Bringing You the Wonder of Yesterday – Today






















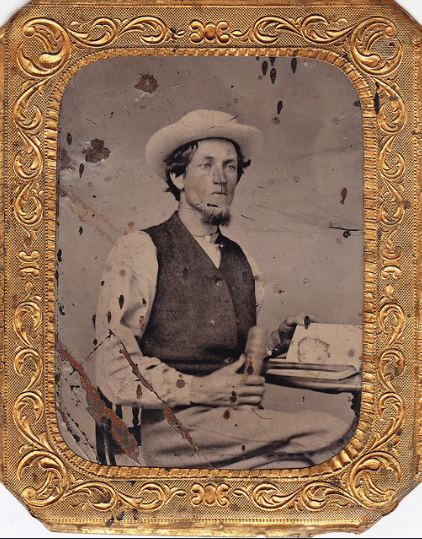
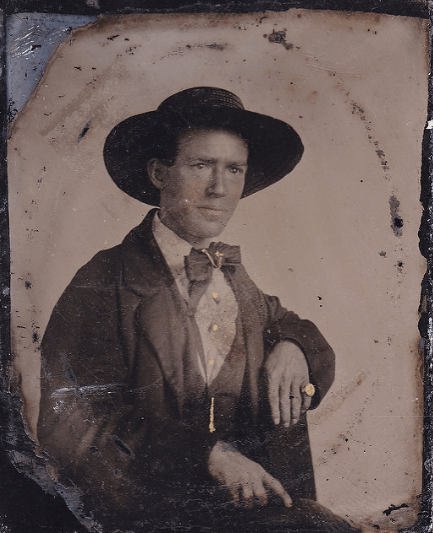
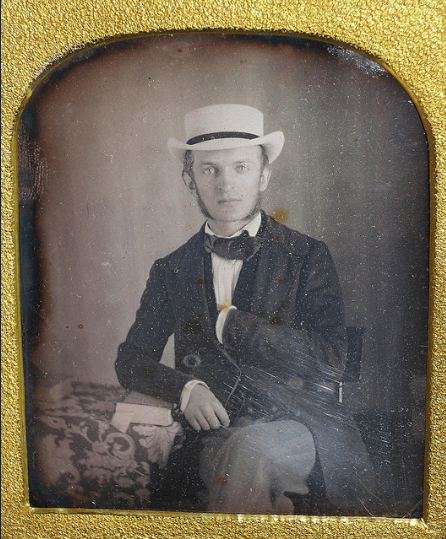
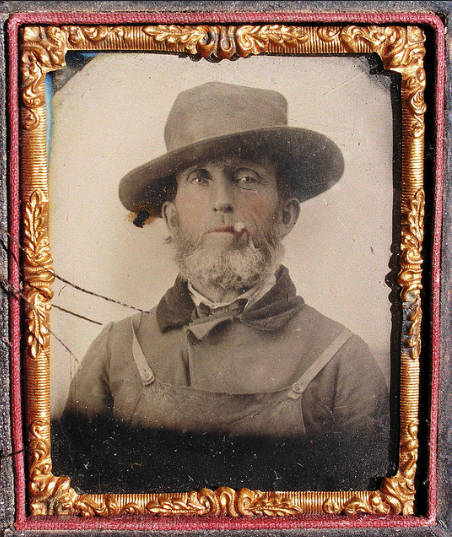
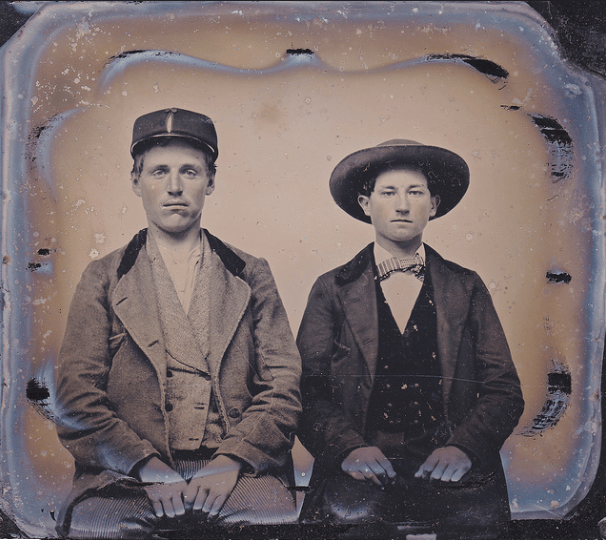
Here’s what looked like the British criminal women in the 1900s! These vintage mugshots are a selection from a photo album of prisoners, brought before the police court of North Shields. Most of these women were arrested for shoplifting and larceny.
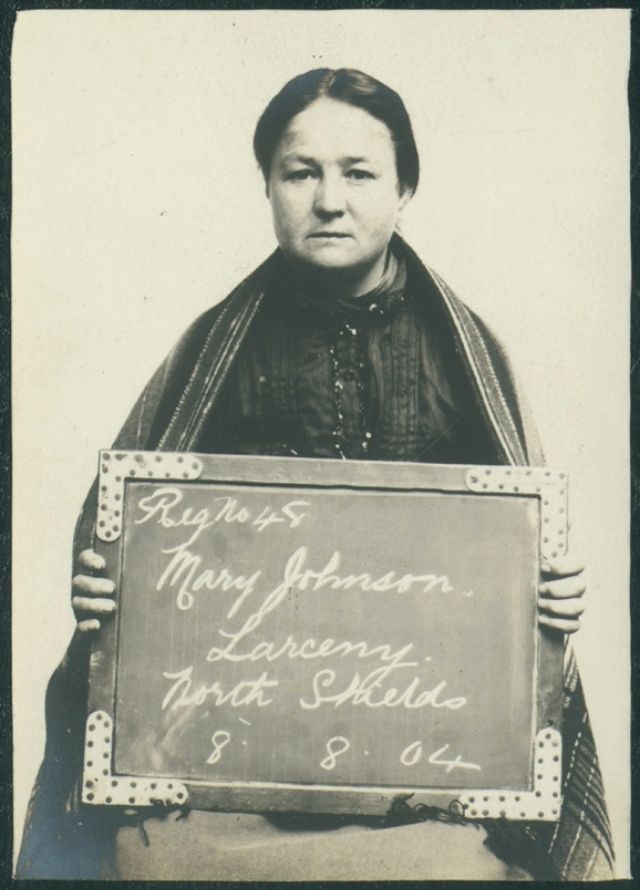
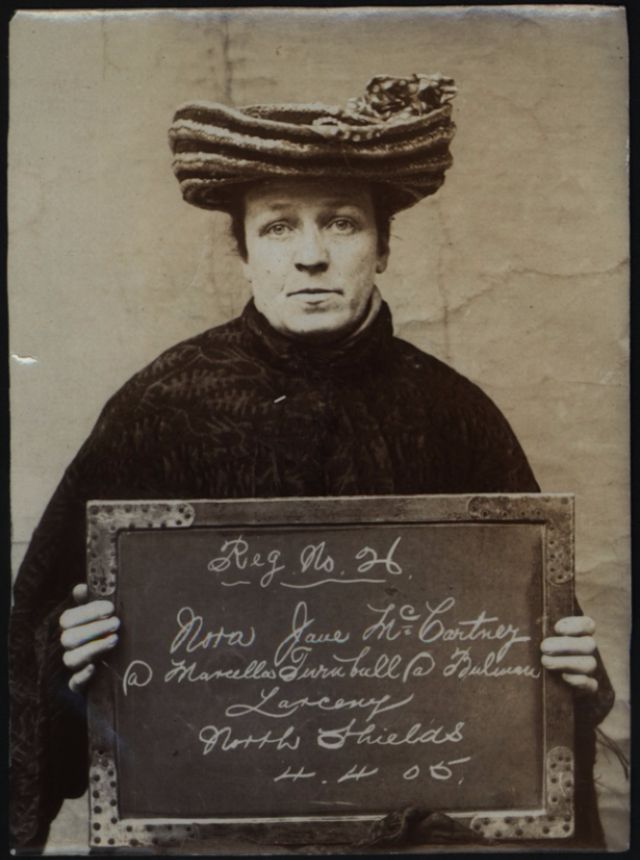

















(Photos from Tyne & Wear Archives & Museums)

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.
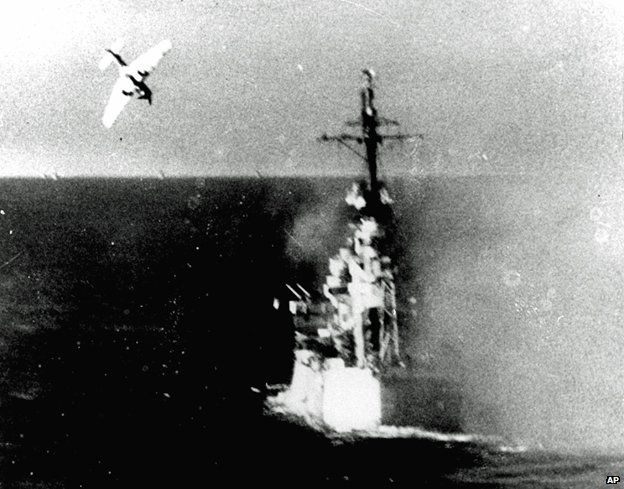
“There was a hypnotic fascination to the sight so alien to our Western philosophy. We watched each plunging kamikaze with the detached horror of one witnessing a terrible spectacle rather than as the intended victim. We forgot self for the moment as we groped hopelessly for the thought of that other man up there.”
Vice Admiral C.R. Brown, US Navy
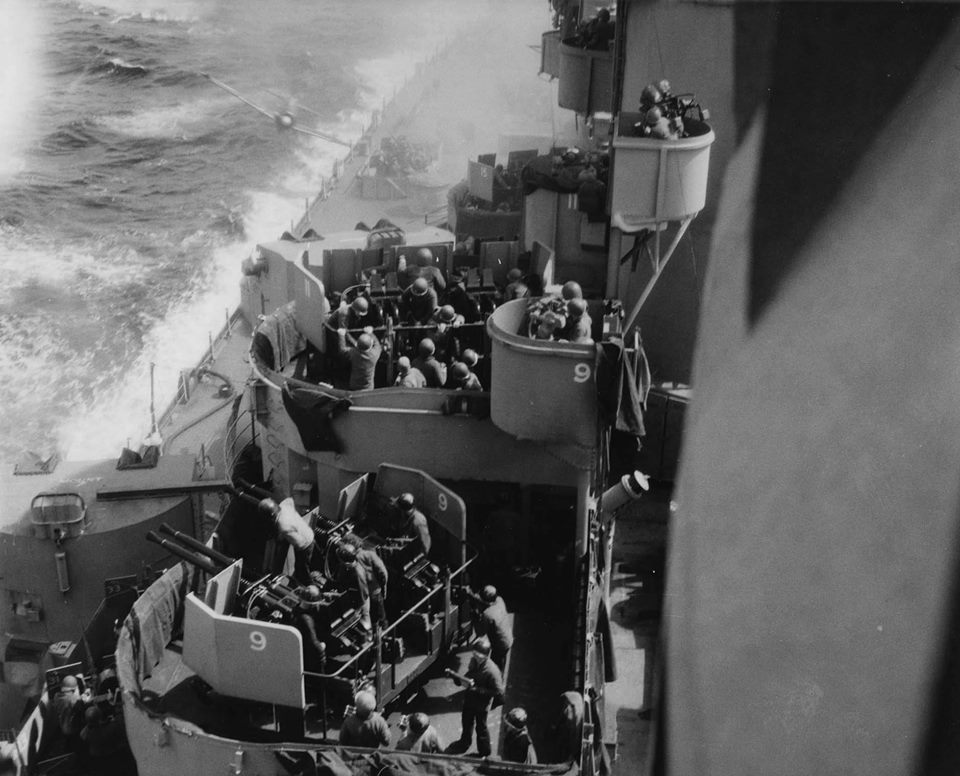
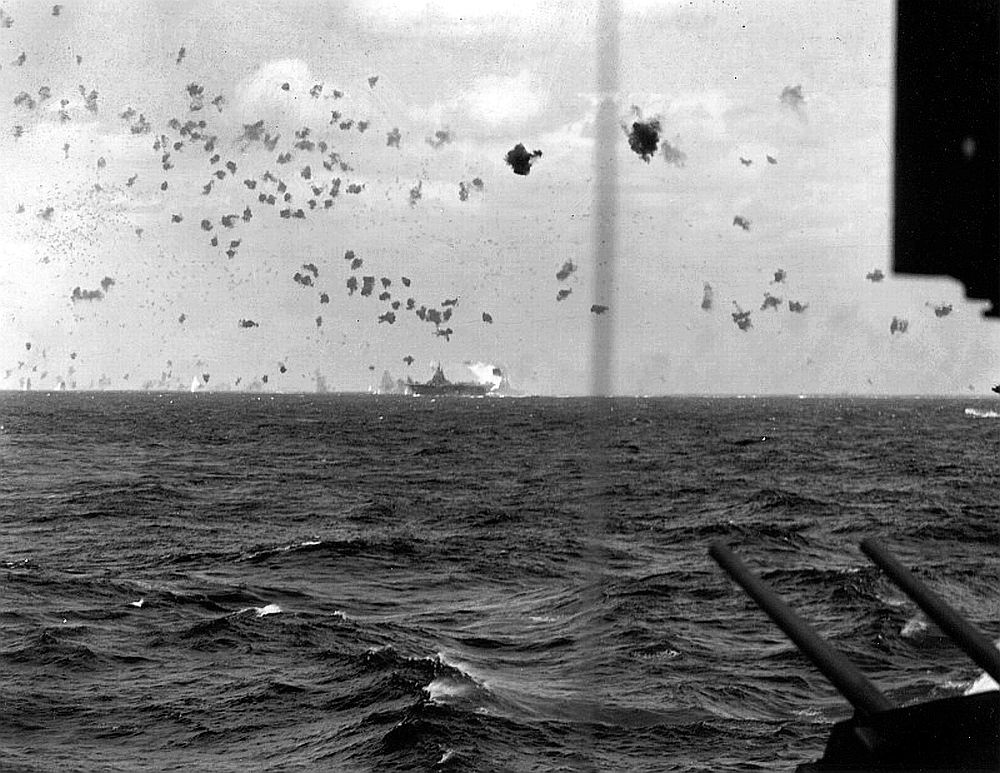
Kamikaze (神風, pronounced [kamiꜜkaze]; “divine wind” or “spirit wind”), officially Shinpū Tokubetsu Kōgekitai (神風特別攻撃隊, “Divine Wind Special Attack Unit”), were a part of the Japanese Special Attack Units of military aviators who flew suicide attacks for the Empire of Japan against Allied naval vessels in the closing stages of the Pacific campaign of World War II, intending to destroy warships more effectively than with conventional air attacks. About 3,800 kamikaze pilots died during the war, and more than 7,000 naval personnel were killed by kamikaze attacks.
