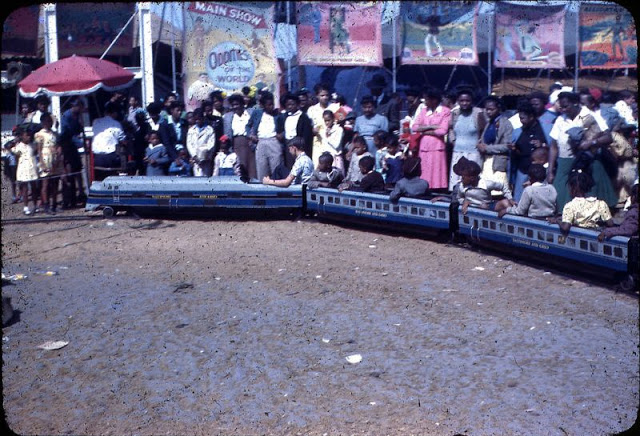
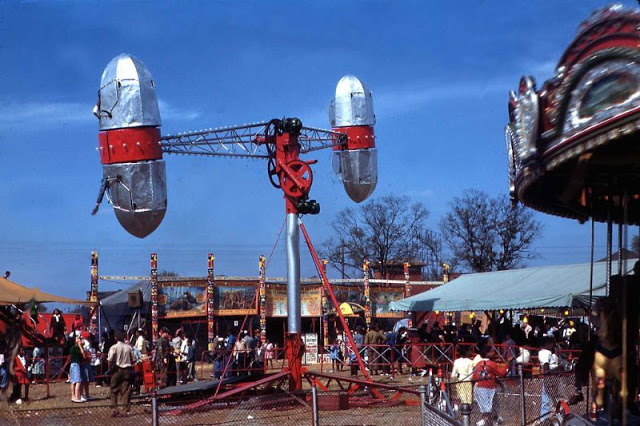
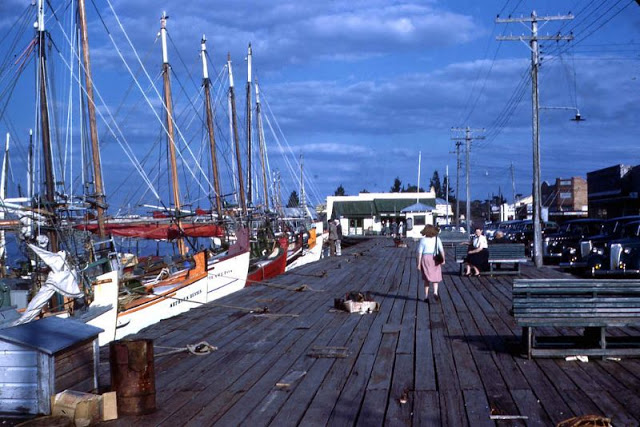
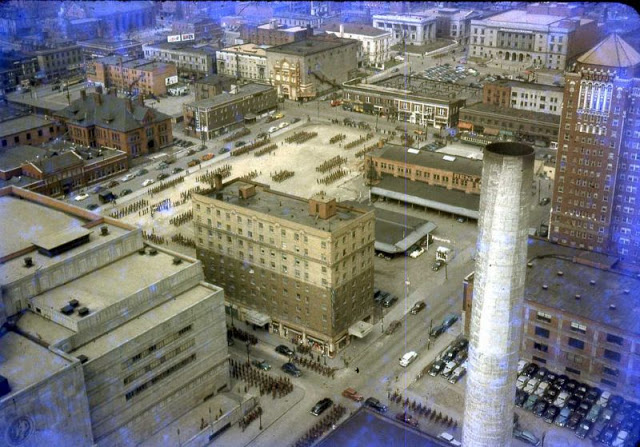
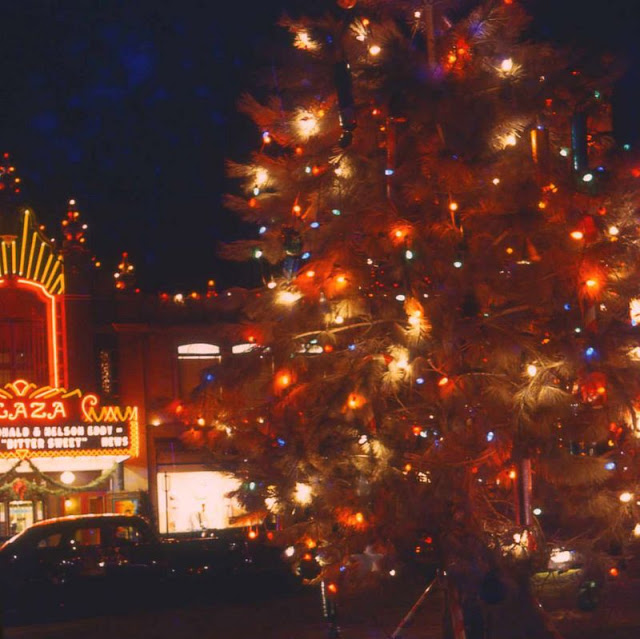
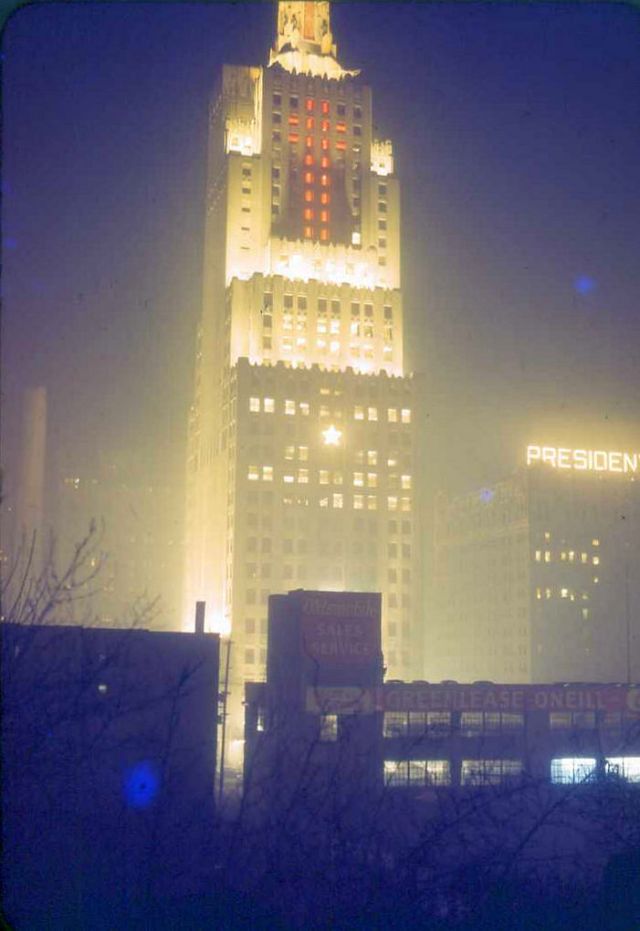
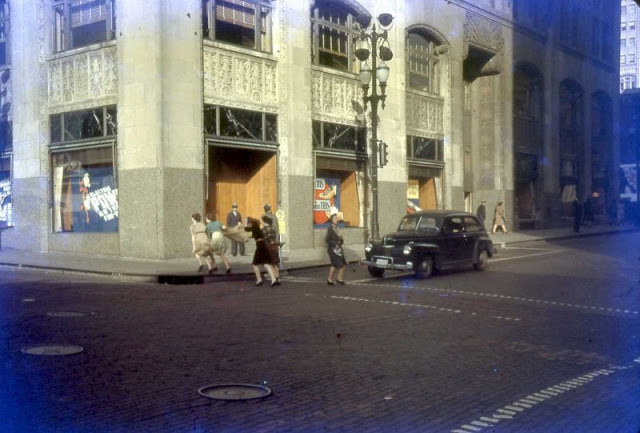
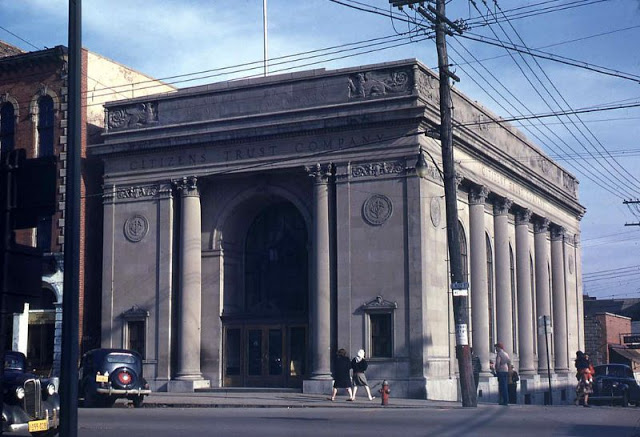
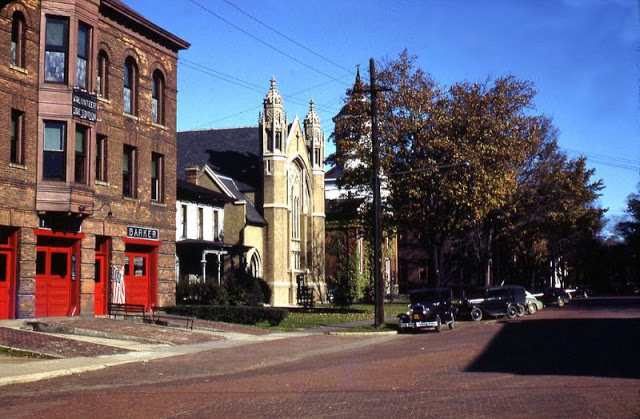
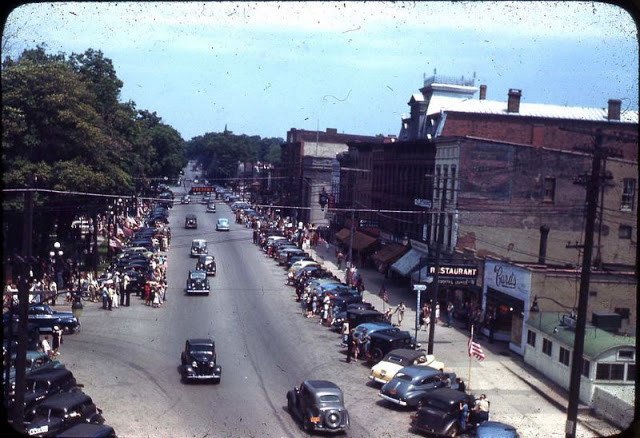
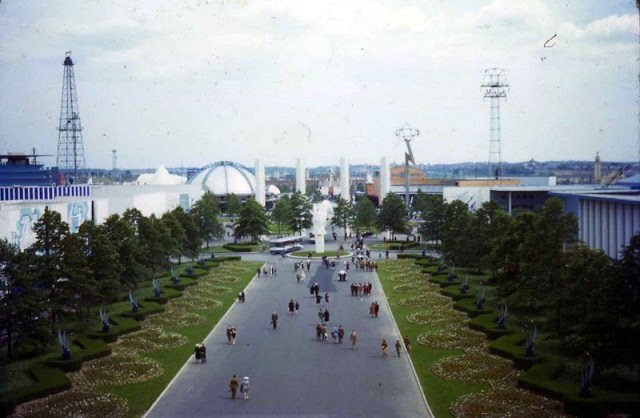
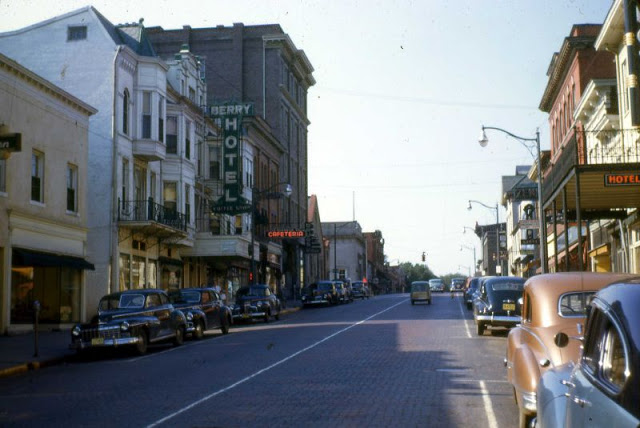
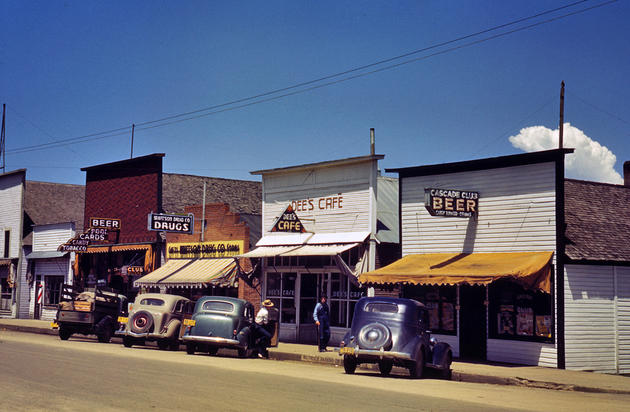
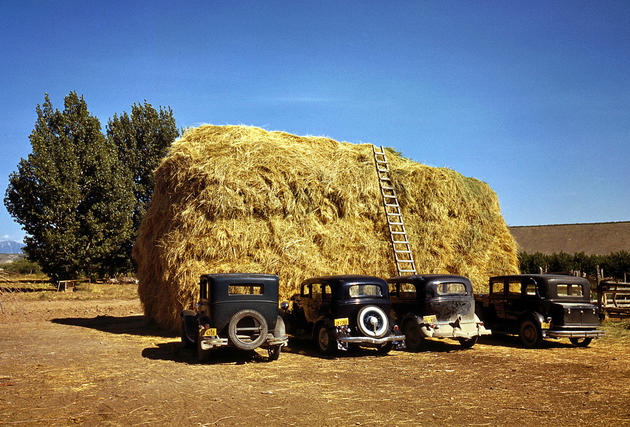
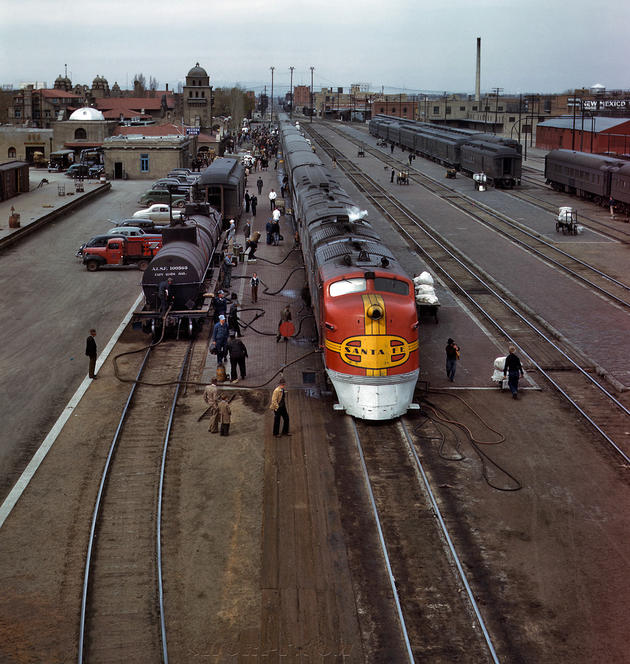
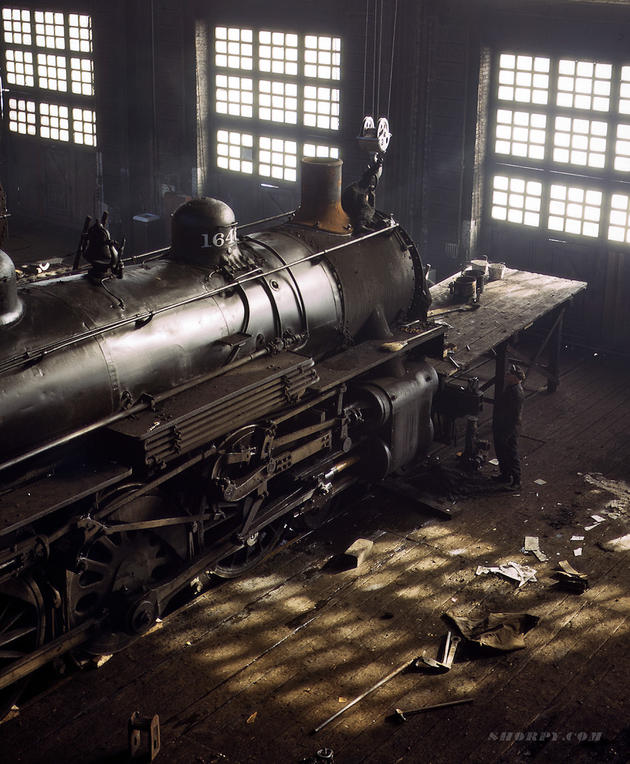
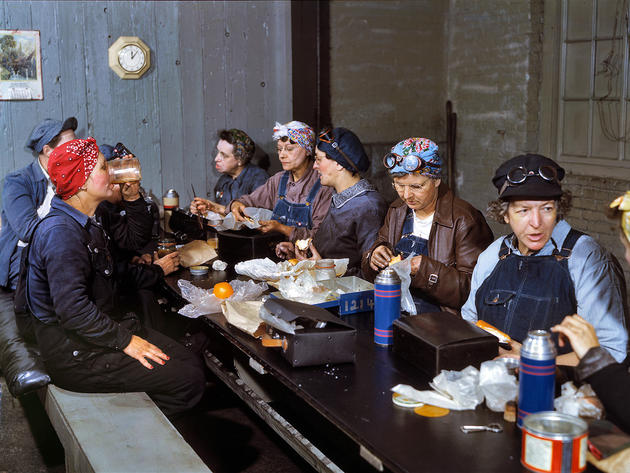
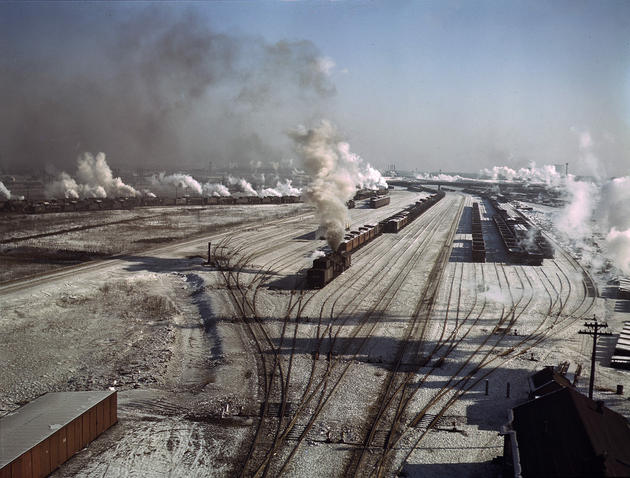
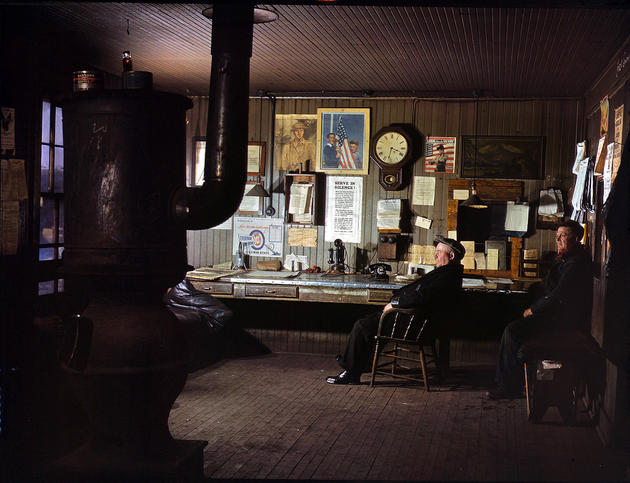
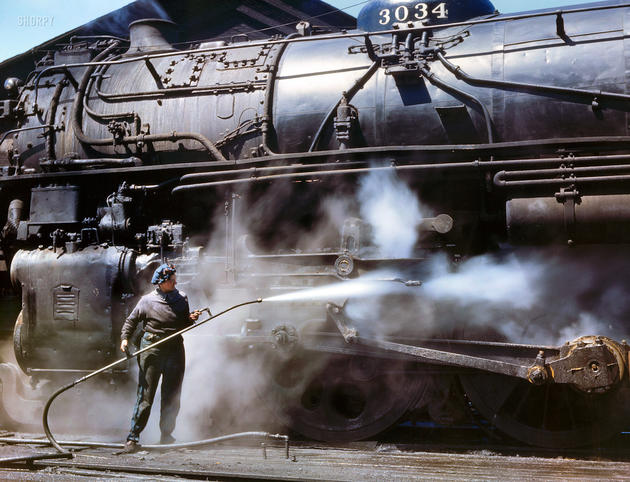
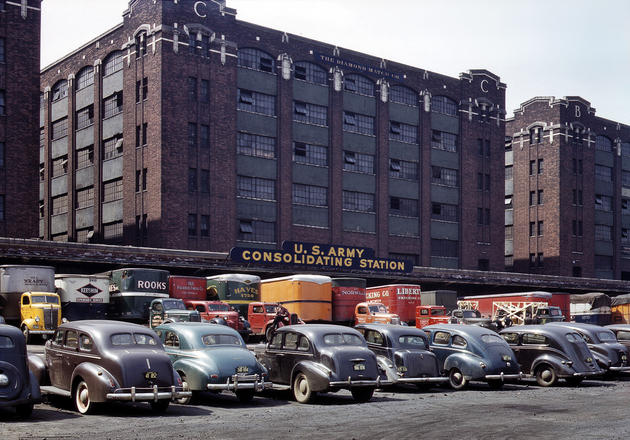
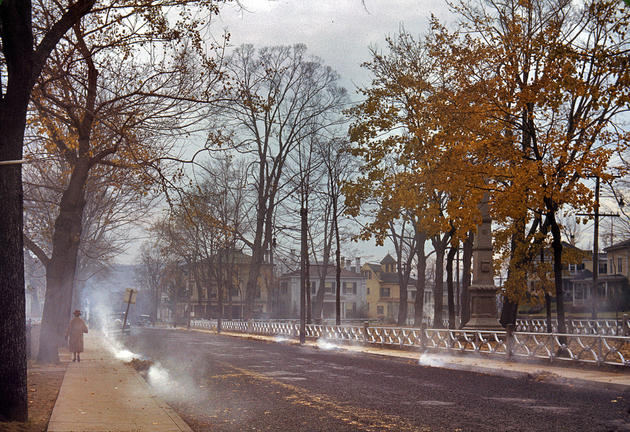
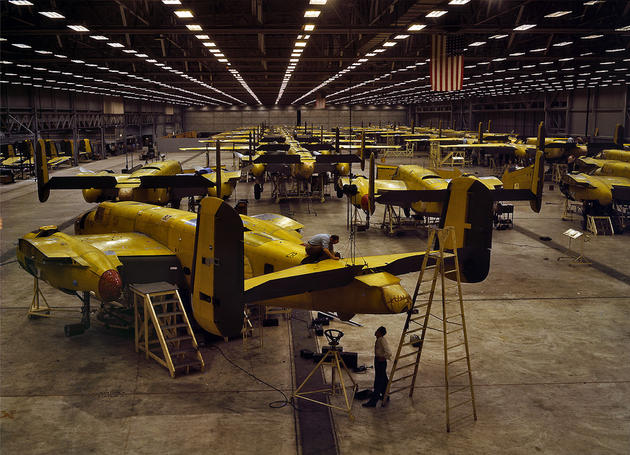
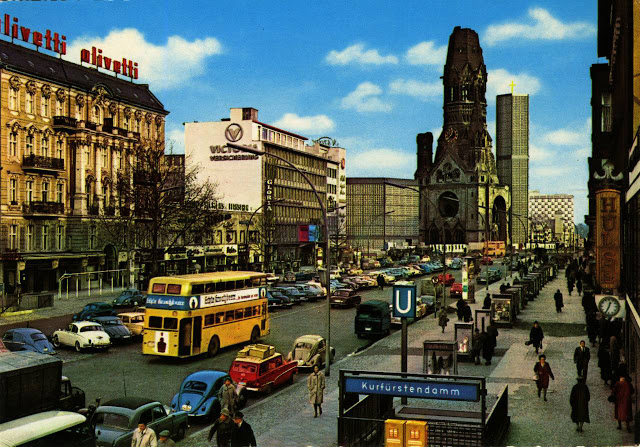



















































