Vintage ads are often terrible, but these holiday ads take terrible to a new low. Whether it’s Santa as a sex object or a cigarette carton for a sleigh, these ads are festive, fun, and totally inappropriate.




















Bringing You the Wonder of Yesterday – Today

Vintage ads are often terrible, but these holiday ads take terrible to a new low. Whether it’s Santa as a sex object or a cigarette carton for a sleigh, these ads are festive, fun, and totally inappropriate.
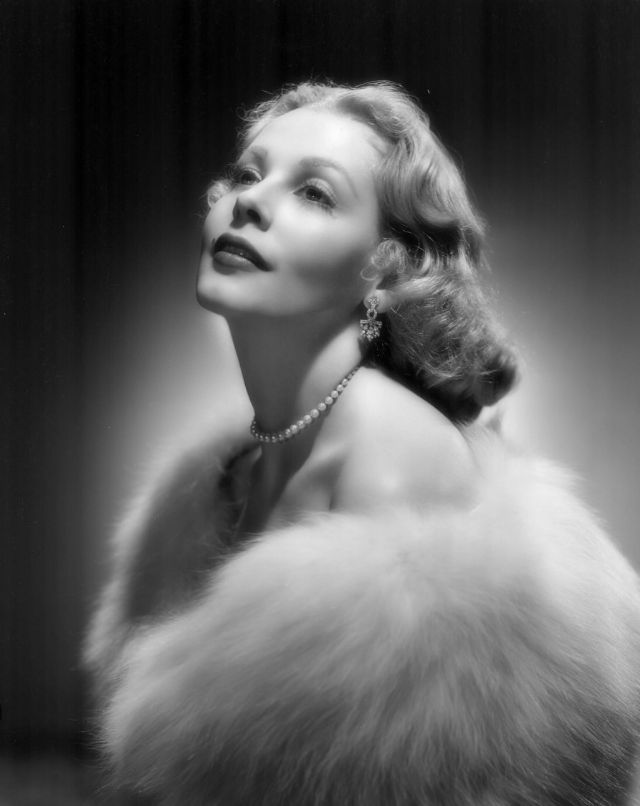






















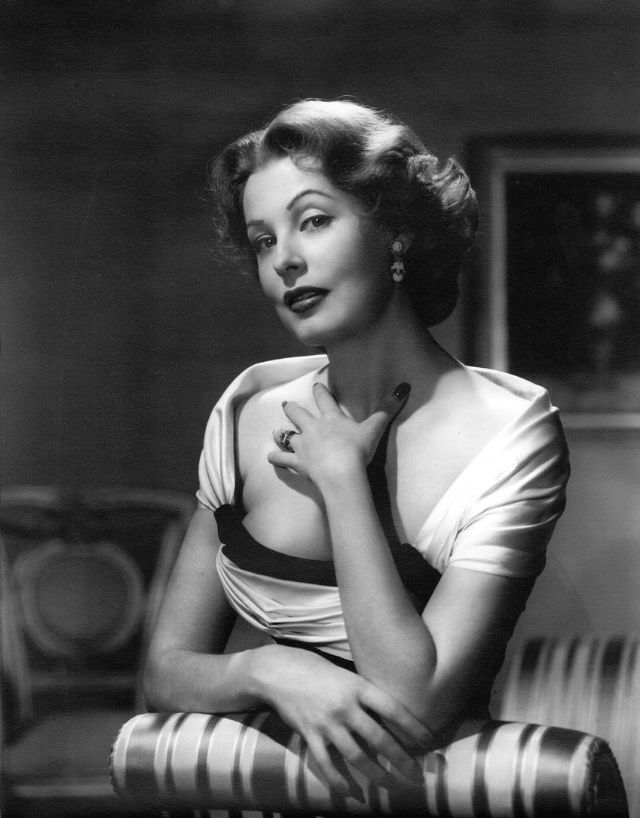
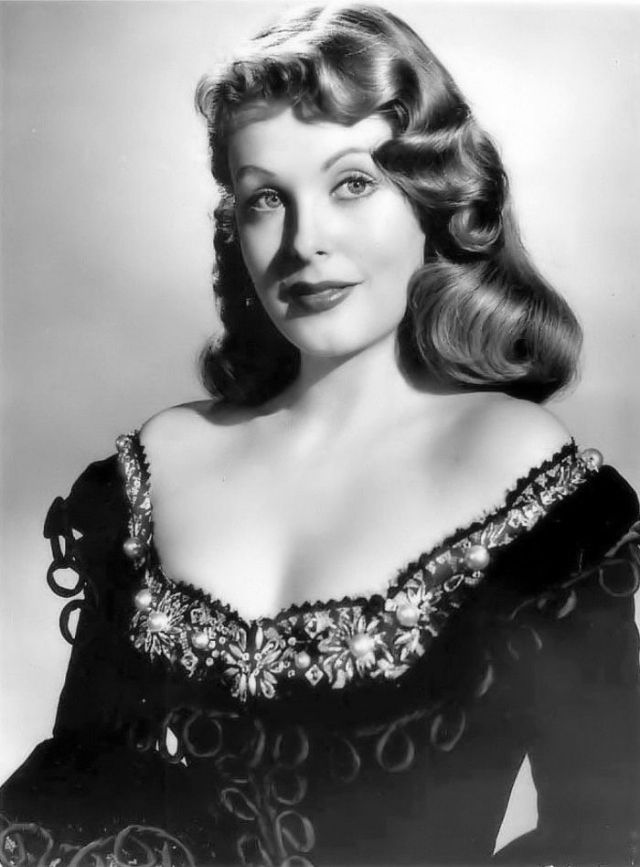
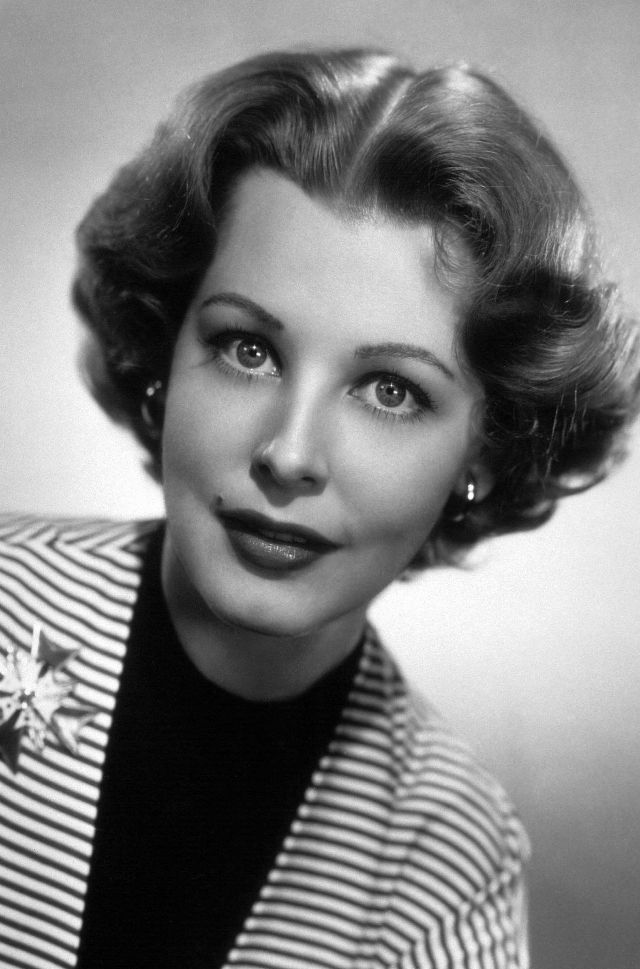
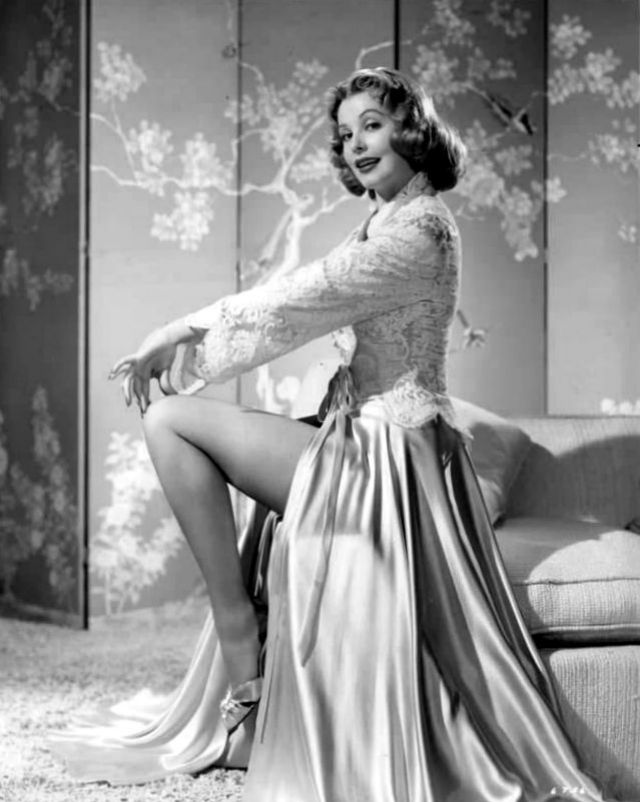
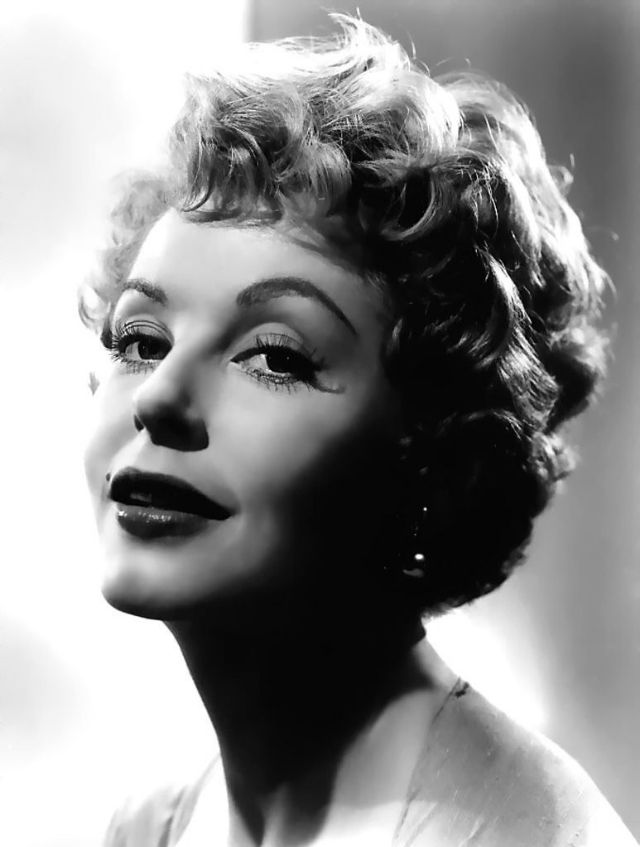
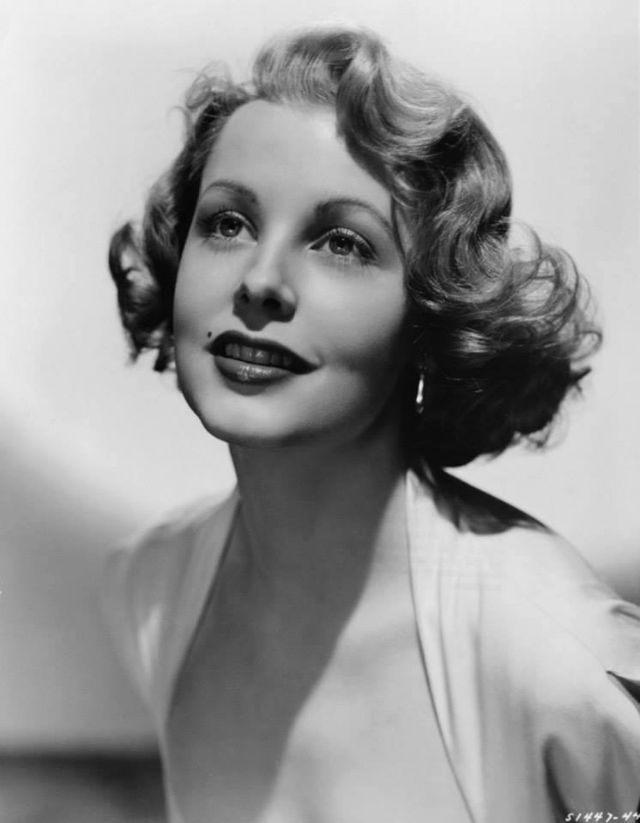
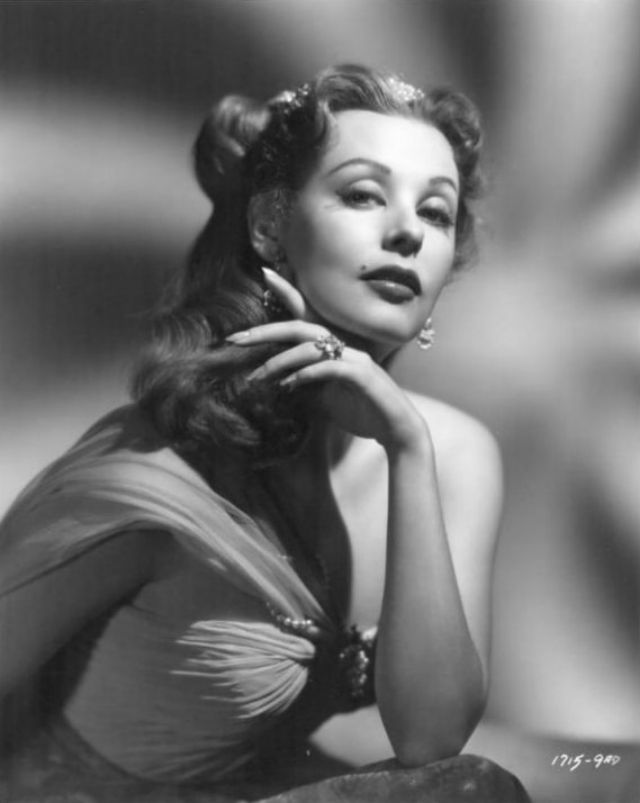