Kamikaze aircraft were essentially pilot-guided explosive missiles, purpose-built or converted from conventional aircraft. Pilots would attempt to crash their aircraft into enemy ships in what was called a “body attack” (tai-atari) in aircraft loaded with bombs, torpedoes or other explosives. About 19% of kamikaze attacks were successful. The Japanese considered the goal of damaging or sinking large numbers of Allied ships to be a just reason for suicide attacks; kamikaze were more accurate than conventional attacks, and often caused more damage. Some kamikazes were still able to hit their targets even after their aircraft had been crippled.
The attacks began in October 1944, at a time when the war was looking increasingly bleak for the Japanese. They had lost several important battles, many of their best pilots had been killed, their aircraft were becoming outdated, and they had lost command of the air. Japan was losing pilots faster than it could train their replacements, and the nation’s industrial capacity was diminishing relative to that of the Allies. These factors, along with Japan’s unwillingness to surrender, led to the use of kamikaze tactics as Allied forces advanced towards the Japanese home islands.
The tradition of death instead of defeat, capture, and shame was deeply entrenched in Japanese military culture; one of the primary values in the samurai life and the Bushido code was loyalty and honor until death. In addition to kamikazes, the Japanese military also used or made plans for non-aerial Japanese Special Attack Units, including those involving Kairyu (submarines), Kaiten human torpedoes, Shinyo speedboats and Fukuryu divers. (Wikipedia)



Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.
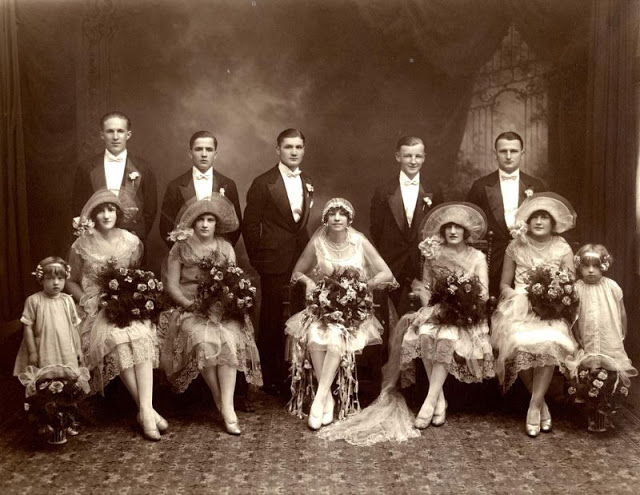
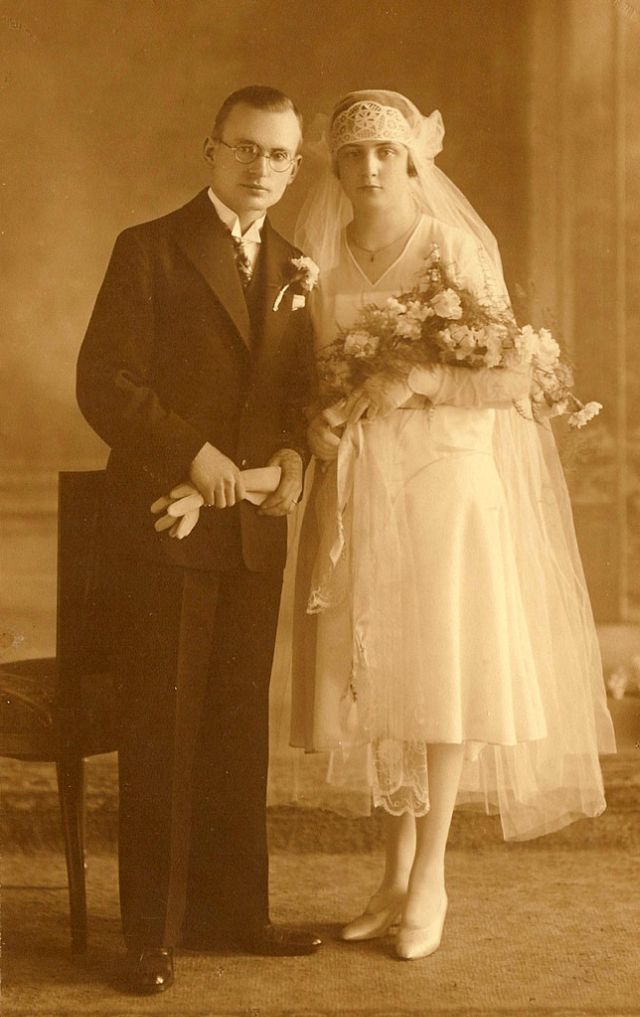
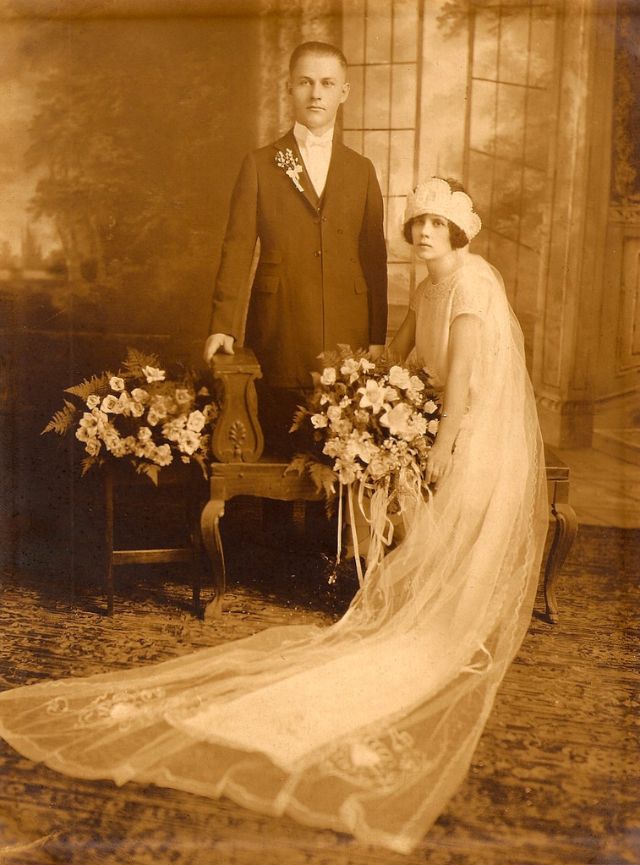
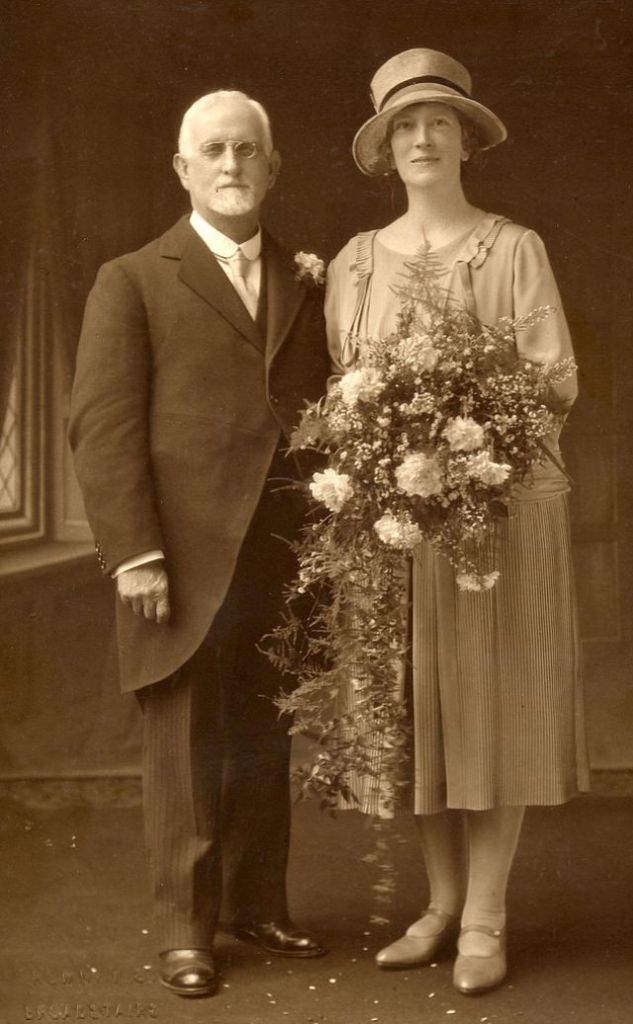
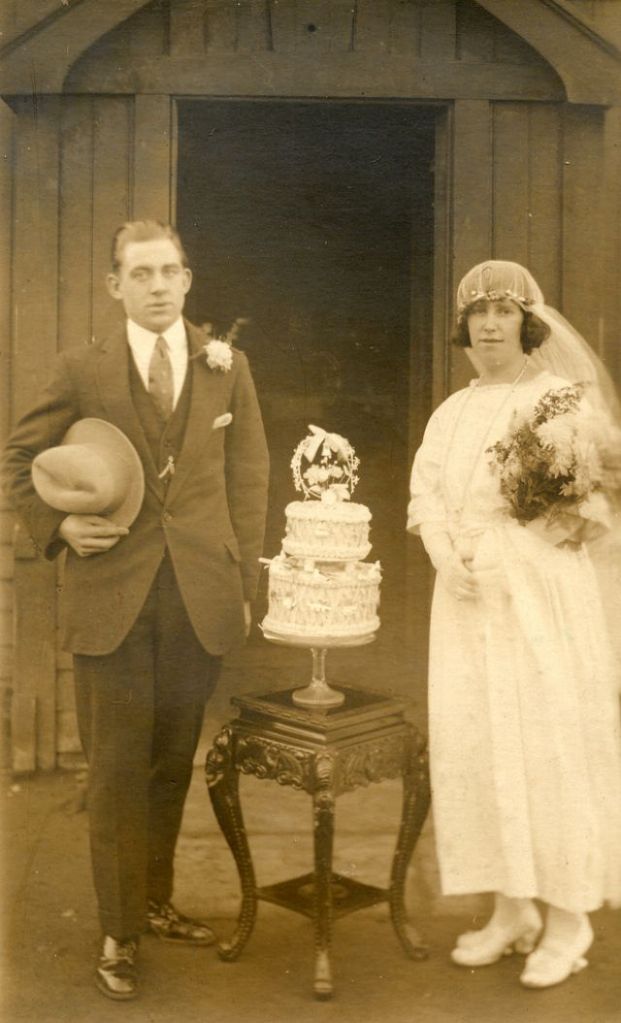
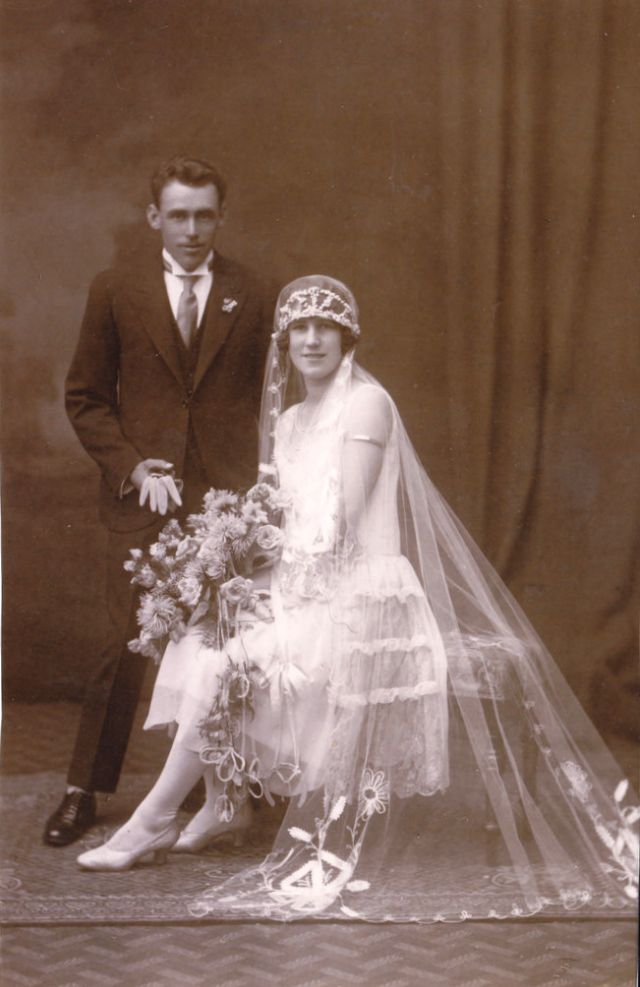
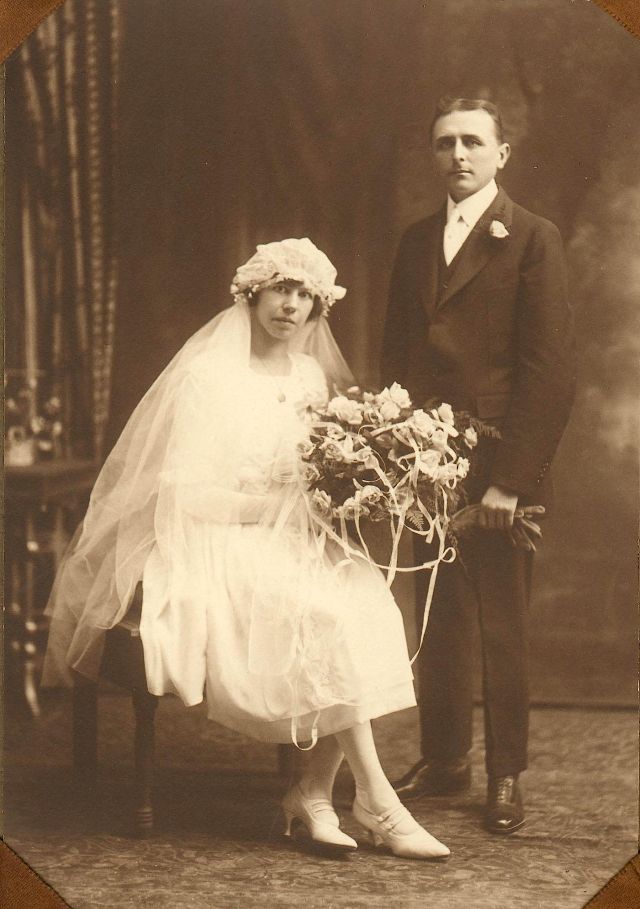
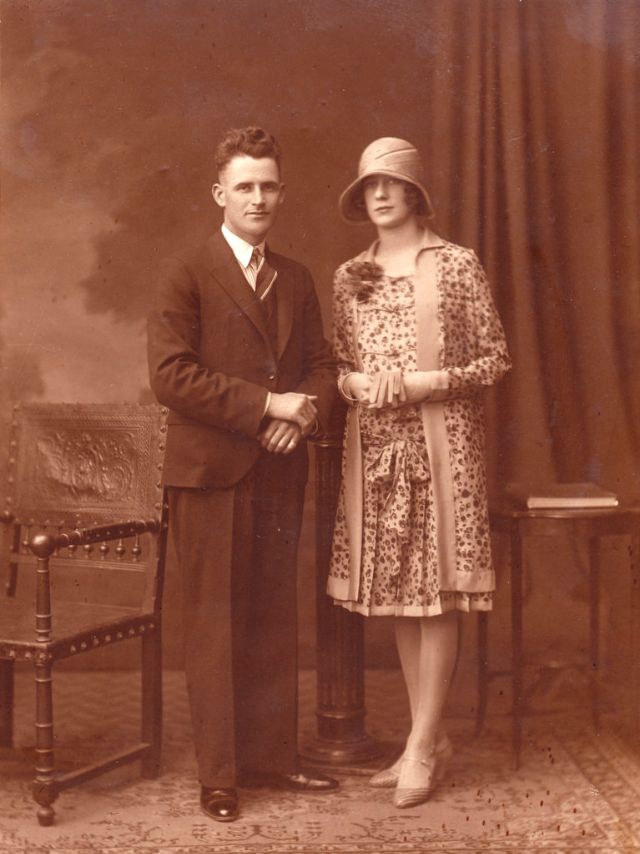
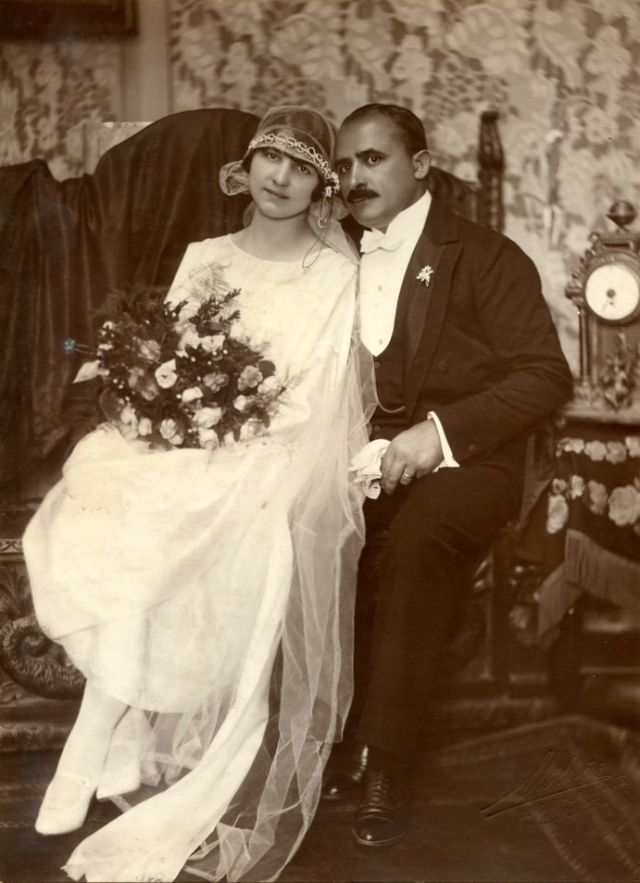
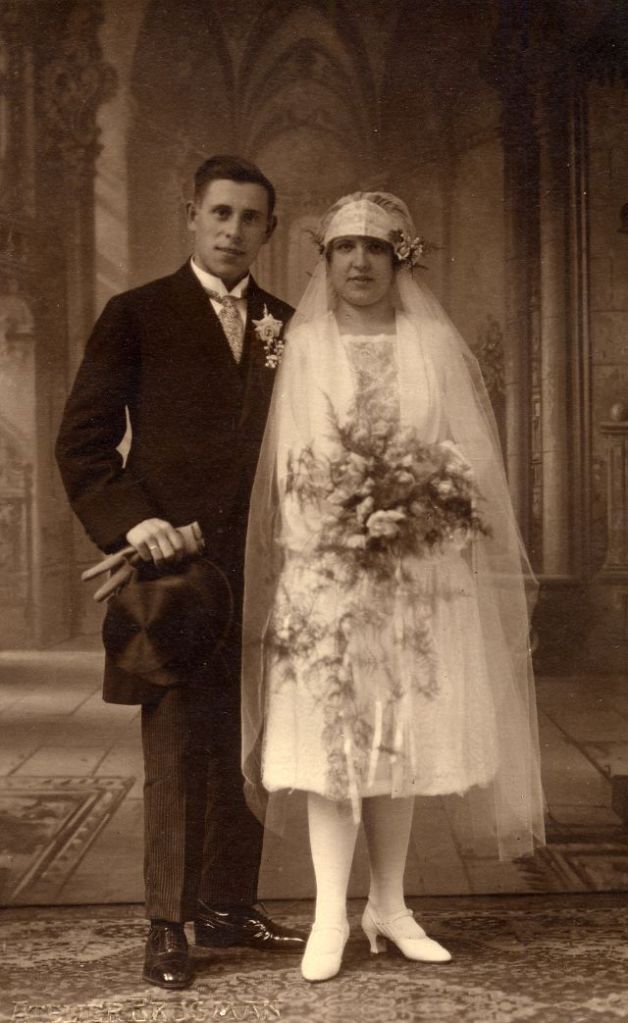
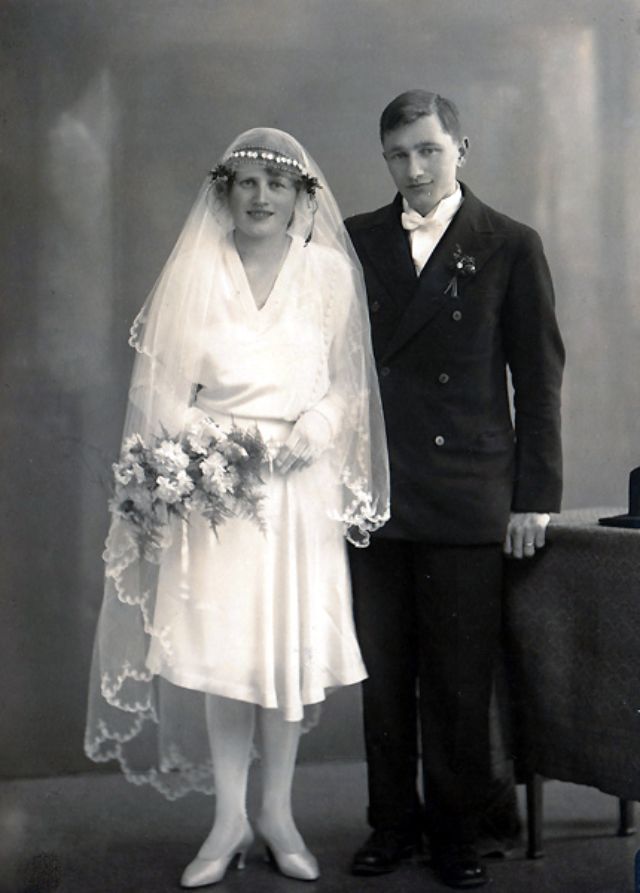
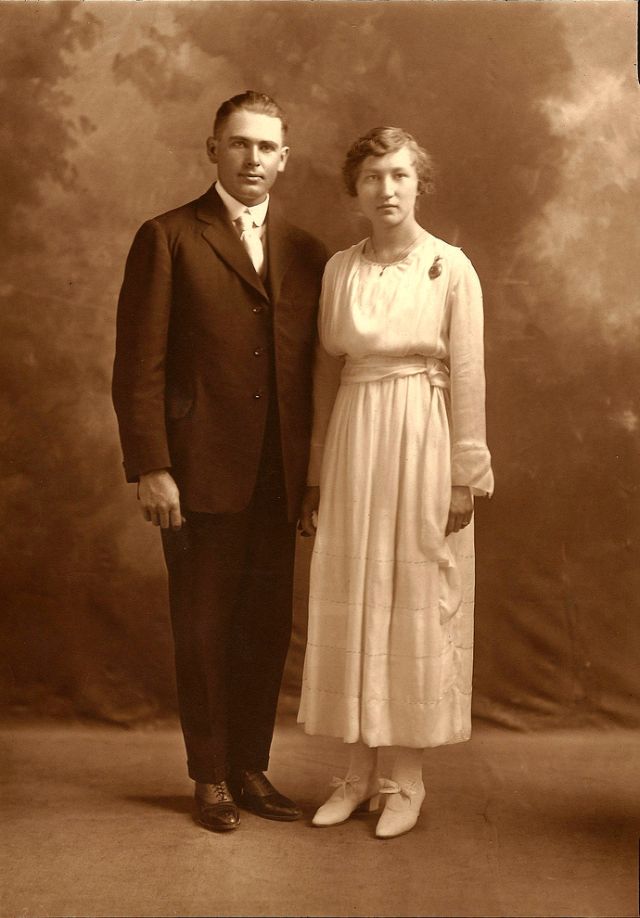
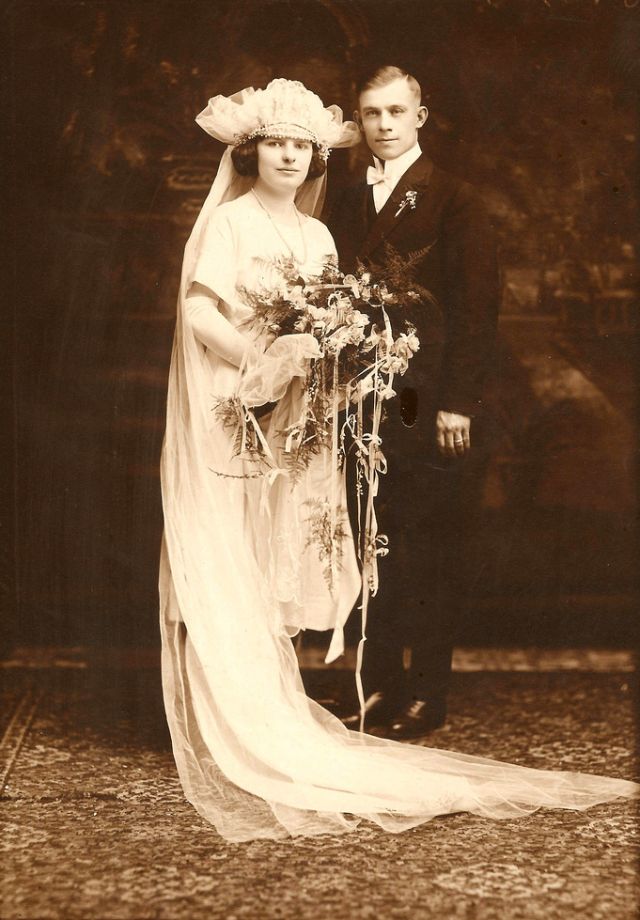
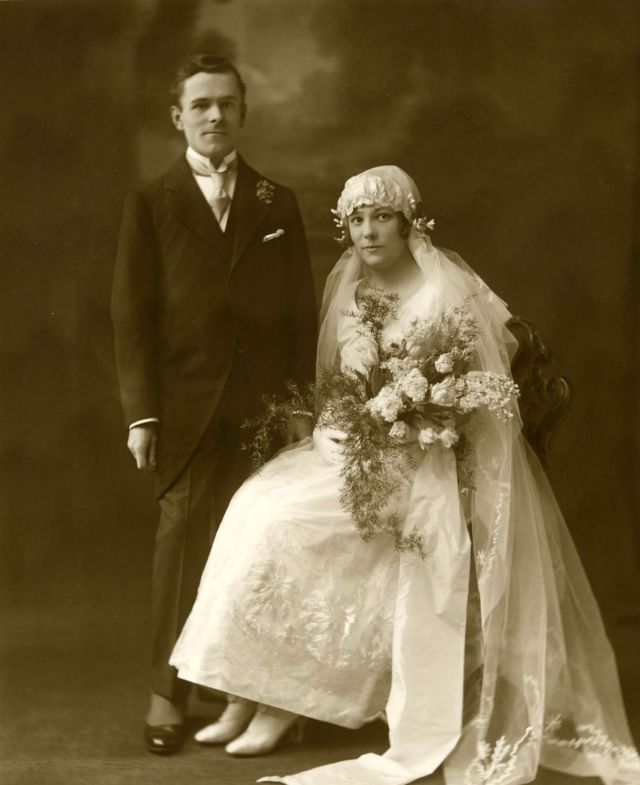
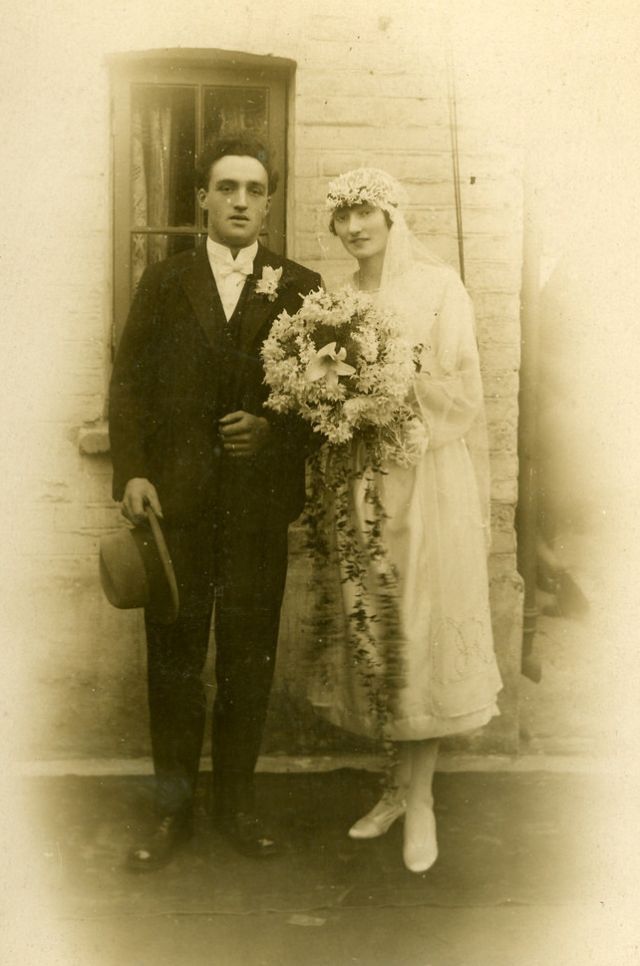
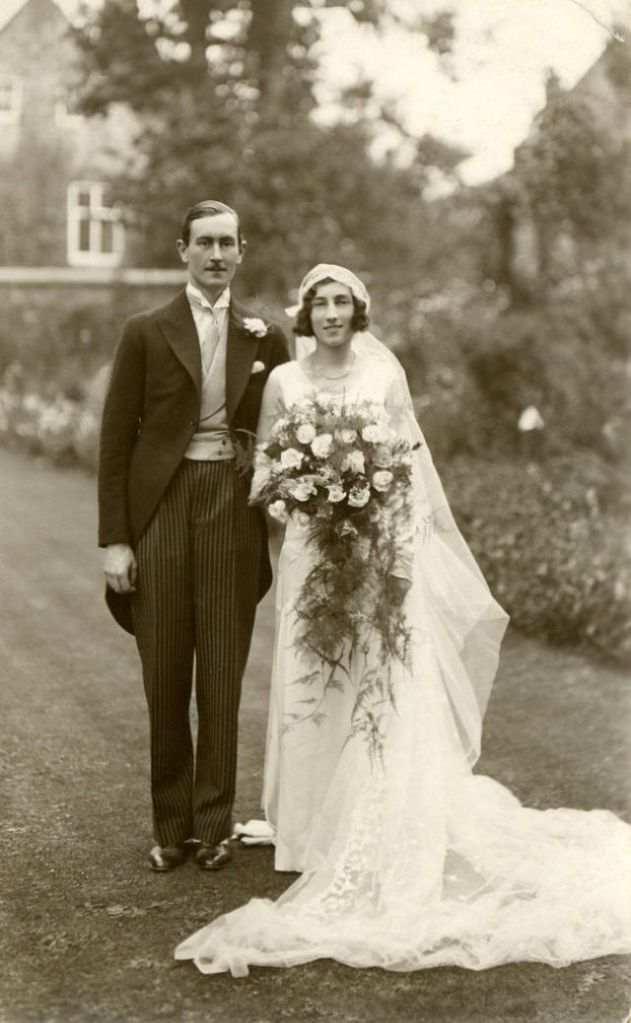
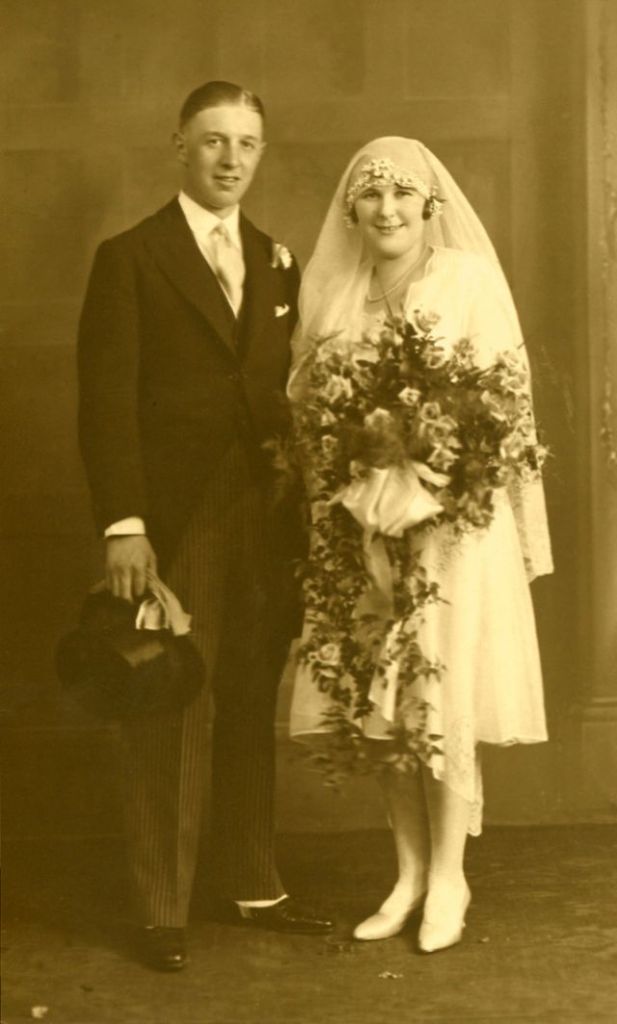
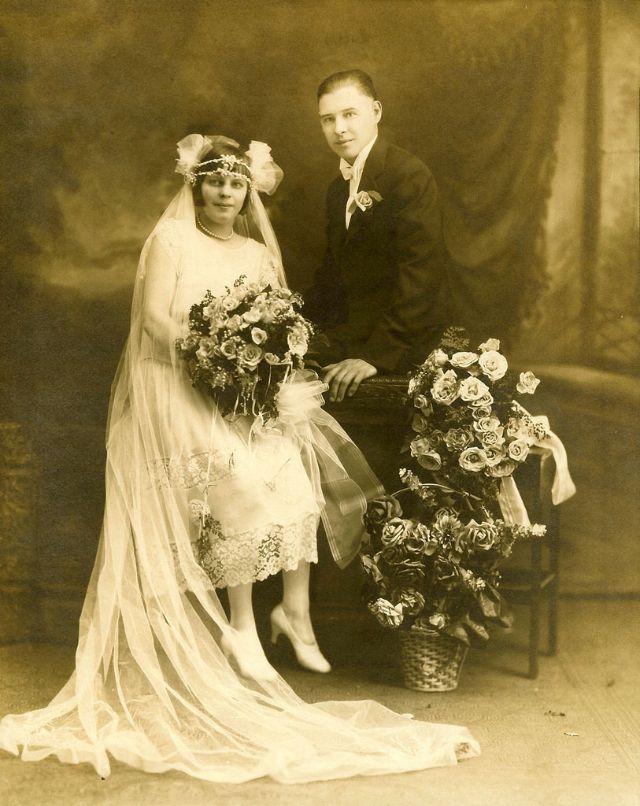
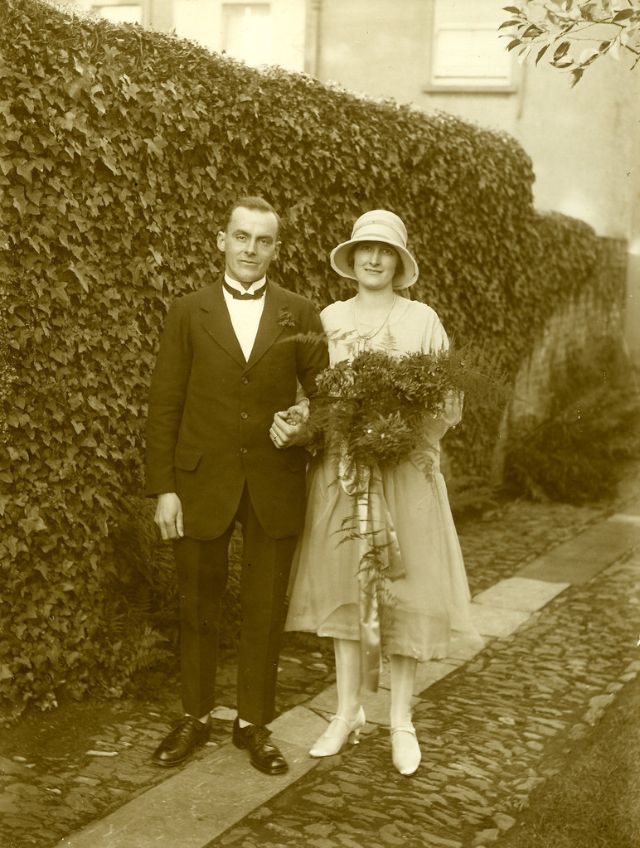
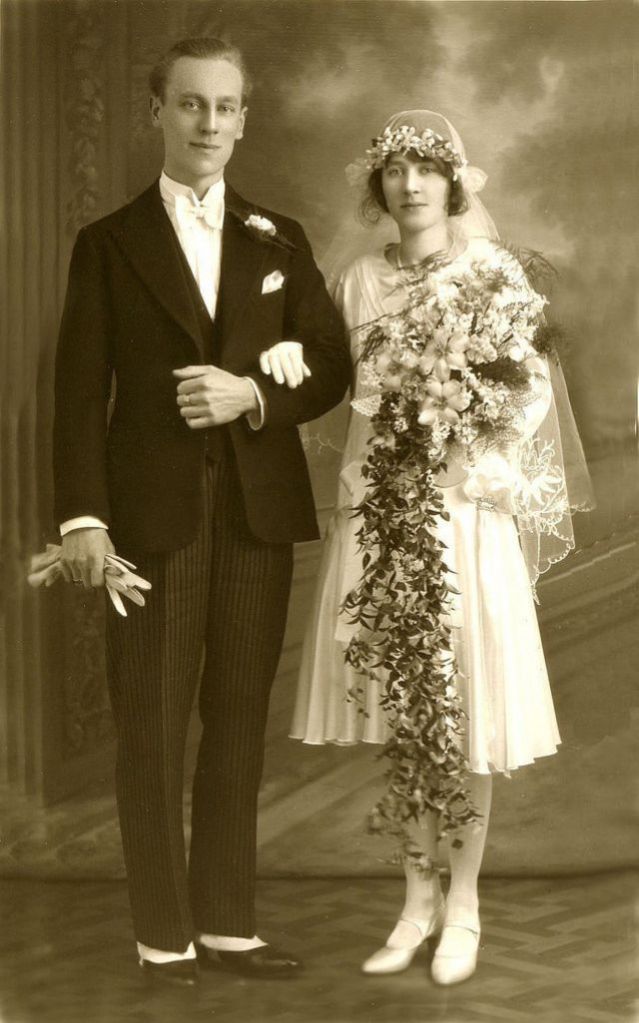
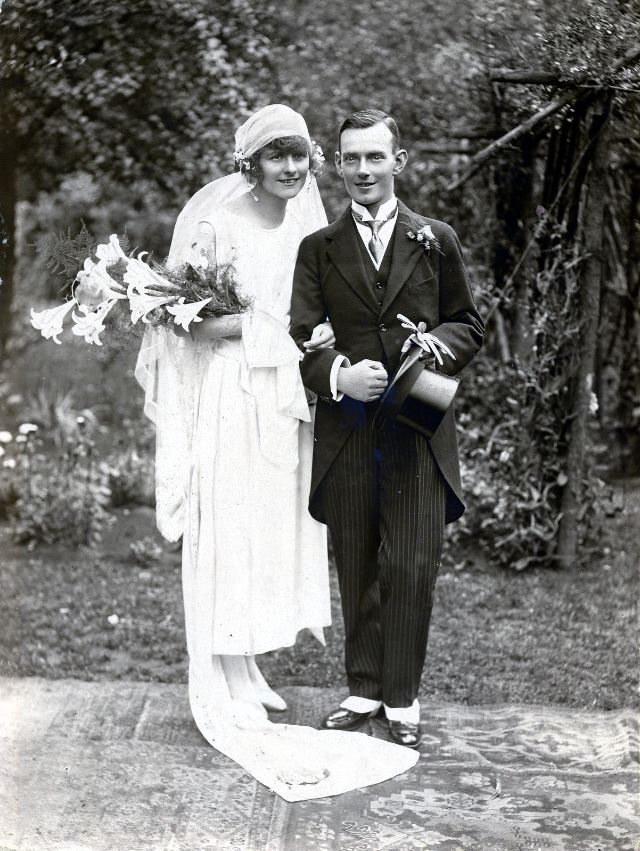
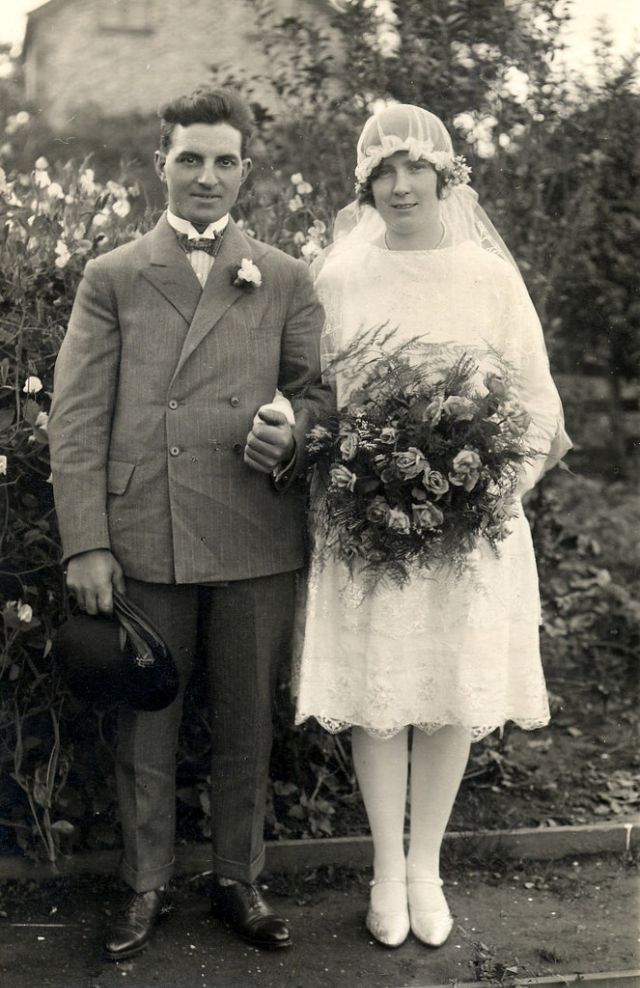
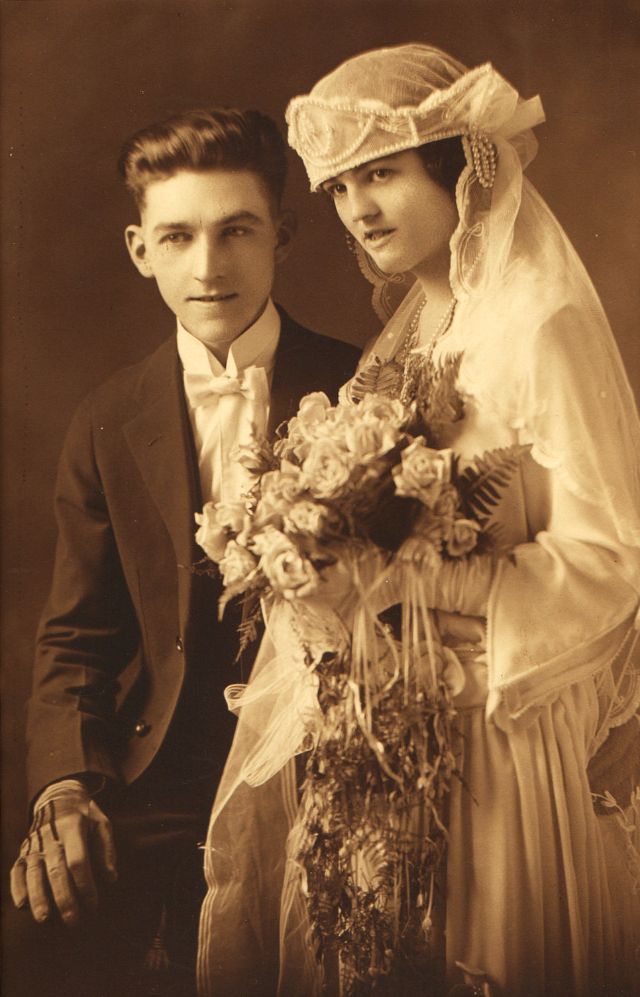
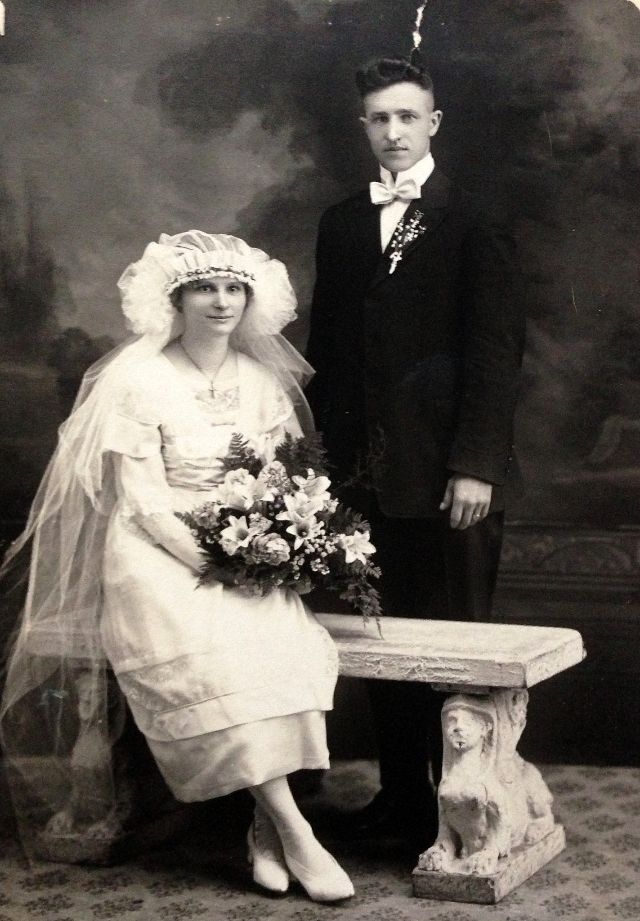
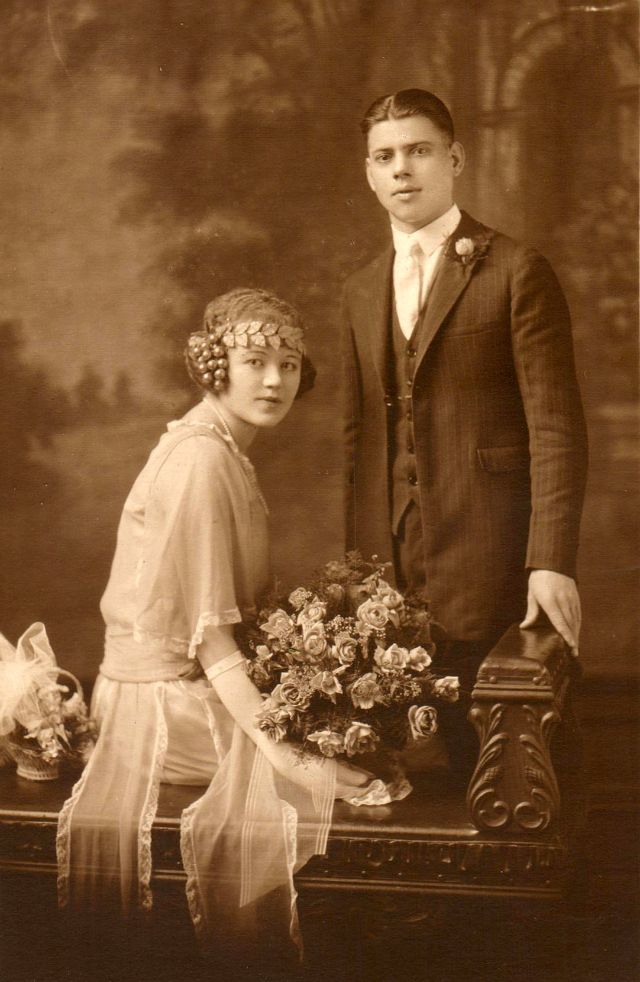
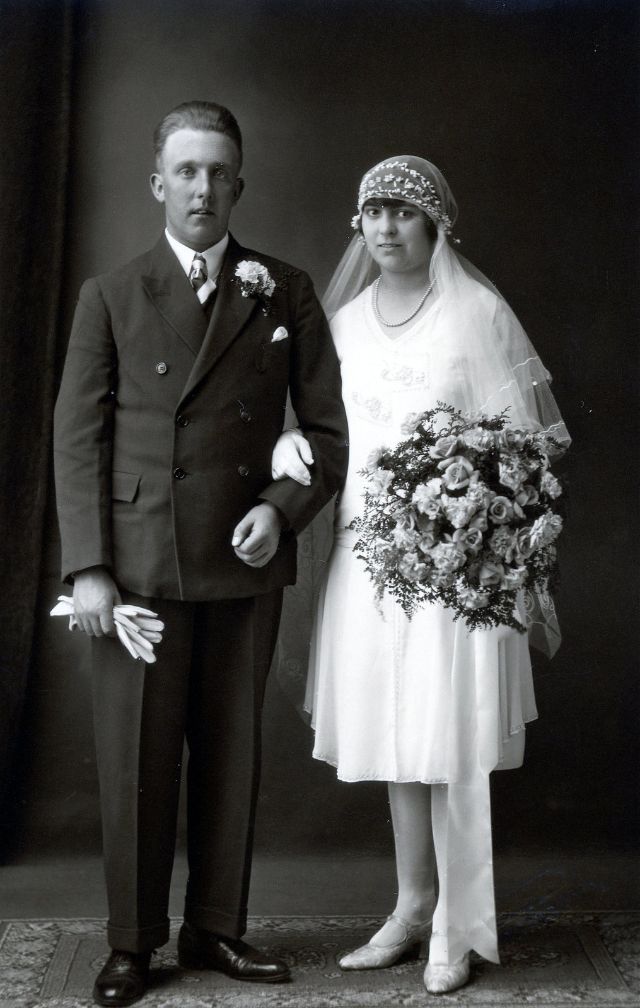
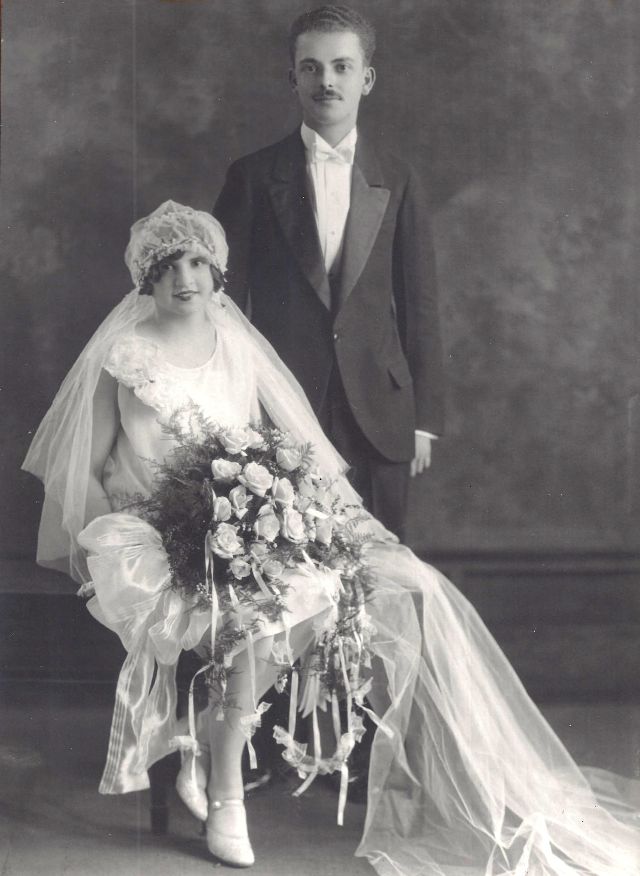
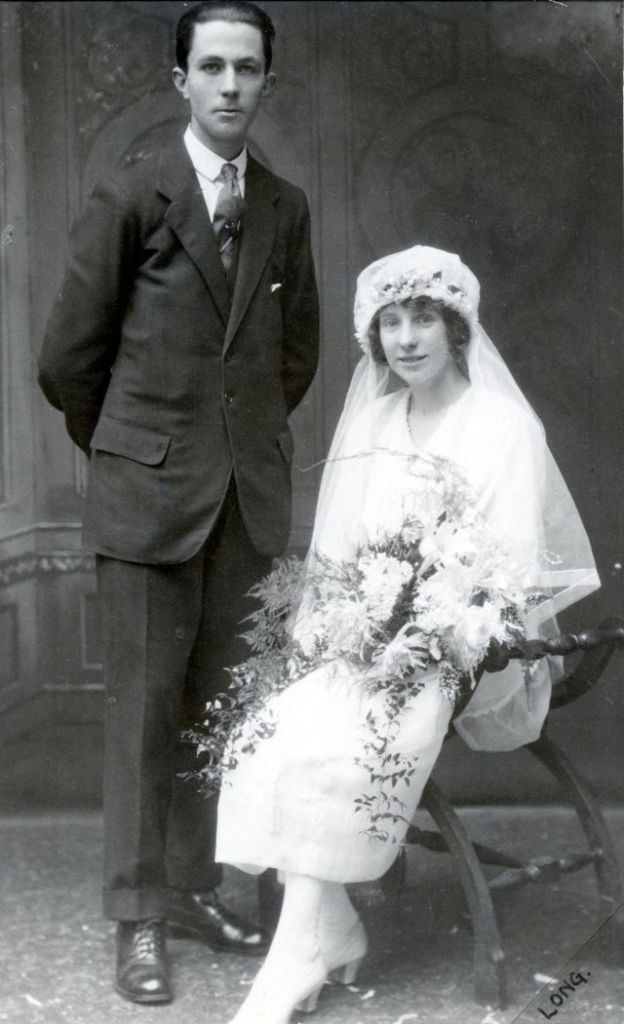
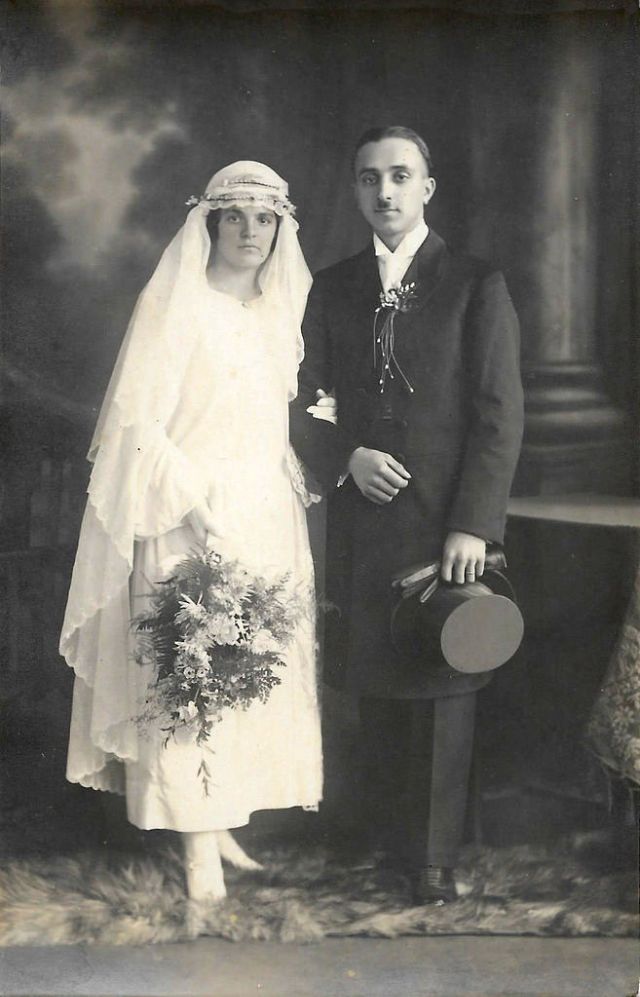
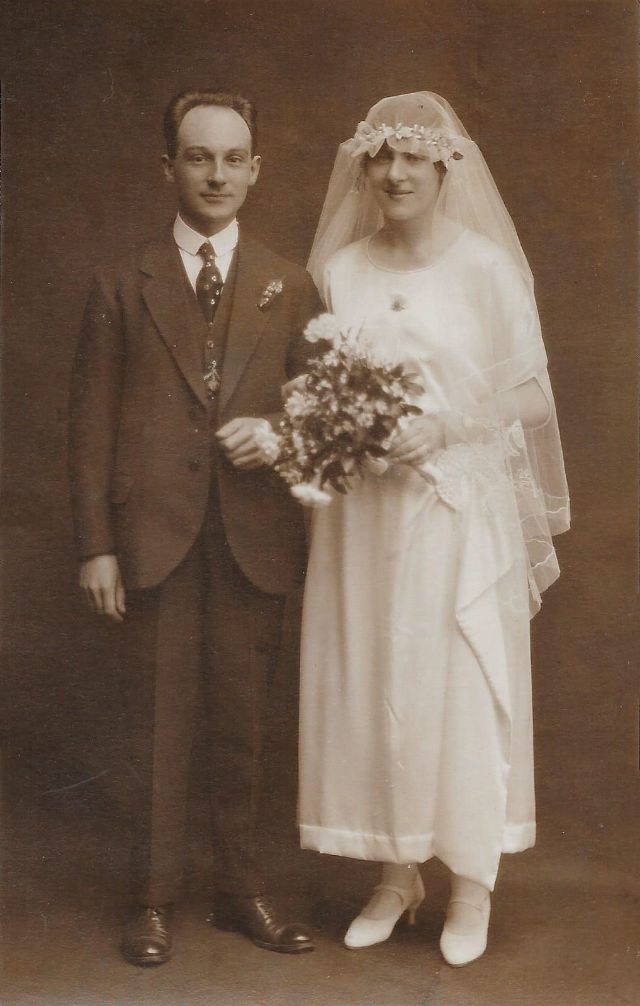
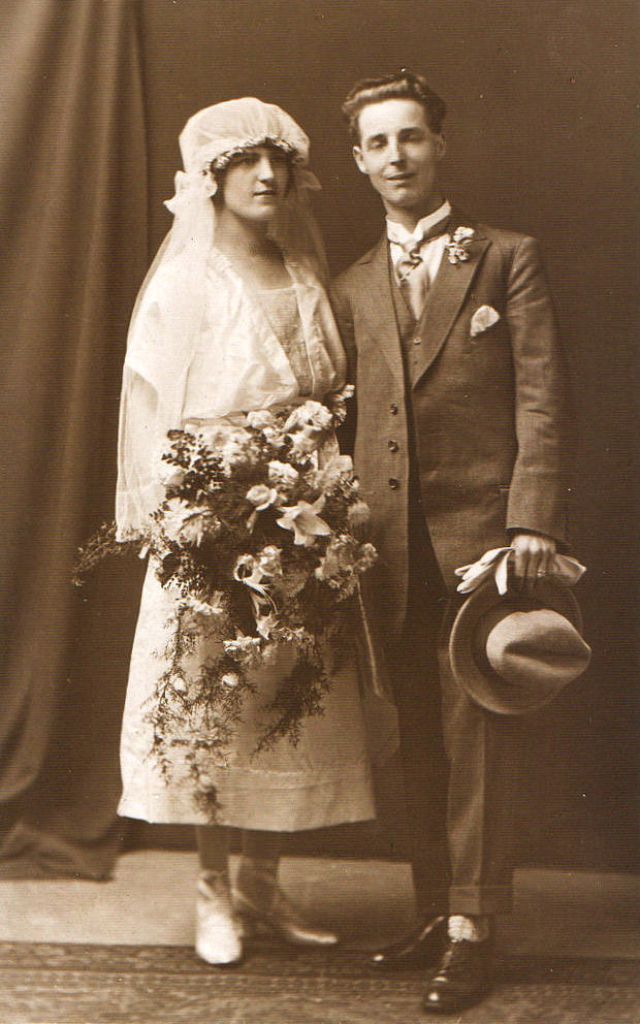
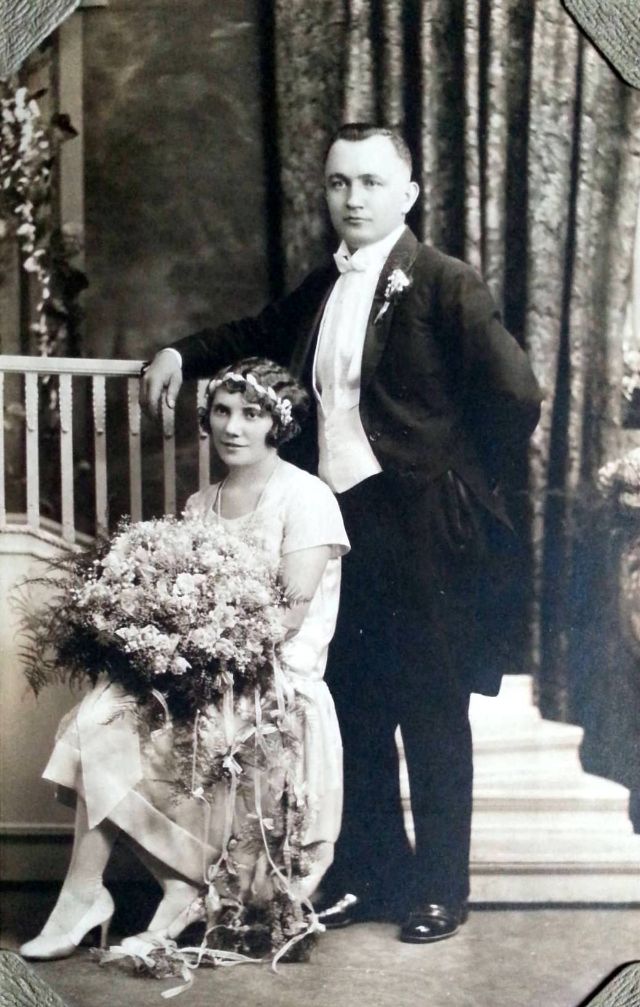
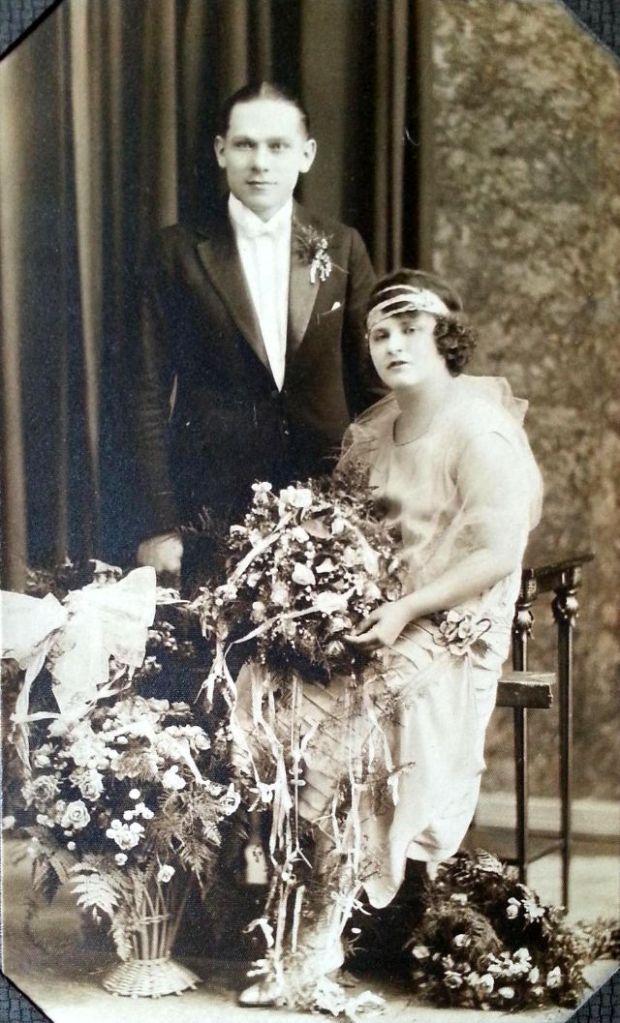
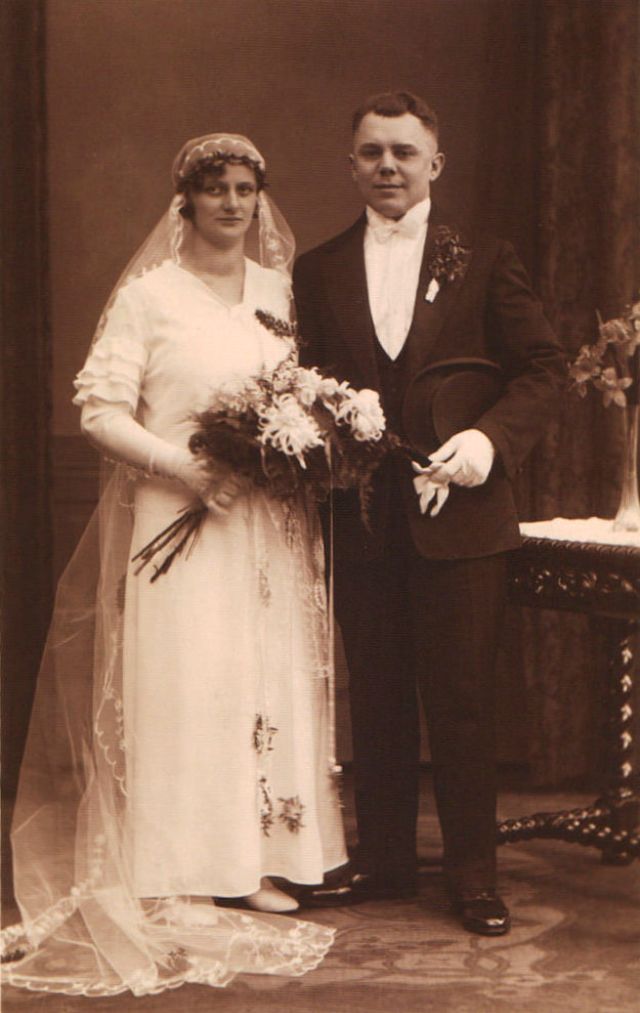
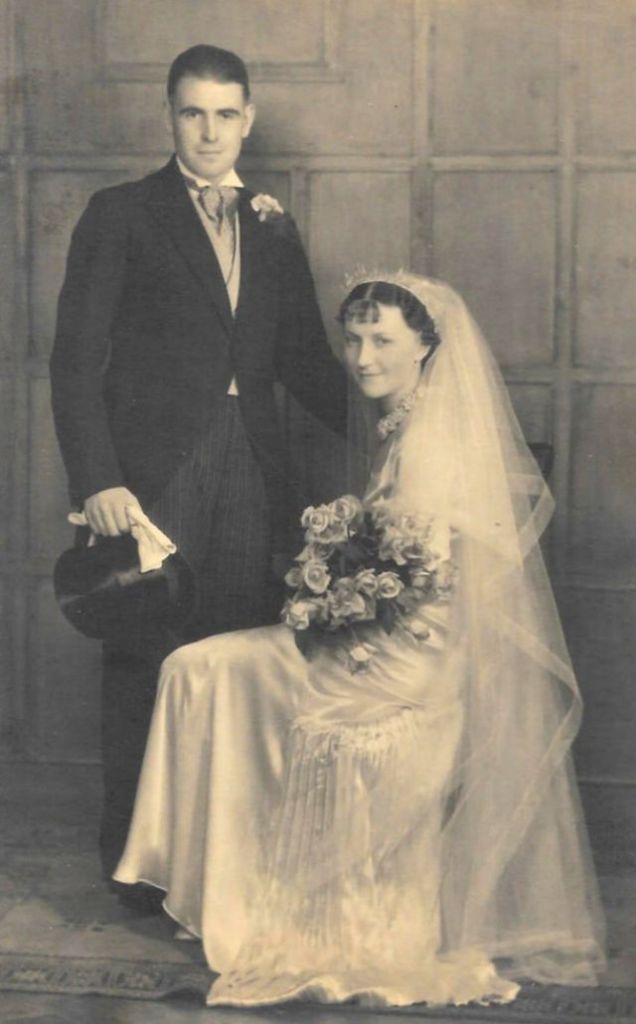