West Berlin (German: Berlin (West) or West-Berlin) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although not a part of the Federal Republic of Germany, West Berlin aligned itself politically in 1949 and after with it and was directly or indirectly represented in its federal institutions.
West Berlin was formally controlled by the Western Allies and entirely surrounded by the Soviet-controlled East Berlin and East Germany. West Berlin had great symbolic significance during the Cold War, as it was widely considered by westerners an “island of freedom” and America’s most loyal counterpart in Europe. It was heavily subsidised by West Germany as a “showcase of the West”. A wealthy city, West Berlin was noted for its distinctly cosmopolitan character, and as a centre of education, research and culture. With about two million inhabitants, West Berlin had the largest population of any city in Germany during the Cold War era.
West Berlin was 160 kilometres (100 mi) east and north of the Inner German border and only accessible by land from West Germany by narrow rail and highway corridors. It consisted of the American, British, and French occupation sectors established in 1945. The Berlin Wall, built in 1961, physically separated West Berlin from its East Berlin and East German surroundings until it fell in 1989. On 3 October 1990, the day Germany was officially reunified, East and West Berlin formally reunited, joined the Federal Republic as a city-state and, eventually, once again became the capital of Germany. (Wikipedia)
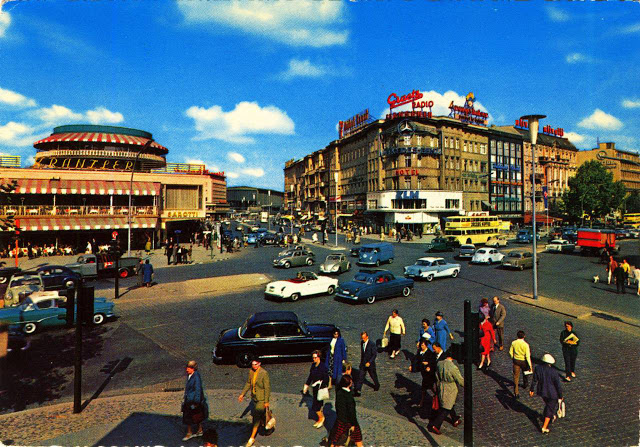
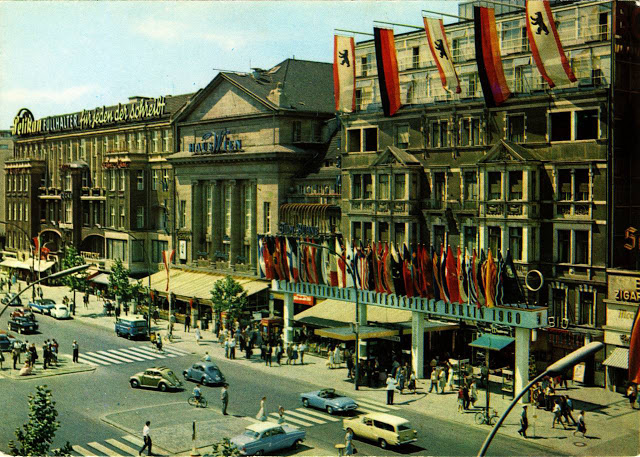
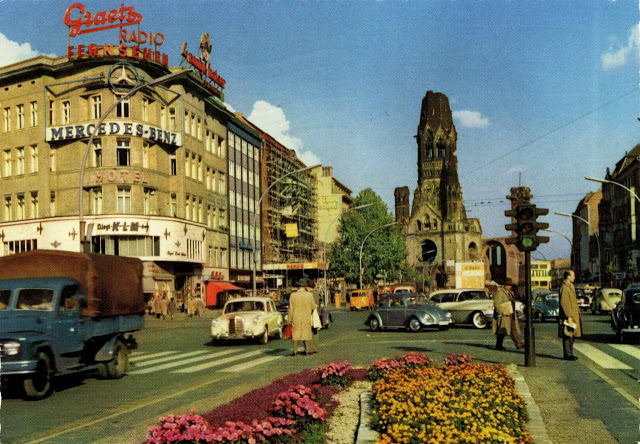
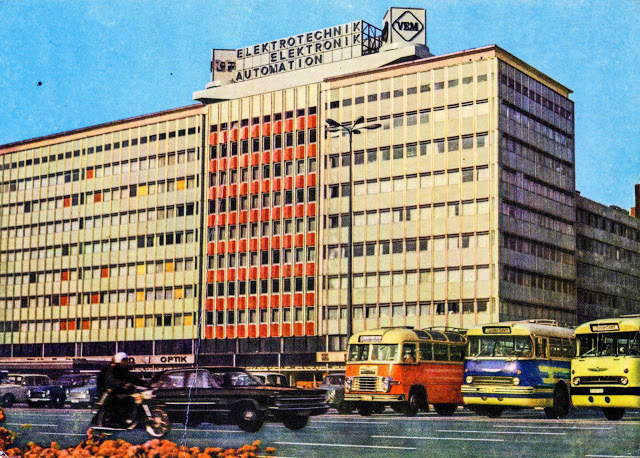
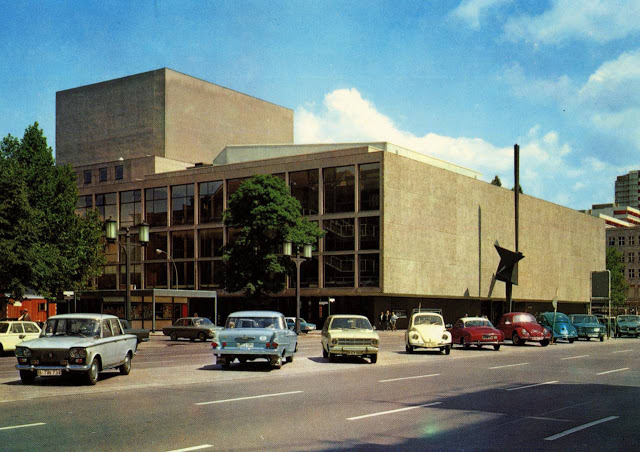
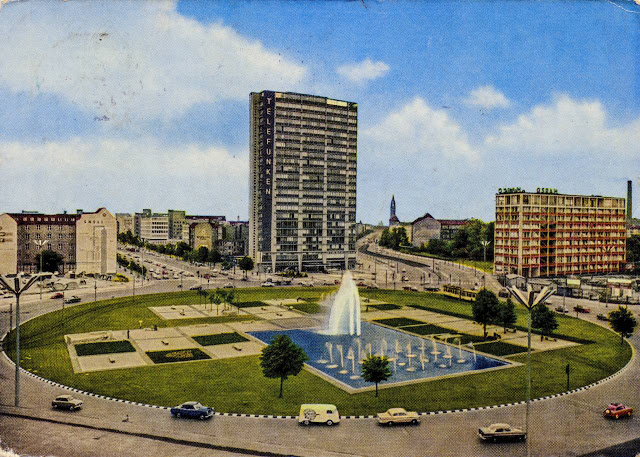
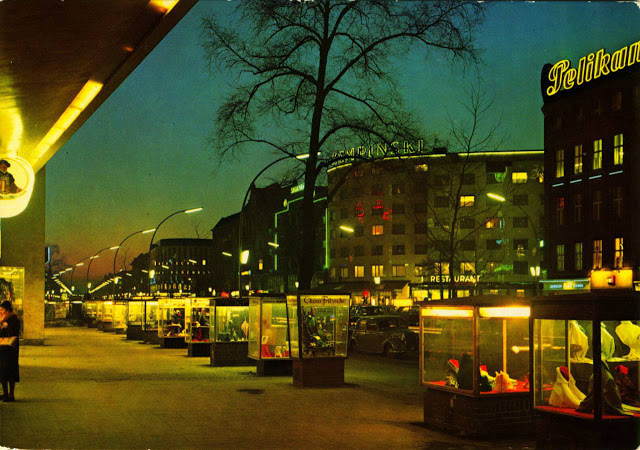
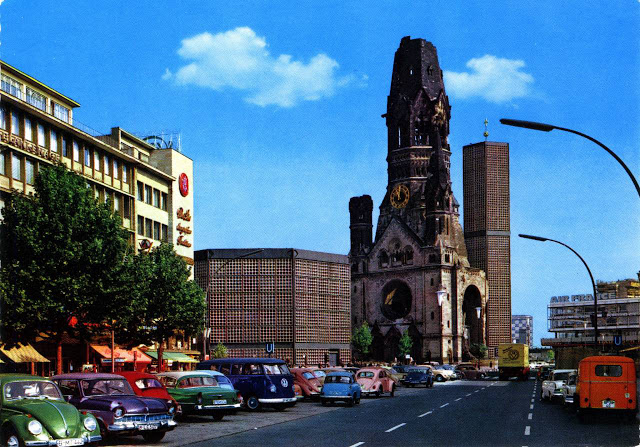
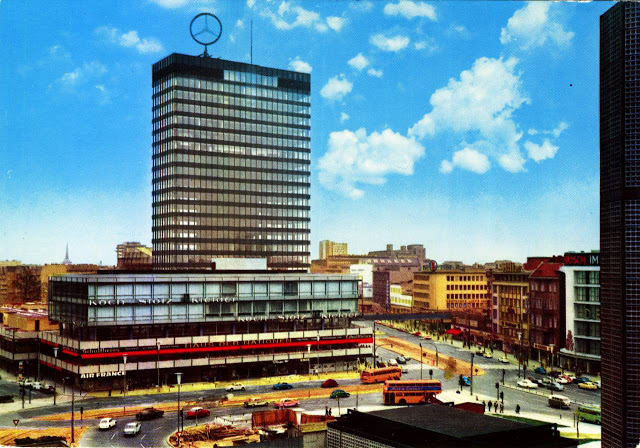
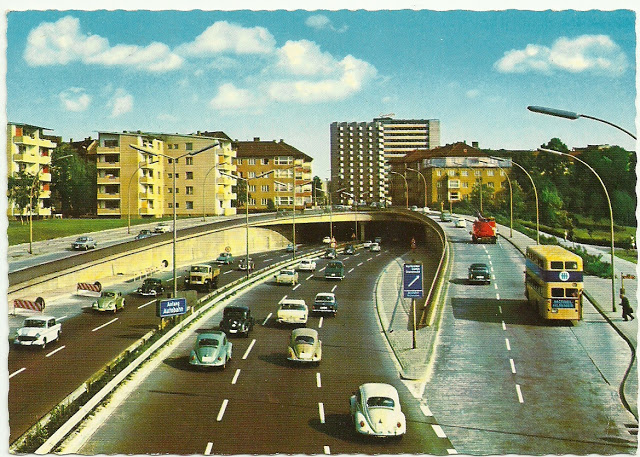
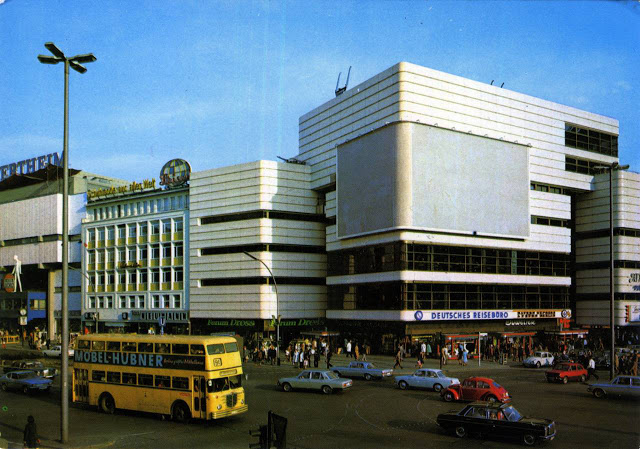
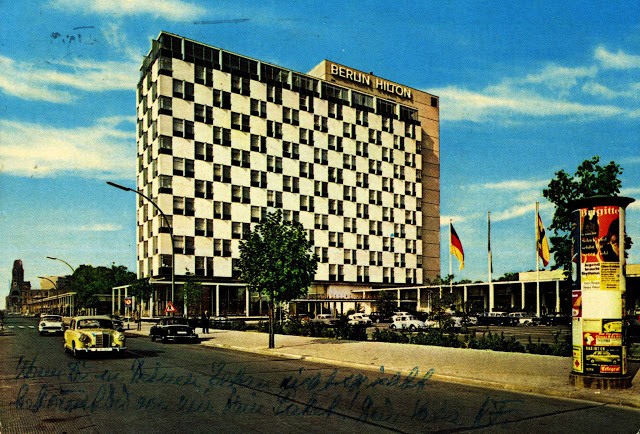
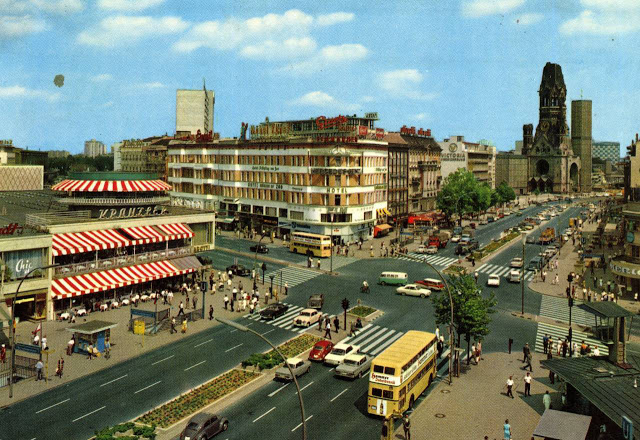
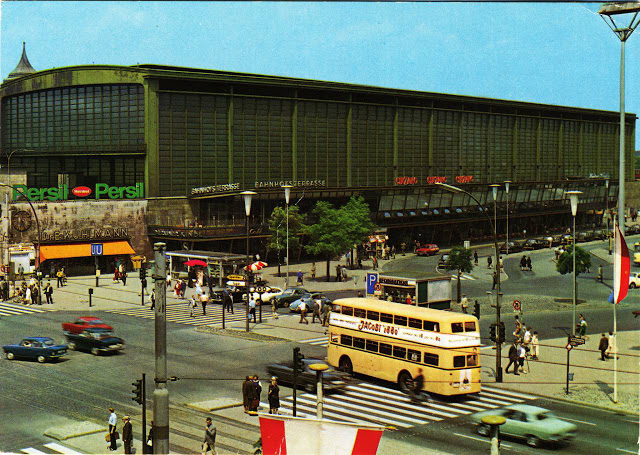
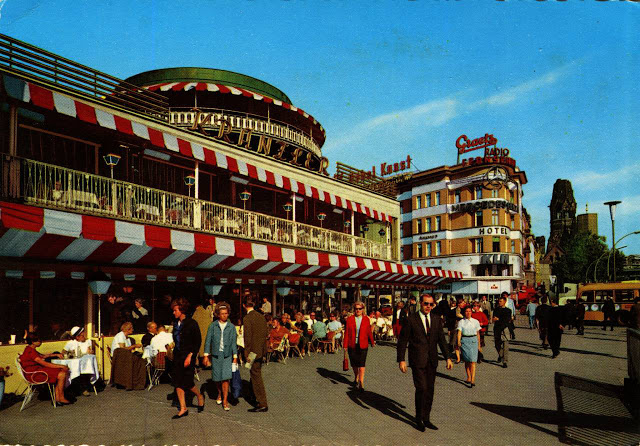
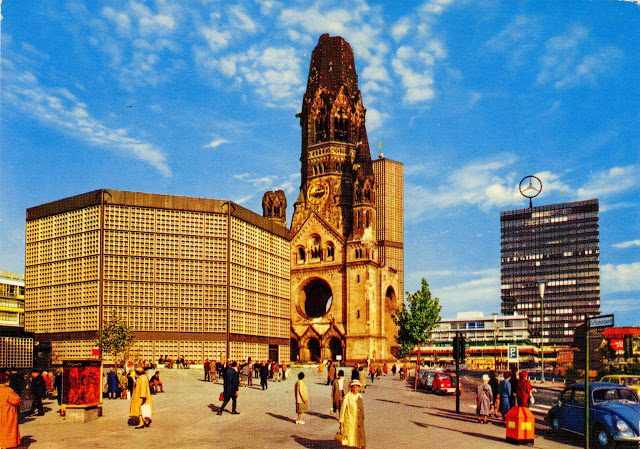
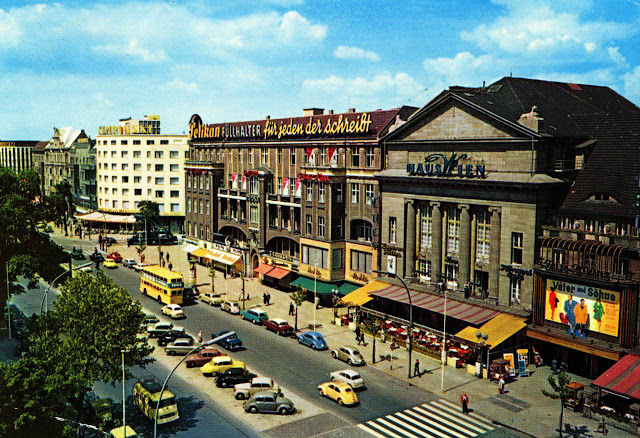
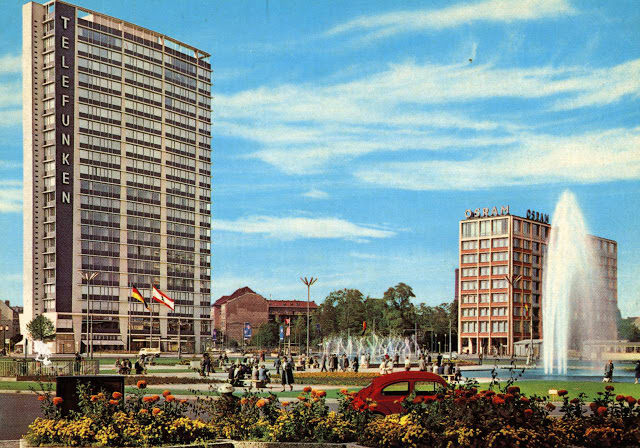
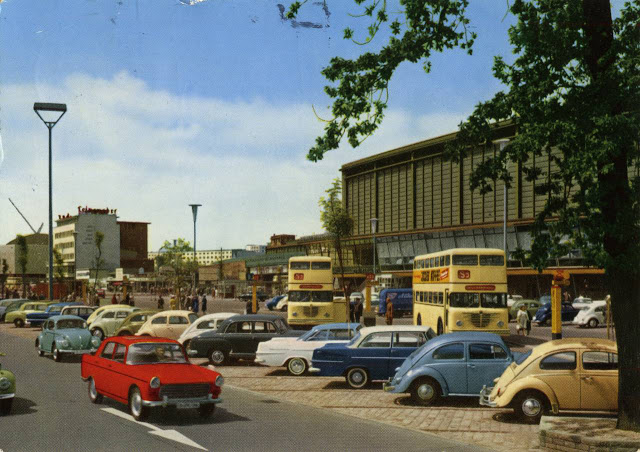
These vintage postcards are of West Berlin from between the 1950s and ’70s.