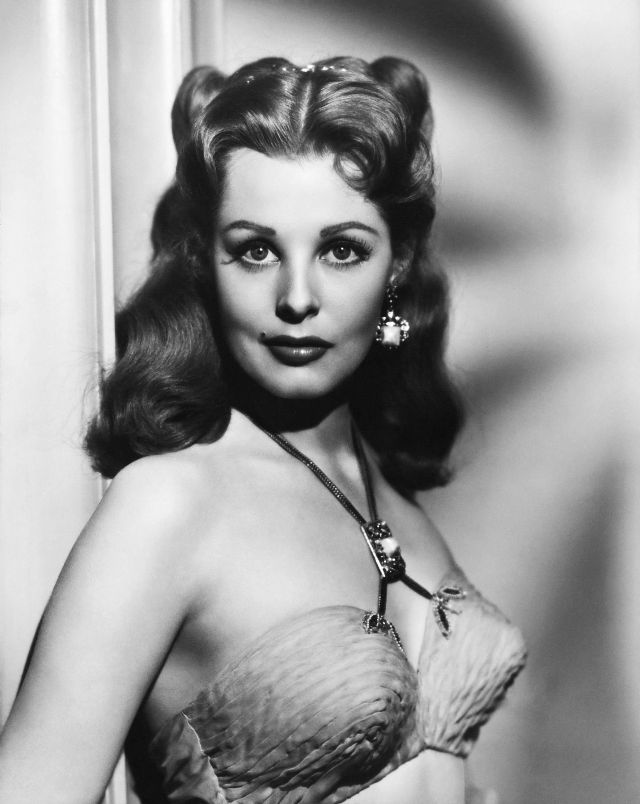
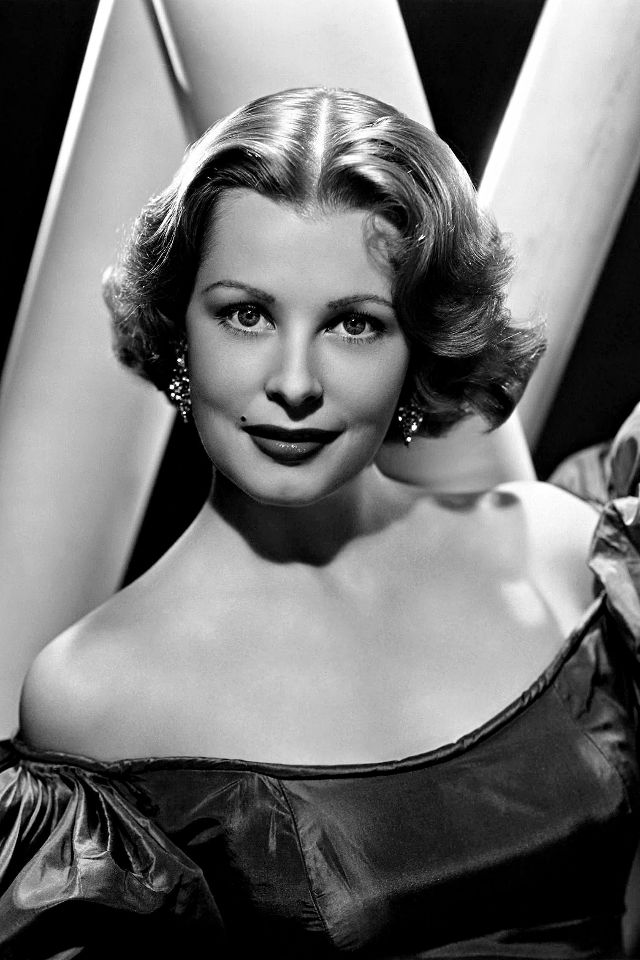
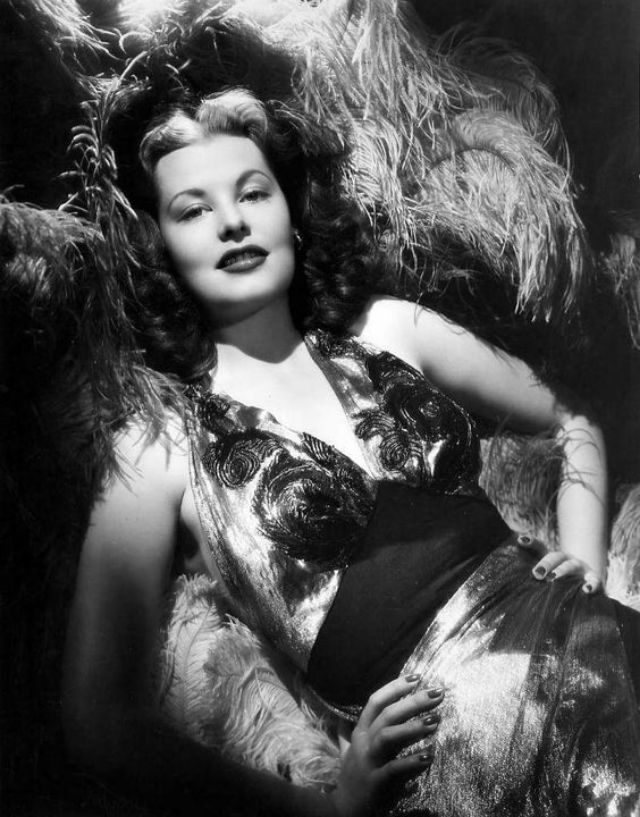
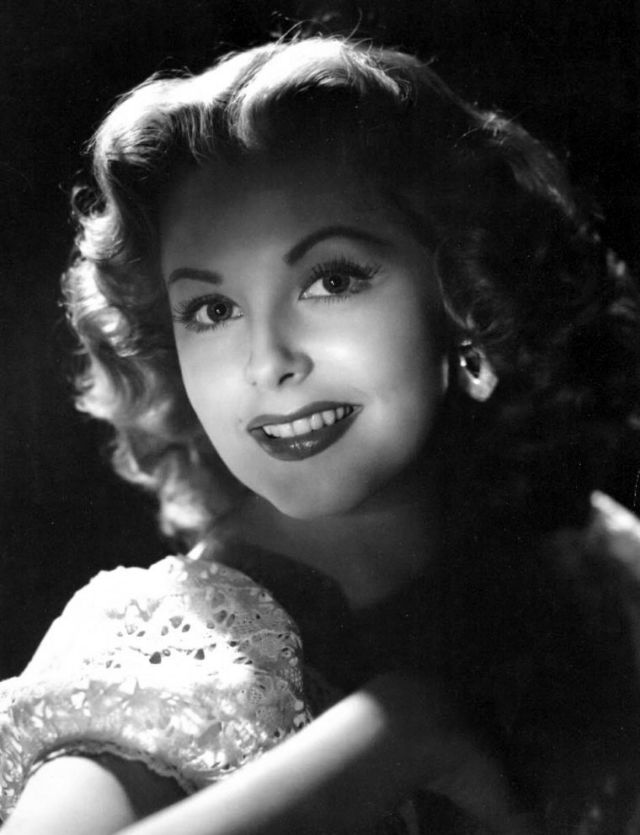
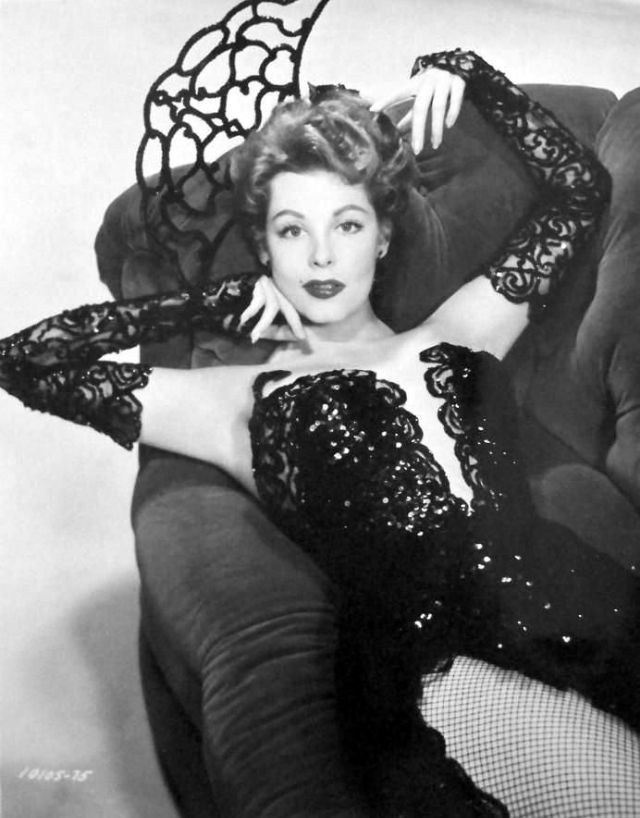
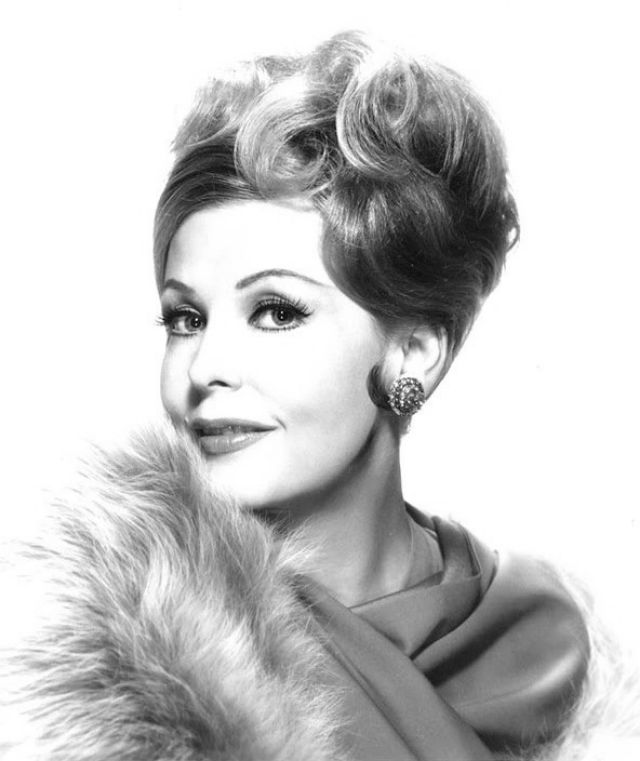
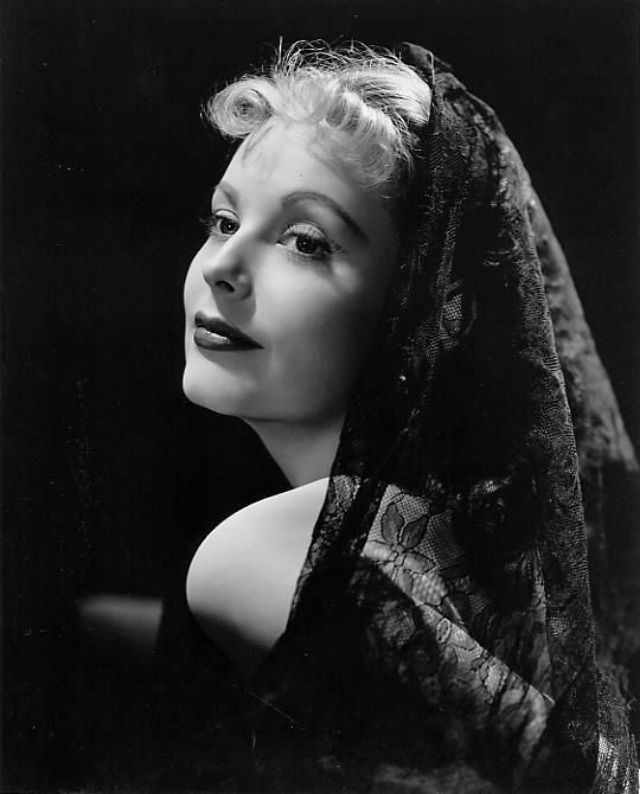
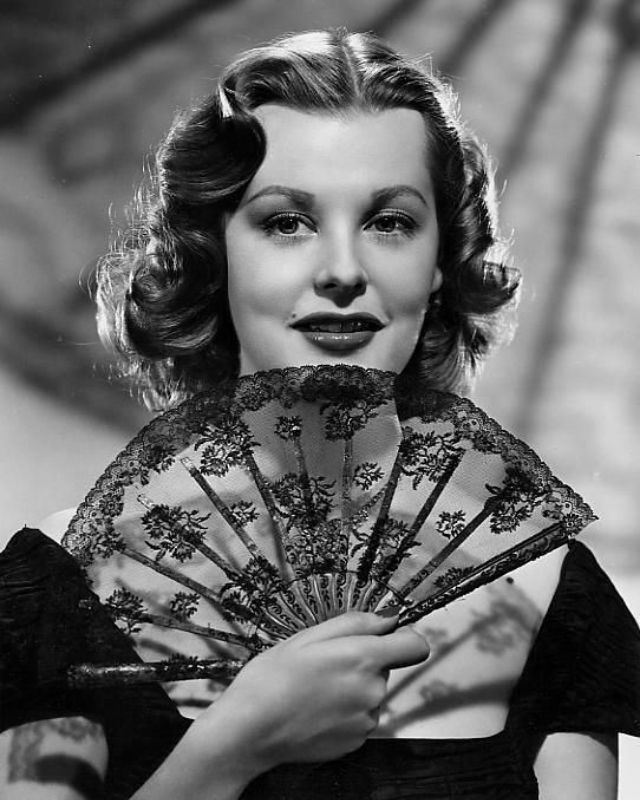
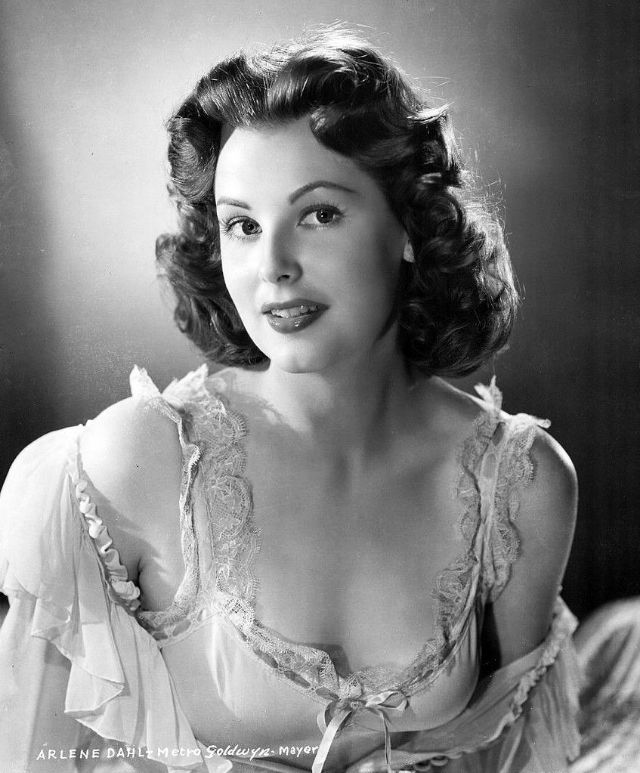
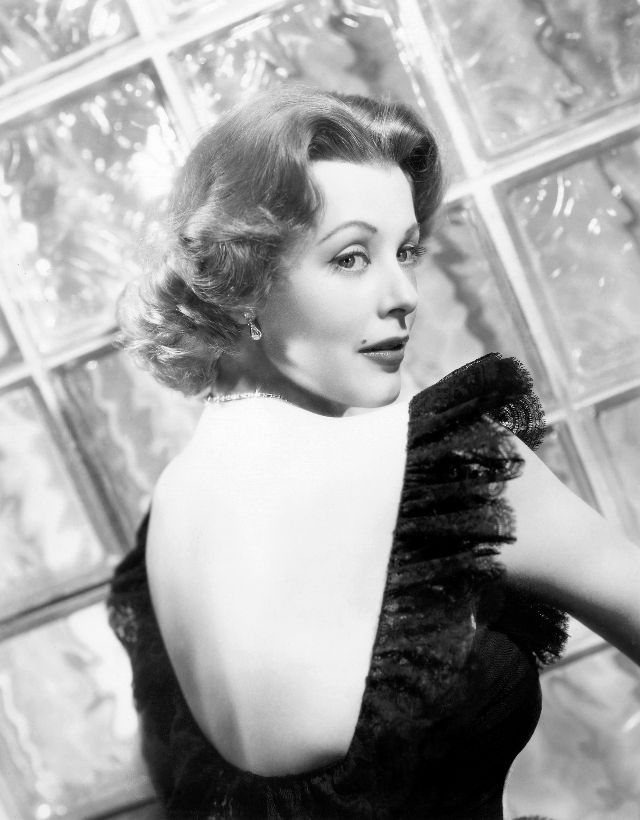
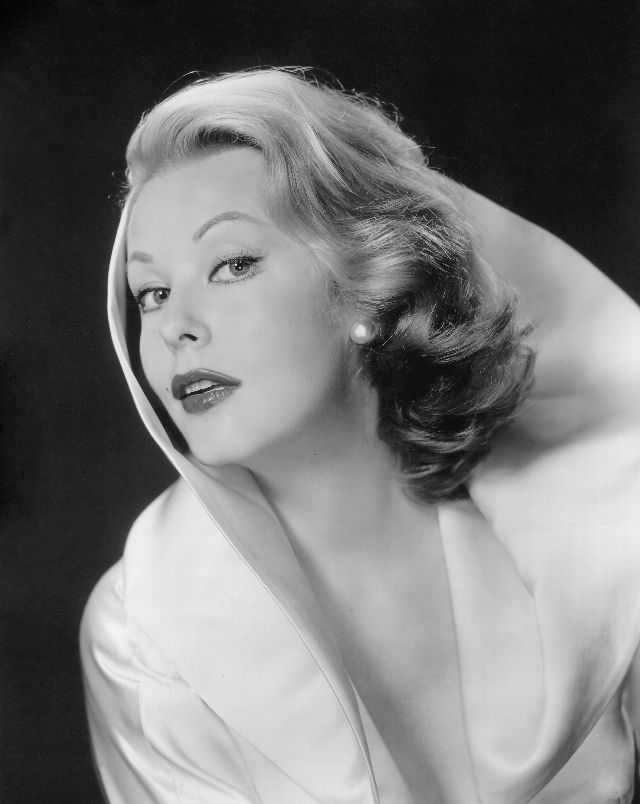
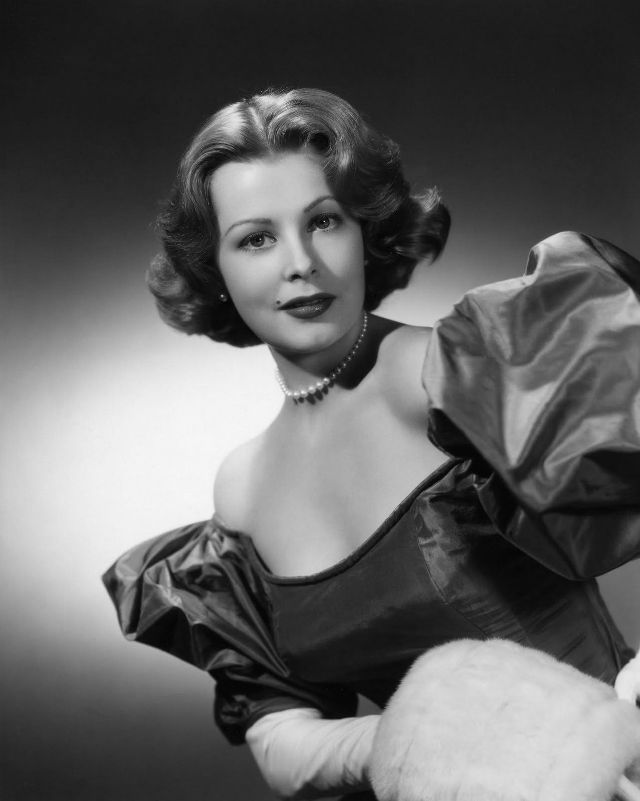
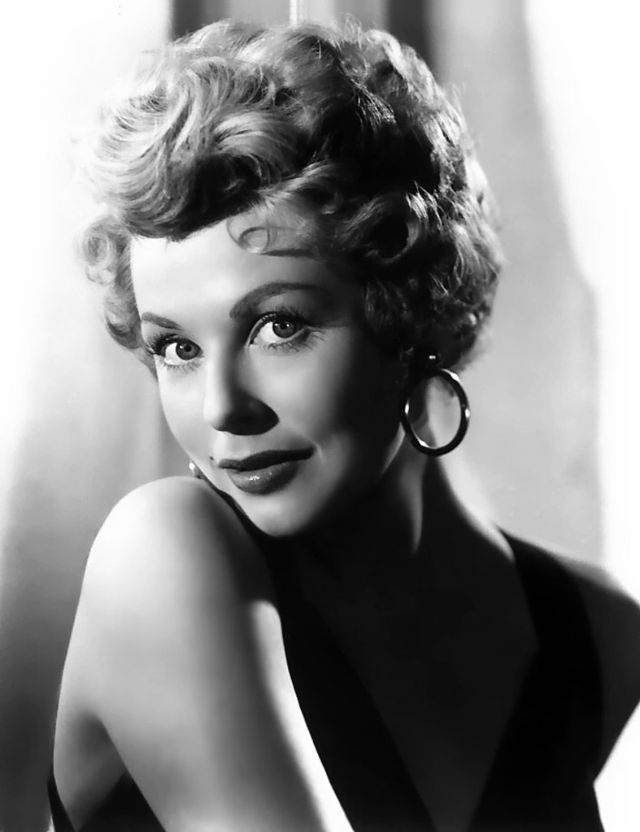
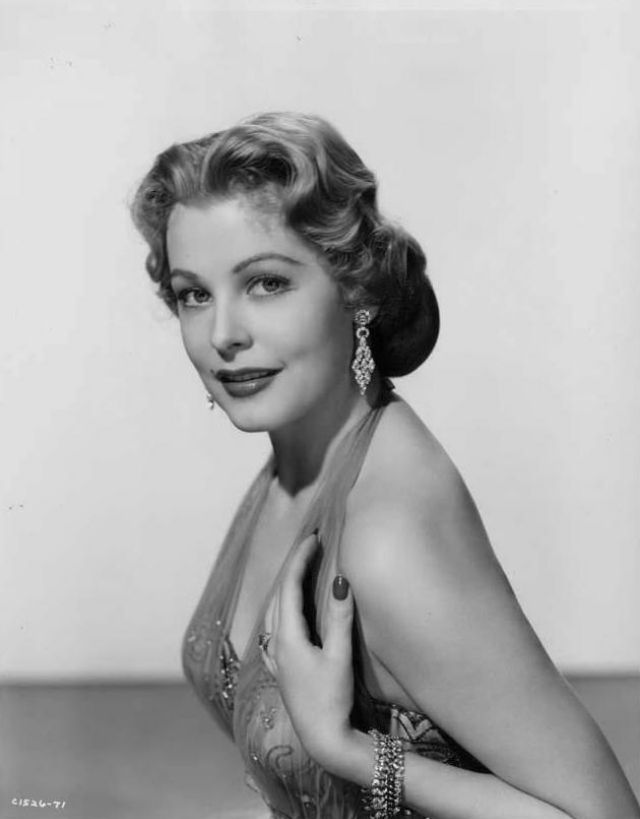
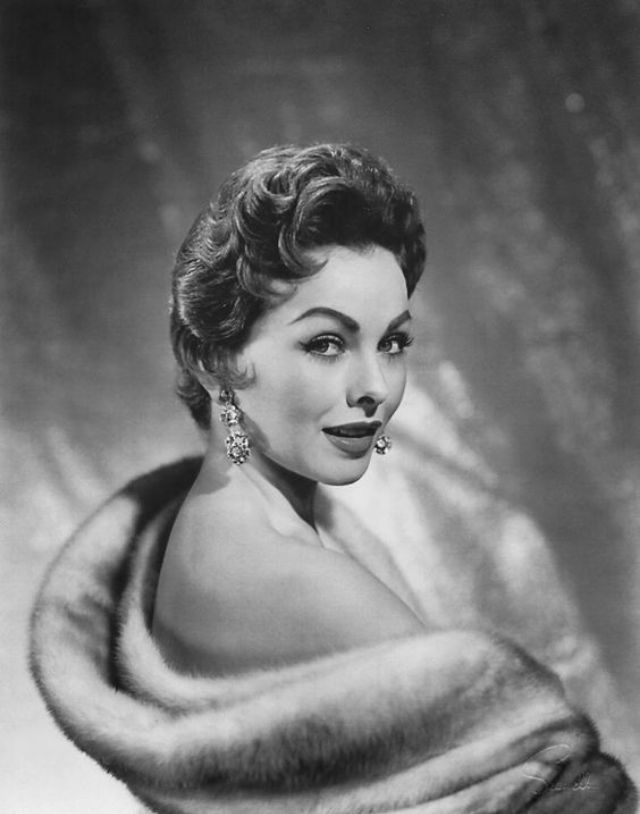
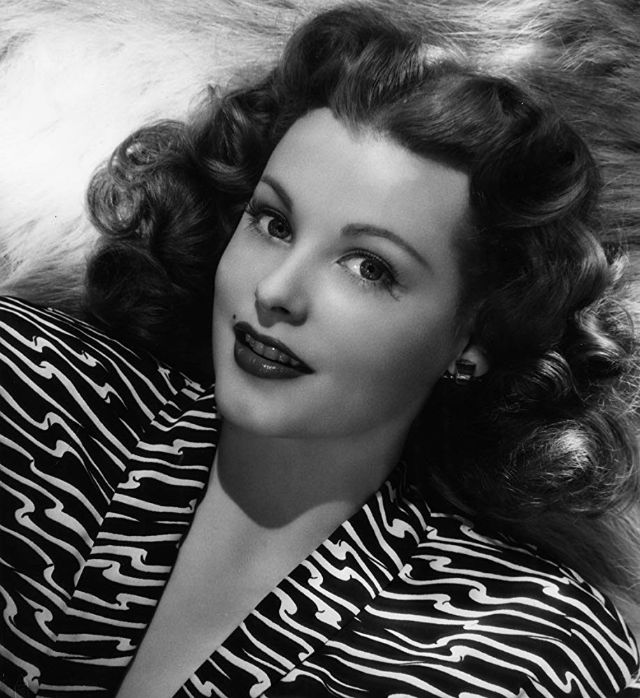
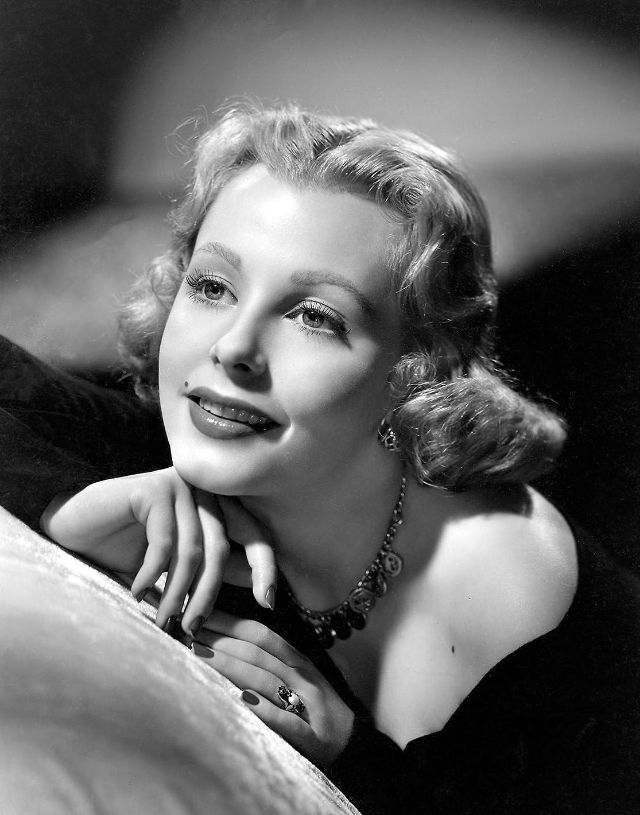
Elegance and femininity are fitting descriptions for Arlene Dahl. She is considered to be one of the most beautiful actresses to have graced the screen during the postwar