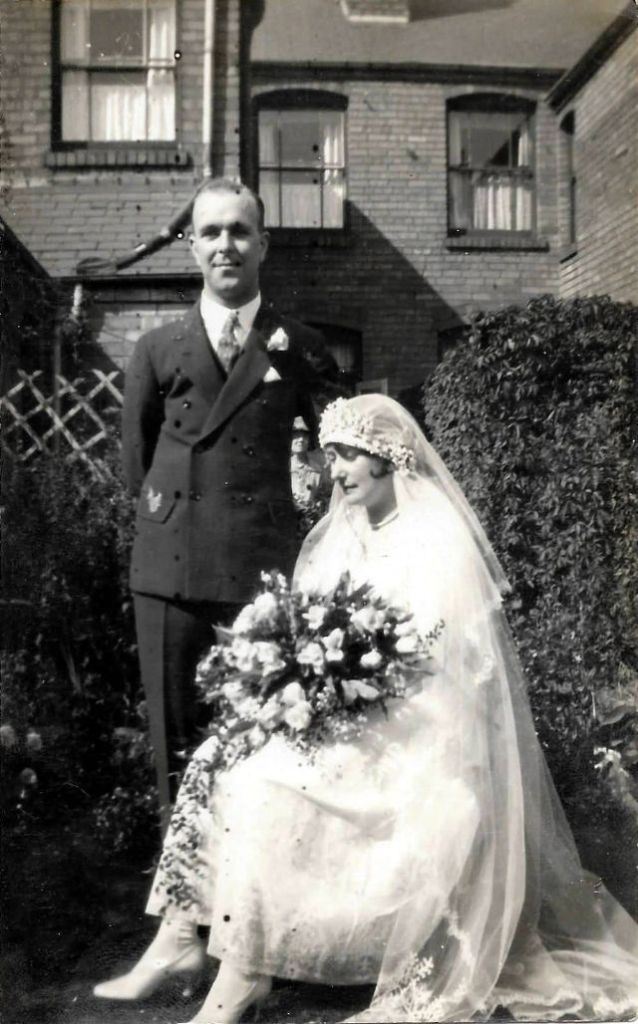
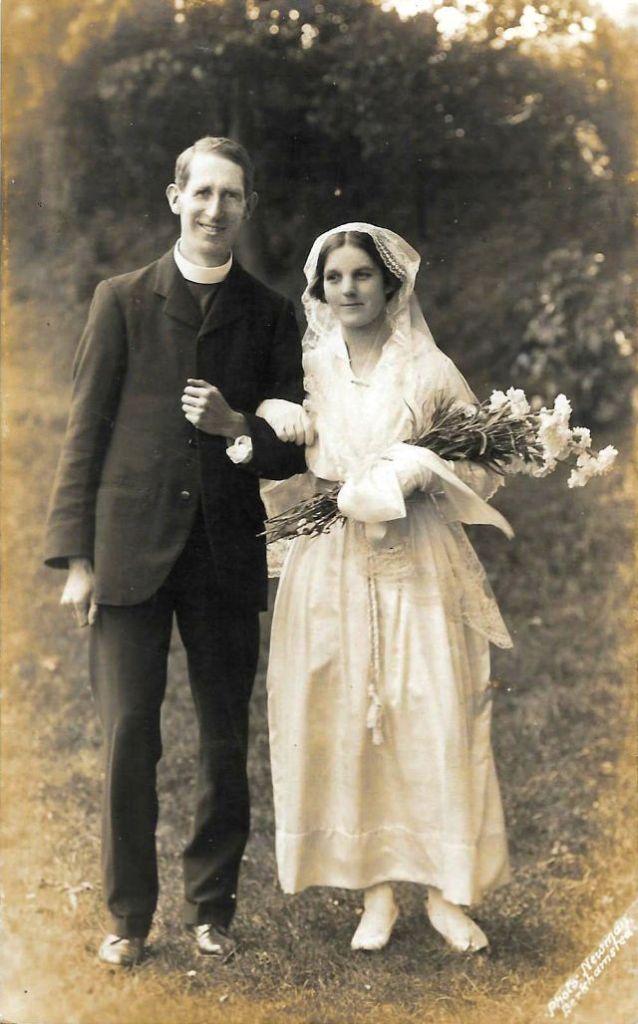
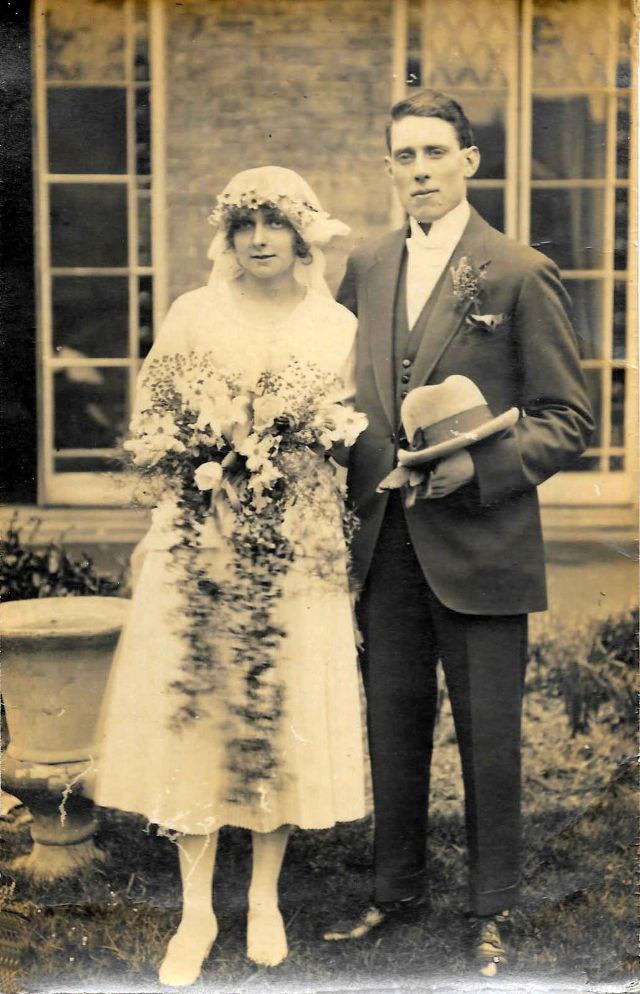
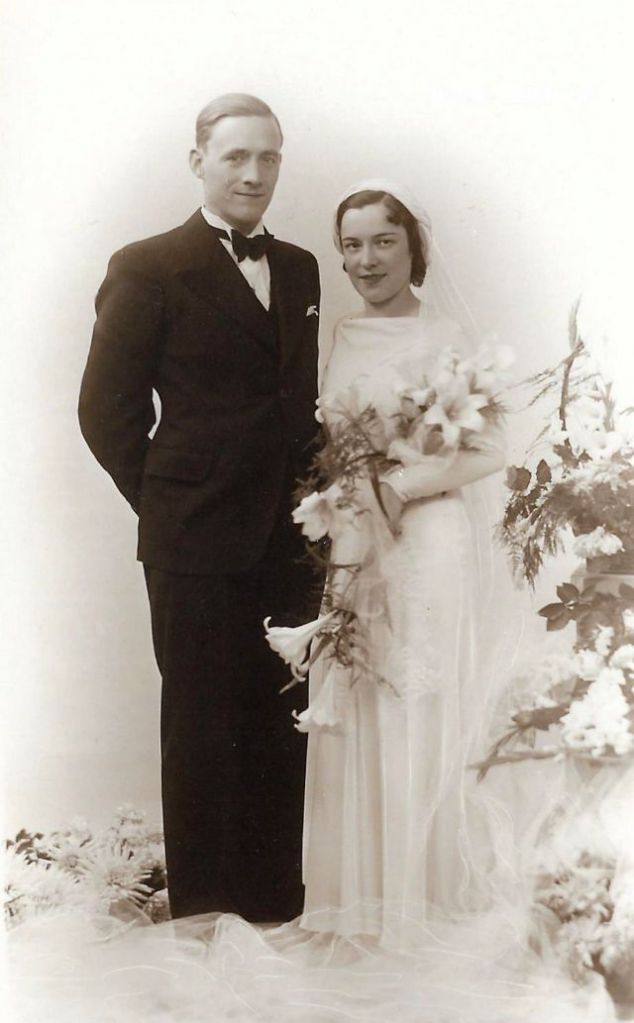
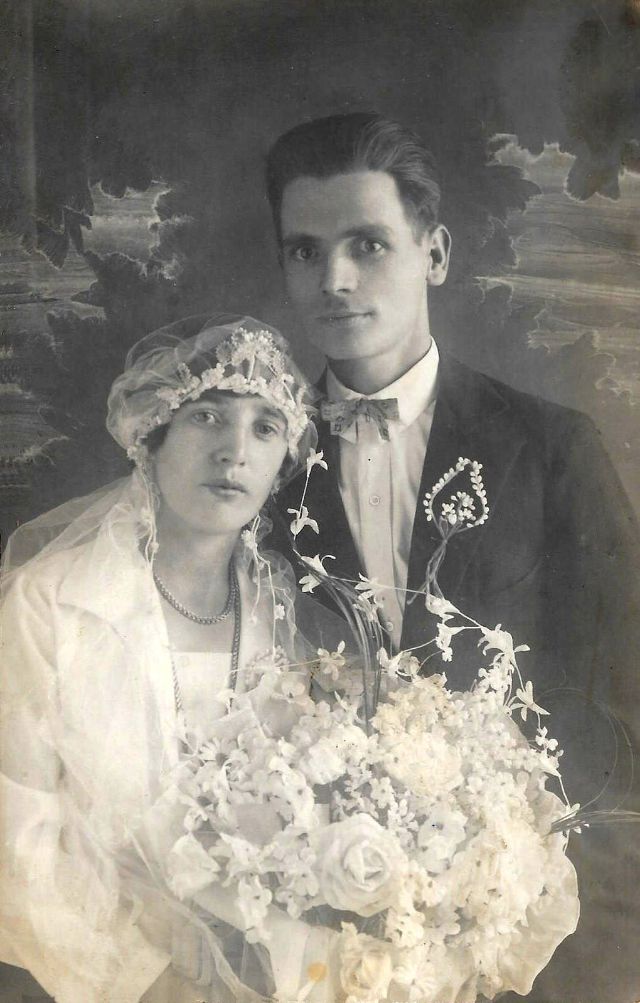
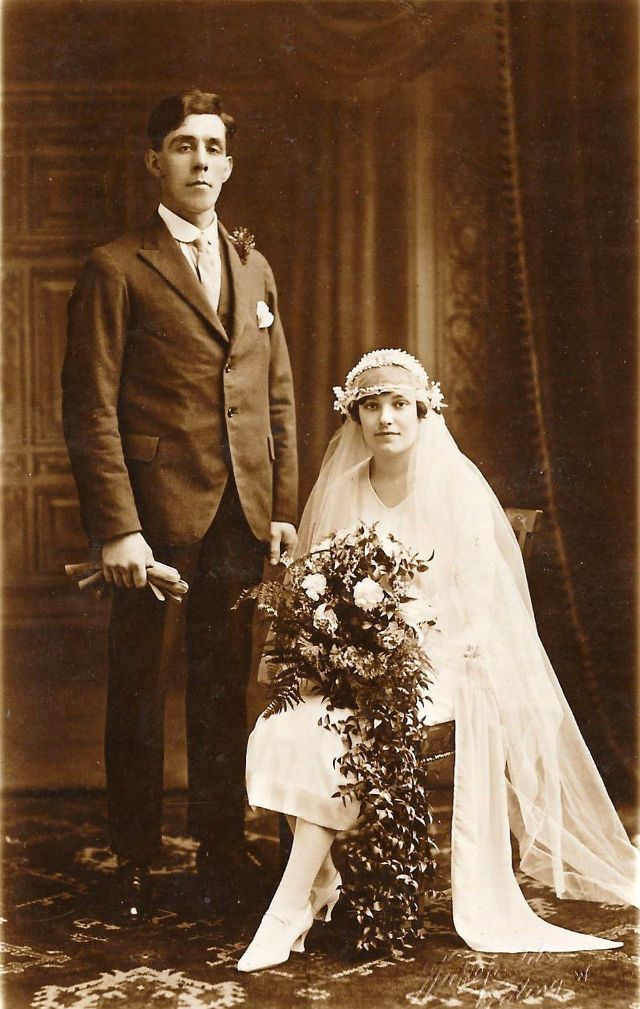
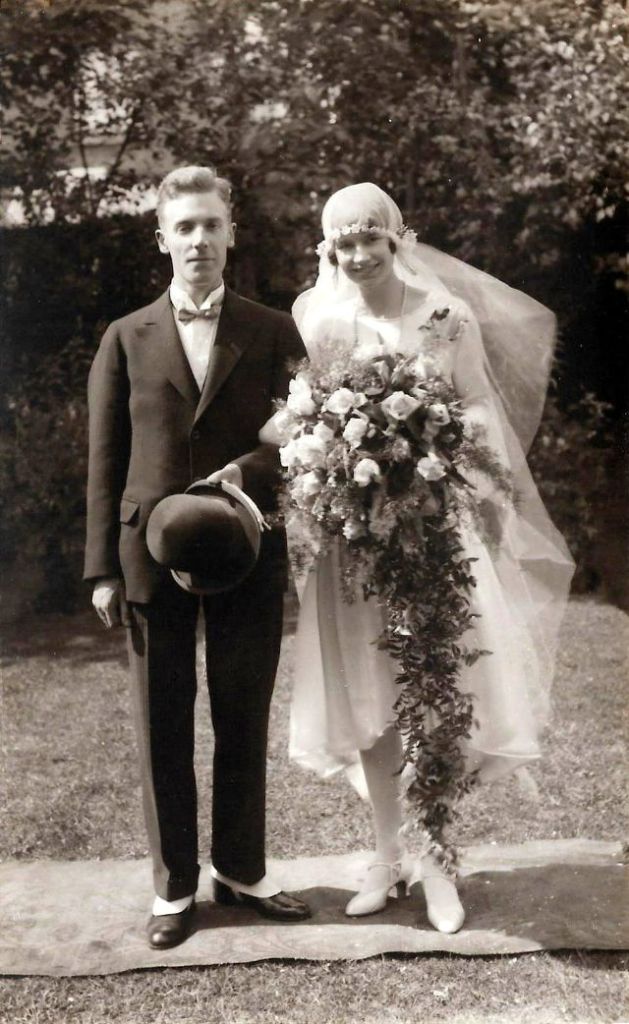
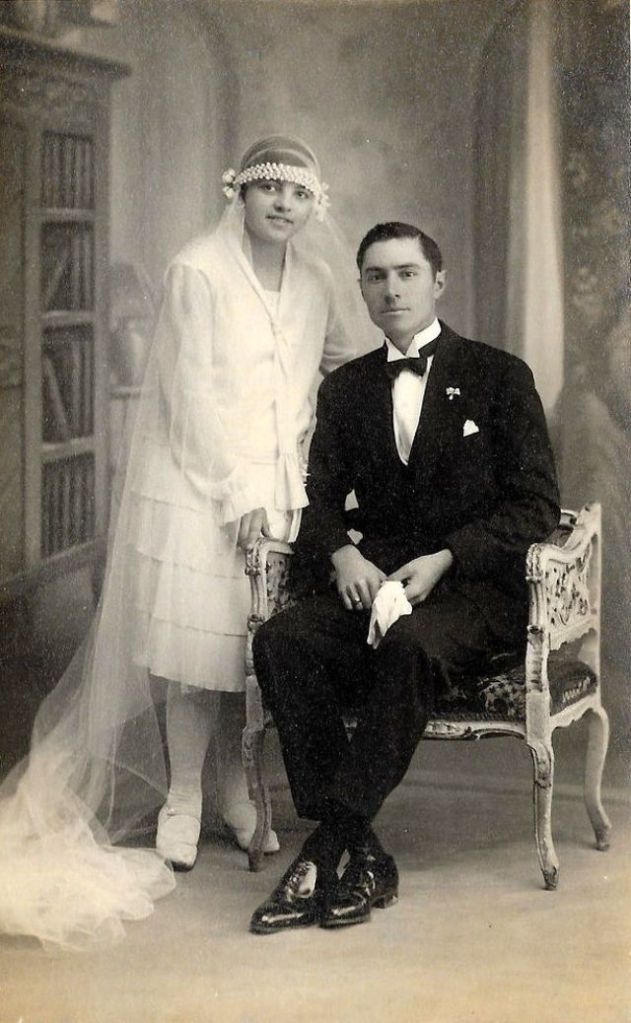
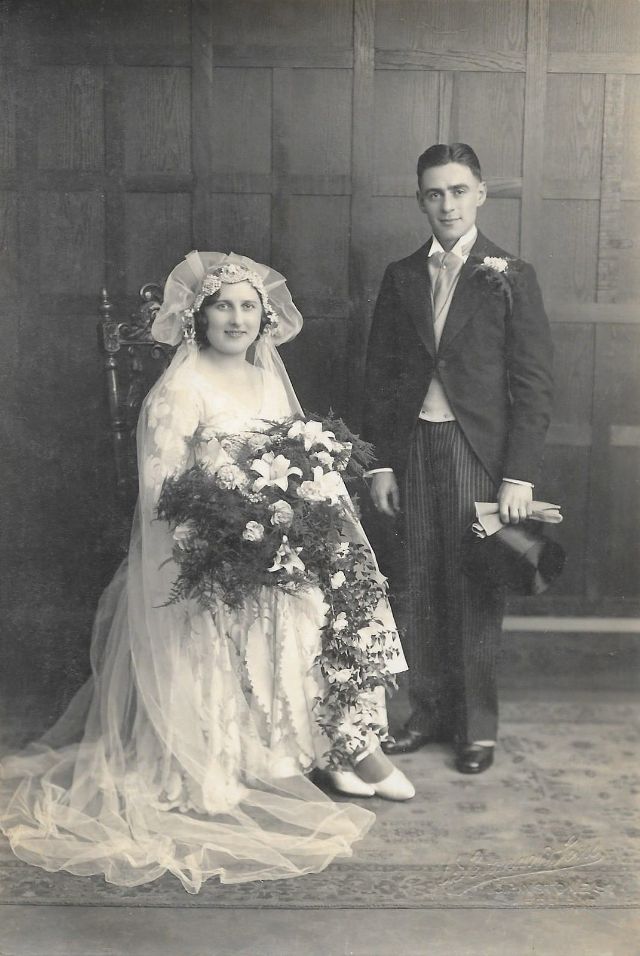
























































Read more of this content when you subscribe today.
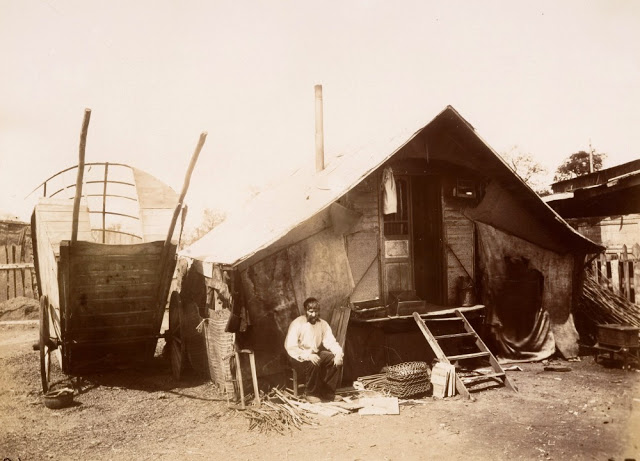
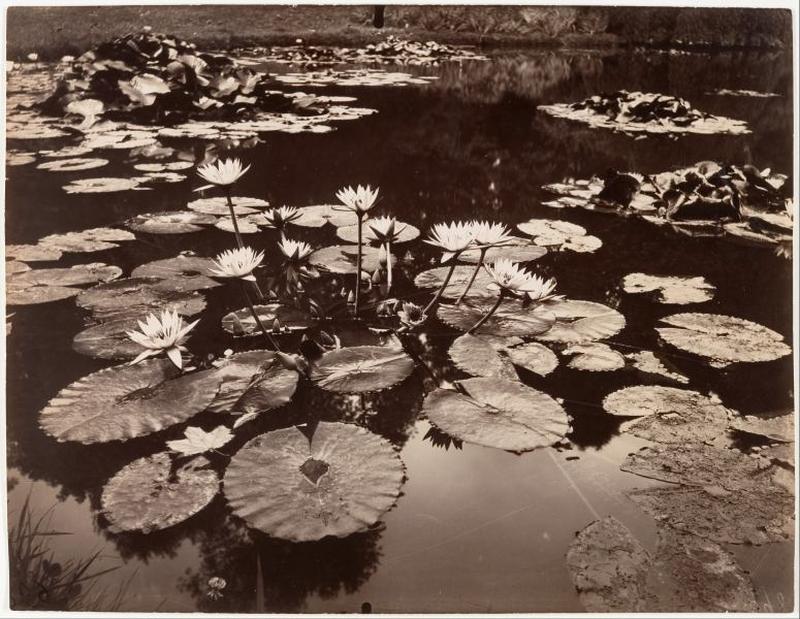
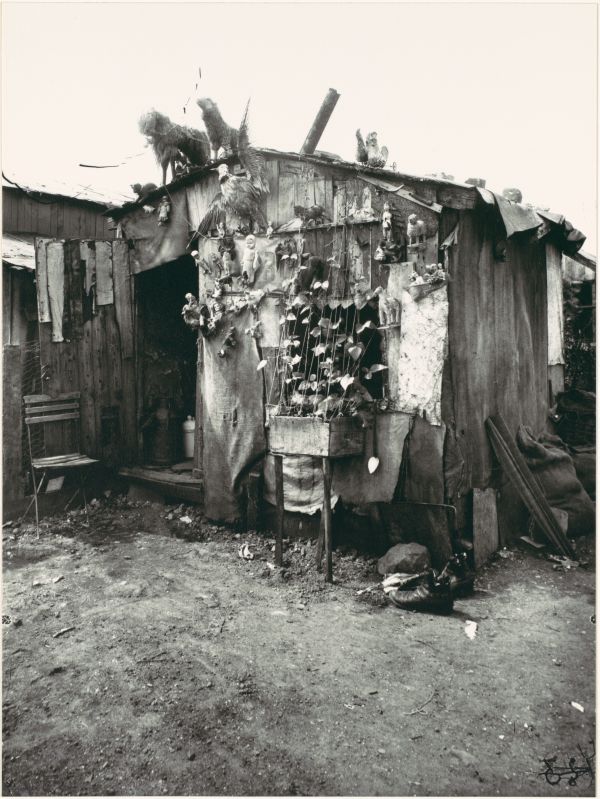
More than any other artist, Walker Evans invented the images of essential America that we have long since accepted as fact, and his work has influenced not only modern photography but also literature, film and visual arts in other mediums.
Walker Evans (1903-1975) took up photography upon his return to New York in 1927, following a year in Paris when his aspiration to become a writer withered in the shadow of Fitzgerald, Hemingway and Joyce. In 1935, Evans was commissioned by the Farm Security Administration to photograph the effects of the Great Depression in the Southeast. During this time he took many of the photographs that appeared in his collaboration with James Agee, Let Us Now Praise Famous Men (1941), a book which has become a defining document of that era. Evans joined the staff of Time magazine in 1945 and shortly thereafter became an editor at Fortune, where he stayed for the next two decades. In 1964, he became a professor at the Yale University School of Art, where he taught until his death in 1975.