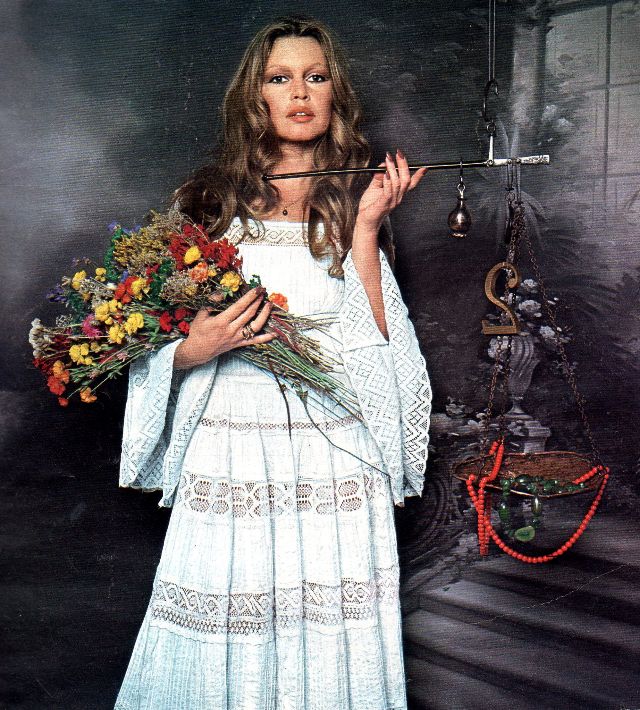

































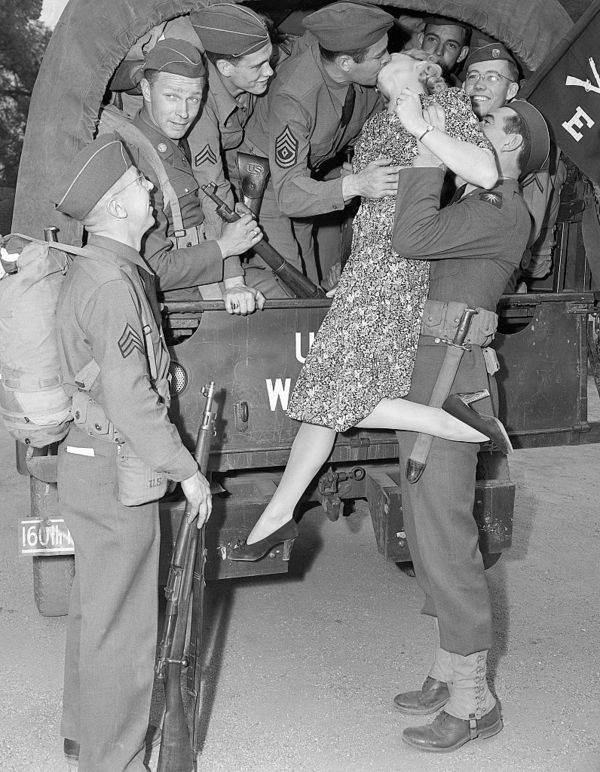


















































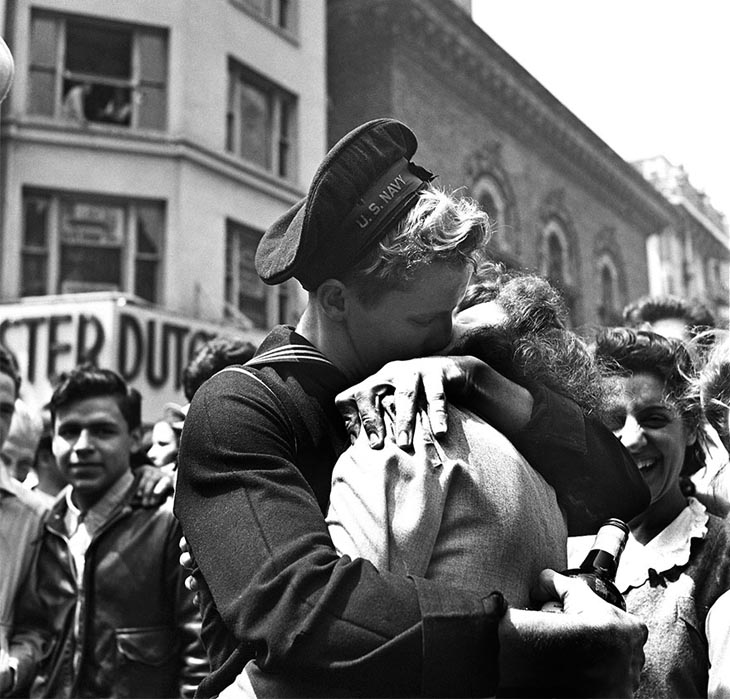















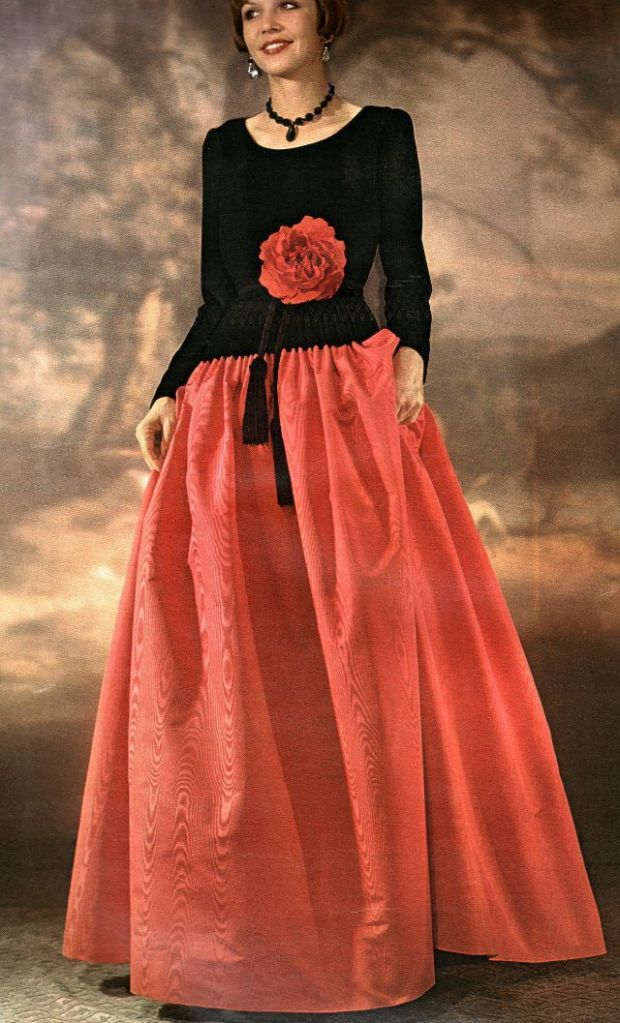
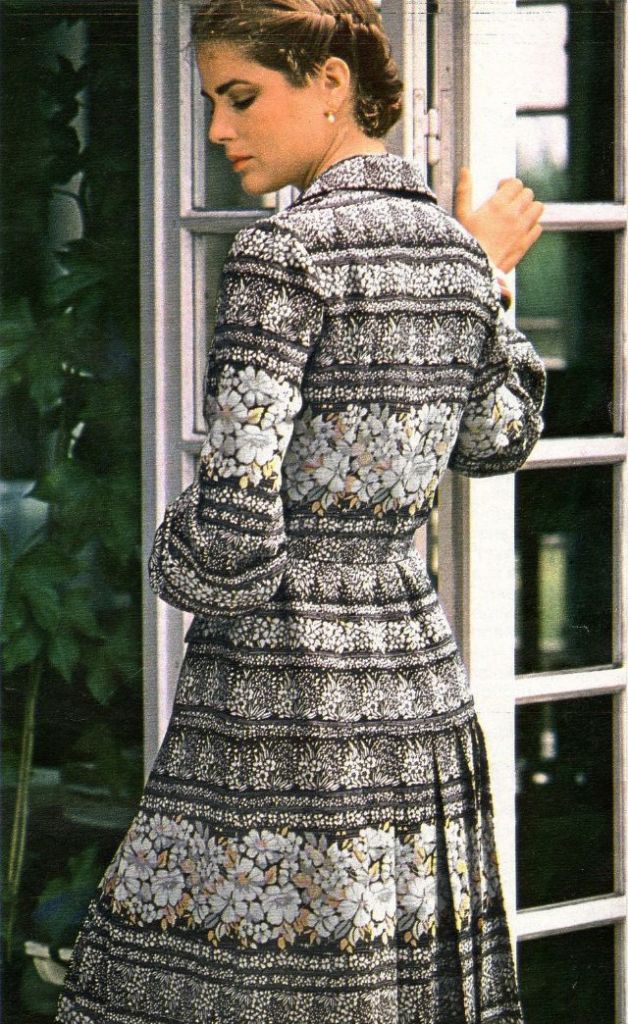
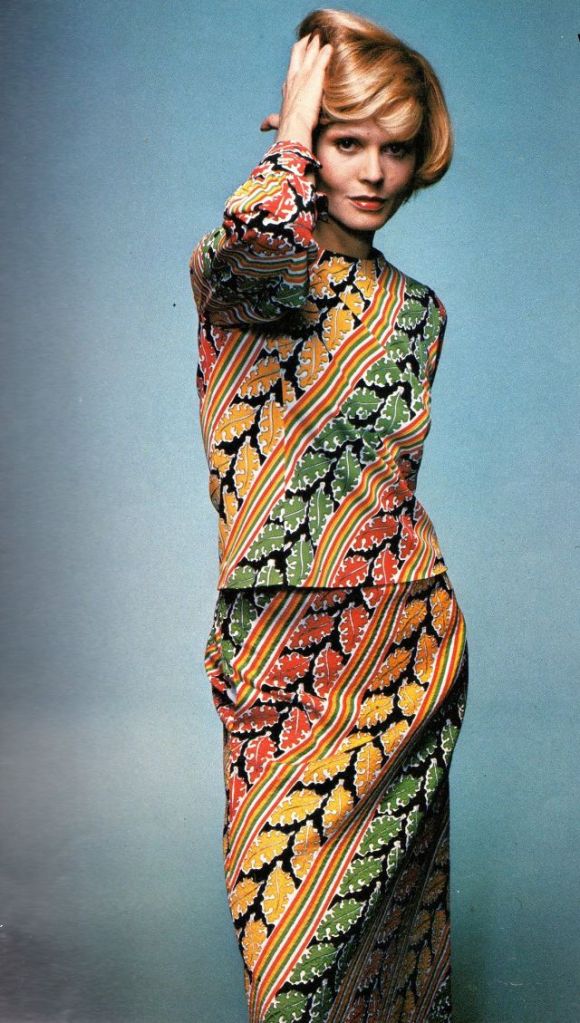
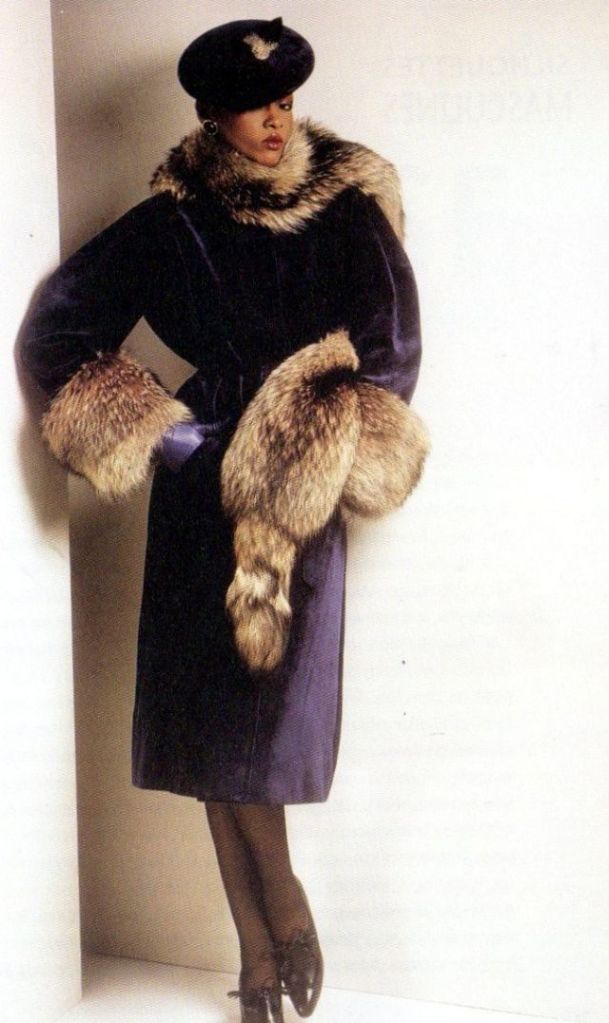
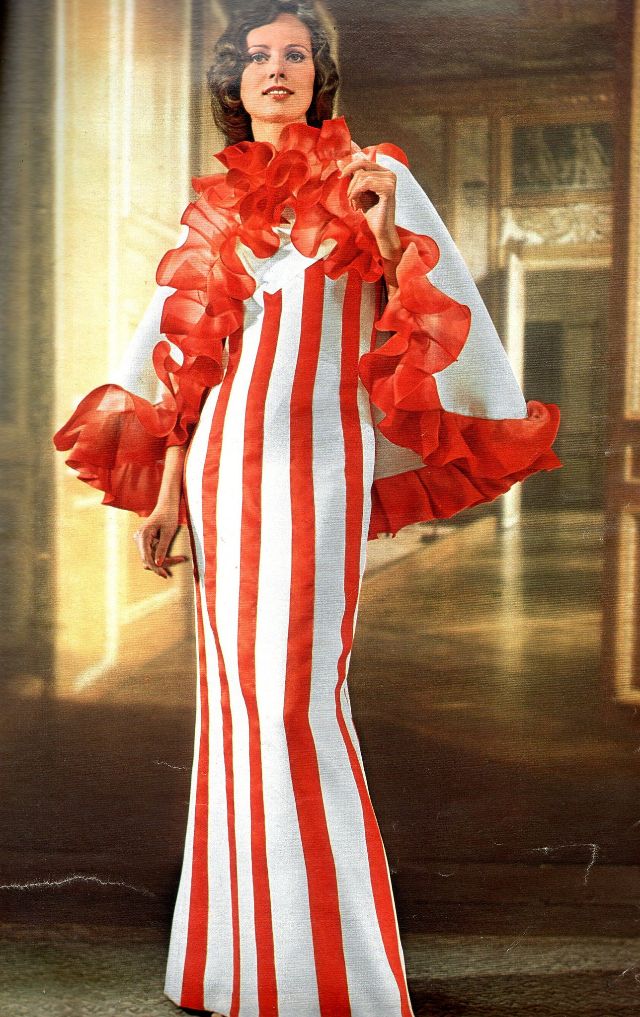
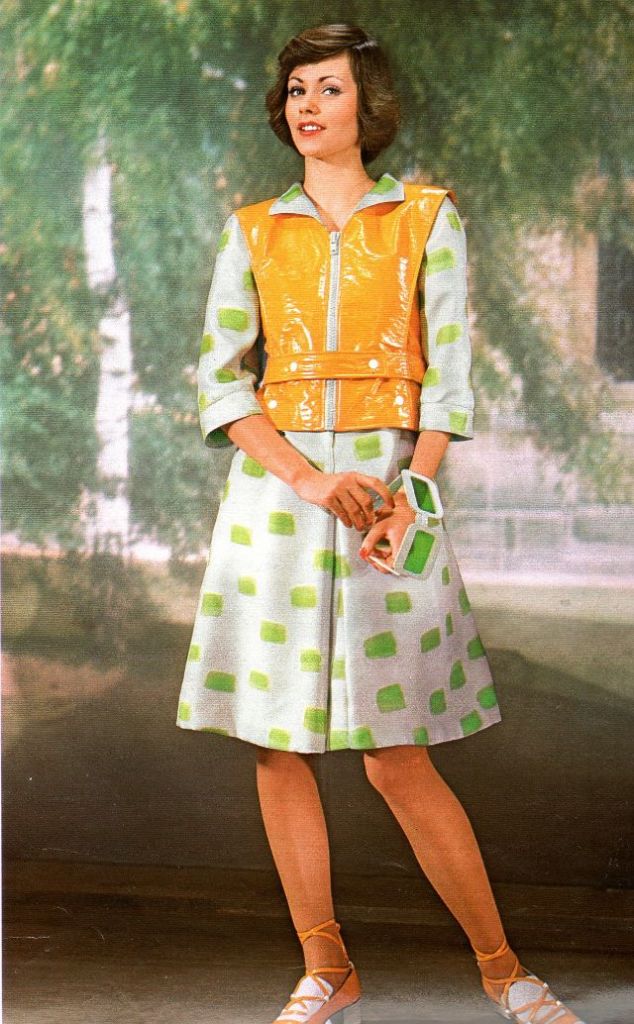
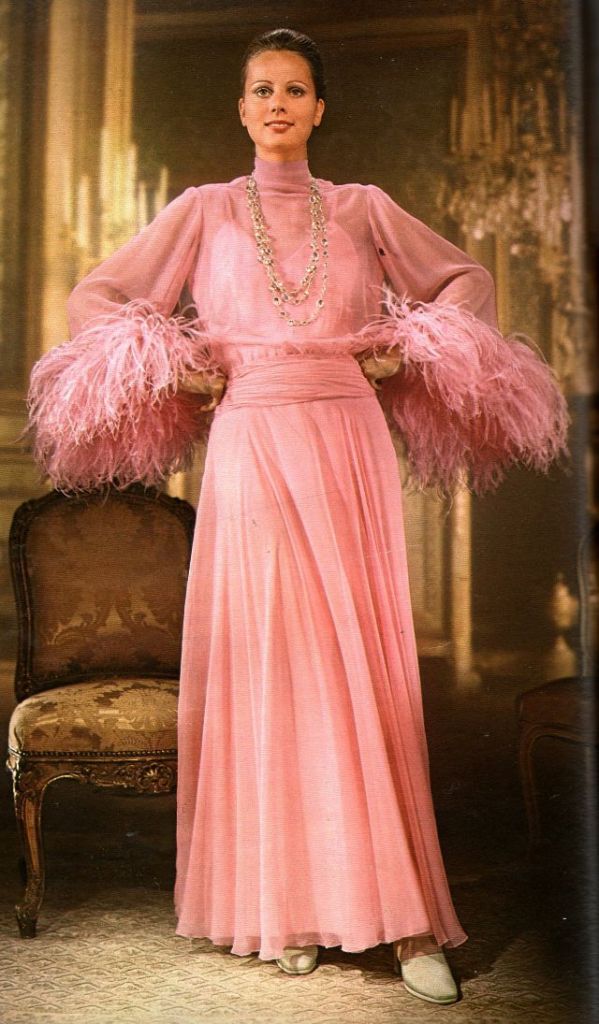
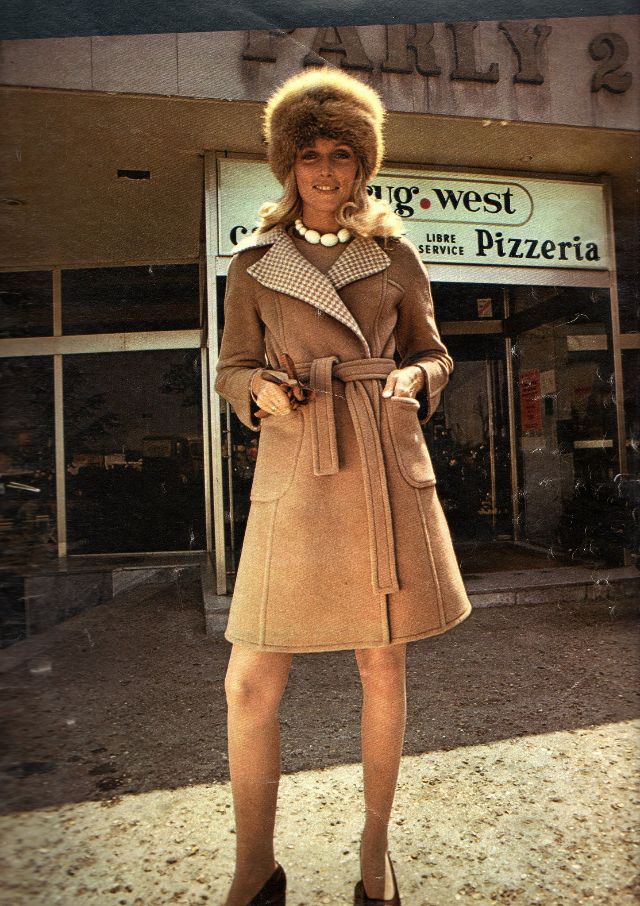