period. Audiences were captivated by her breathtaking beauty and the way she used to it to her advantage, progressing from claimer to character roles.
Of Norwegian extraction, Miss Dahl was born in Minneapolis. Following high school she joined a local drama group, supporting herself with a variety of jobs, including modeling for a number of department stores. Arriving in Hollywood in 1946, she signed a brief contract with Warner Brothers, but she is best remembered for her work at MGM. The Bride Goes Wild (1948) was her first work at Metro. It was an odd but rather humorous love story, which starred Van Johnson and June Allyson.
Although her beauty captivated audiences, it ultimately limited her to smaller roles, and the mark she made at MGM was small. Some of her best films were Reign of Terror (1949), which actually required some acting and she acquitted herself quite well, Three Little Words (1950), Woman’s World (1954), Slightly Scarlet (1956) and Journey to the Center of the Earth (1959).
Leaving films behind her in 1959, her typecasting would pay off financially as she became a beauty columnist and writer. She later established herself as a businesswoman, founding Arlene Dahl Enterprises which marketed lingerie and cosmetics.
She was married six times, two of whom were actors actors Lex Barker and Fernando Lamas. She is the mother of actor / action star Lorenzo Lamas, and actually made a guest appearance in his film Night of the Warrior (1991).
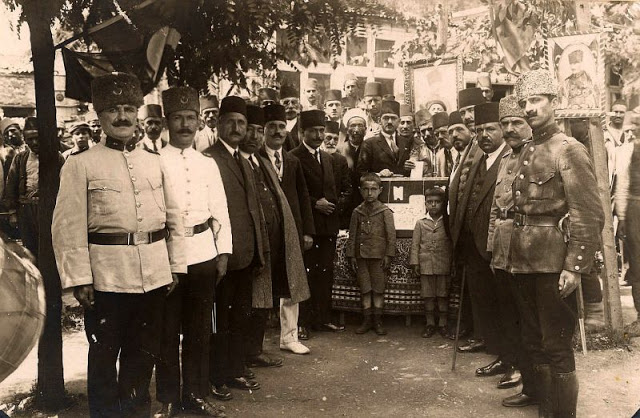









































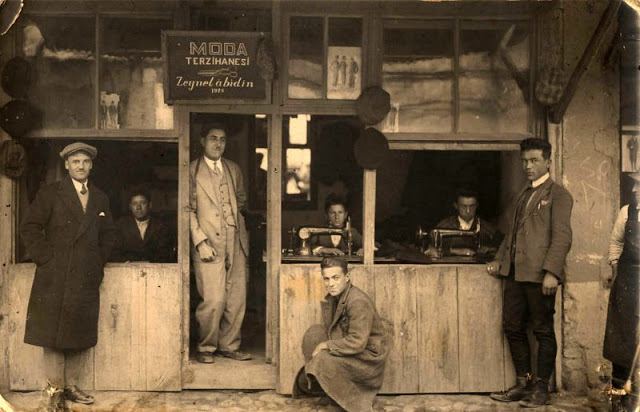
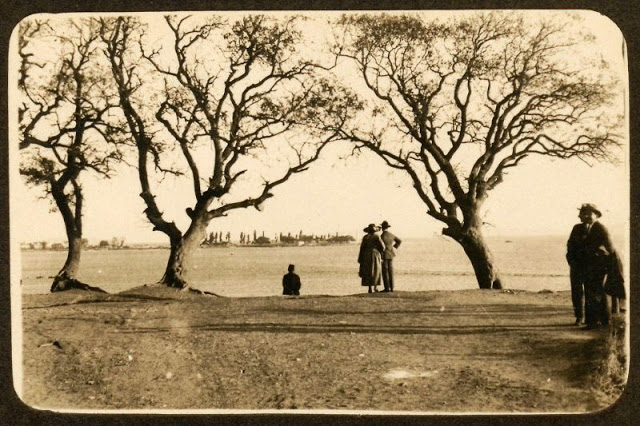
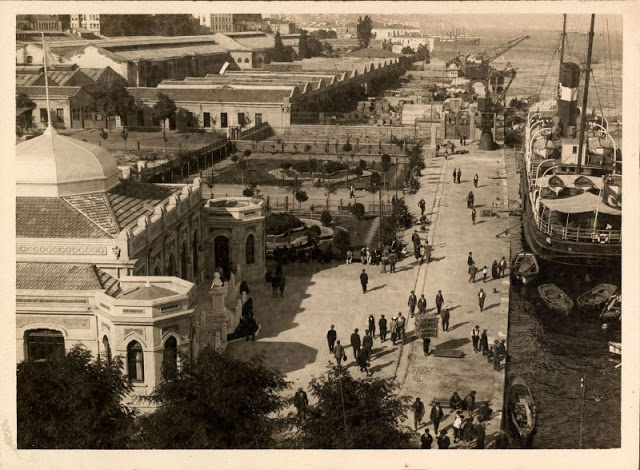
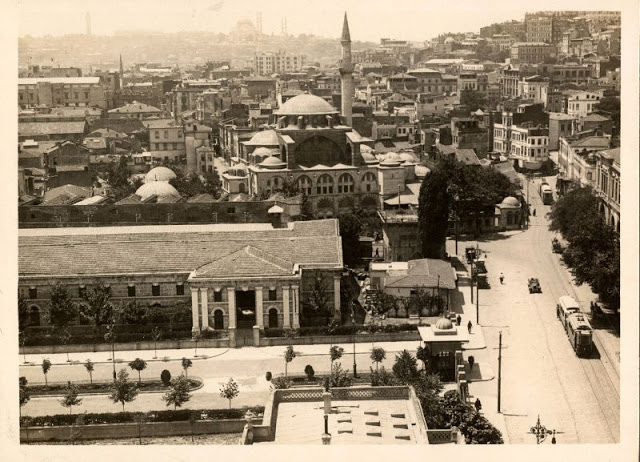