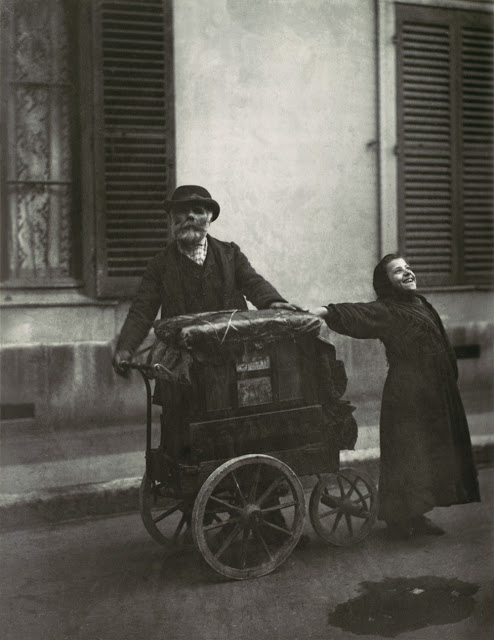
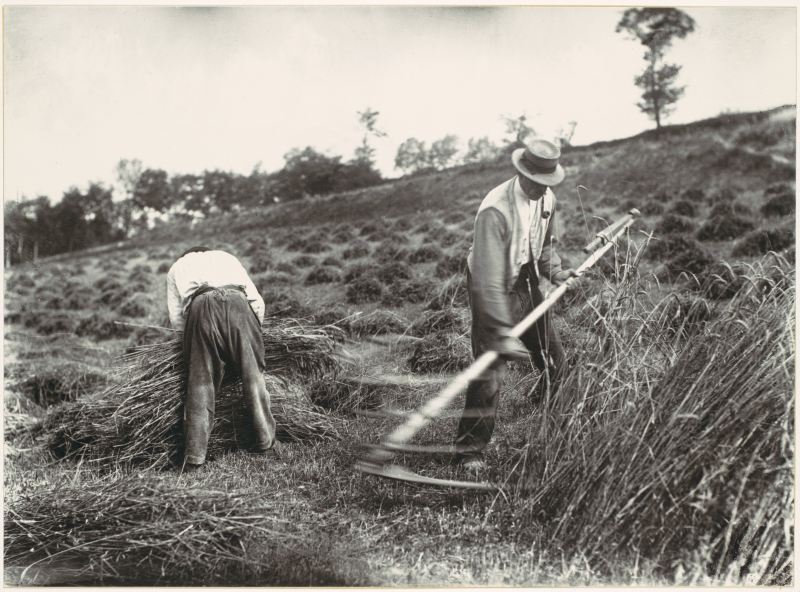
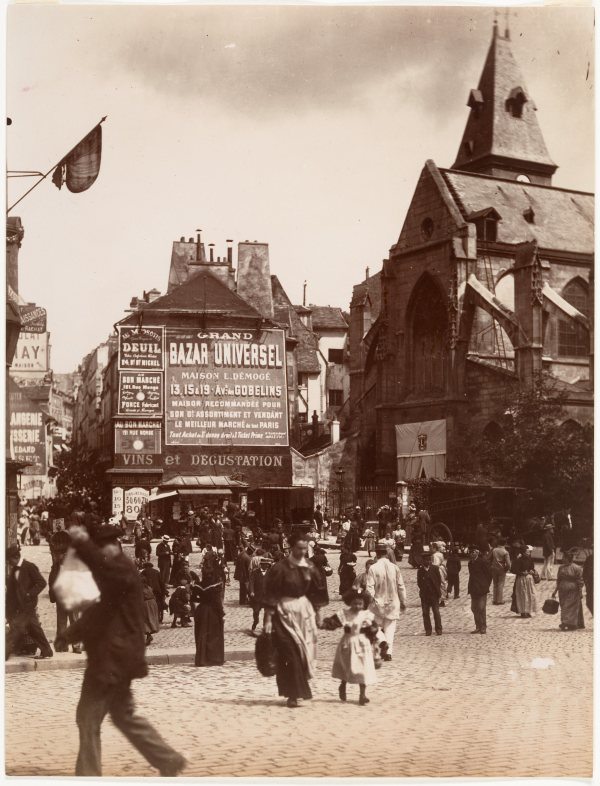
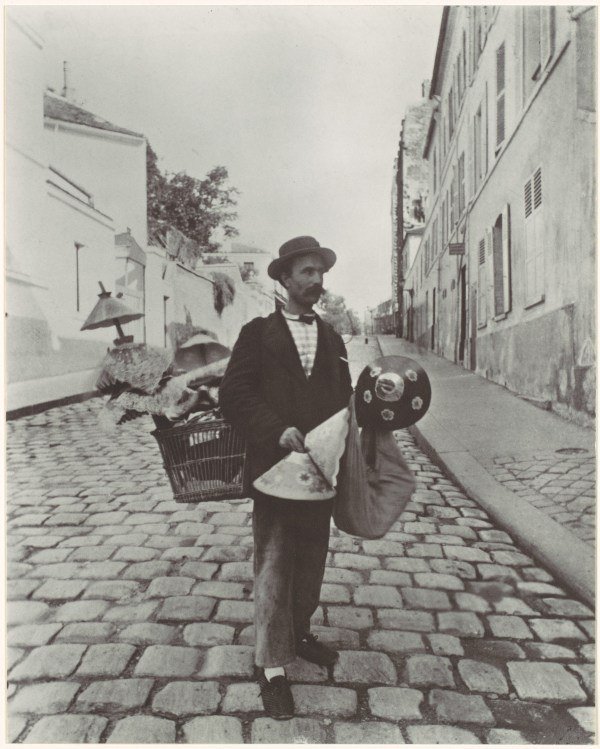
Below is a collection of 20 impressive color photographs taken by Walker Evans in New York in the 1950s.


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.

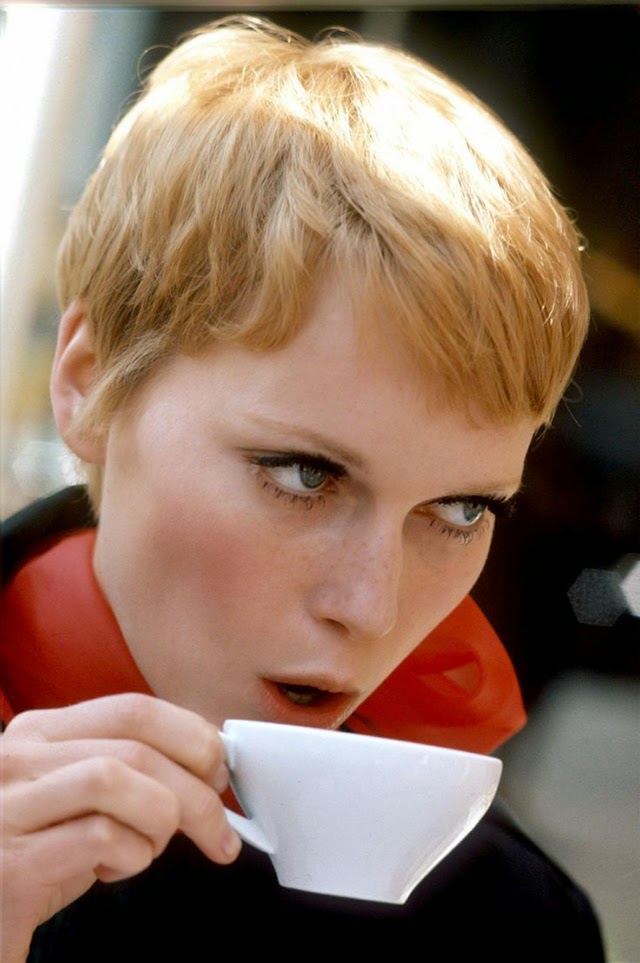
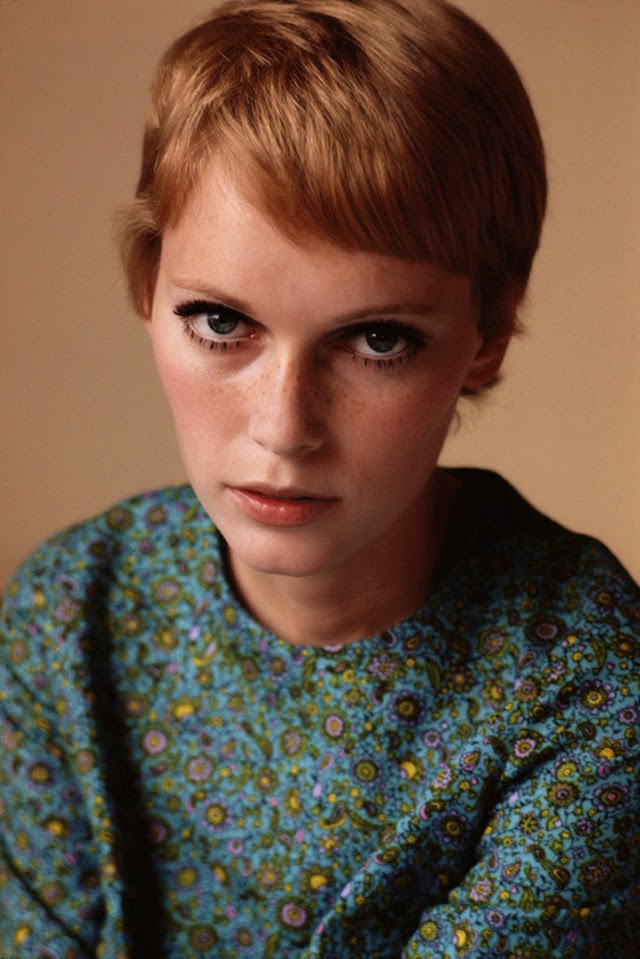
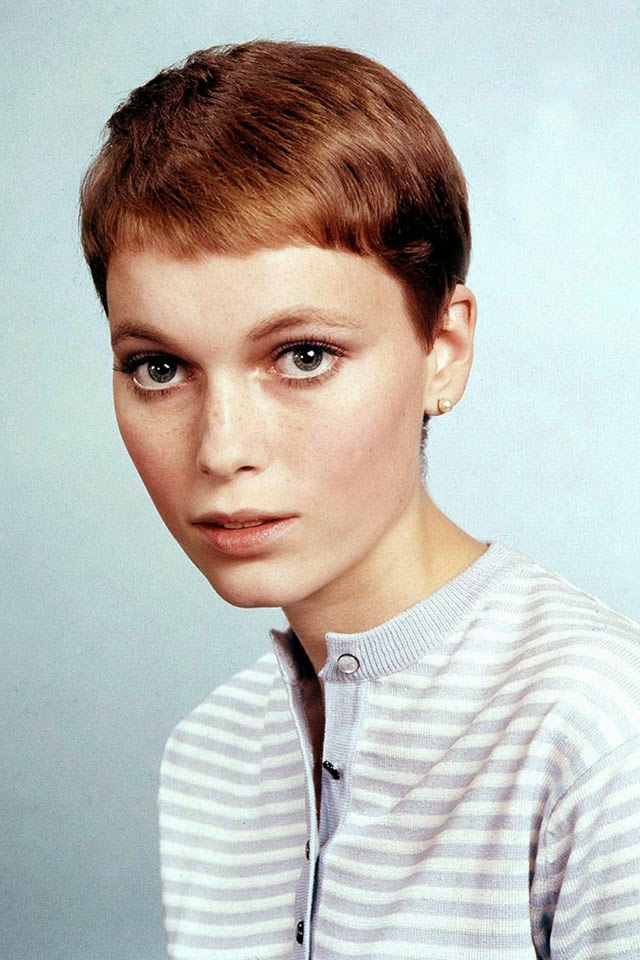
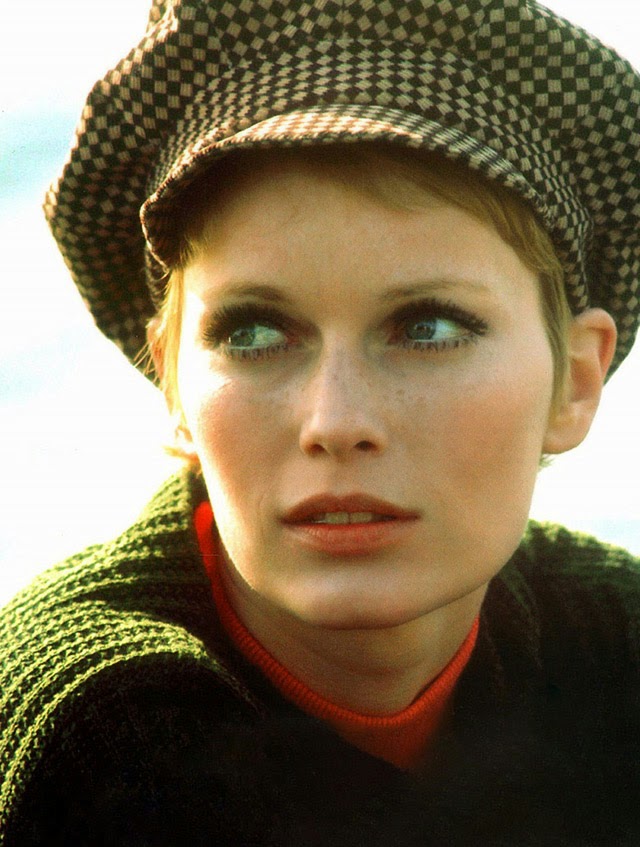
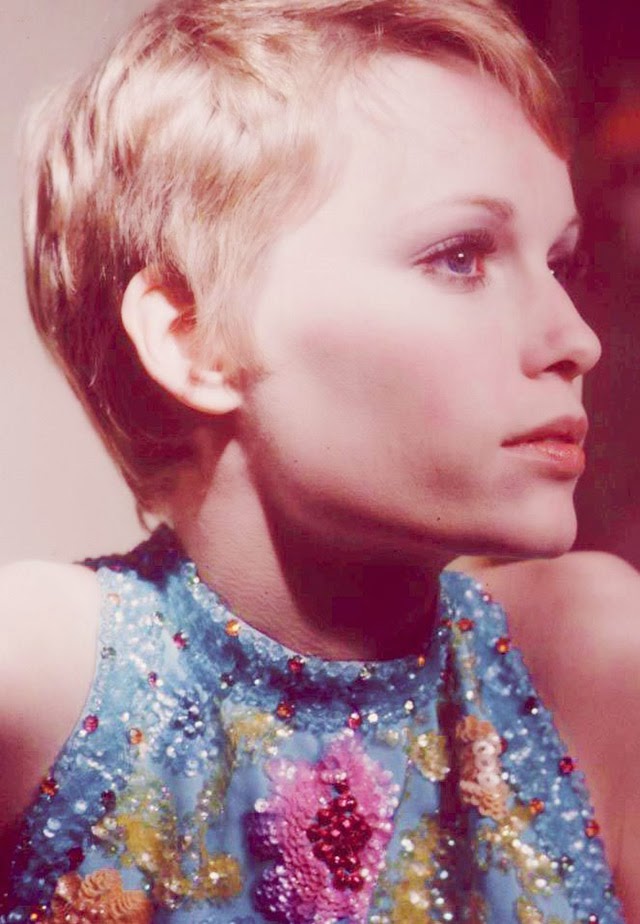
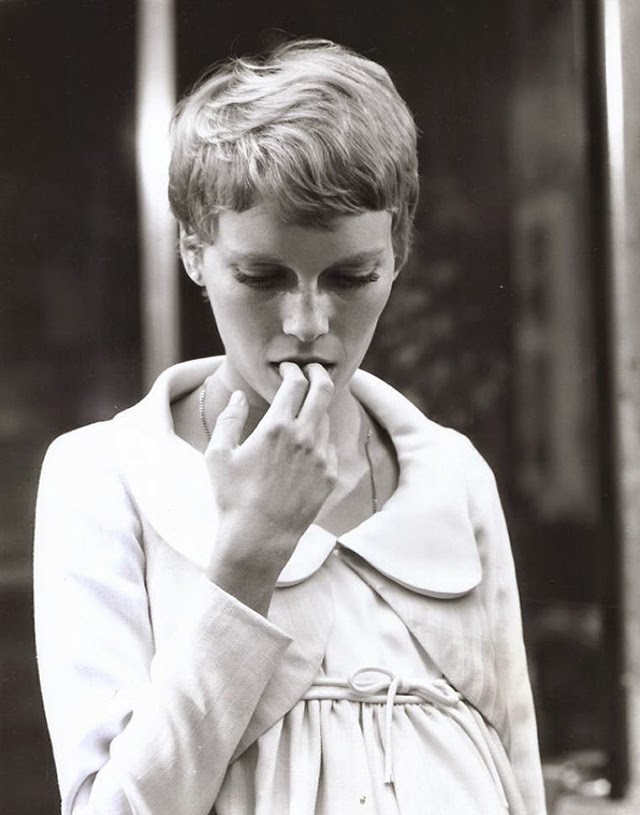
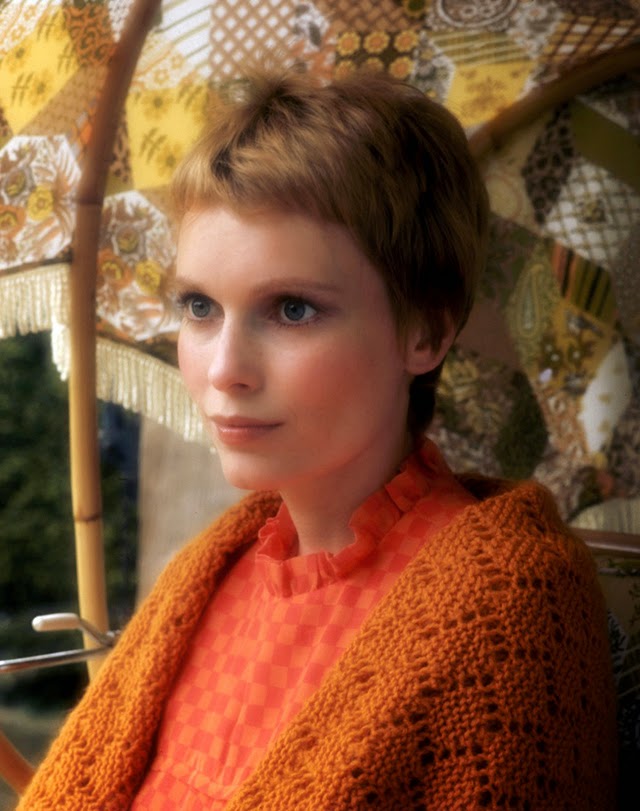
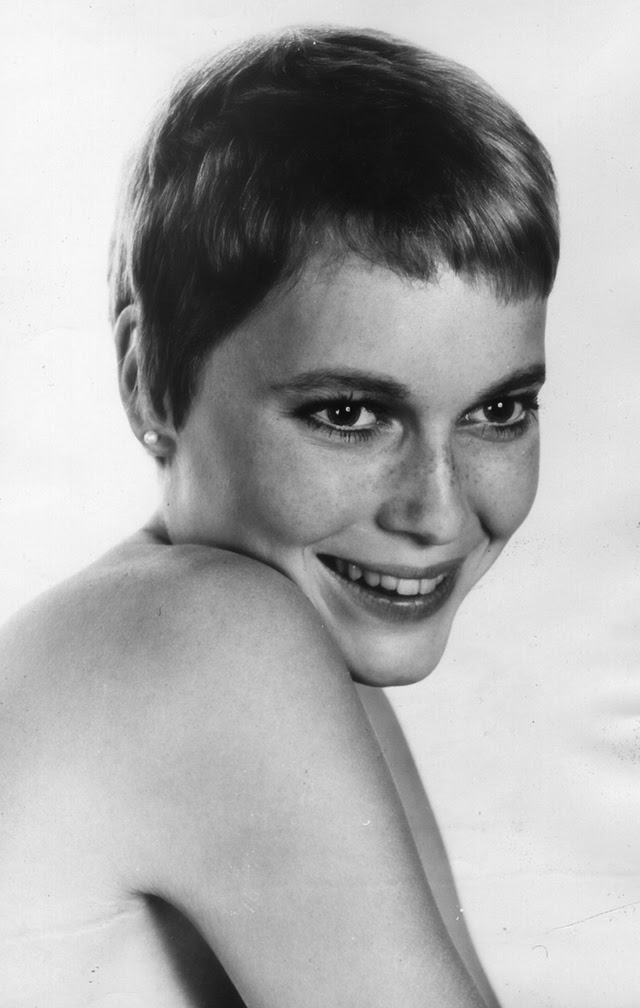
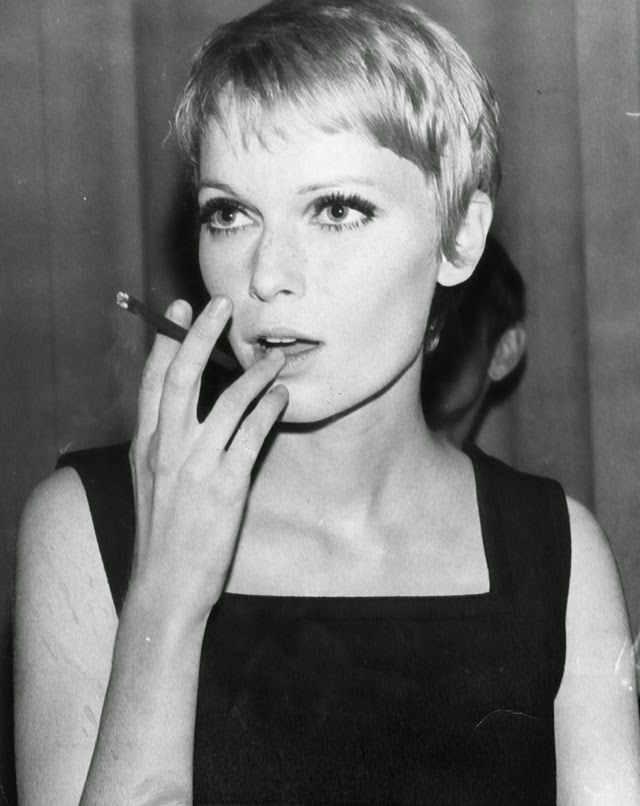
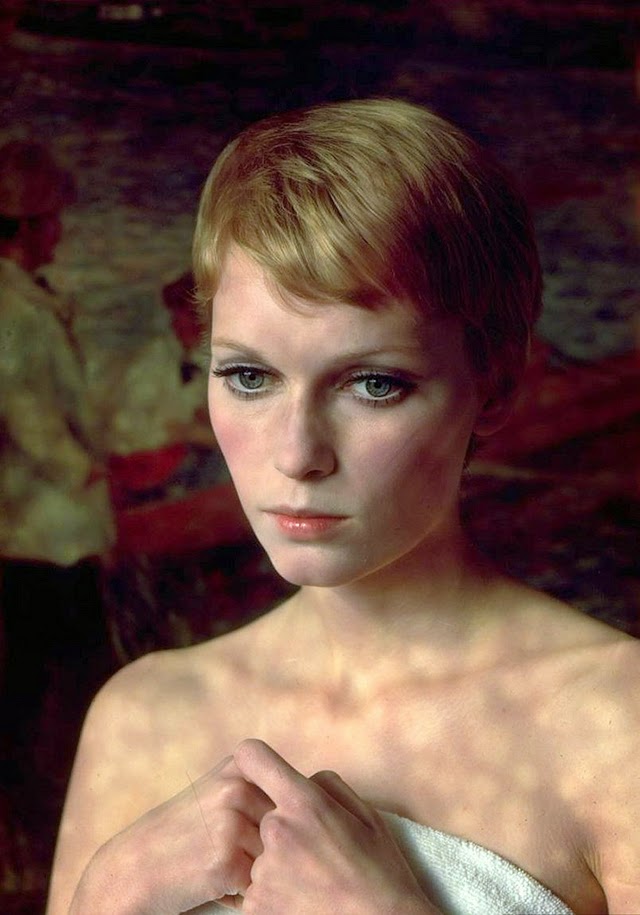
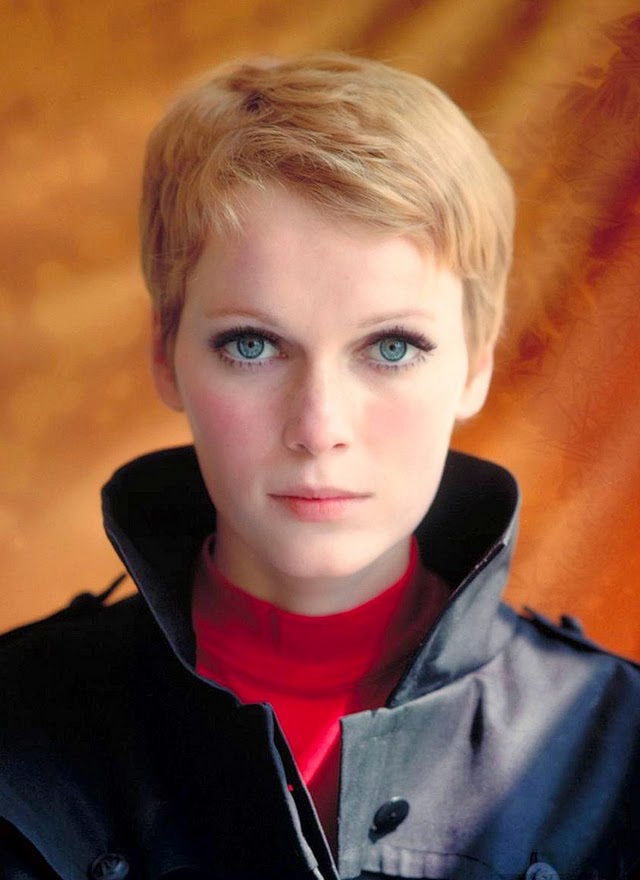
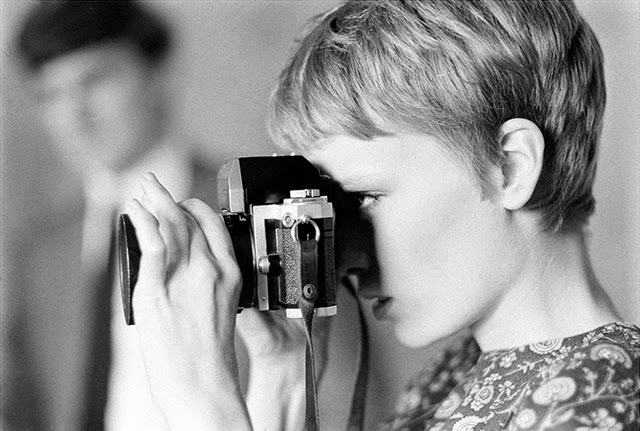
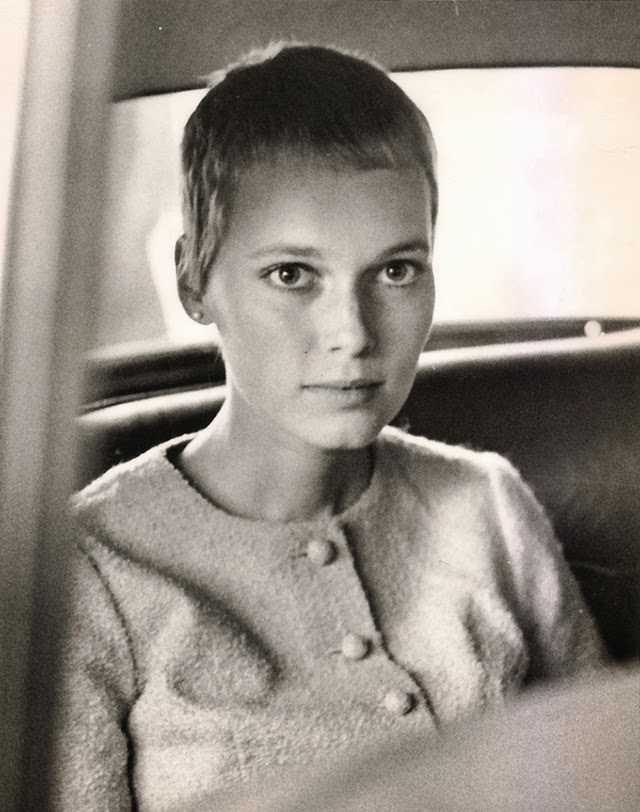
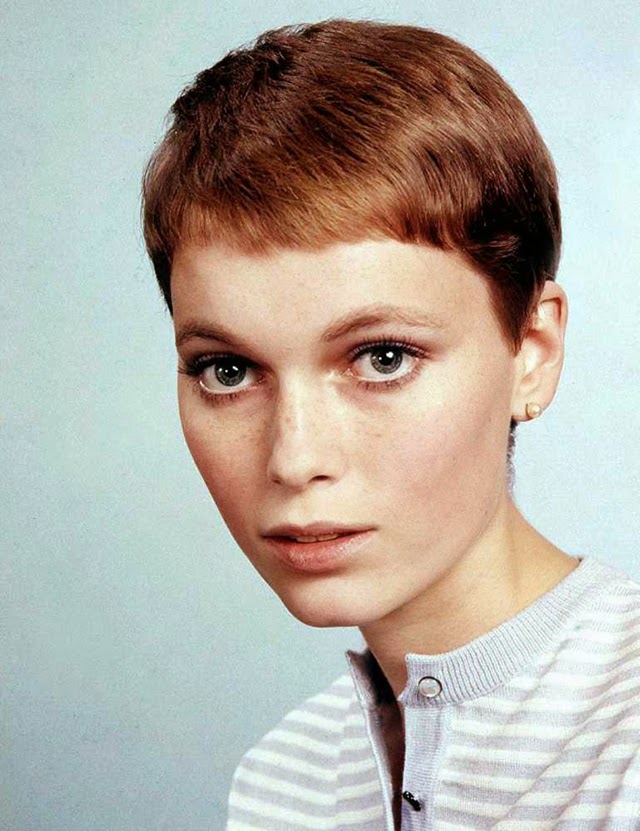
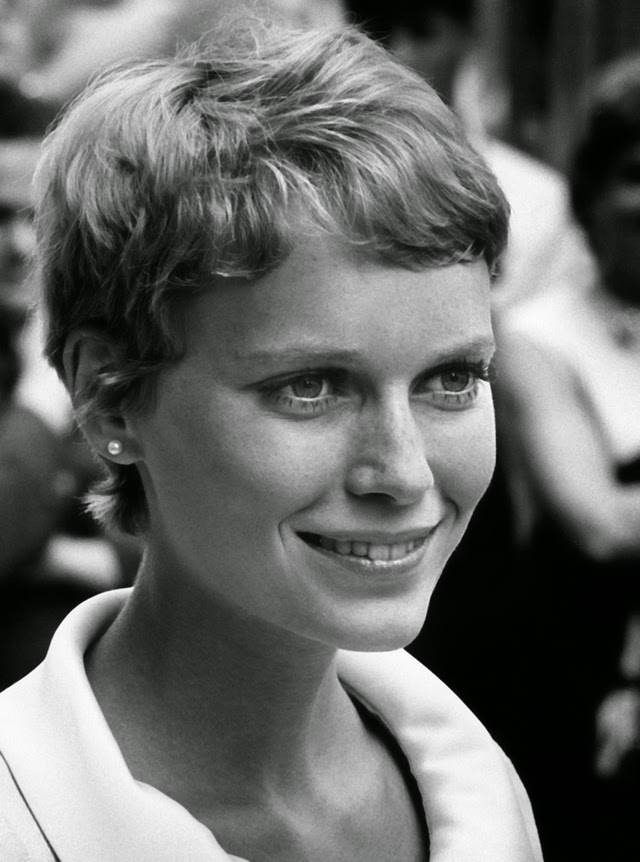
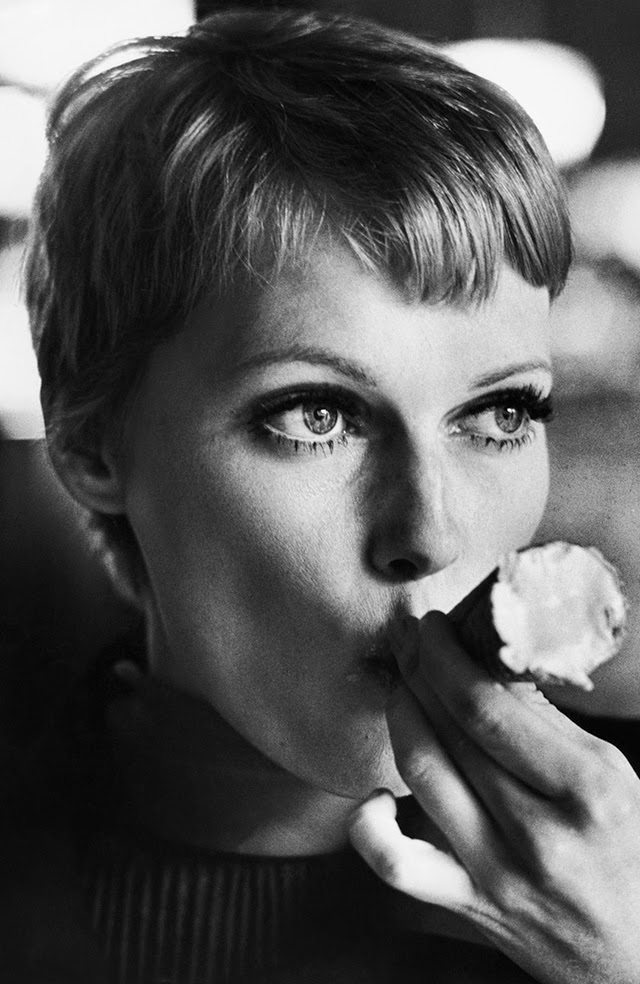
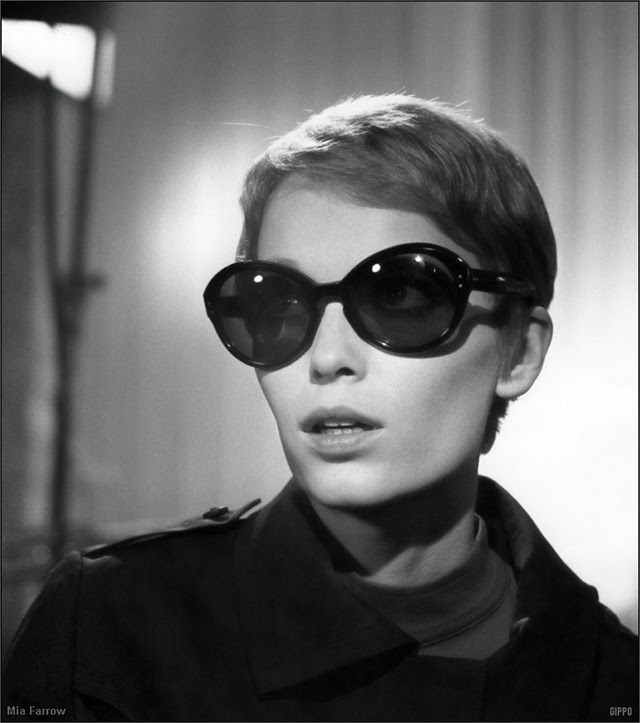
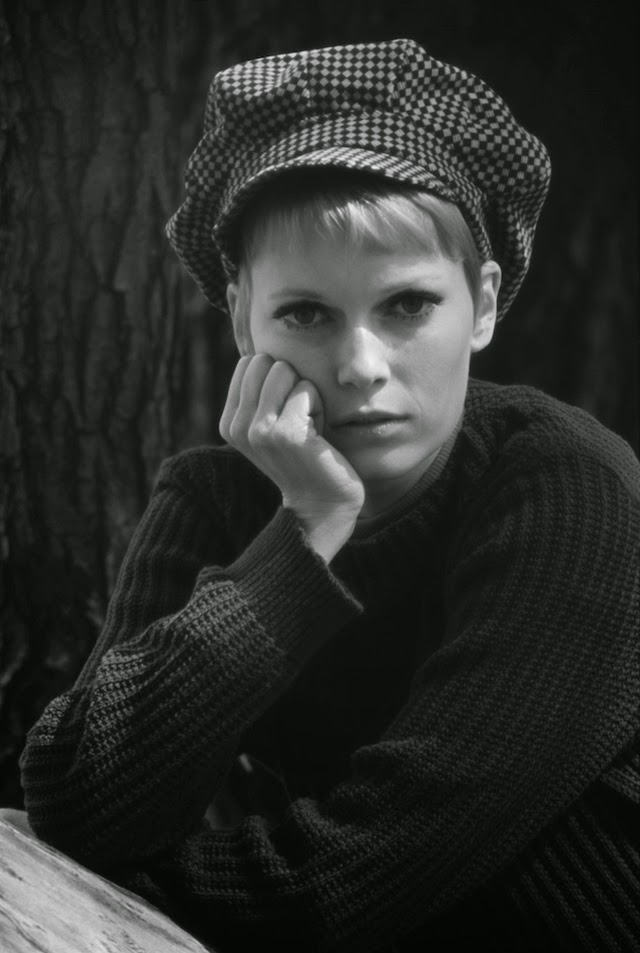
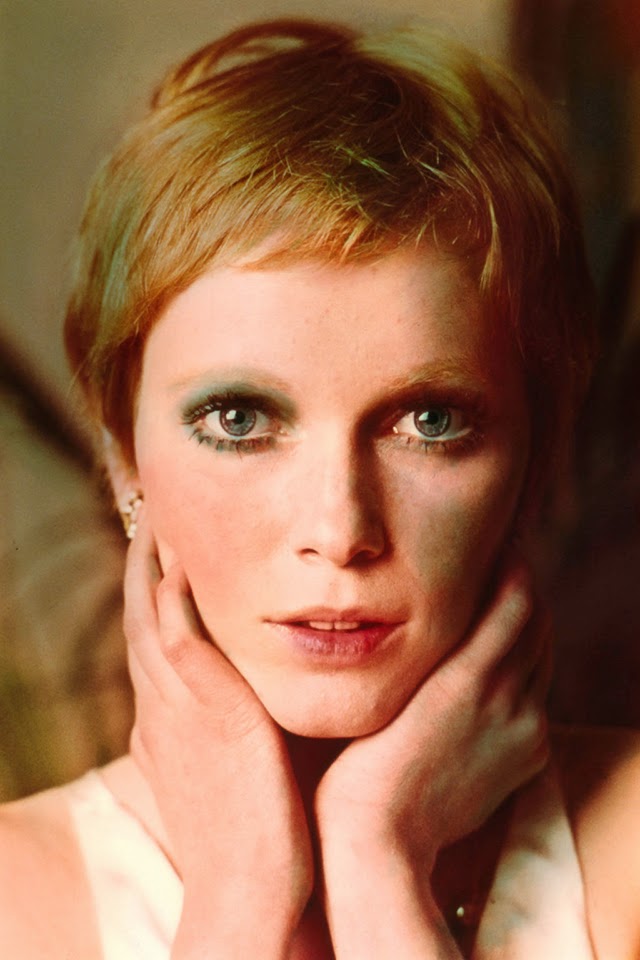
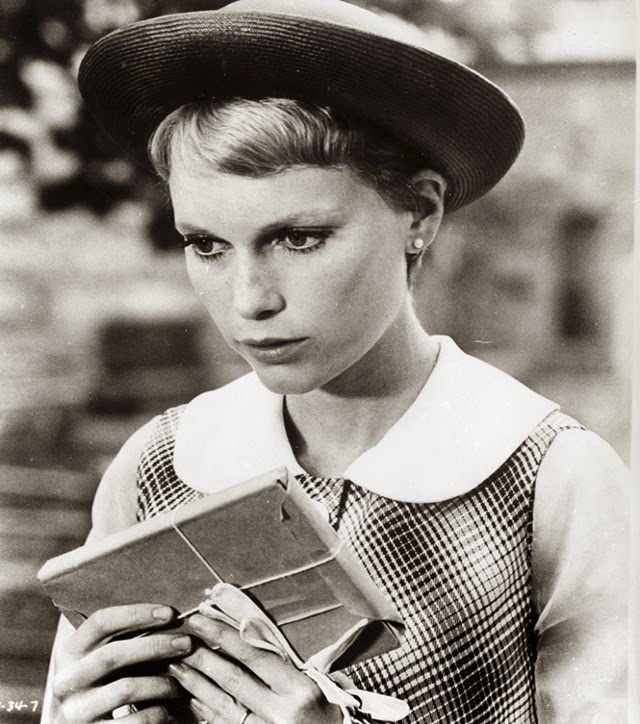
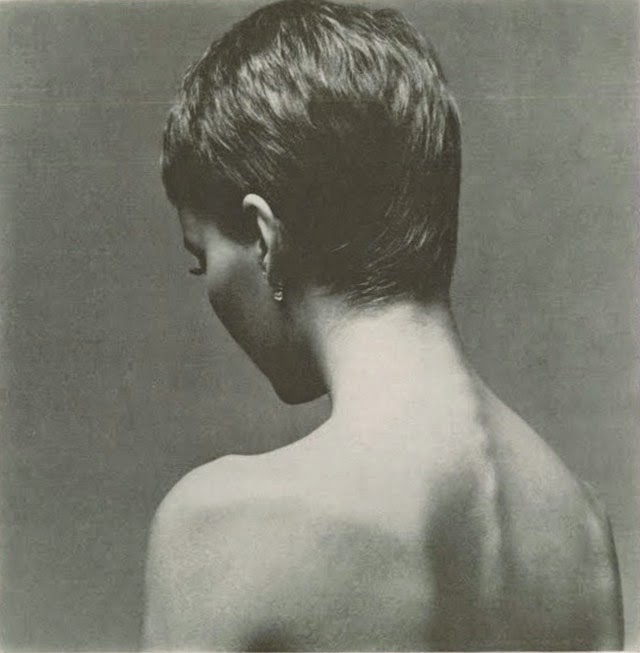
Maria de Lourdes Villiers “Mia” Farrow (born February 9, 1945) is an American actress, activist, and former fashion model who has appeared in more than 50 films. She has won numerous awards, including a Golden Globe, and been nominated for three BAFTA Awards. She is also known for her extensive work as a UNICEF Goodwill Ambassador, including her humanitarian activities in Darfur, Chad and the Central African Republic. In 2008 Time magazine named her one of the most influential people in the world.
The eldest daughter of Australian director John Farrow and Irish actress Maureen O’Sullivan, Farrow had a strict Catholic upbringing in Beverly Hills, California. After working as a fashion model during her teenage years, she first gained notice for her role as Allison MacKenzie in the television soap opera Peyton Place (1964–1966). Her credited feature film debut in Guns at Batasi (1964) earned her a Golden Globe Award for New Star of the Year, and she gained further recognition for her subsequent two-year marriage to Frank Sinatra, whom she married at age 21. Her portrayal of Rosemary Woodhouse in Roman Polanski’s horror film Rosemary’s Baby (1968) earned her a nomination for a BAFTA Award and a Golden Globe Award for Best Actress. She received a third Golden Globe nomination for her role in John and Mary (1969).
In 1971, Farrow became the first American actress in history to join the Royal Shakespeare Company, appearing as Joan of Arc in a production of Jeanne d’Arc au bûcher. This was followed by stage productions of Mary Rose (1972), Three Sisters (1973), and Ivanov (1976). She also starred in several films throughout the 1970s, including the 1974 film adaptation of The Great Gatsby and Robert Altman’s comedy A Wedding (1978).