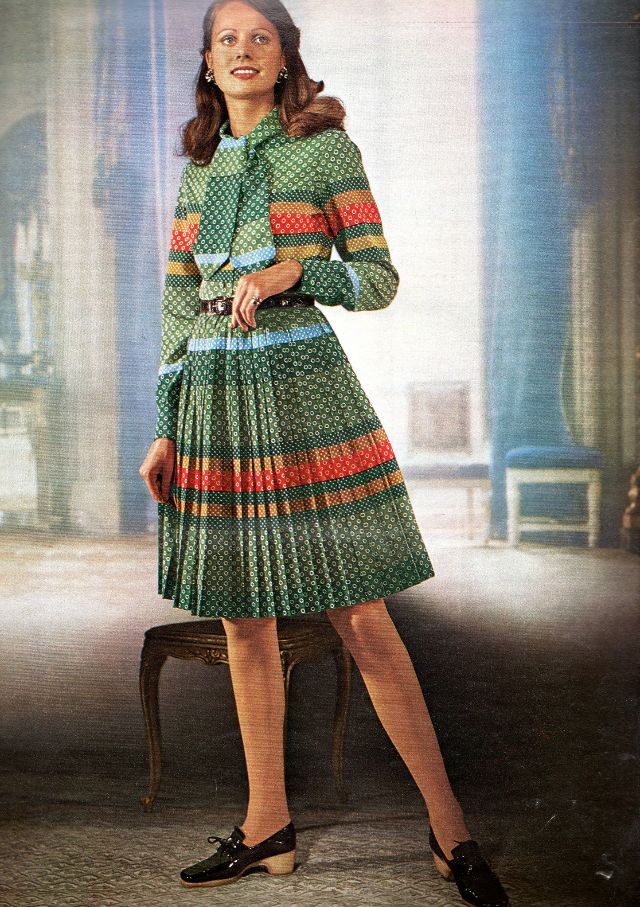
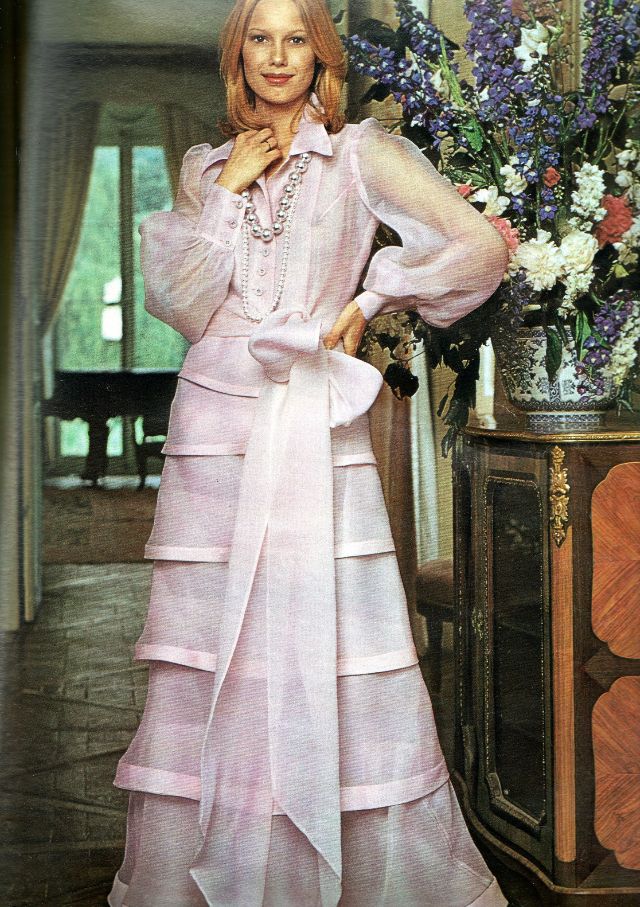
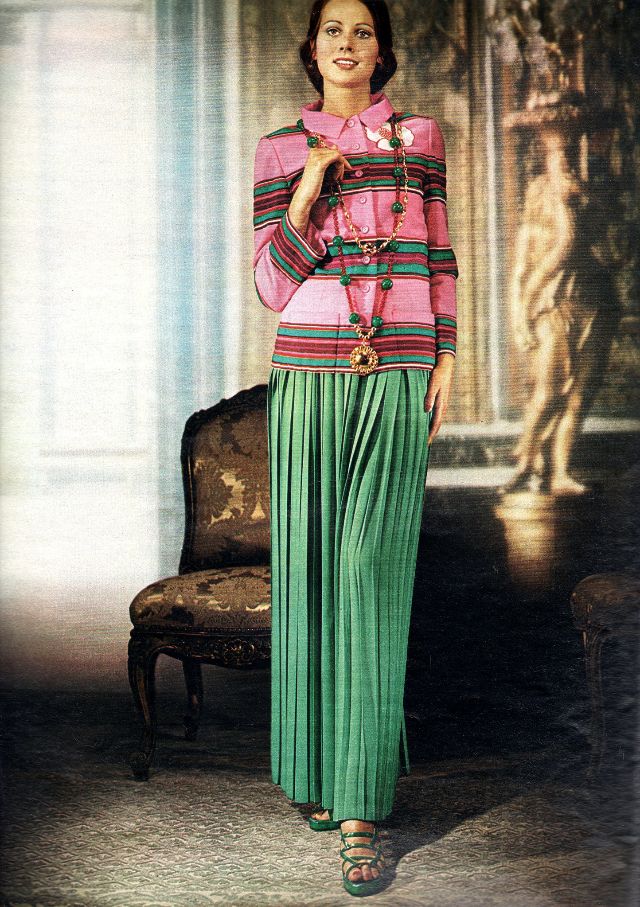
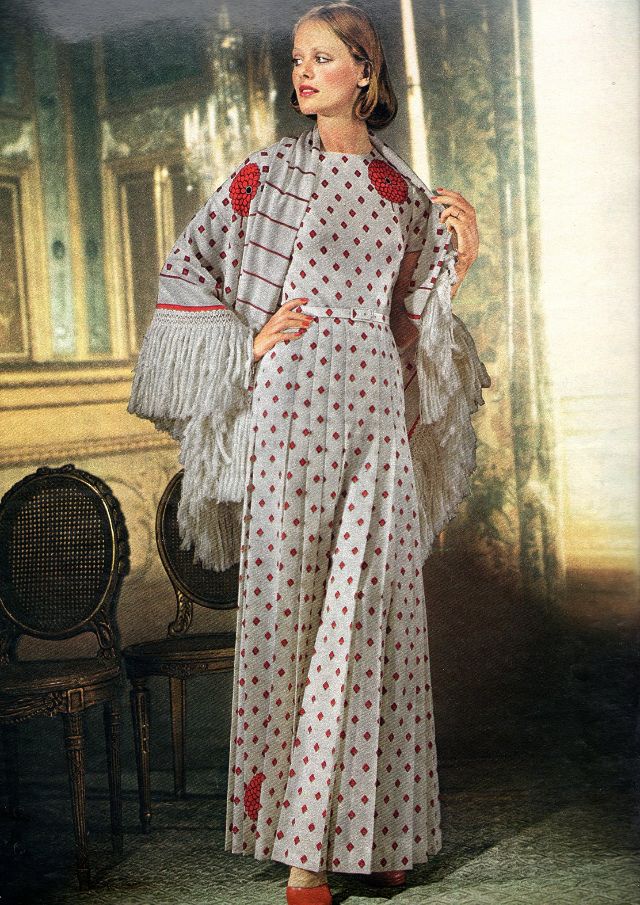
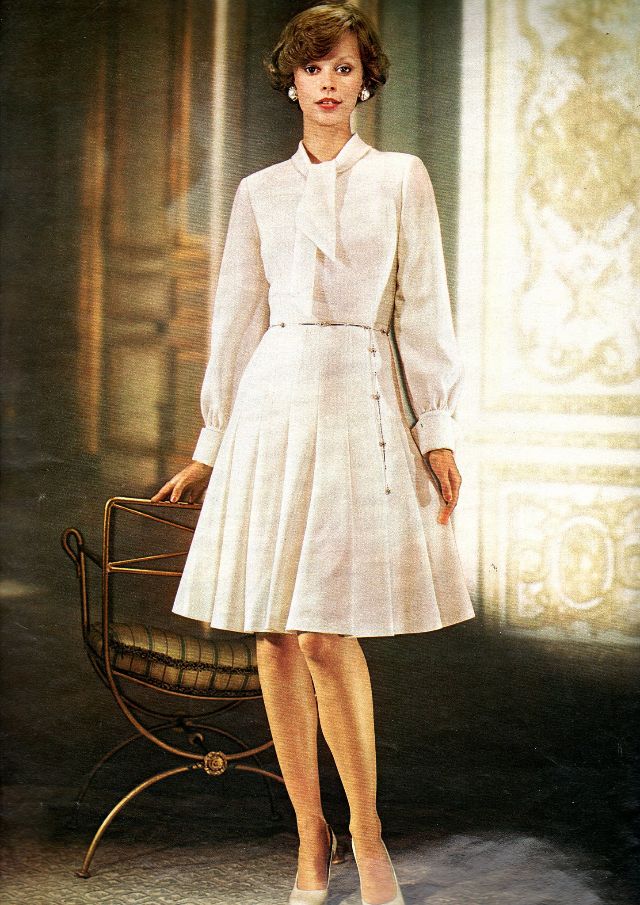
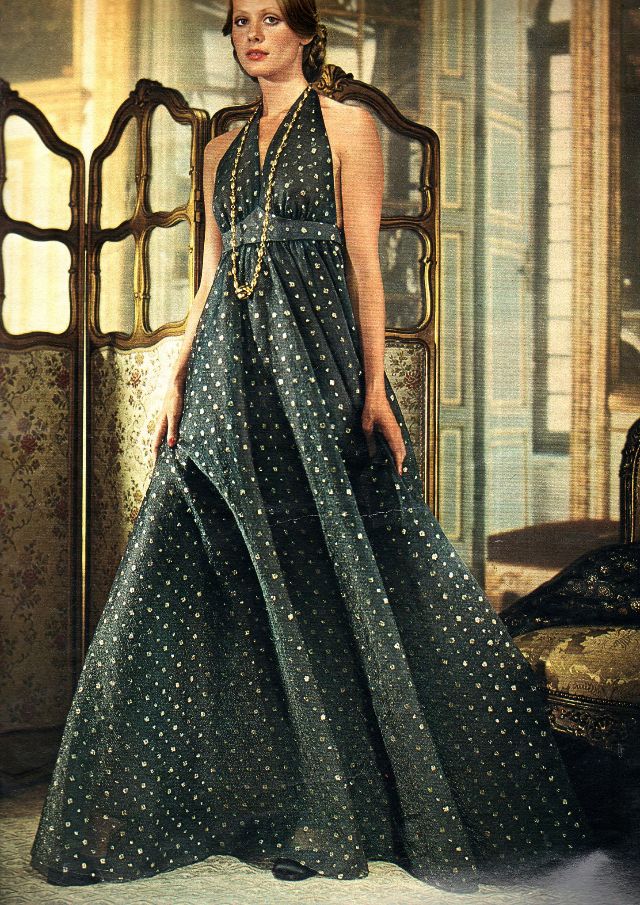
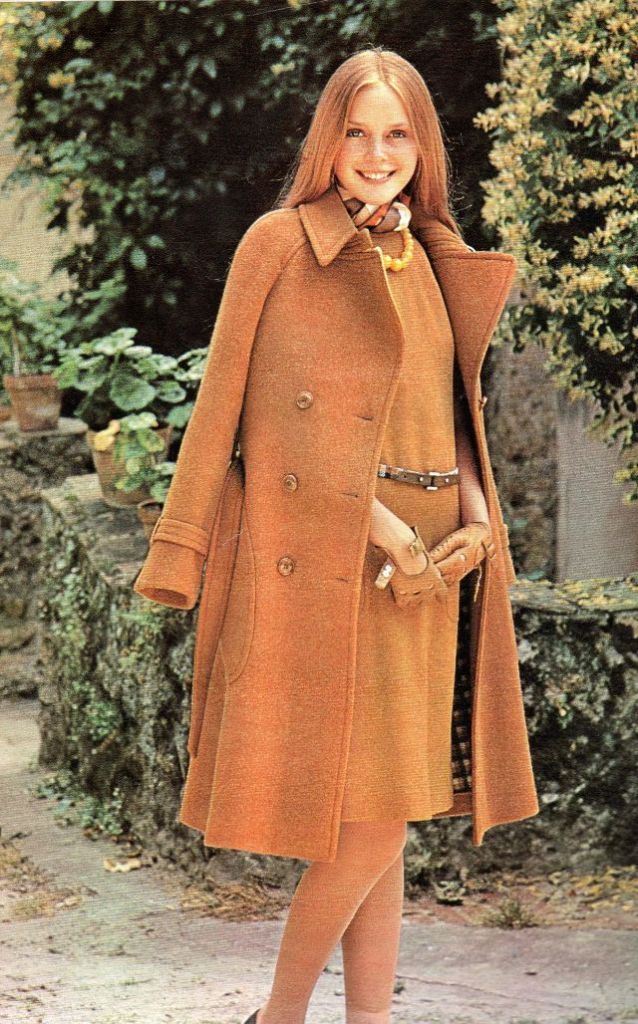
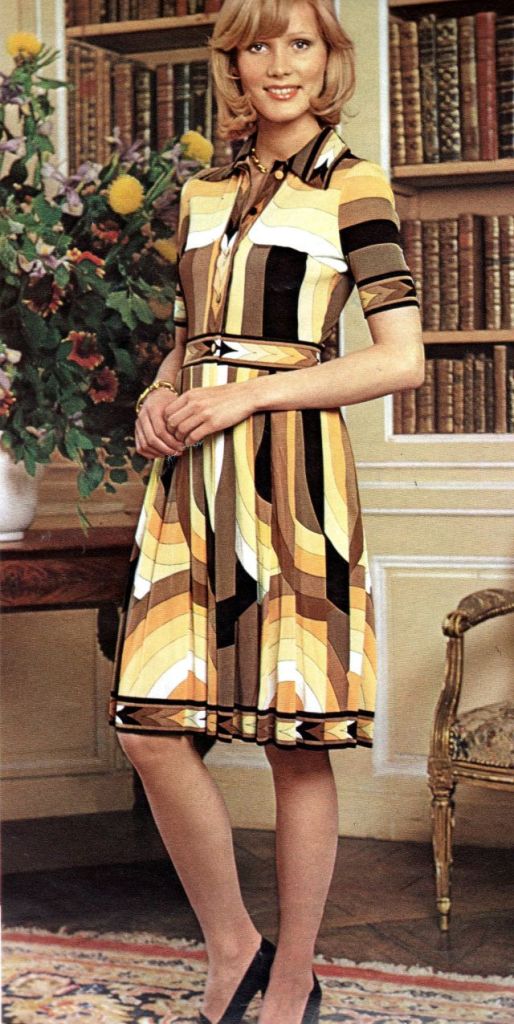
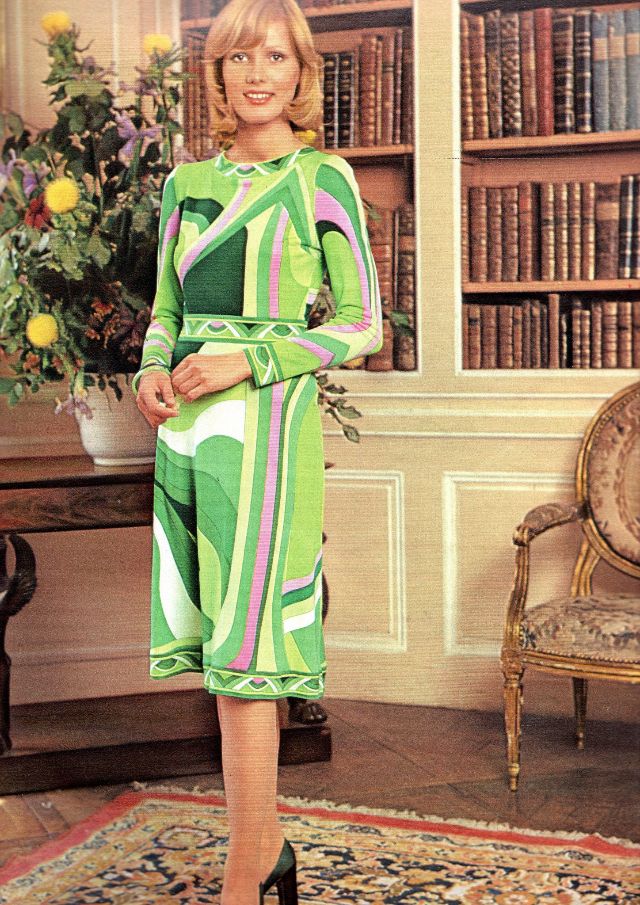
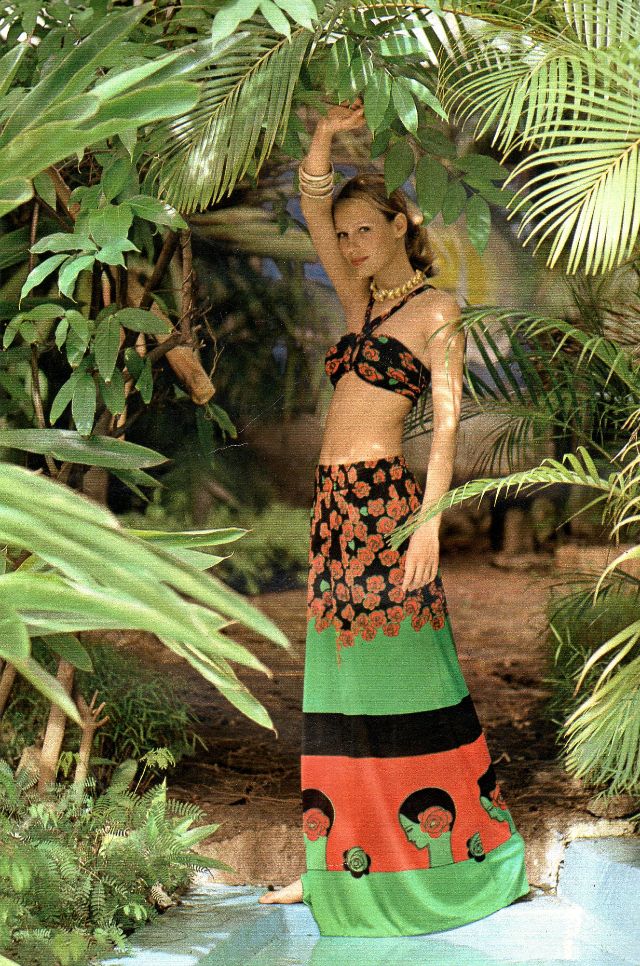
Easy to see the 1970s fashion trend was so colorful. Especially for dresses such as evening gowns and skirts.