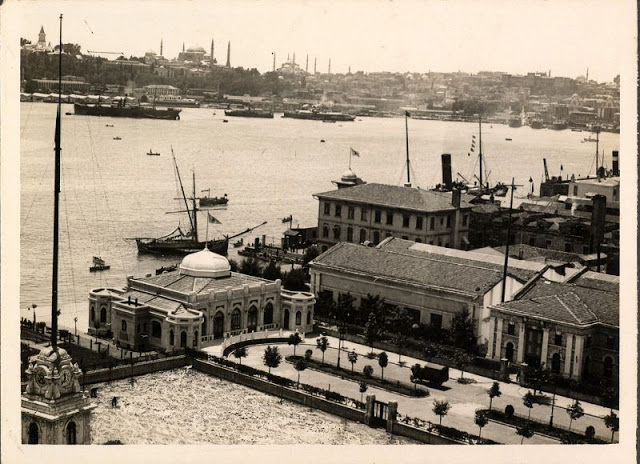
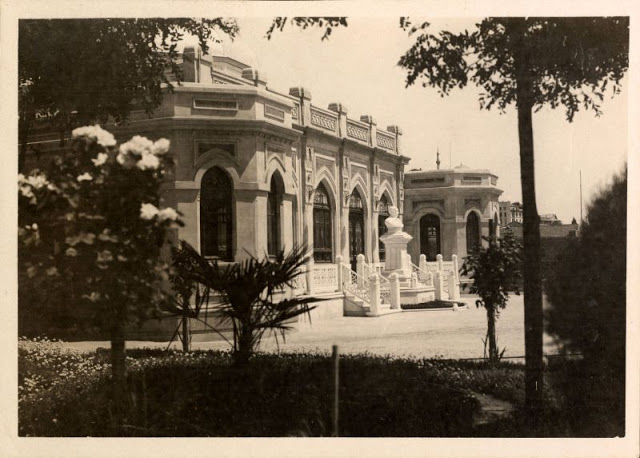
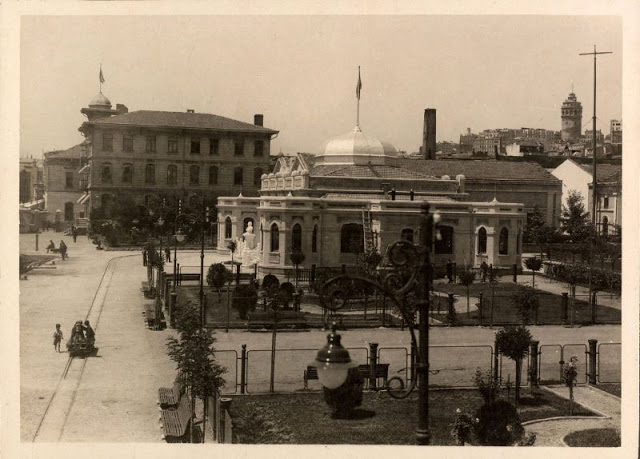
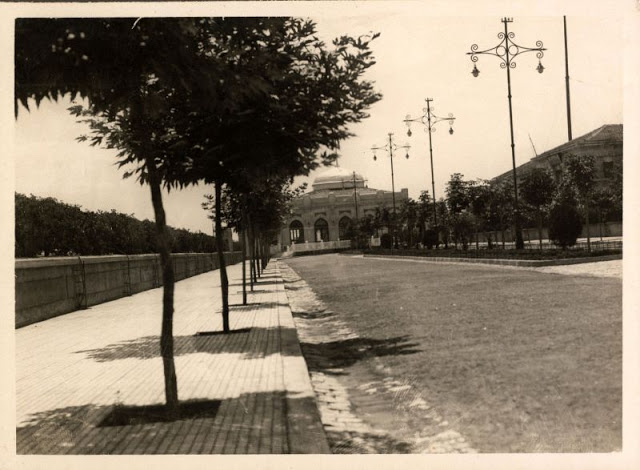
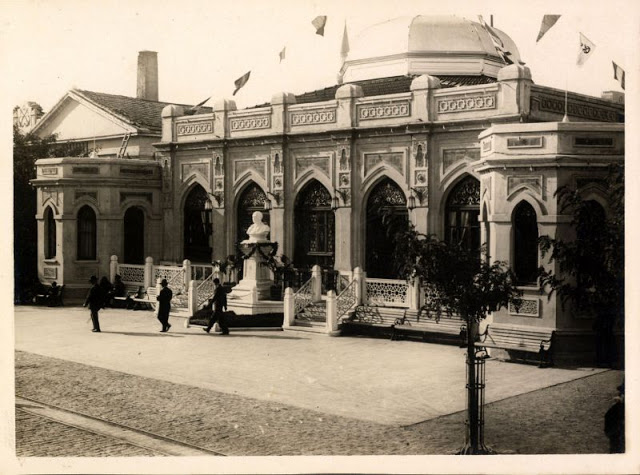
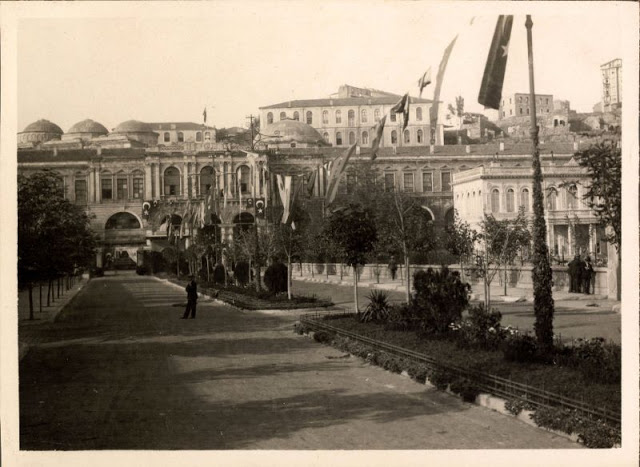
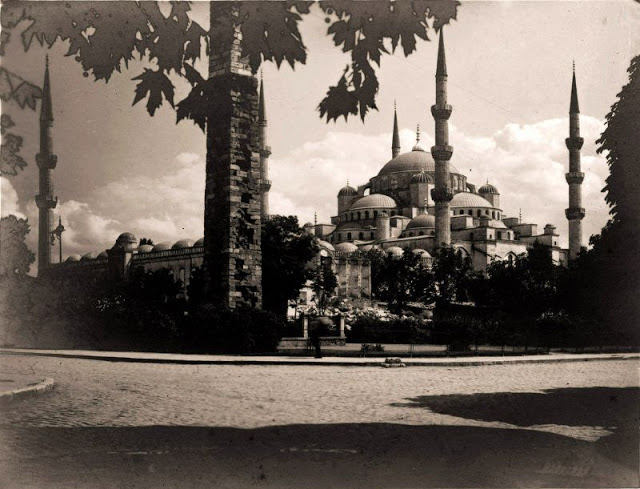
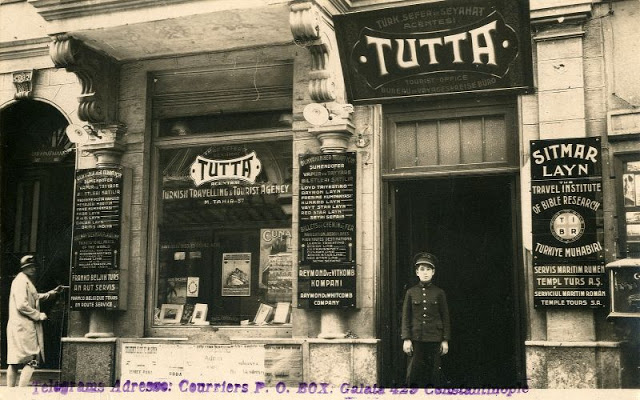
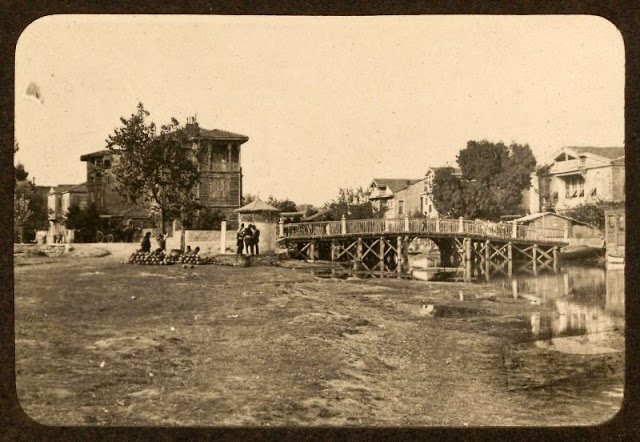
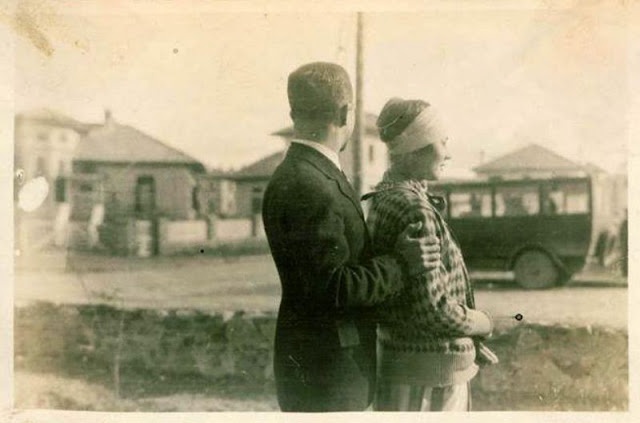
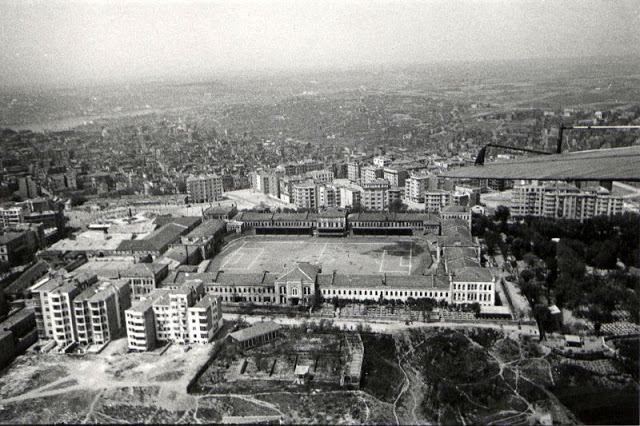
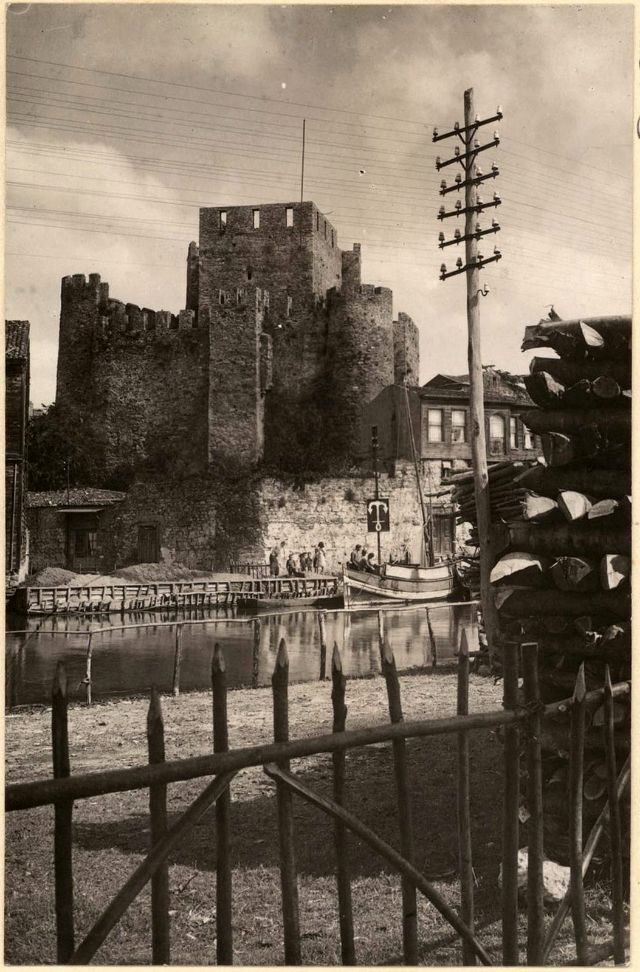
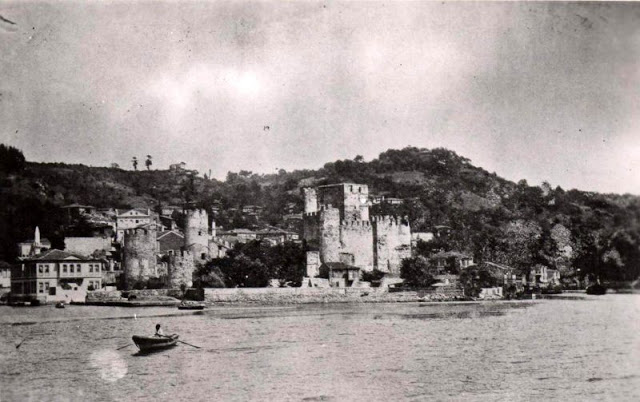
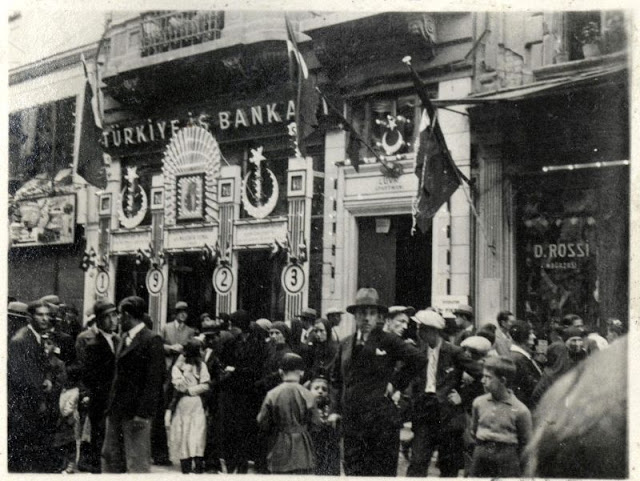
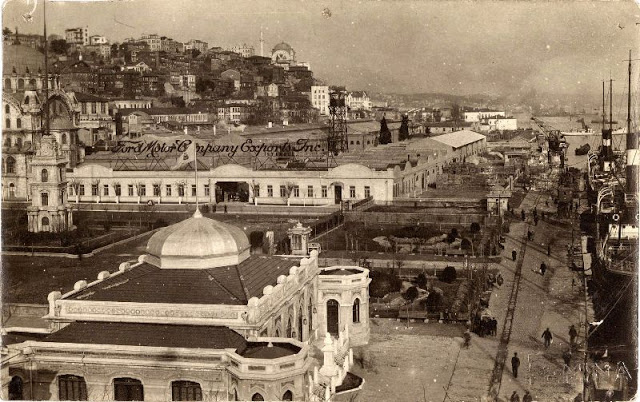
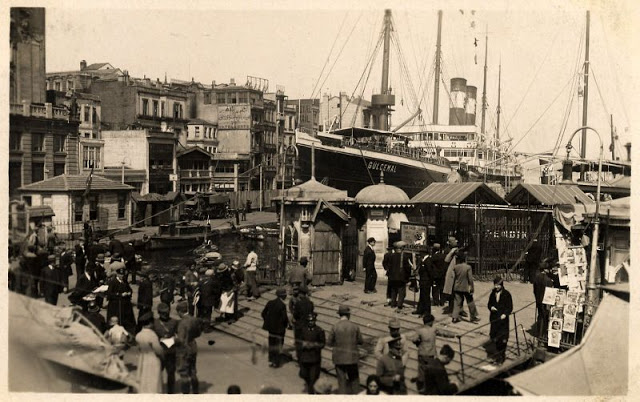
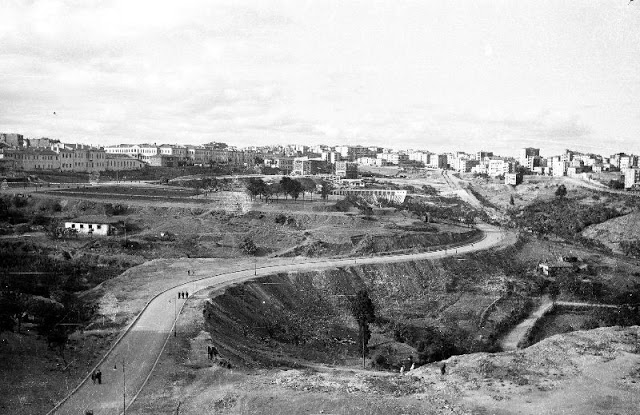
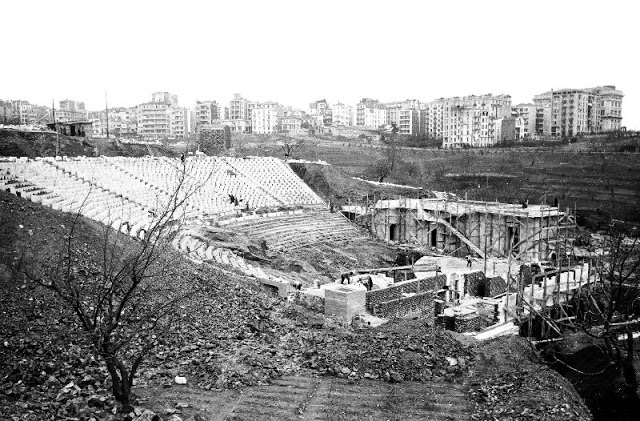
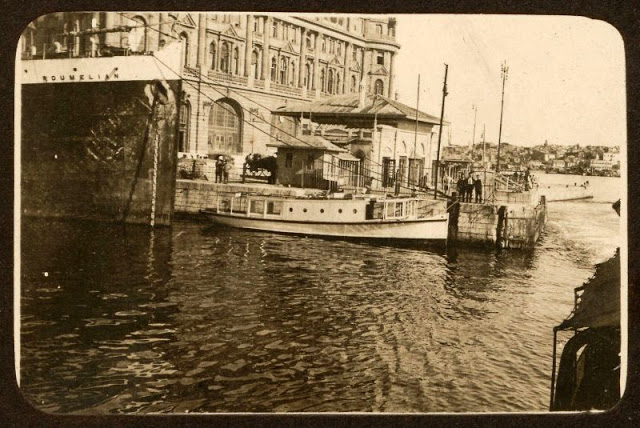
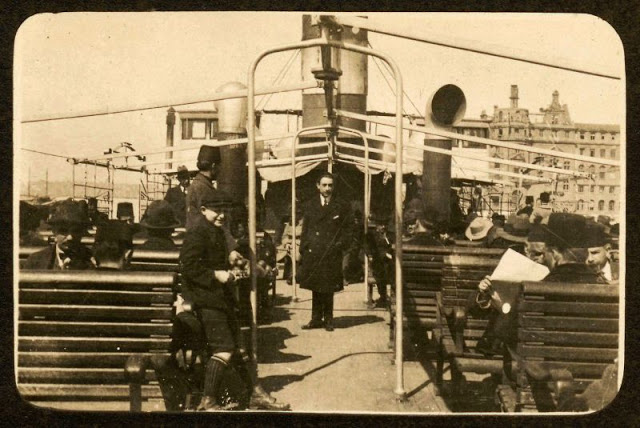