Farrow began a relationship with filmmaker Woody Allen in 1979, and over a decade-long period starred in 13 of his films, beginning with A Midsummer Night’s Sex Comedy (1982). She received numerous critical accolades for her performances in several Allen films, including Golden Globe Award nominations for Broadway Danny Rose (1984), The Purple Rose of Cairo (1985), and Alice (1990), as well as a BAFTA nomination for Hannah and Her Sisters (1986). After separating from Allen in 1992, she made public allegations that he sexually assaulted their seven-year-old adopted daughter, Dylan. She retained custody of Dylan, and Allen was never charged with a crime and has vigorously denied the allegation. These claims received significant renewed public attention after Dylan recounted the alleged assault in a 2013 interview.
Since the 2000s, Farrow has made occasional appearances on television, including a recurring role on Third Watch (2001–2003). She has also had supporting parts in films such as The Omen (2006), Be Kind Rewind (2008), and Dark Horse (2011). She appeared in a Broadway revival of Love Letters in 2014. She has dedicated significant periods to raising her adopted and biological children, and taken part in humanitarian efforts abroad, particularly involving human rights in African countries. (Wikipedia)
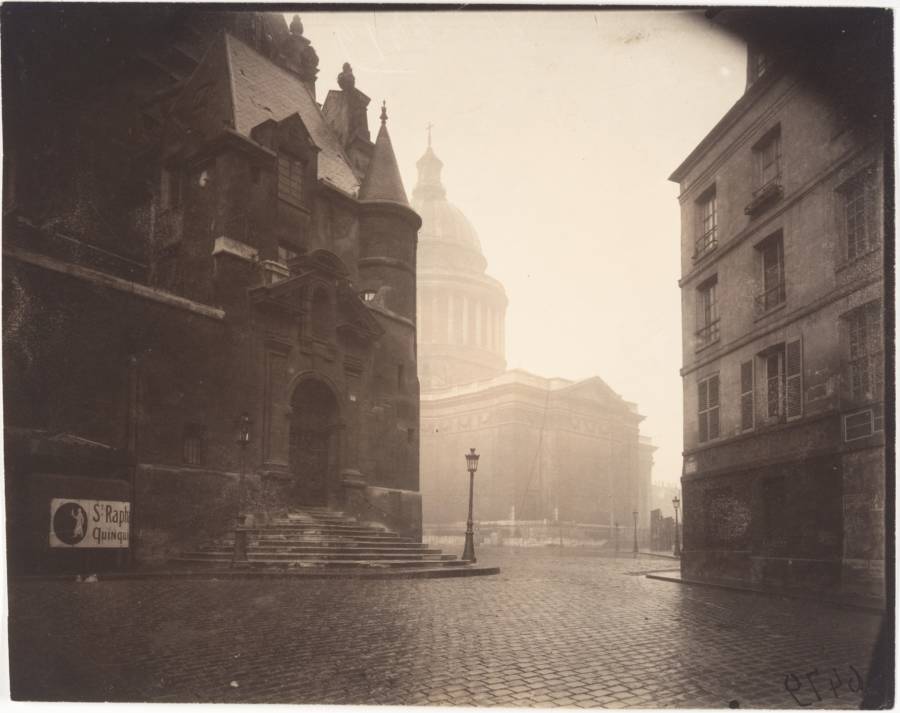






























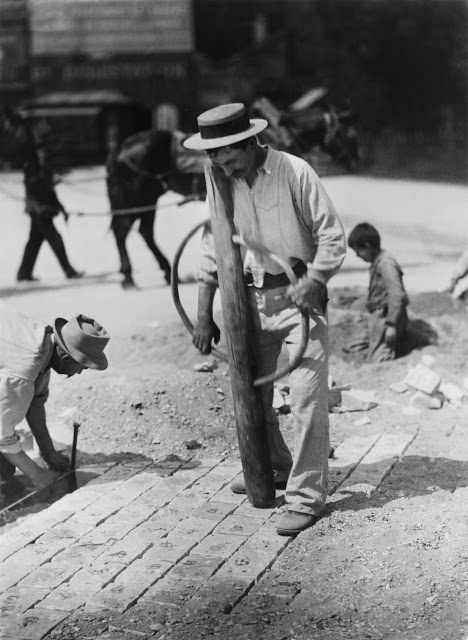
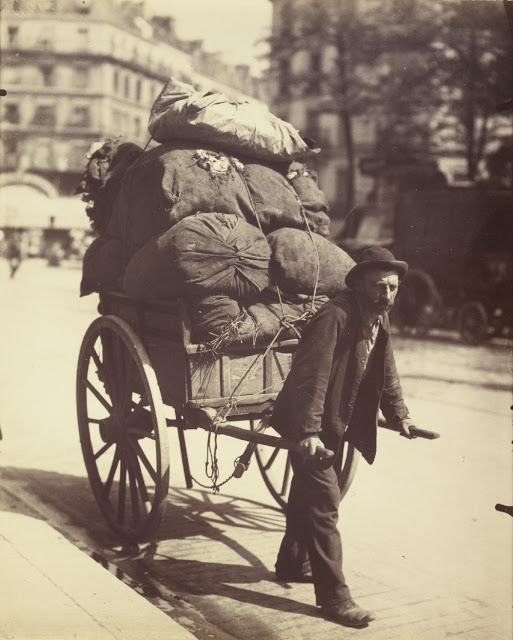
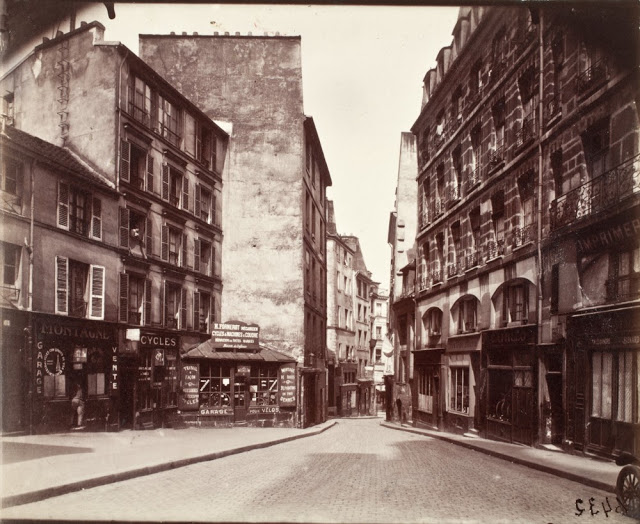
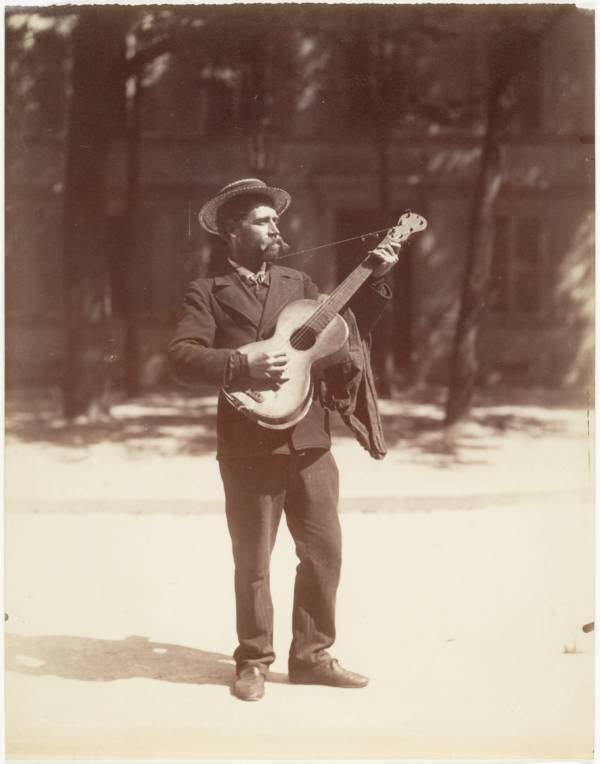
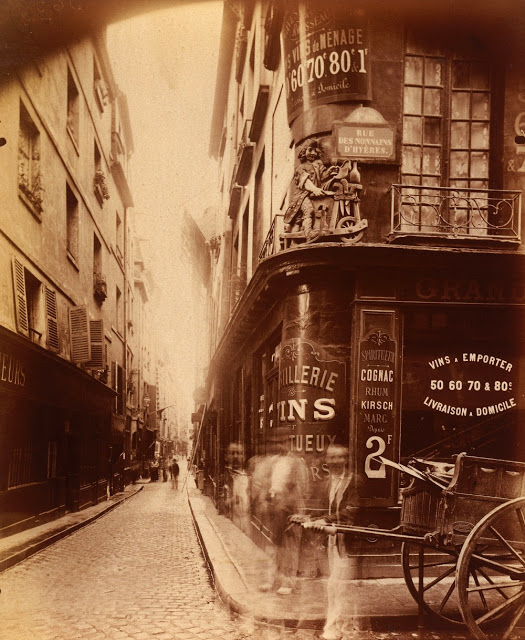
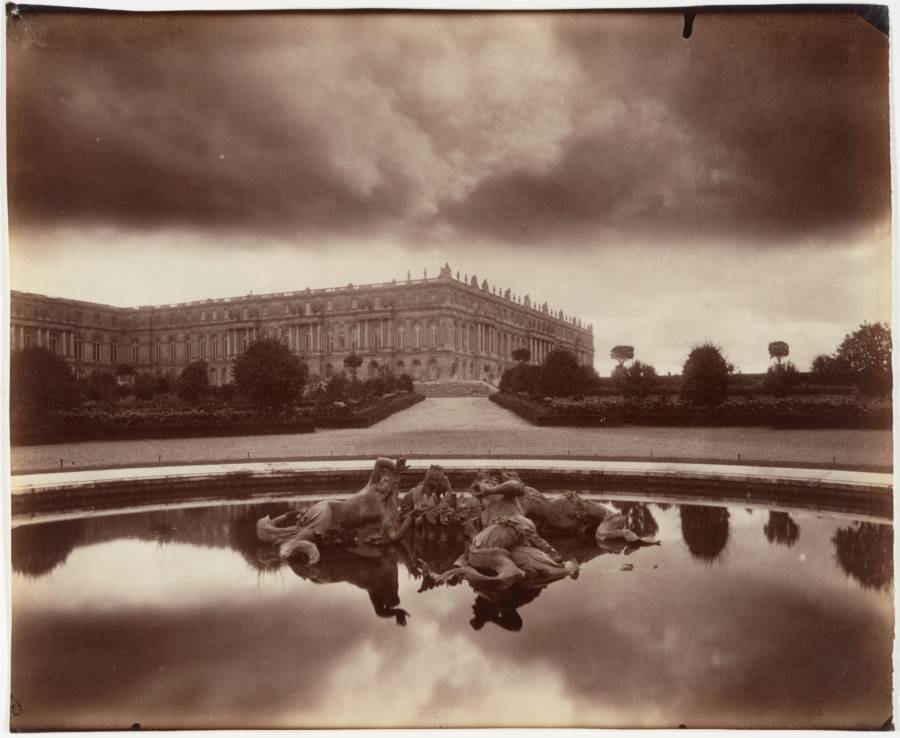
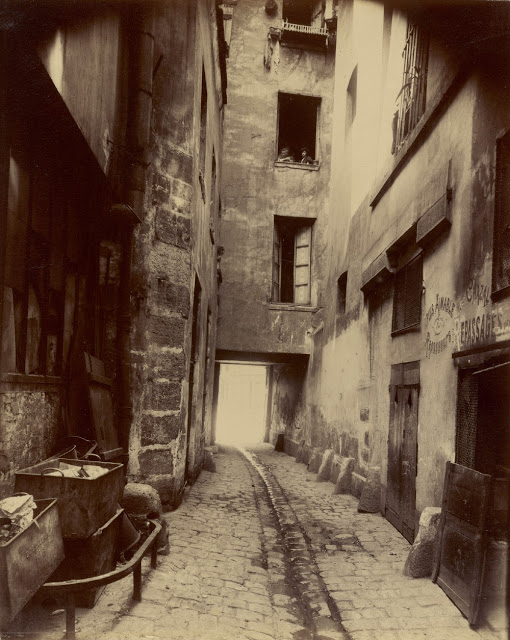
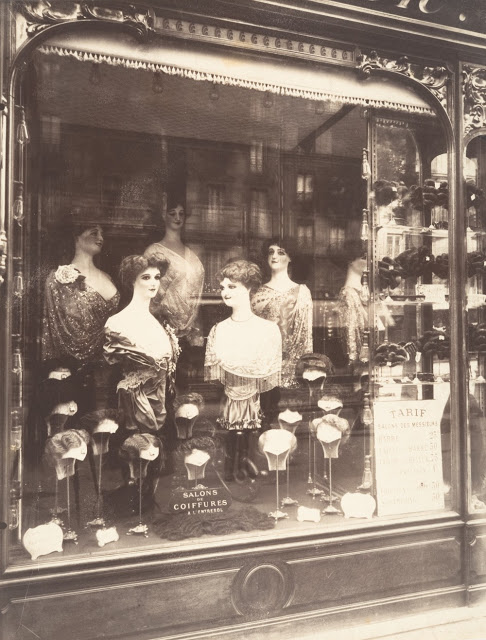
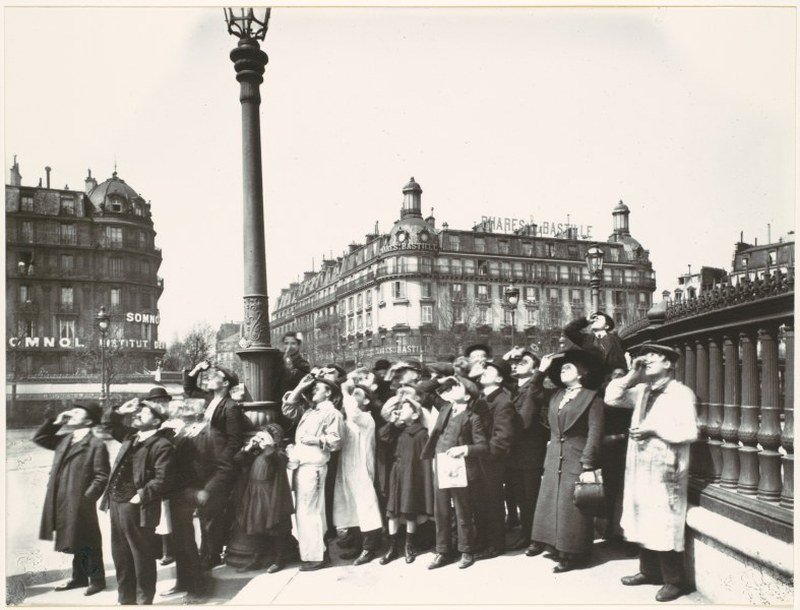
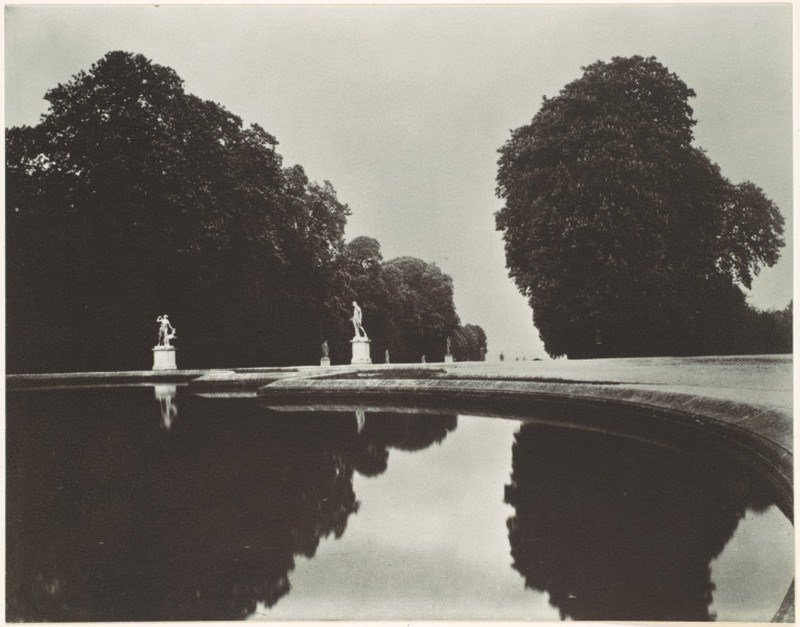
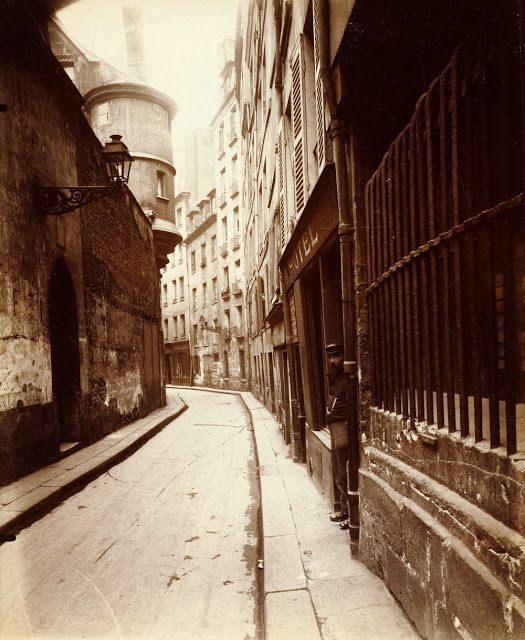
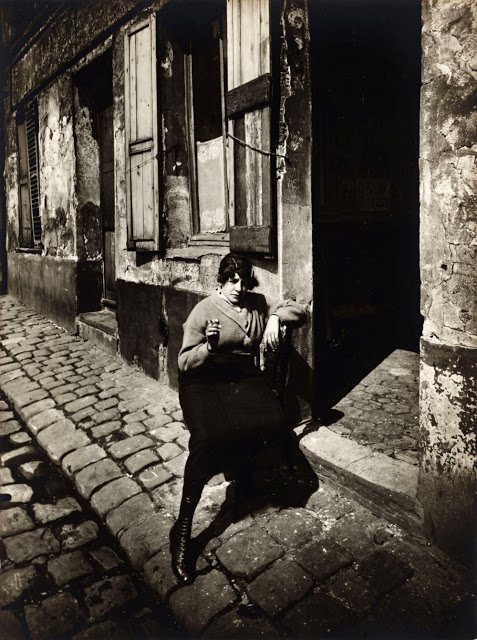
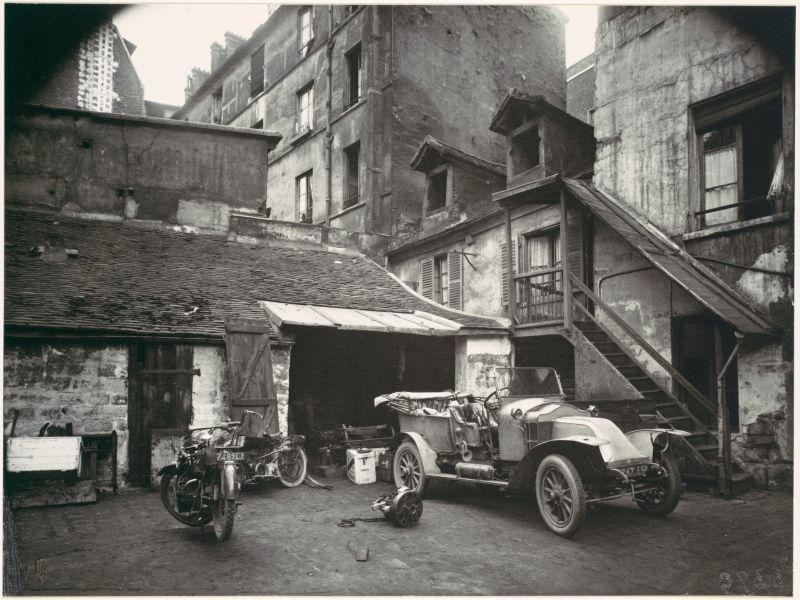
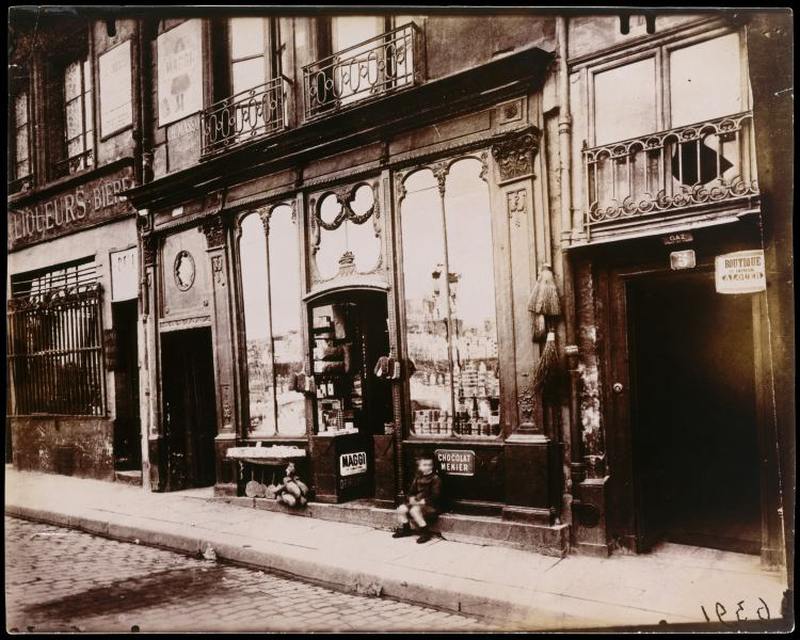
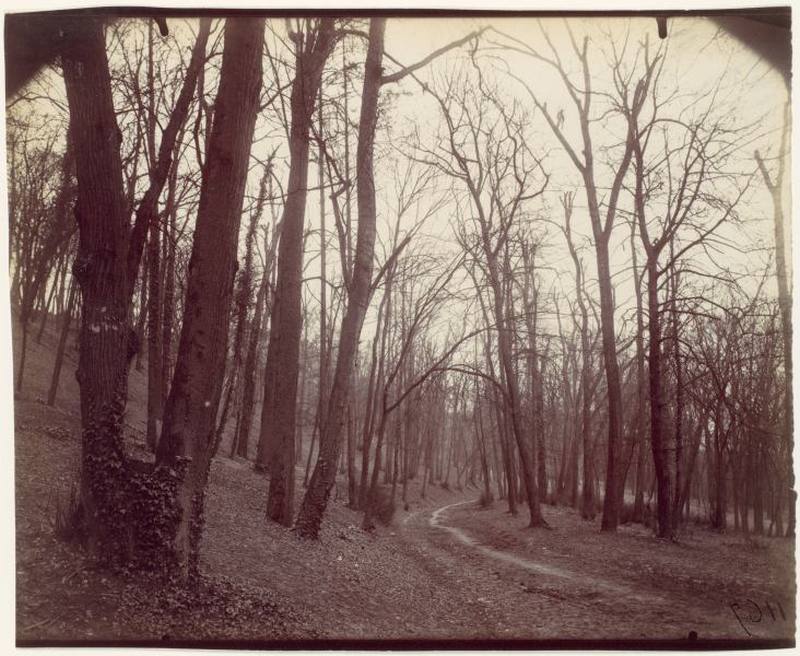
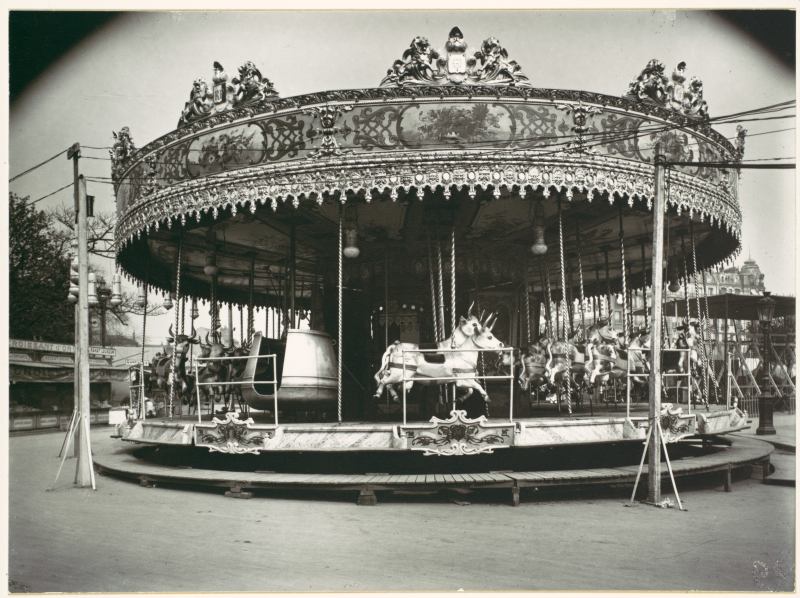
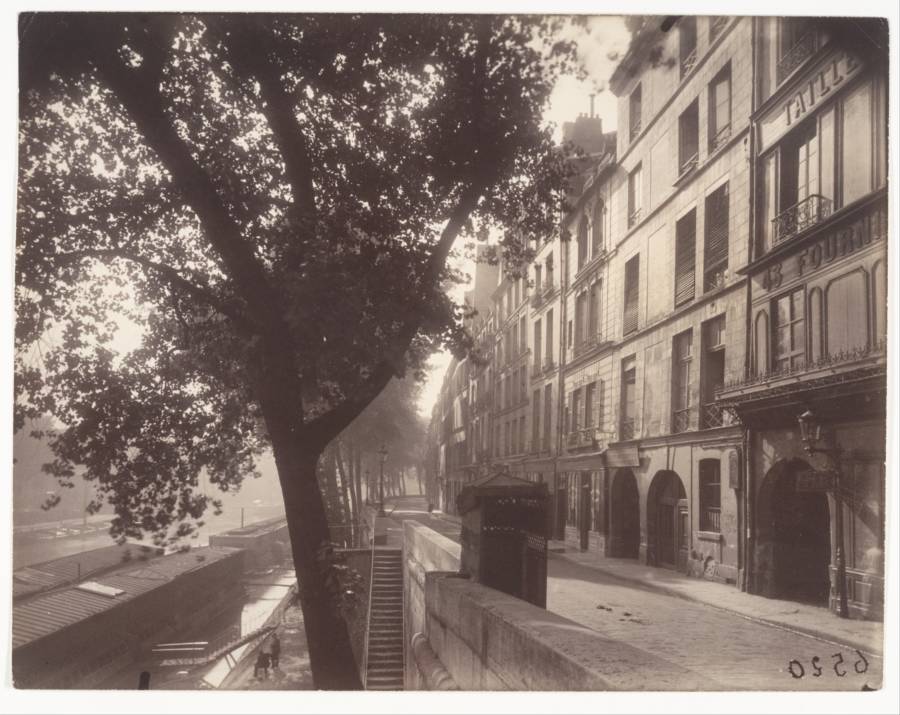
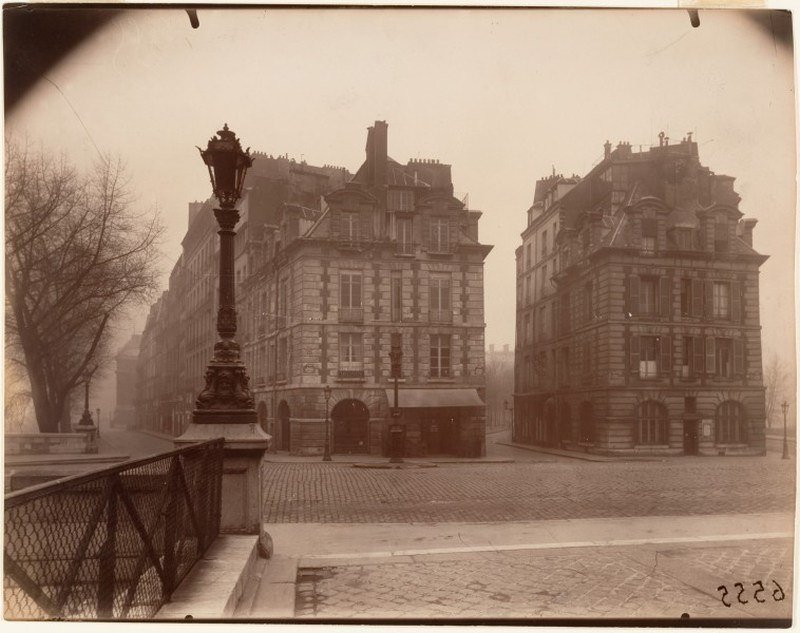
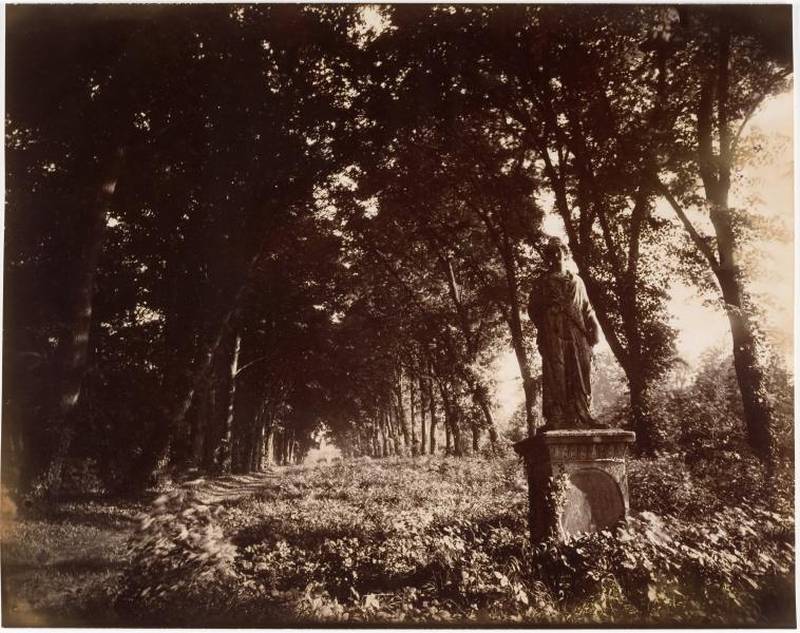
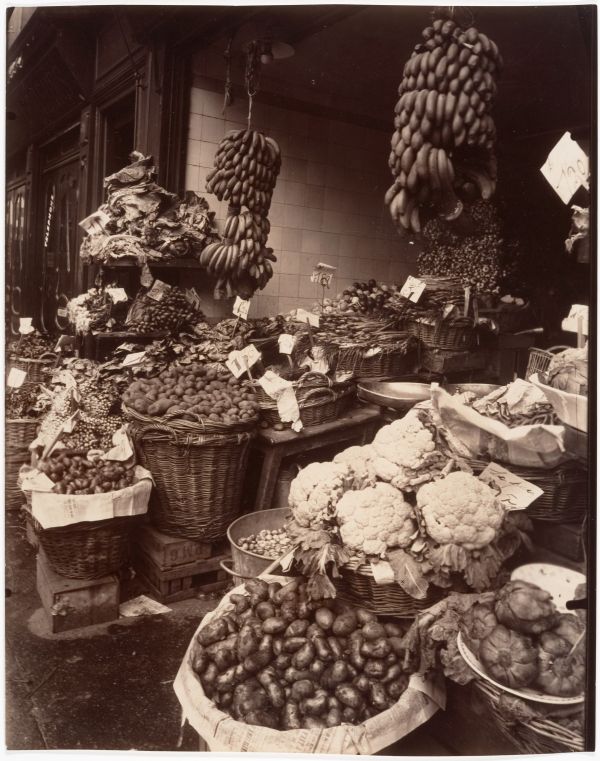
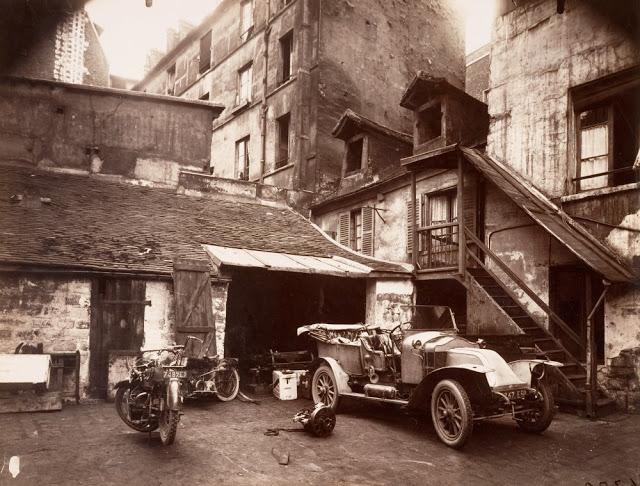
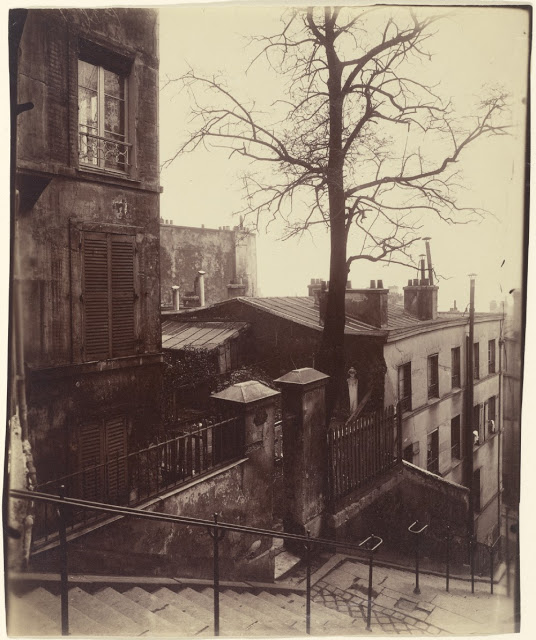
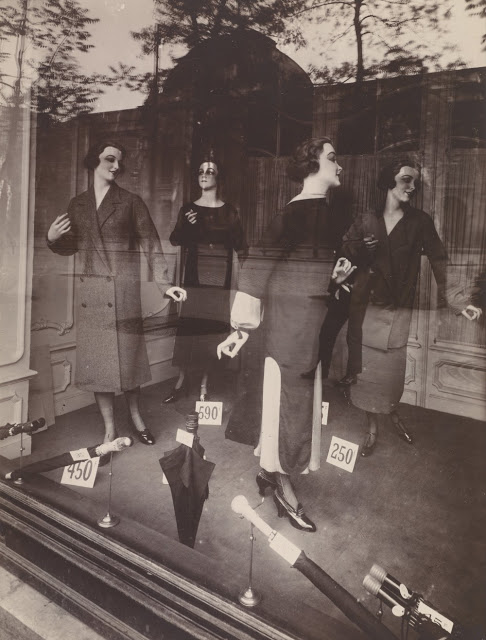