Many women had different dresses for different occasions. They wore evening gowns at home, which were silky smooth, loose fitting and very comfortable. They were also known as ankle sweepers.
The hemline was all over the place. Both short dresses and long dresses could be worn in almost any situation. Typically, younger women preferred the shorter skirts.
Belts were also a very popular accessory to a 1970s dress. As were bows, necklaces and jackets. Other dresses had dramatic collars.
Take a look at these colorful pics to see what dresses in the 1970s looked like.

































Read more of this content when you subscribe today.


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.
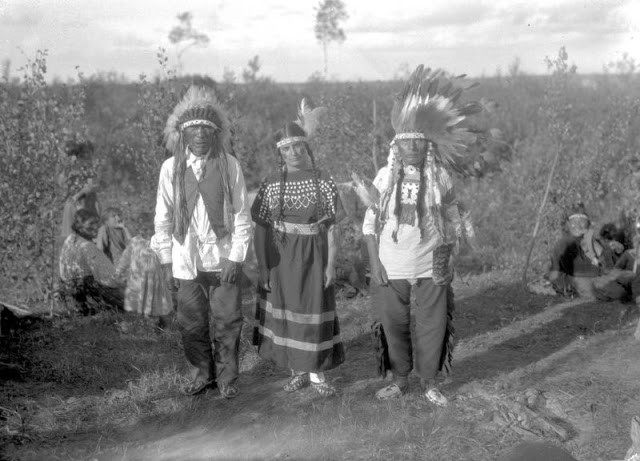

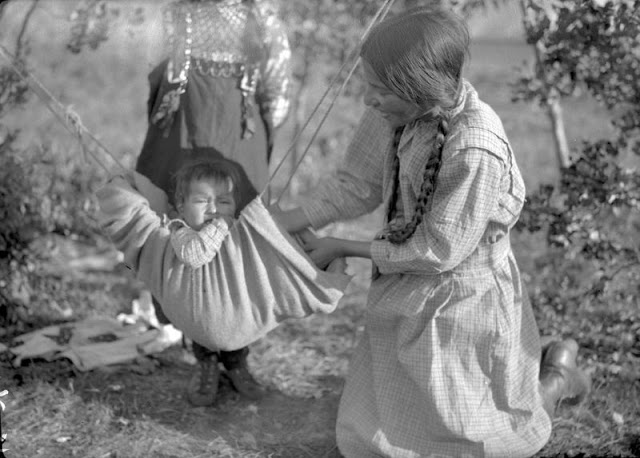
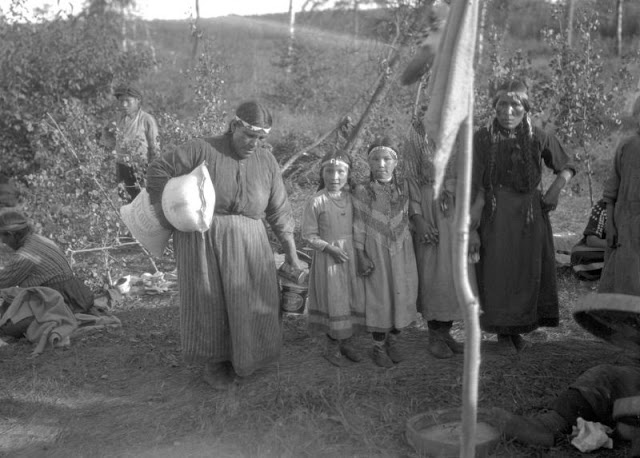
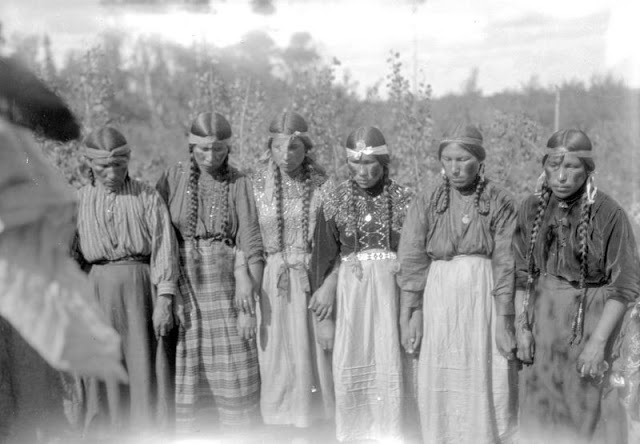
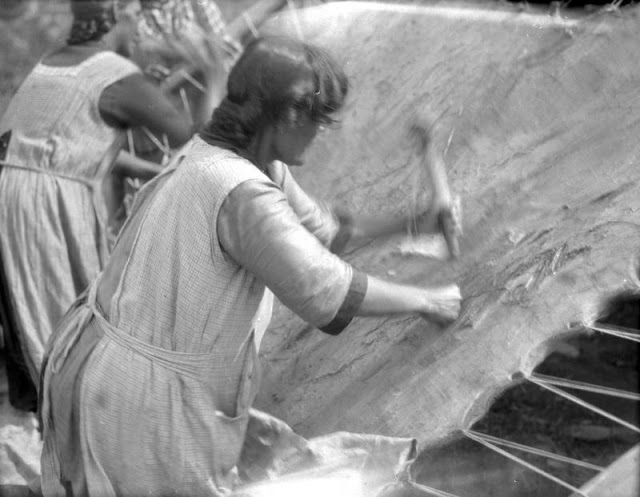
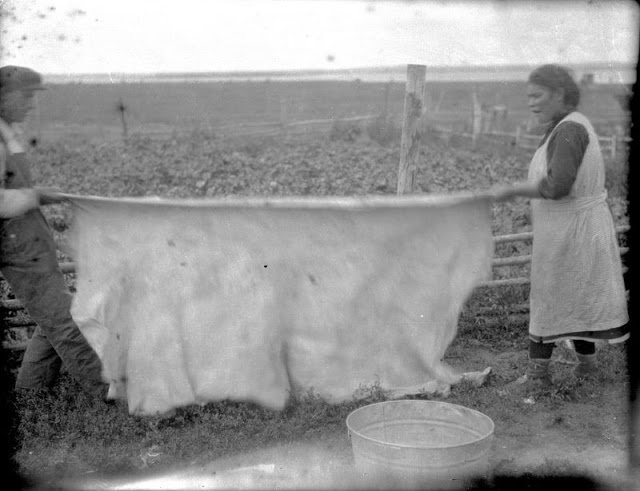