Istanbul, formerly known as Constantinople, is the largest city in Turkey and the country’s economic, cultural and historic center. The city straddles the Bosporus strait, and lies in both Europe and Asia, with a population of over 15 million residents, comprising 19% of the population of Turkey. Istanbul is the most populous city in Europe, and the world’s fifteenth-largest city.
Founded as Byzantion by Megarian colonists in the 7th century BCE, and renamed by Constantine the Great first as New Rome (Nova Roma) during the official dedication of the city as the new Roman capital in 330 CE, which he soon afterwards changed to Constantinople (Constantinopolis), the city grew in size and influence, becoming a beacon of the Silk Road and one of the most important cities in history. It served as an imperial capital for almost sixteen centuries, during the Roman/Byzantine (330–1204), Latin (1204–1261), Byzantine (1261–1453), and Ottoman (1453–1922) empires. The city was instrumental in the advancement of Christianity during Roman and Byzantine times, hosting four (including Chalcedon (Kadiköy) on the Asian side) of the first seven ecumenical councils (all of which were in present-day Turkey), before its transformation to an Islamic stronghold following the Fall of Constantinople in 1453 CE, especially after becoming the seat of the Ottoman Caliphate in 1517. In 1923, after the Turkish War of Independence, Ankara replaced the city as the capital of the newly formed Republic of Turkey. In 1930, the city’s name was officially changed to Istanbul, an appellation Greek speakers used since the eleventh century to colloquially refer to the city.