Paris is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,175,601 residents as of 2018, in an area of more than 105 square kilometres (41 square miles). Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of Europe’s major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, science, and arts. The City of Paris is the centre and seat of government of the region and province of Île-de-France, or Paris Region, which has an estimated population of 12,174,880, or about 18 percent of the population of France as of 2017. The Paris Region had a GDP of €709 billion ($808 billion) in 2017. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit Worldwide Cost of Living Survey in 2018, Paris was the second most expensive city in the world, after Singapore and ahead of Zürich, Hong Kong, Oslo, and Geneva. Another source ranked Paris as most expensive, on par with Singapore and Hong Kong, in 2018.
Paris is a major railway, highway, and air-transport hub served by two international airports: Paris–Charles de Gaulle (the second-busiest airport in Europe) and Paris–Orly. Opened in 1900, the city’s subway system, the Paris Métro, serves 5.23 million passengers daily; it is the second-busiest metro system in Europe after the Moscow Metro. Gare du Nord is the 24th-busiest railway station in the world, but the busiest located outside Japan, with 262 million passengers in 2015. Paris is especially known for its museums and architectural landmarks: the Louvre remained the most-visited museum in the world with 2,677,504 visitors in 2020, despite the long museum closings caused by the COVID-19 virus. The Musée d’Orsay, Musée Marmottan Monet and Musée de l’Orangerie are noted for their collections of French Impressionist art. The Pompidou Centre Musée National d’Art Moderne has the largest collection of modern and contemporary art in Europe. The Musée Rodin and Musée Picasso exhibit the works of two noted Parisians. The historical district along the Seine in the city centre has been classified as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1991; popular landmarks there include the Cathedral of Notre Dame de Paris on the Île de la Cité, now closed for renovation after the 15 April 2019 fire. Other popular tourist sites include the Gothic royal chapel of Sainte-Chapelle, also on the Île de la Cité; the Eiffel Tower, constructed for the Paris Universal Exposition of 1889; the Grand Palais and Petit Palais, built for the Paris Universal Exposition of 1900; the Arc de Triomphe on the Champs-Élysées, and the hill of Montmartre with its artistic history and its Basilica of Sacré-Coeur.
Paris received 12.6 million visitors in 2020, measured by hotel stays, a drop of 73 percent from 2019, due to the COVID-19 virus. The number of foreign visitors declined by 80.7 percent. Museums re-opened in 2021, with limitations on the number of visitors at a time and a requirement that visitors wear masks.