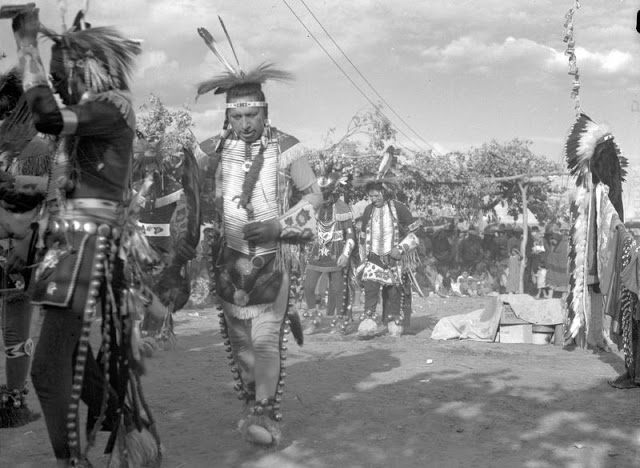
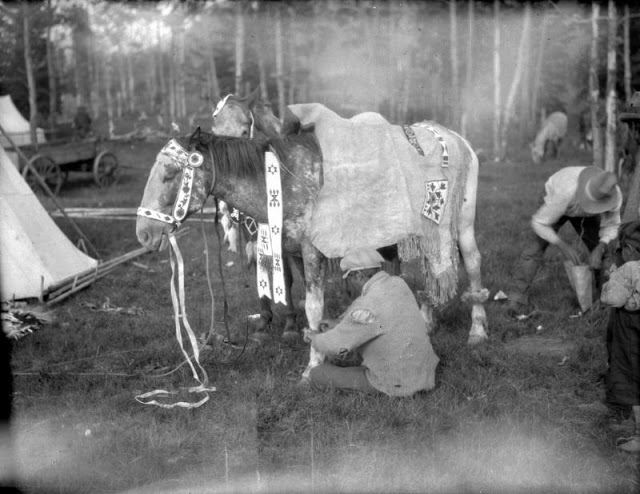
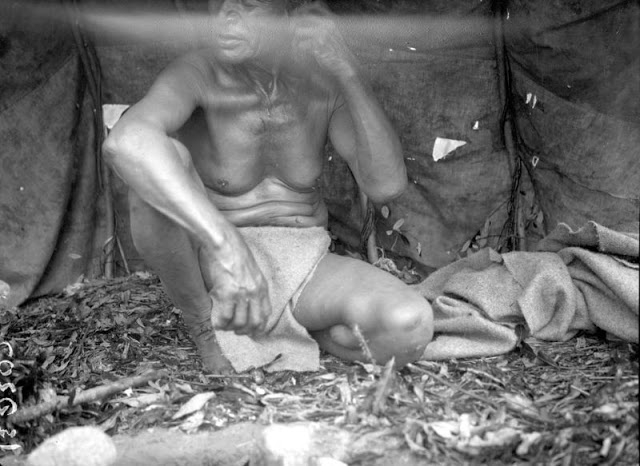
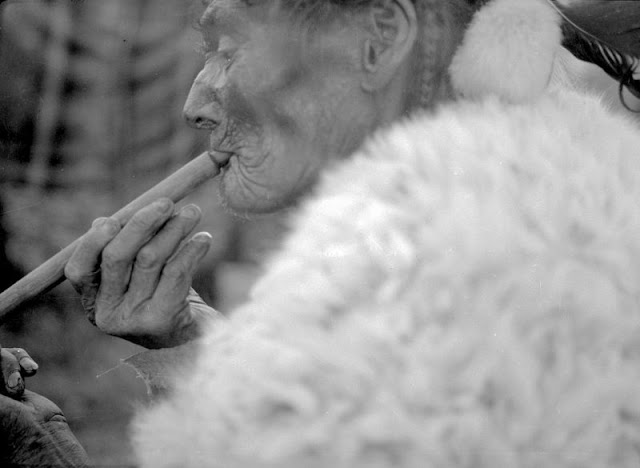
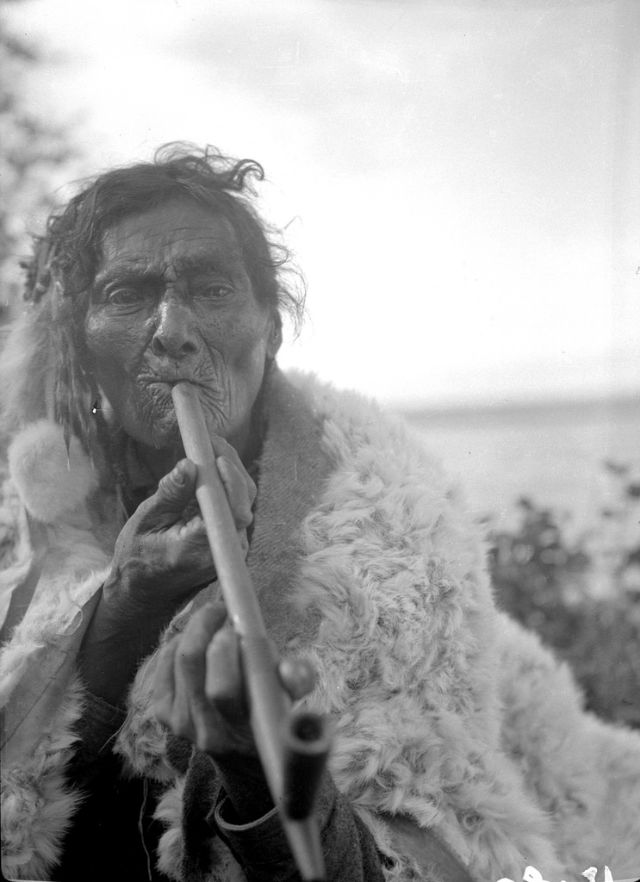
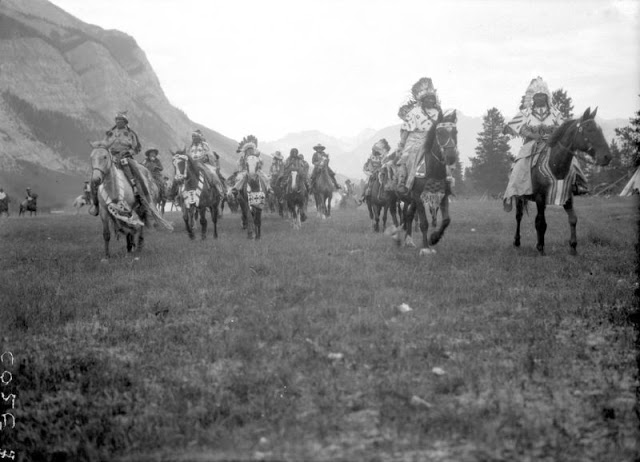
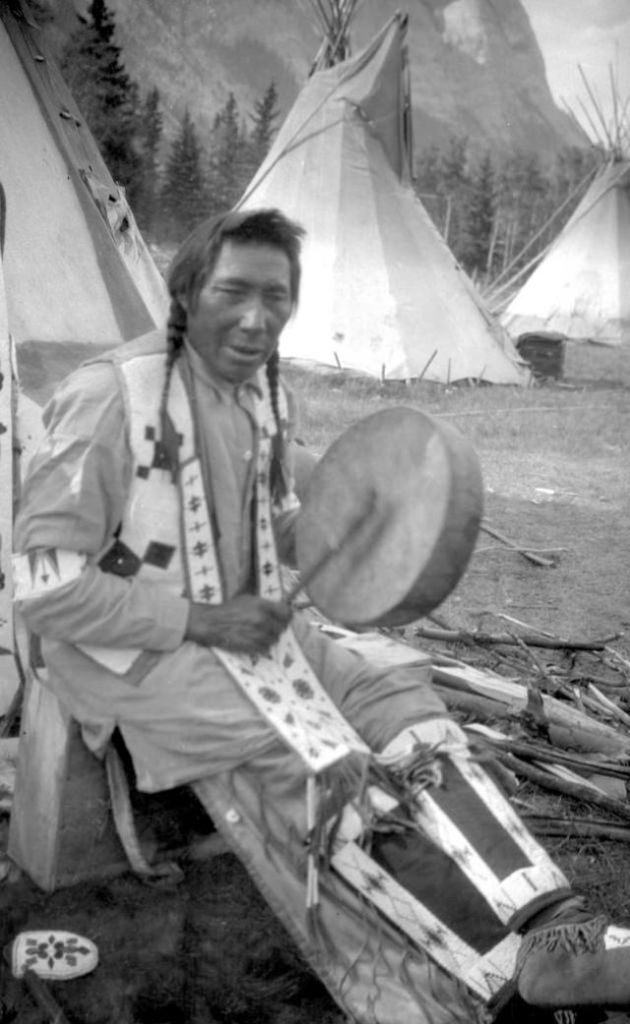
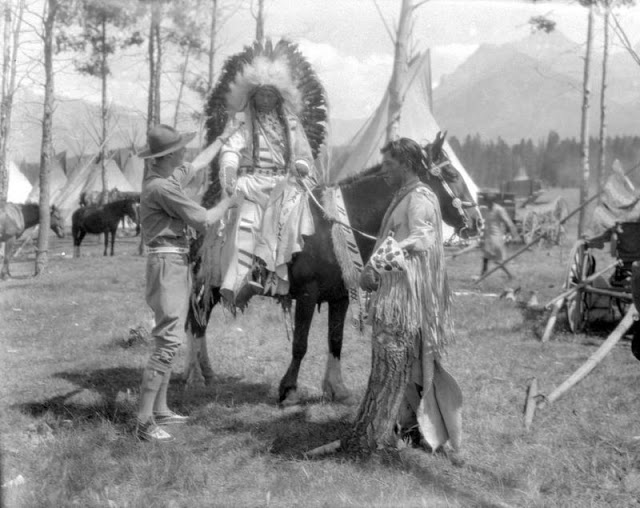
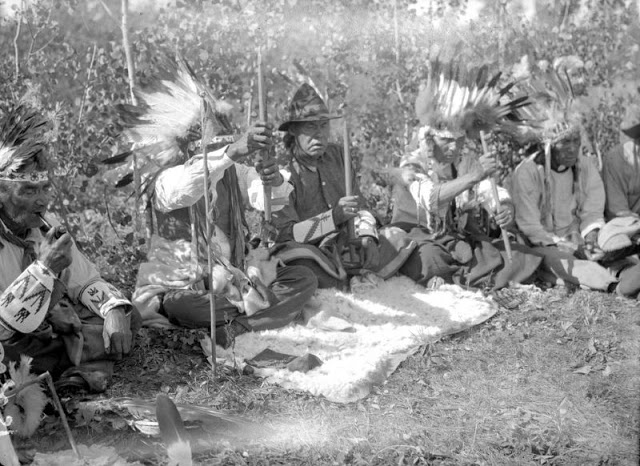
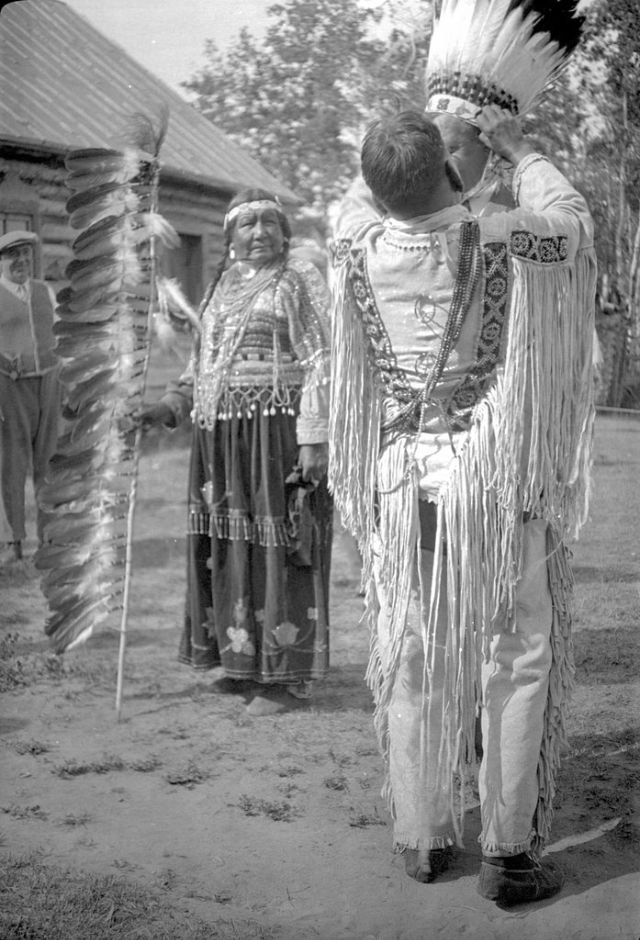
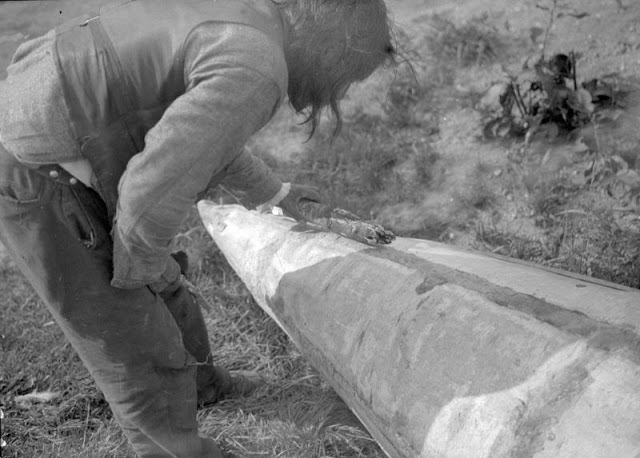
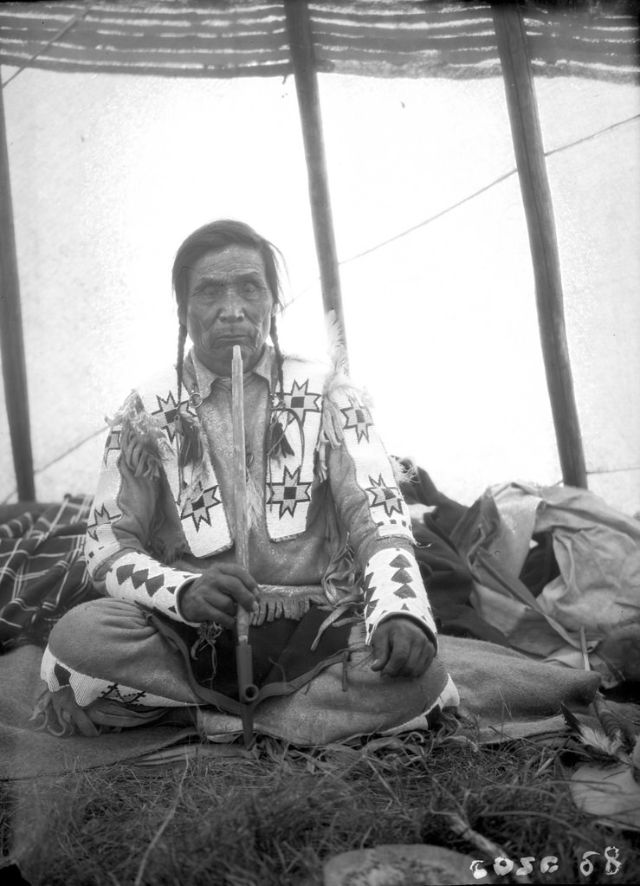
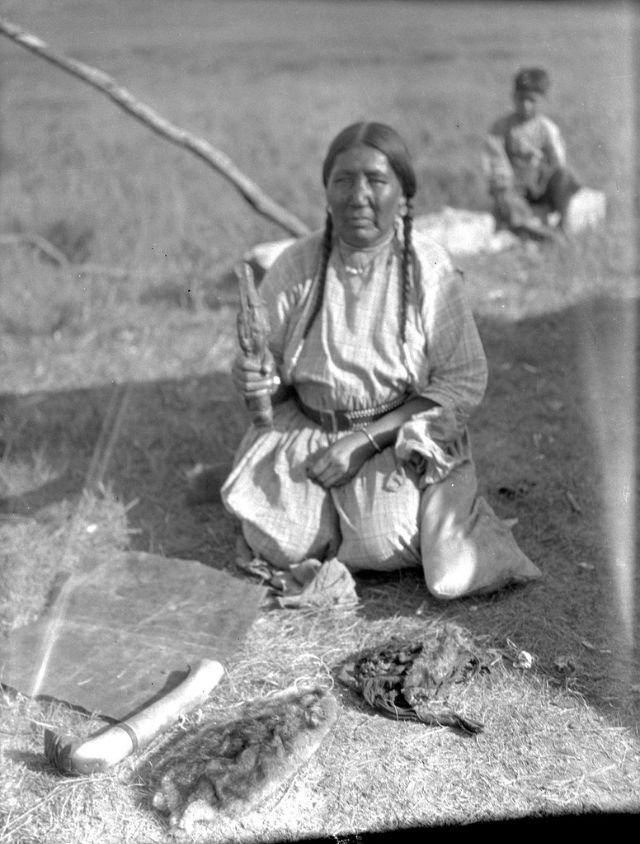
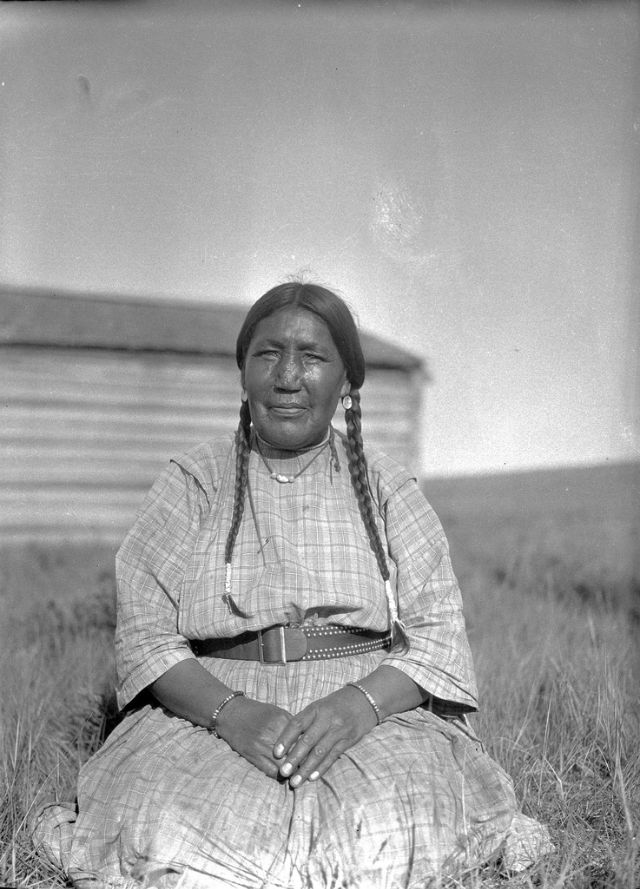
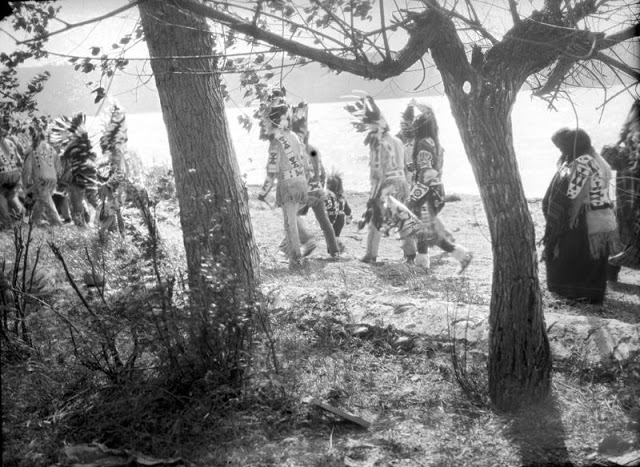
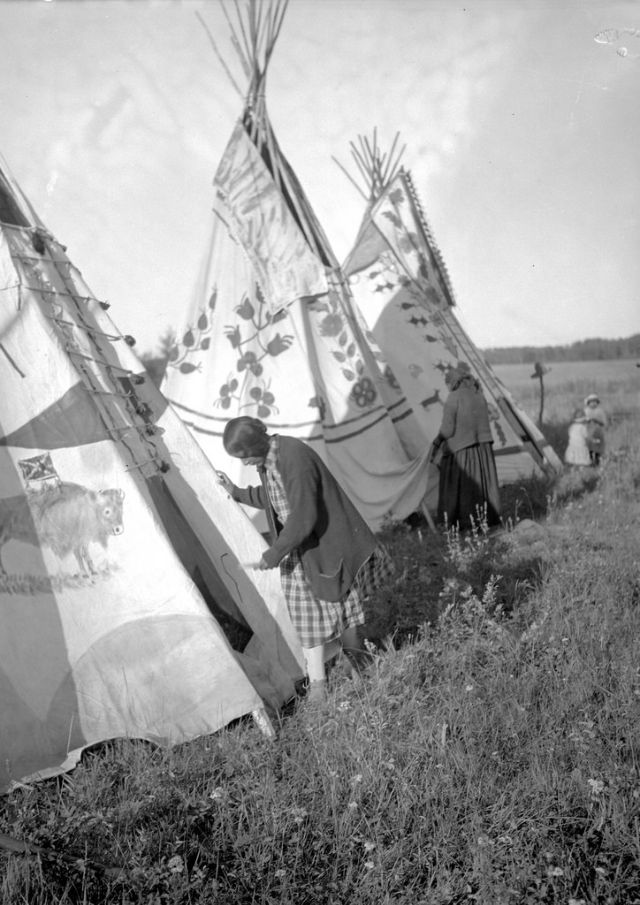
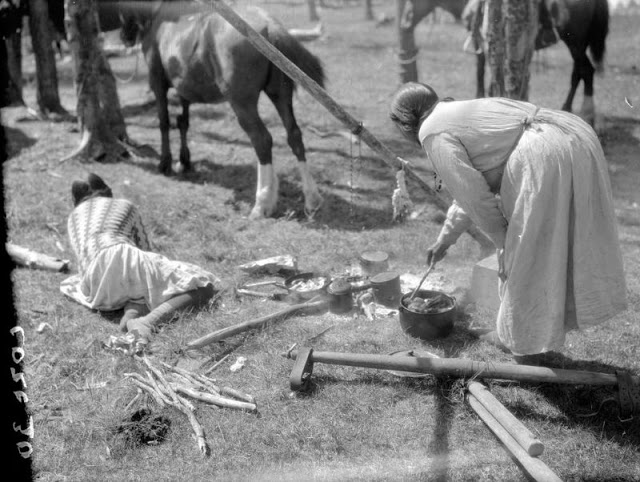
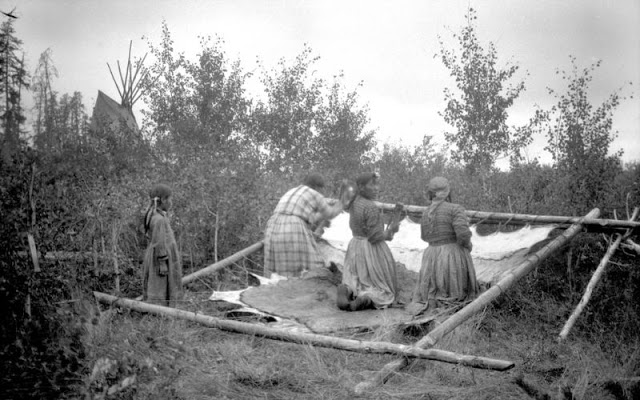
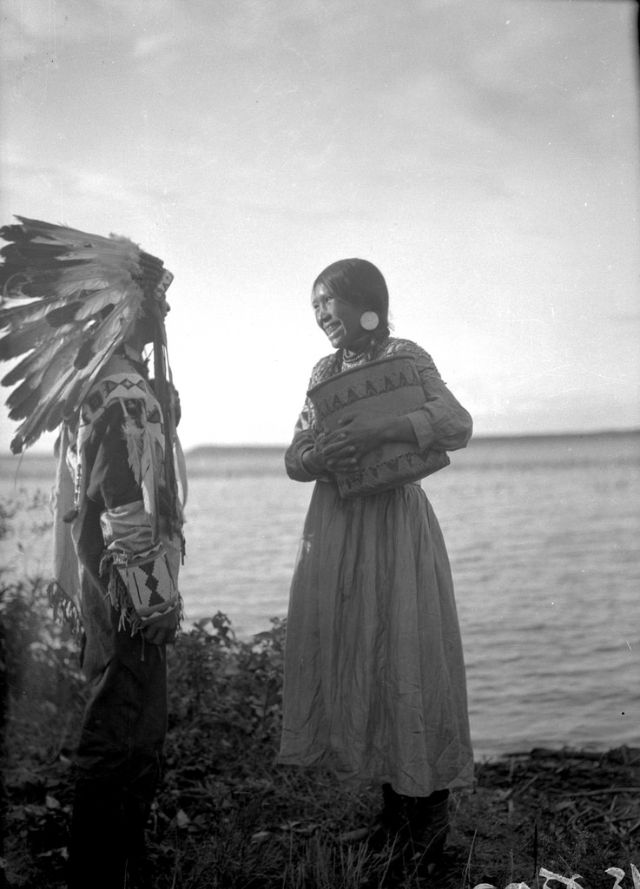
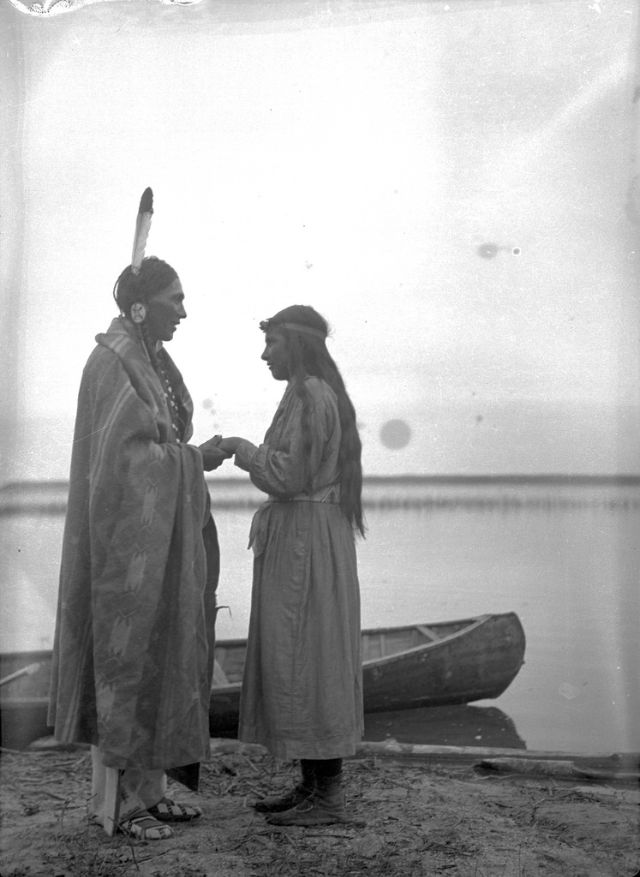
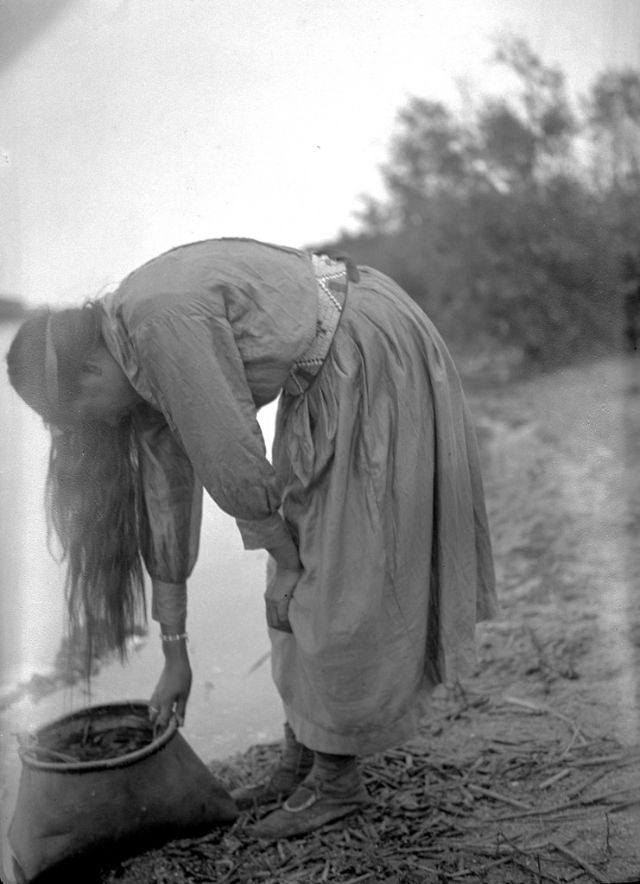
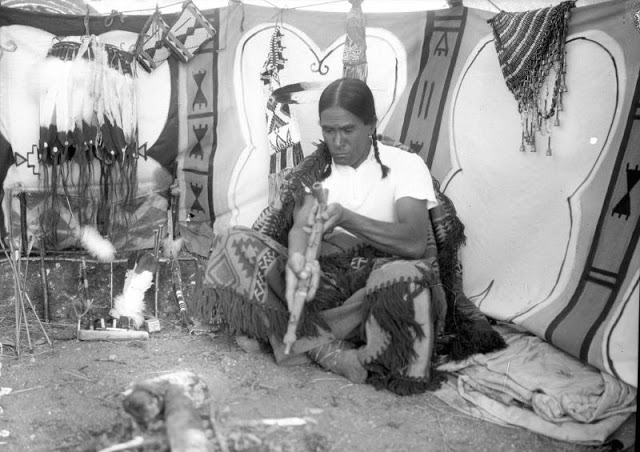
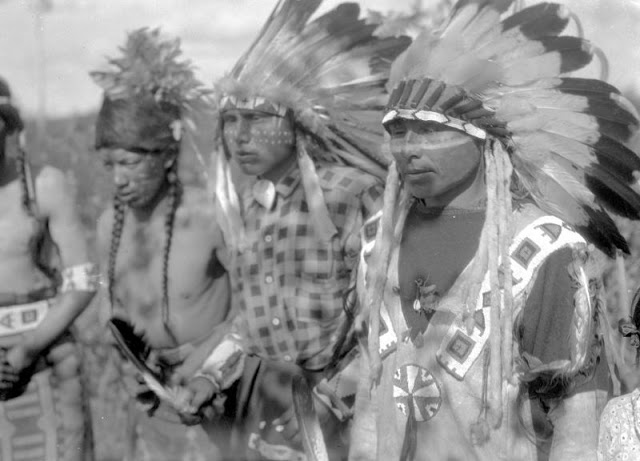
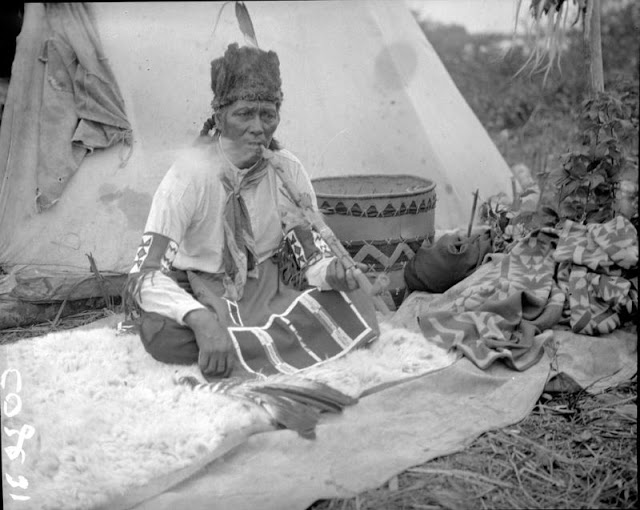
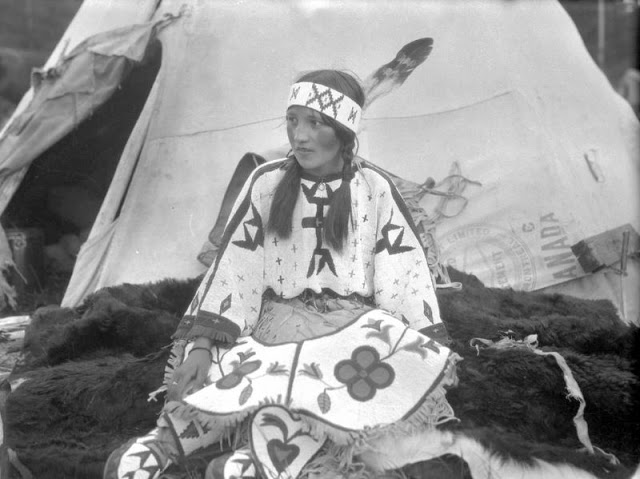
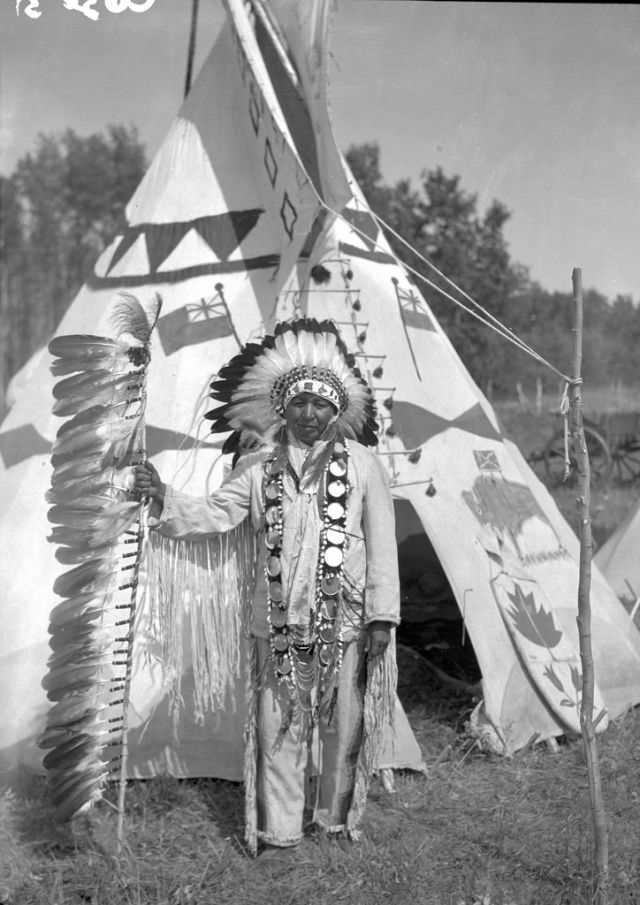
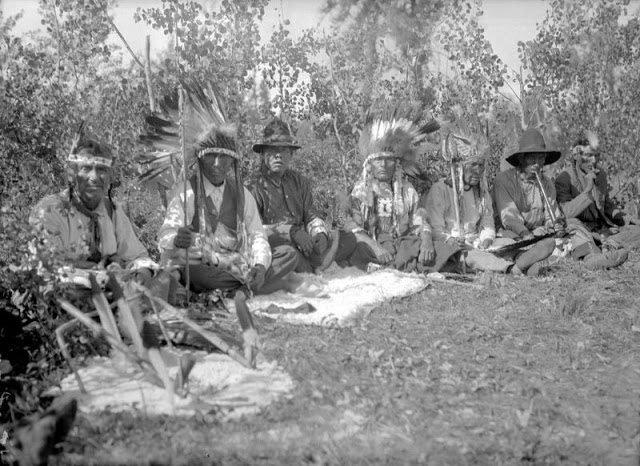
Between 1928 and 1934, the French-American anthropologist, artist, and writer Paul Coze (1903-1974) made four trips across western Canada collecting ethnographic objects for the Musée d’Ethnographie (Trocadero) in Paris and the Heye Foundation in New York.
An ardent admirer of Native American cultures, Coze helped organize the Cercle Wakanda, a group of Parisian “Indian hobbyists” who staged theatrical productions on Aboriginal themes. He also assembled a substantial private collection of ethnographic material from the Canadian Plains and Subarctic.
These photos from Provincial Archives of Alberta that he shot documenting everyday life of Native Americans in Western Canada in the early 1930s.









































(Photos by Paul Coze via Provincial Archives of Alberta)