The football club Paris Saint-Germain and the rugby union club Stade Français are based in Paris. The 80,000-seat Stade de France, built for the 1998 FIFA World Cup, is located just north of Paris in the neighbouring commune of Saint-Denis. Paris hosts the annual French Open Grand Slam tennis tournament on the red clay of Roland Garros. The city hosted the Olympic Games in 1900, 1924 and will host the 2024 Summer Olympics. The 1938 and 1998 FIFA World Cups, the 2007 Rugby World Cup, as well as the 1960, 1984 and 2016 UEFA European Championships were also held in the city. Every July, the Tour de France bicycle race finishes on the Avenue des Champs-Élysées in Paris. (Wikipedia)











































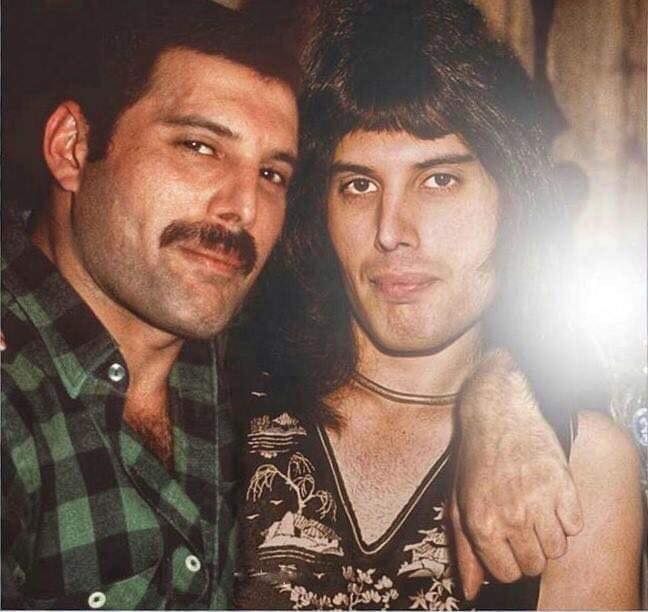
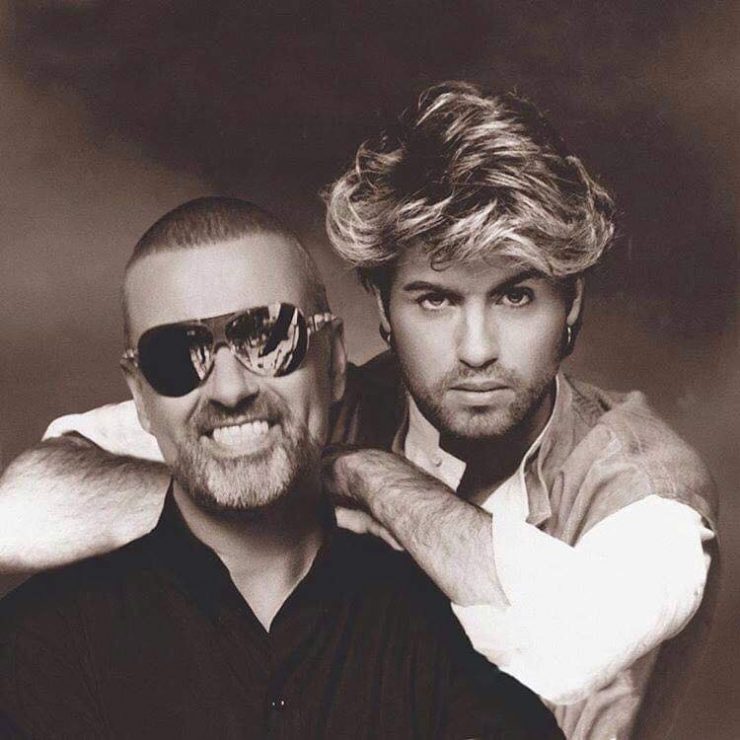
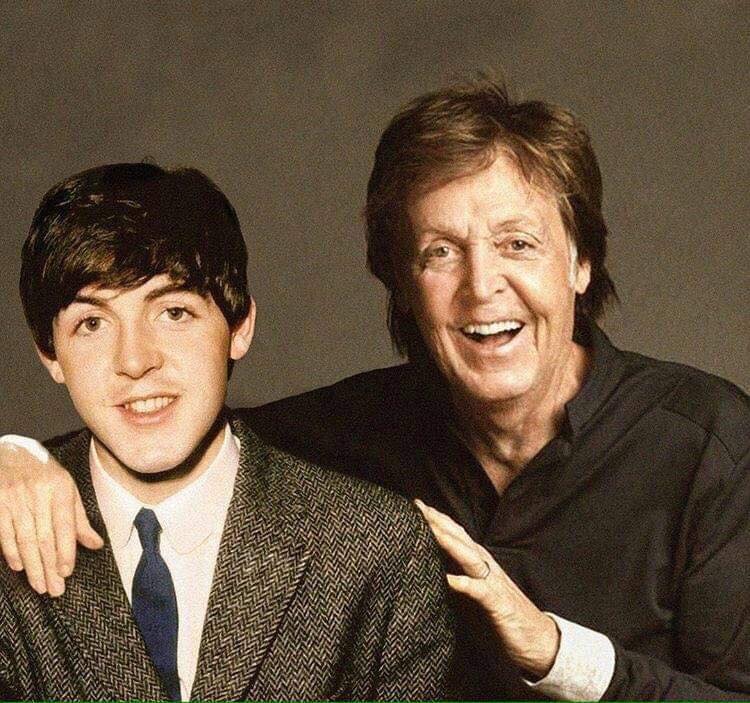
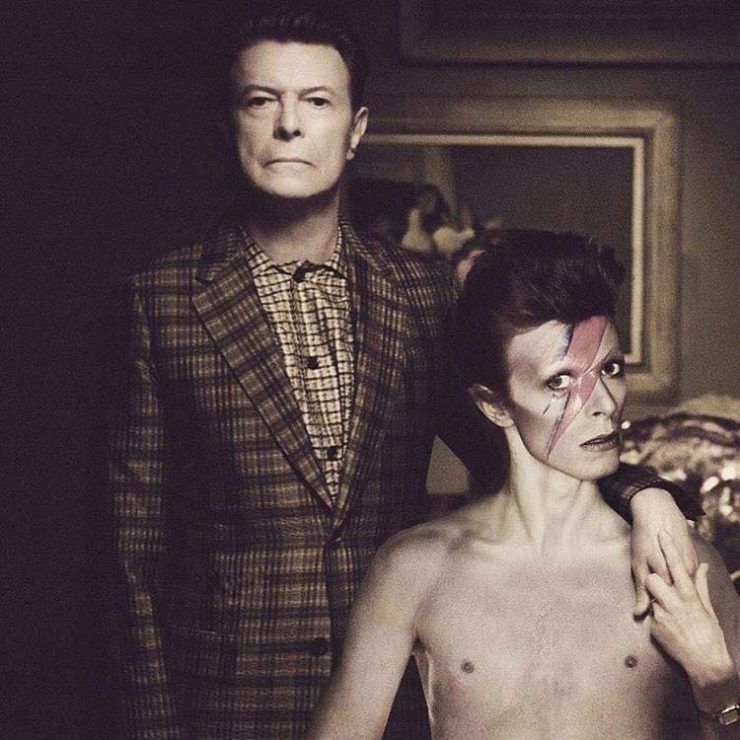
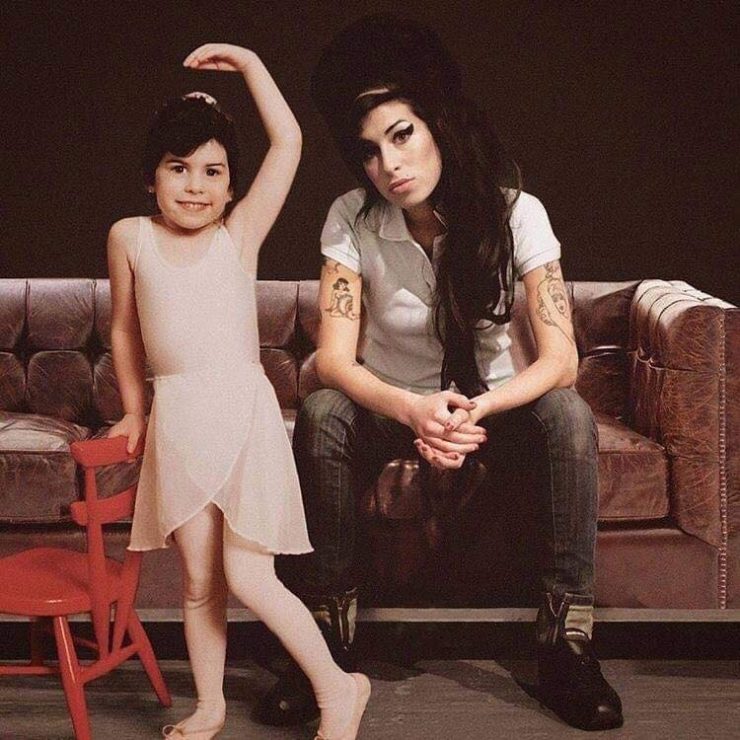
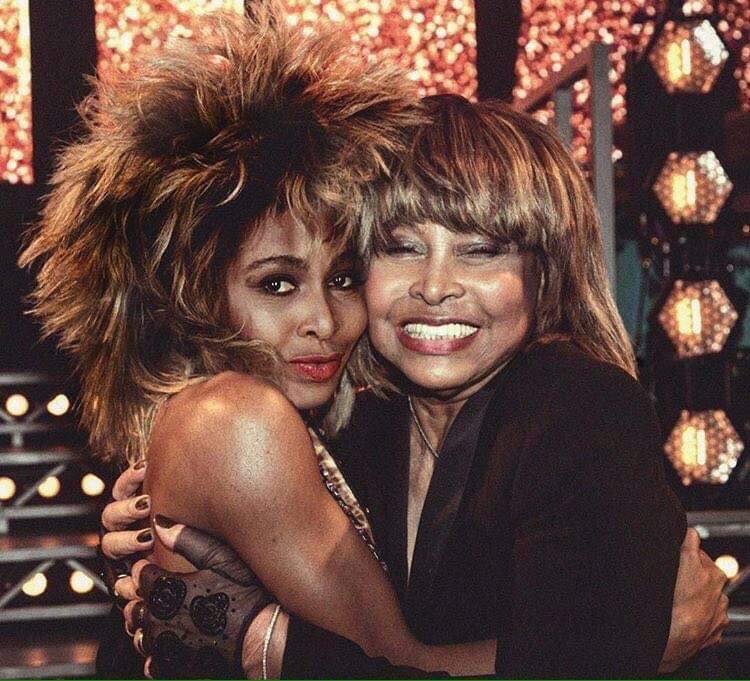
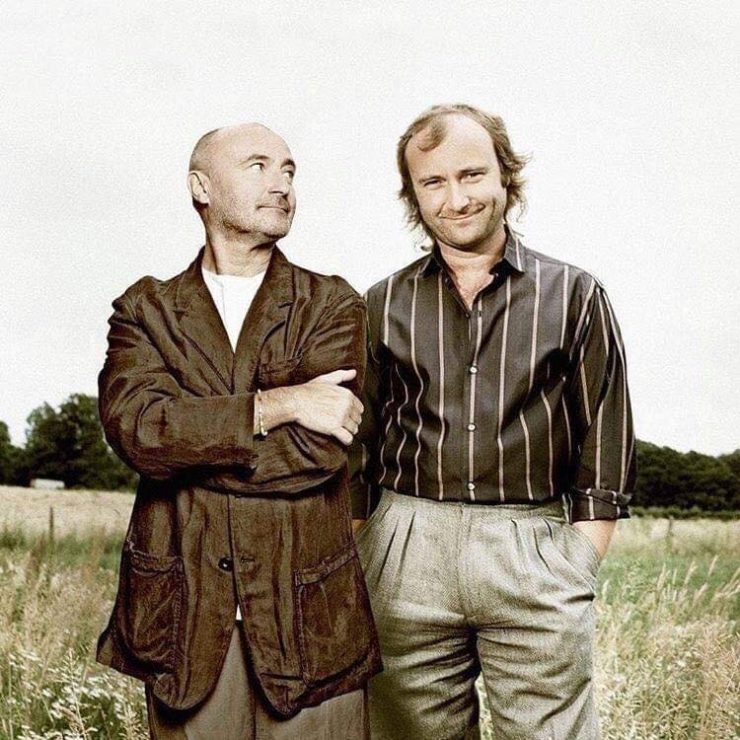
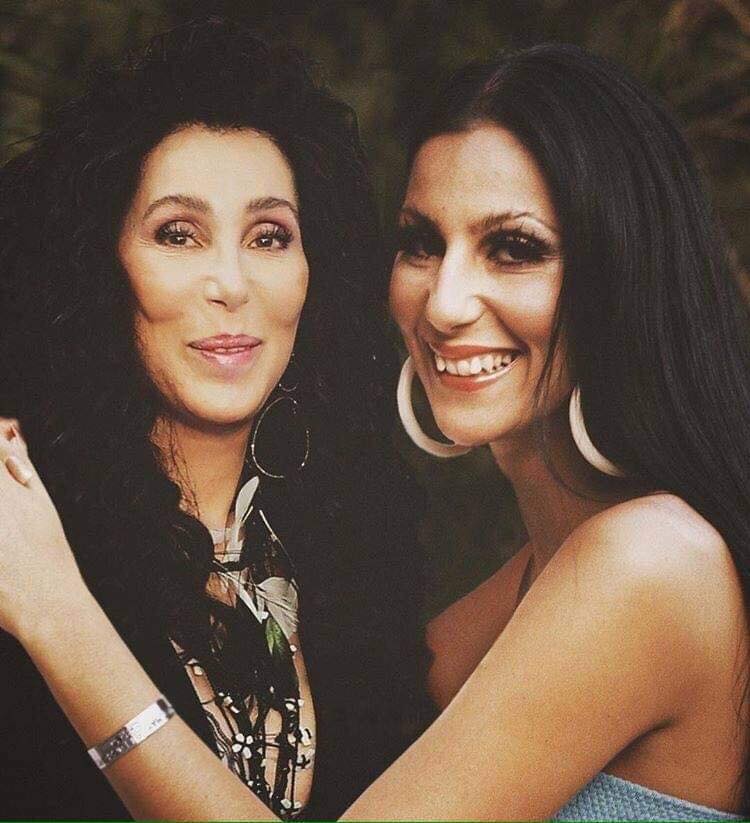
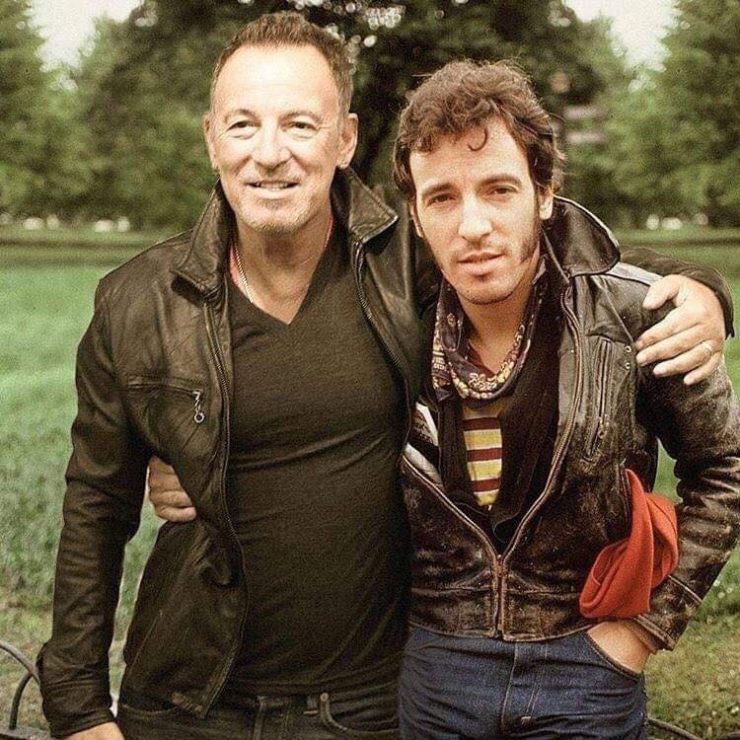
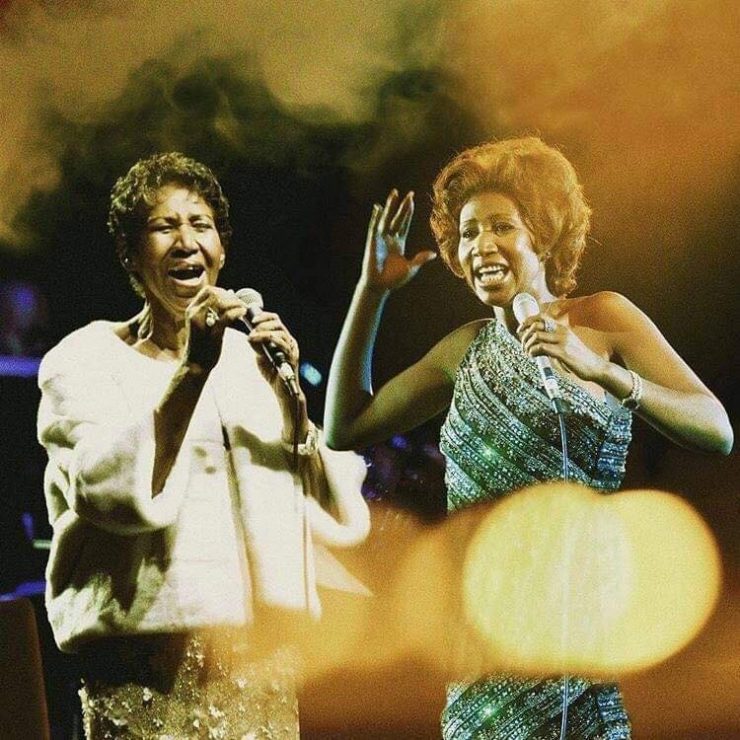
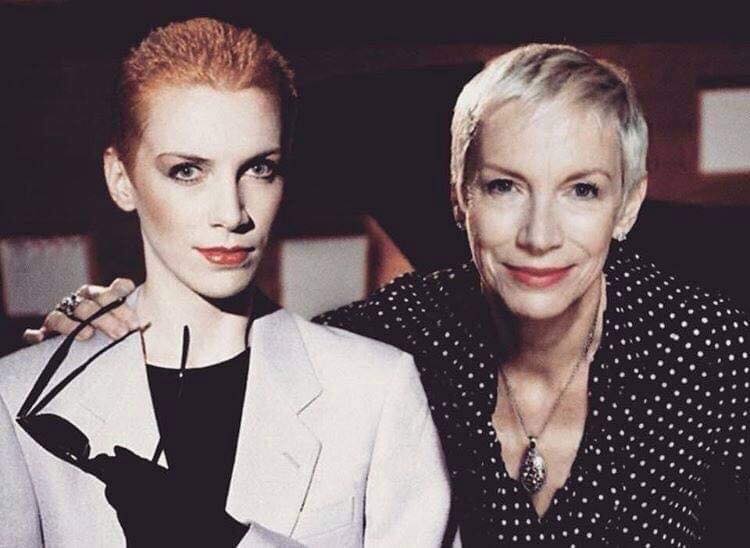
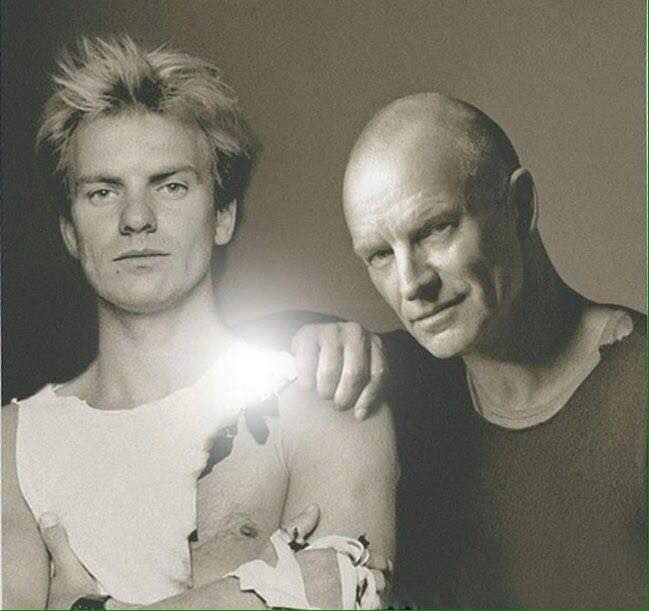
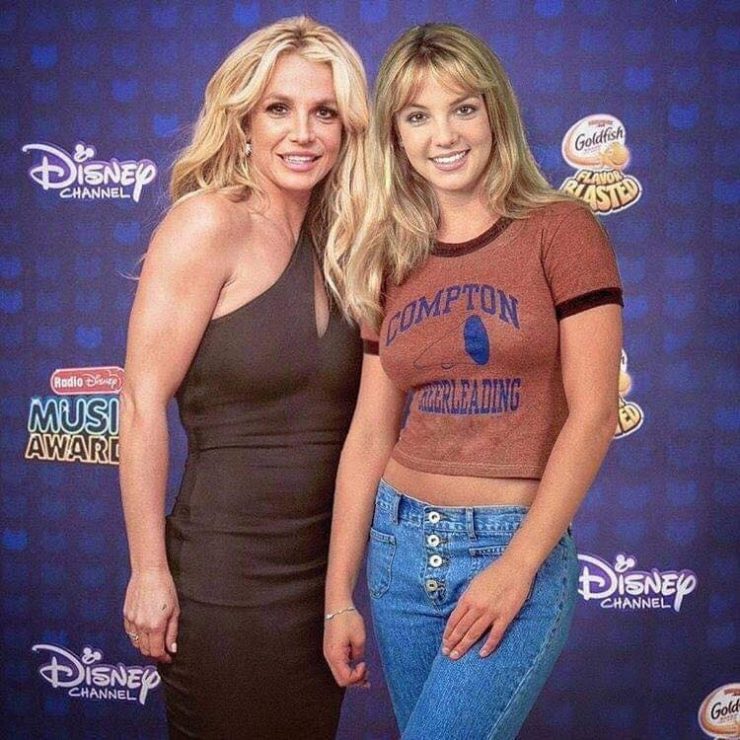
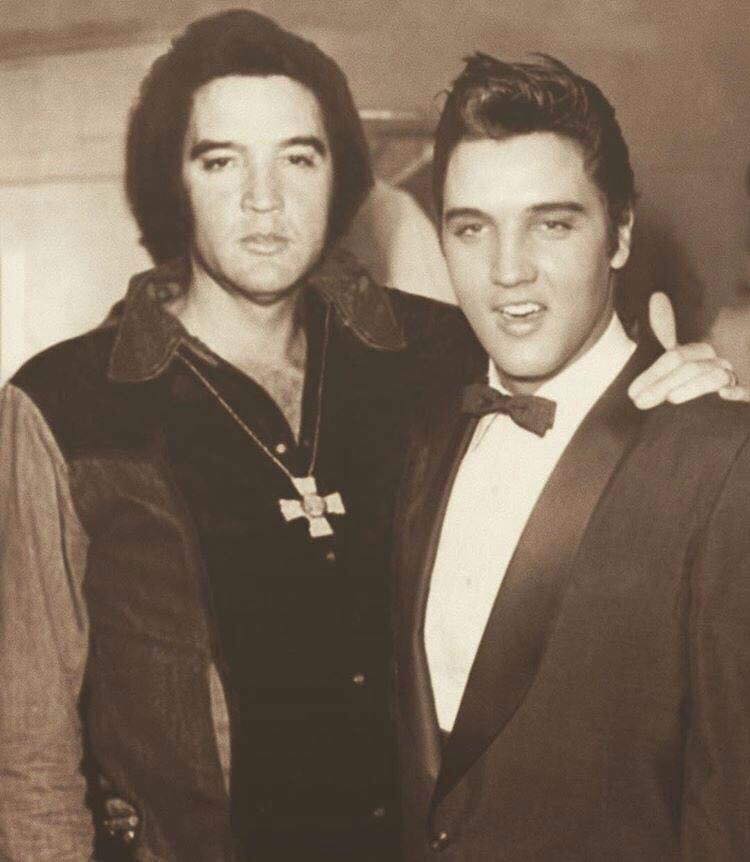
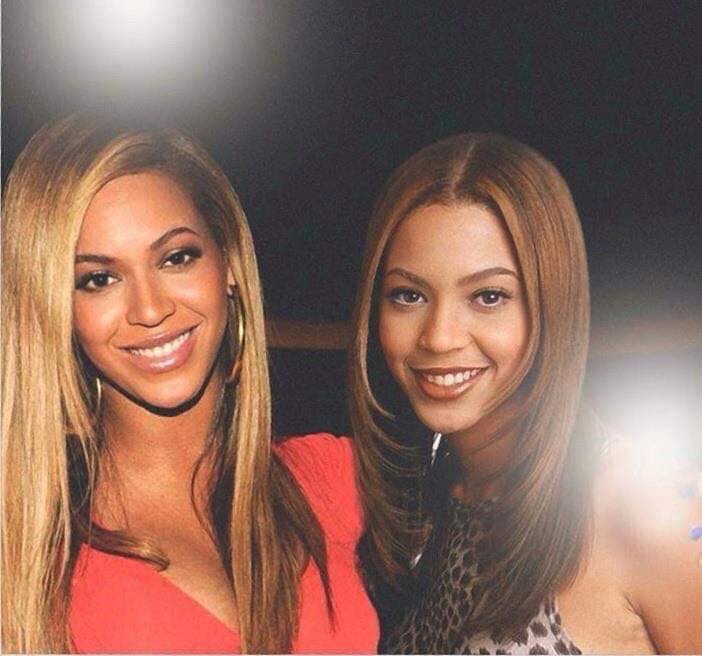
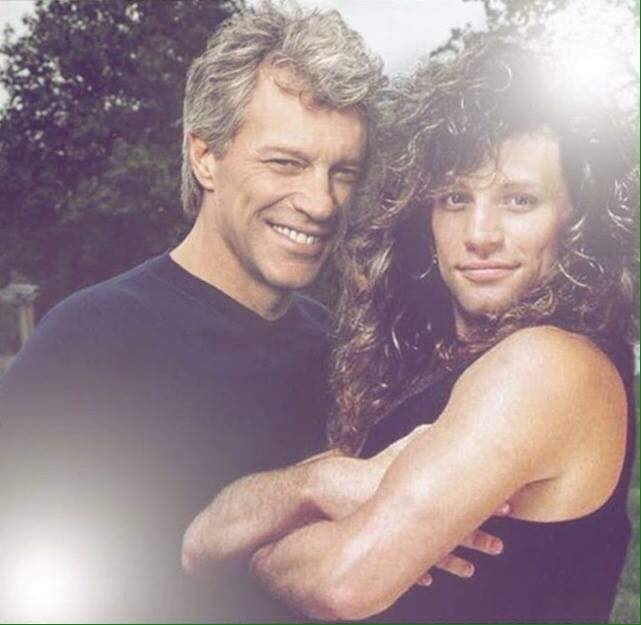
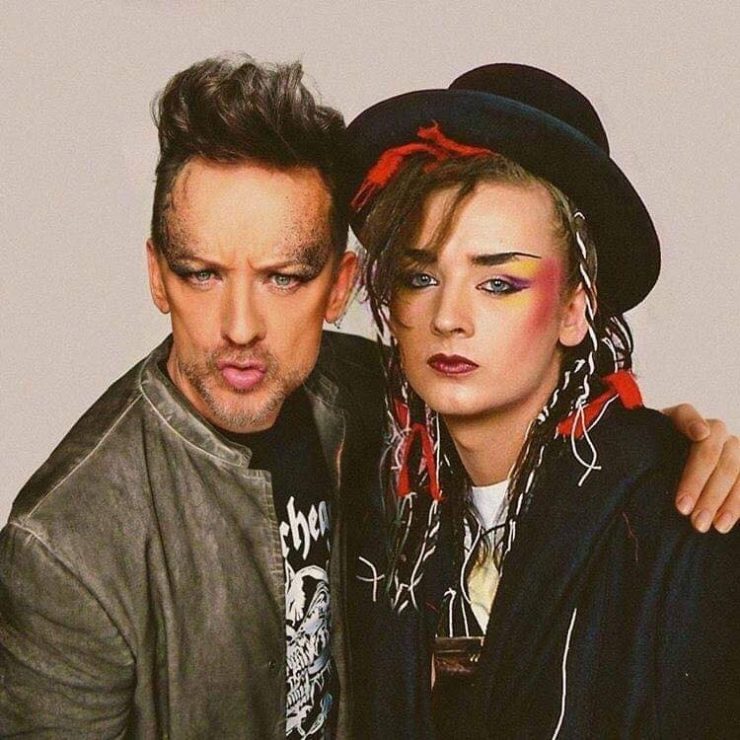
These portraits of pop stars posing with their younger selves are brilliant. No sign of Roger Daltry, the leader singer of The Who, who wished “I hope I die before I get old”, but plenty of: Agnetha Faltskog?, Amy Winehouse, Annie Lennox, Barbra Streisand, Beyonce, Boy George, Britney Spears, Bruce Springsteen, Cher, Cyndi Lauper, David Bowie, Elvis Presley, Freddie Mercury, George Michael, Jon Bon Jovi, Lionel Richie, Madonna, Mariah Carey, Michael Jackson Mick Jagger, Paul McCartney, Phil Collins, Sting, Tina Turner and Whitney Houston.