Over 13.4 million foreign visitors came to Istanbul in 2018, eight years after it was named a European Capital of Culture, making it the world’s eighth most visited city. Istanbul is home to several UNESCO World Heritage Sites, and hosts the headquarters of numerous Turkish companies, accounting for more than thirty percent of the country’s economy. (Wikipedia)
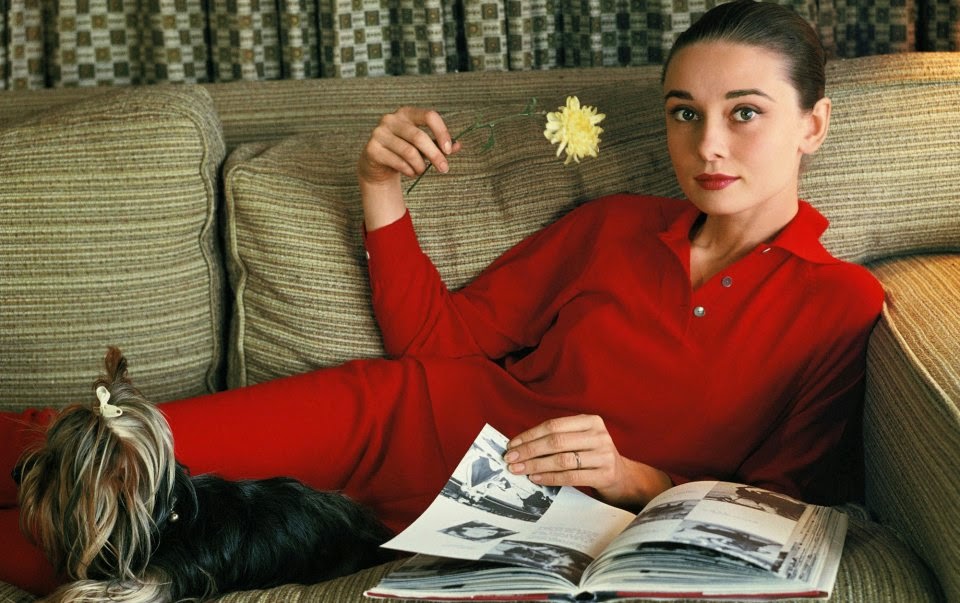














































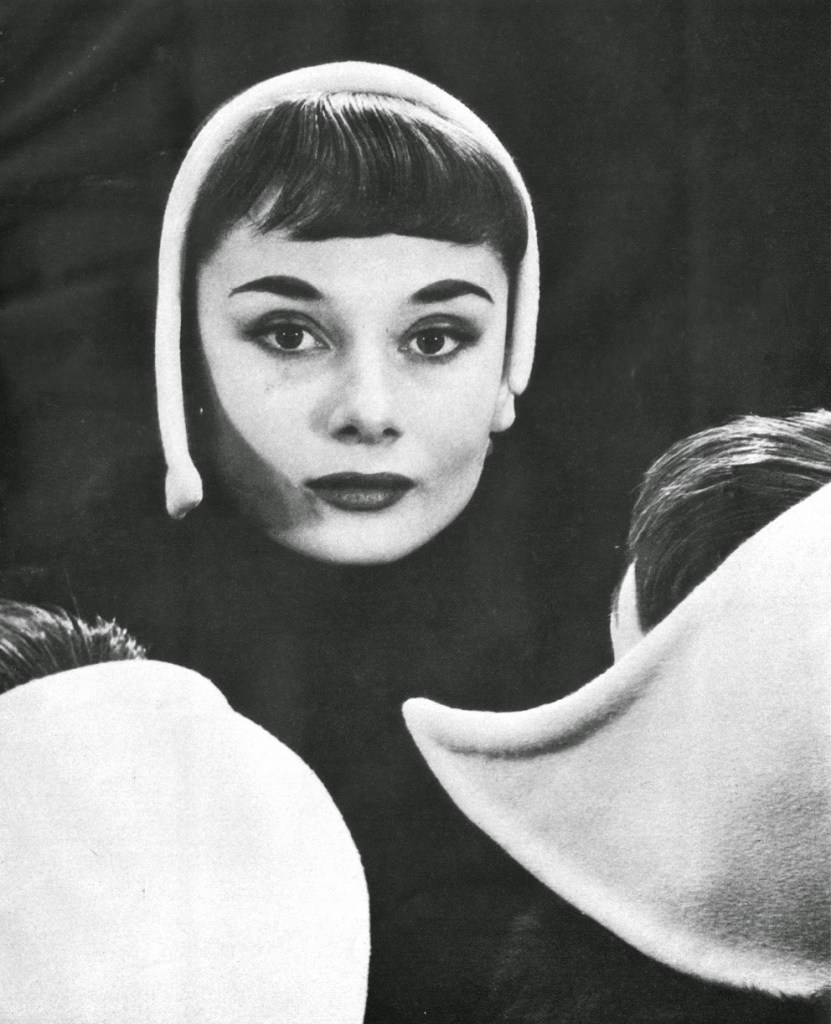
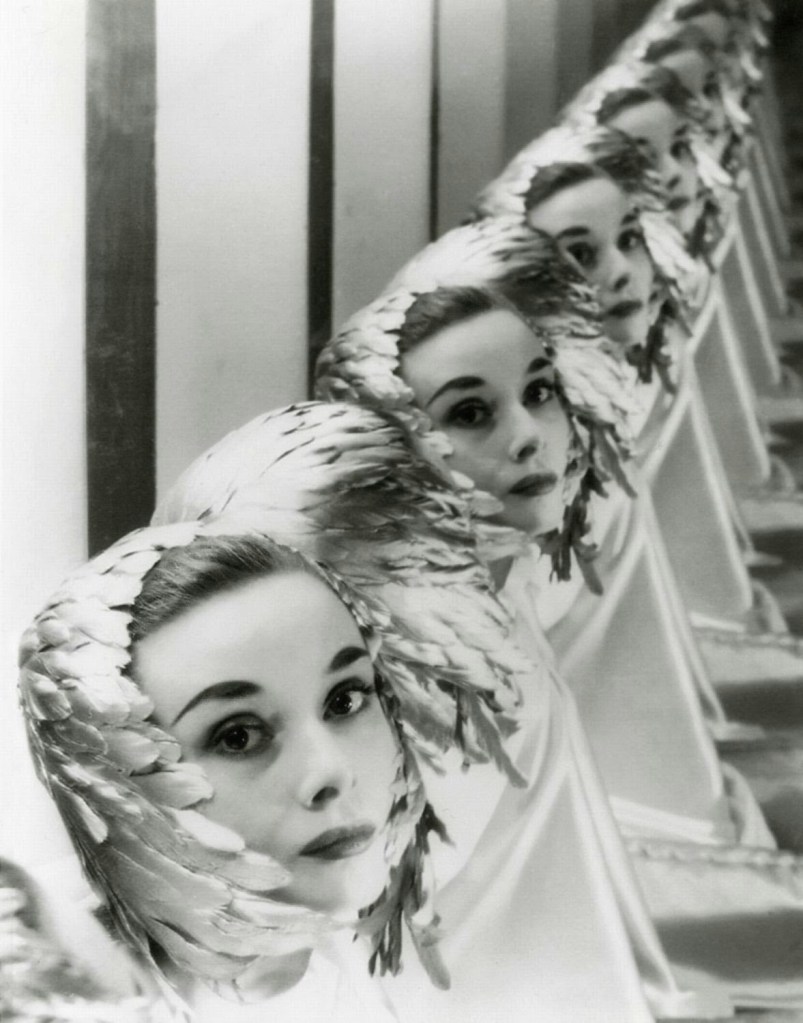
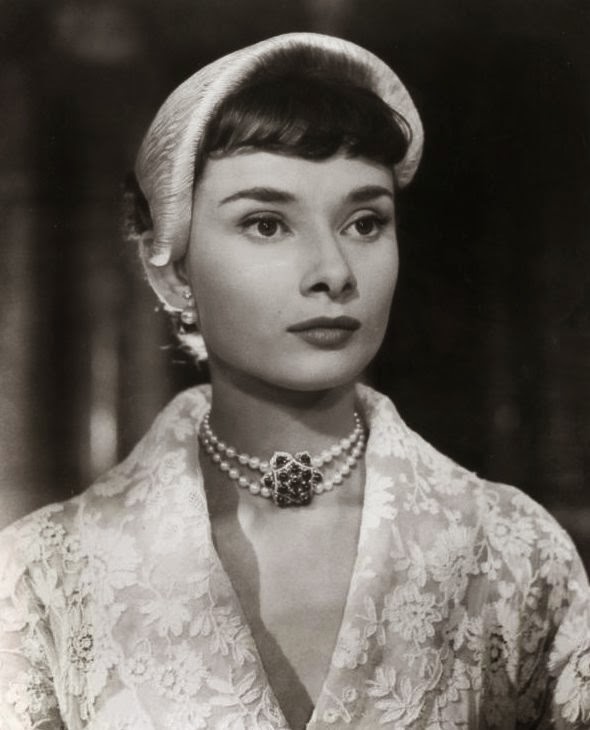
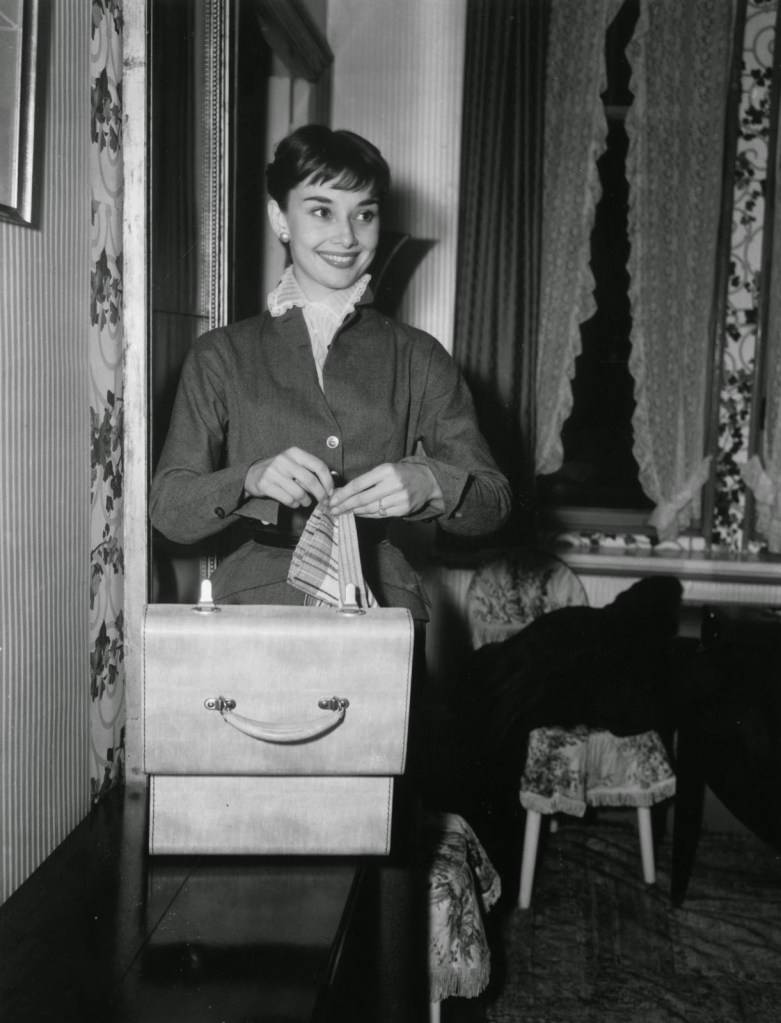
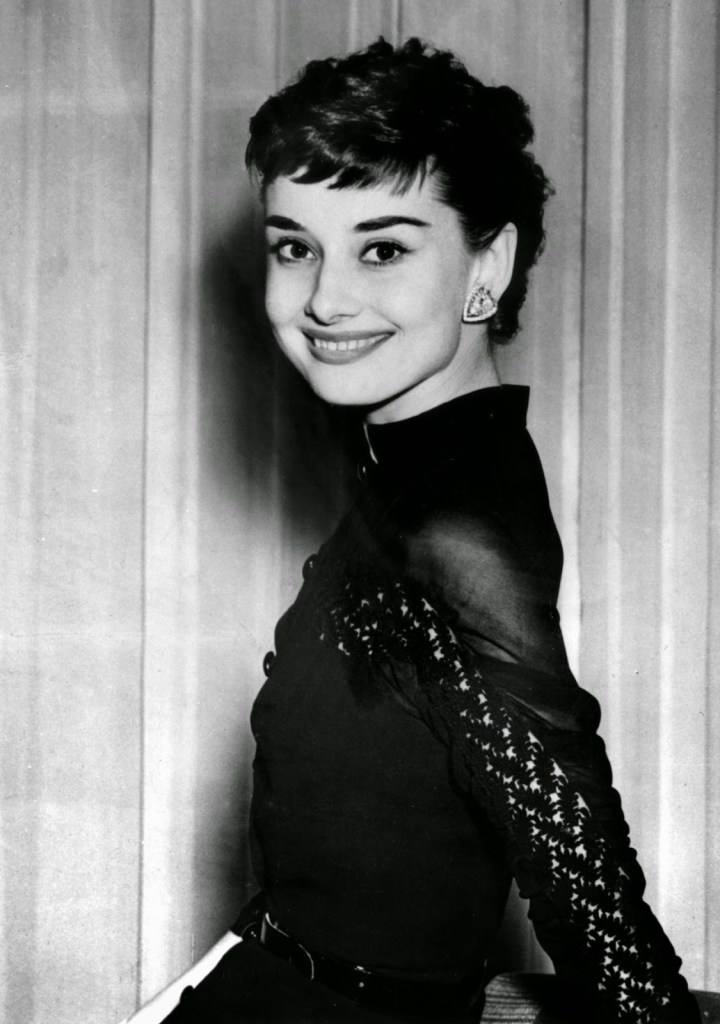
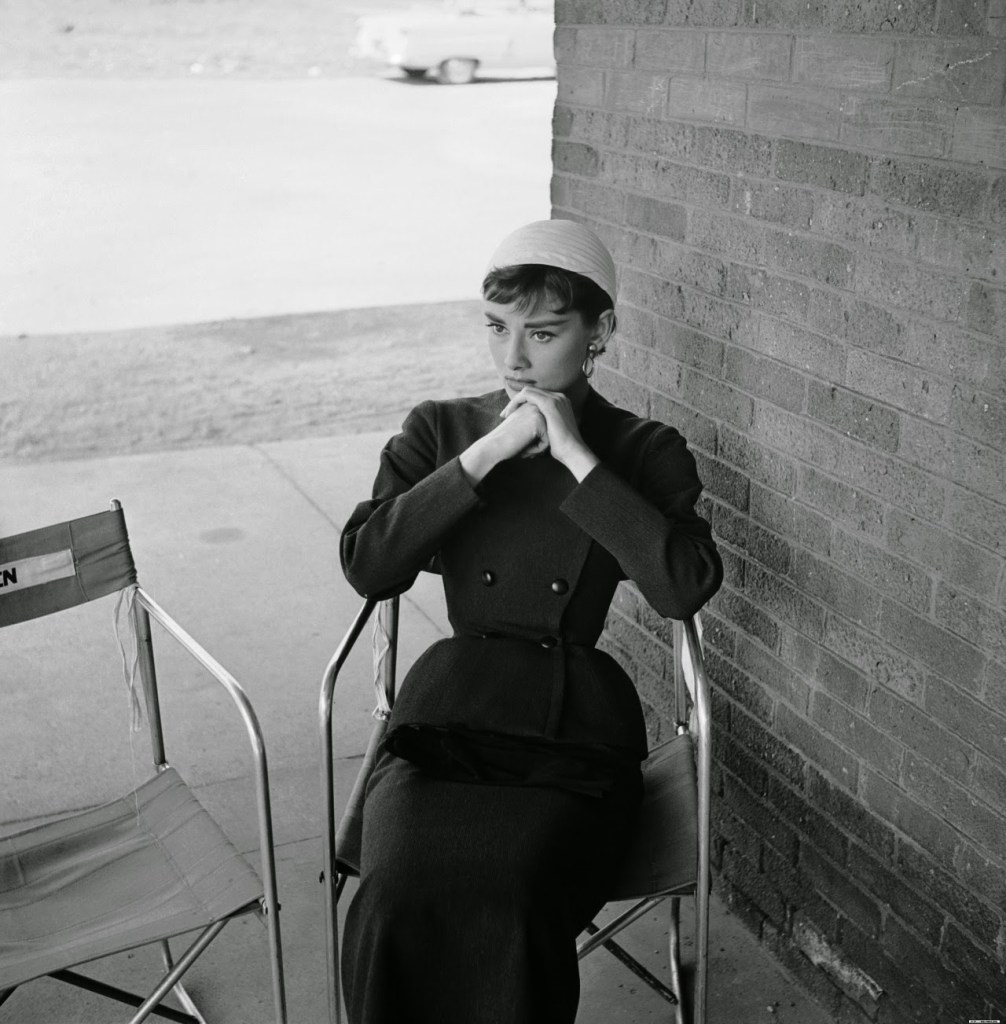
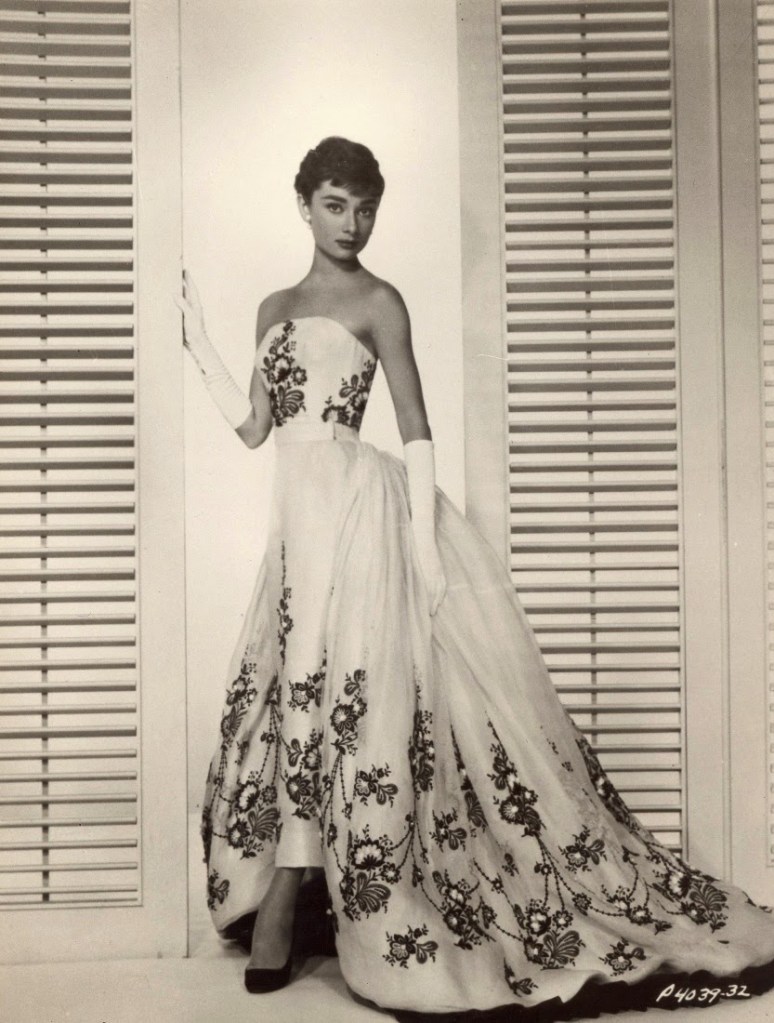
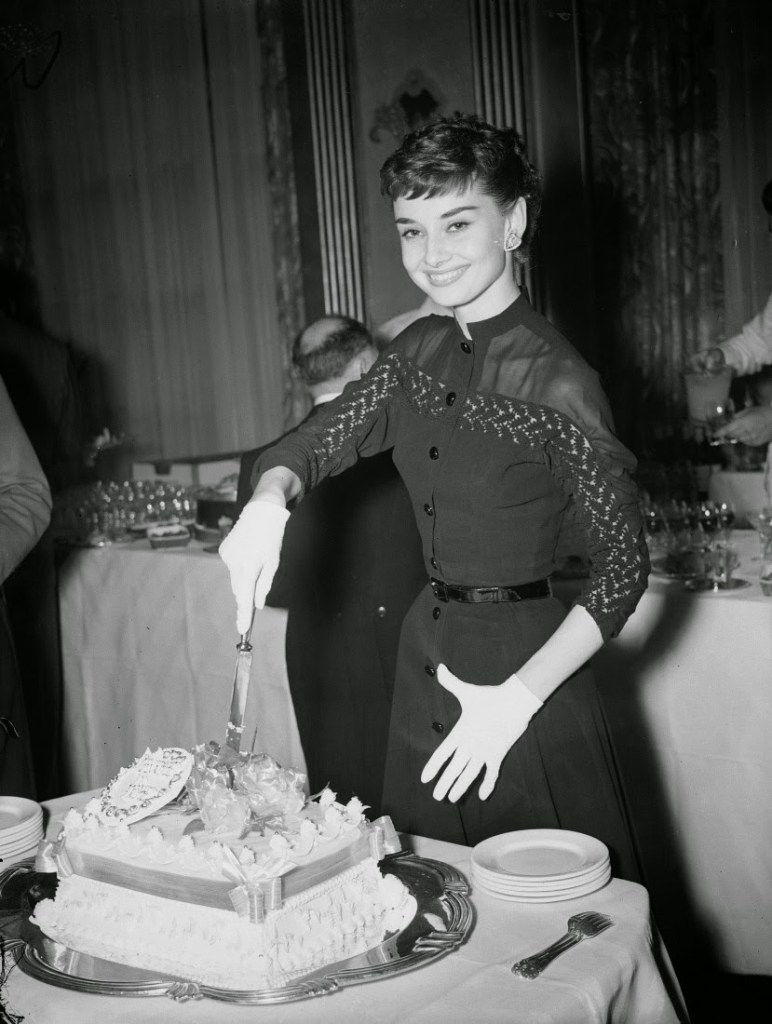
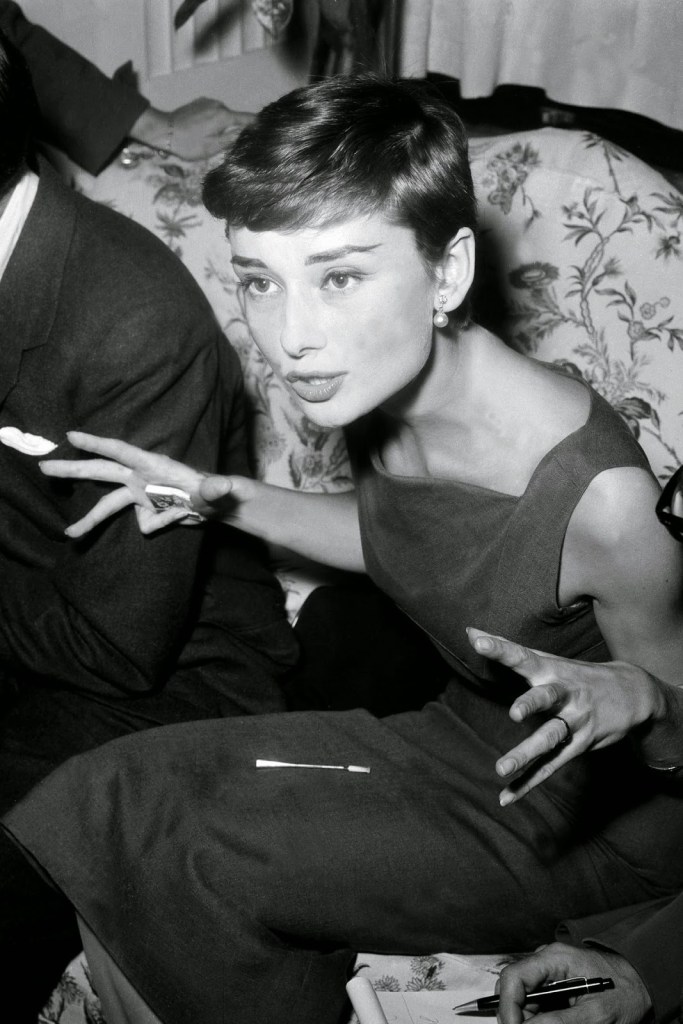
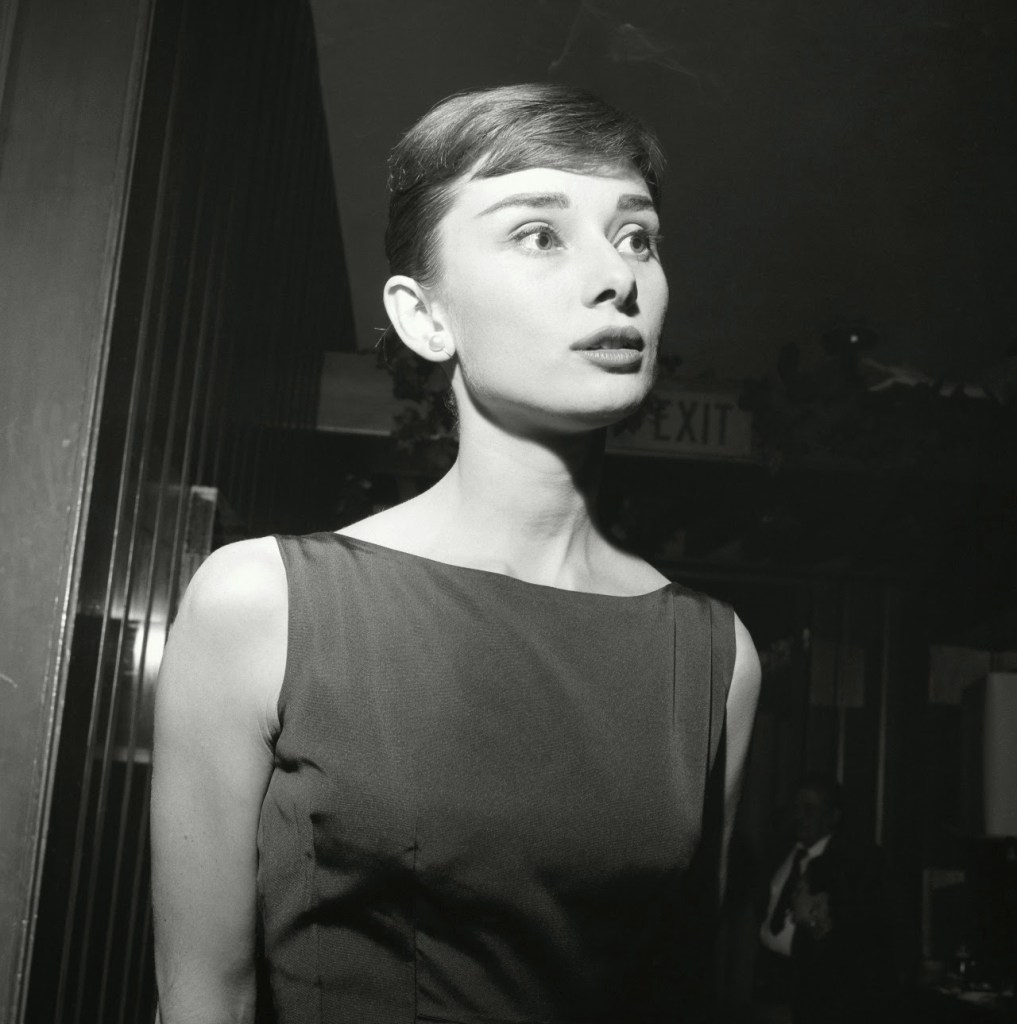
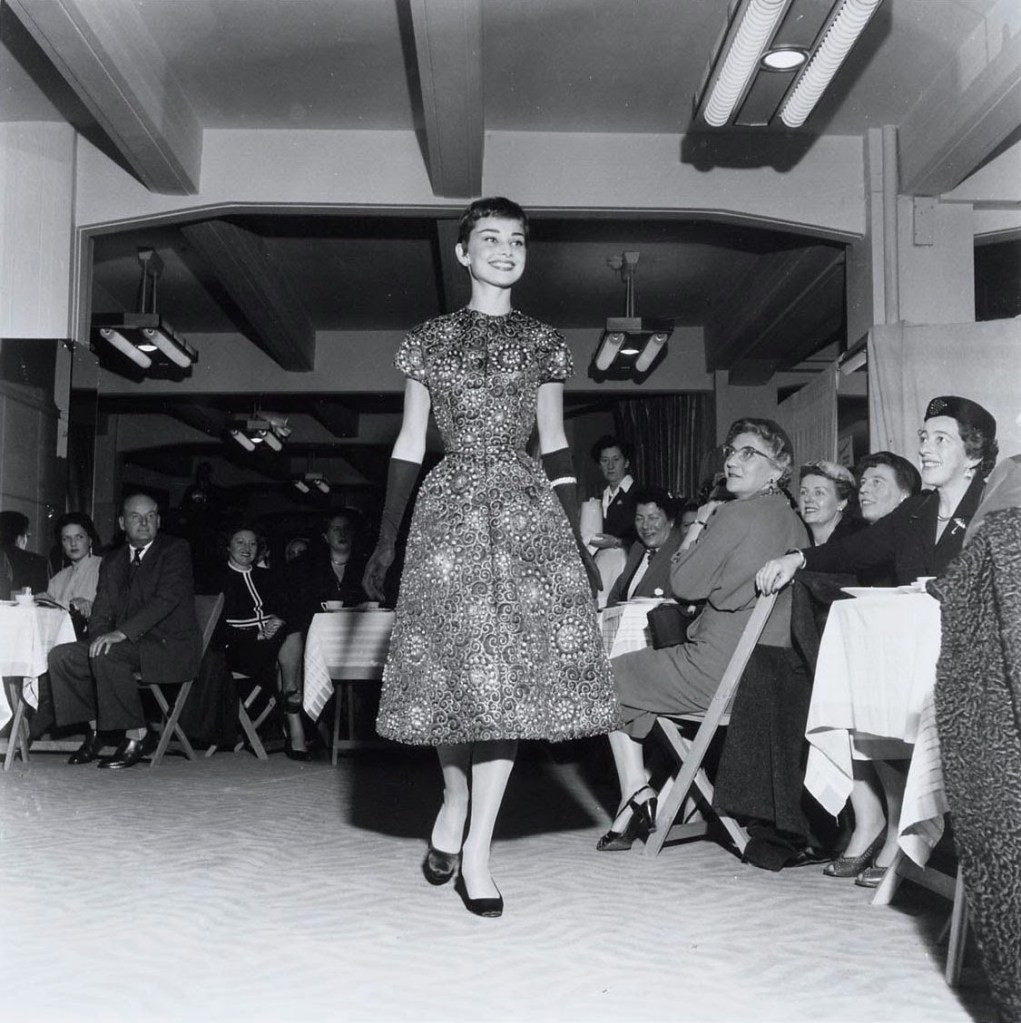
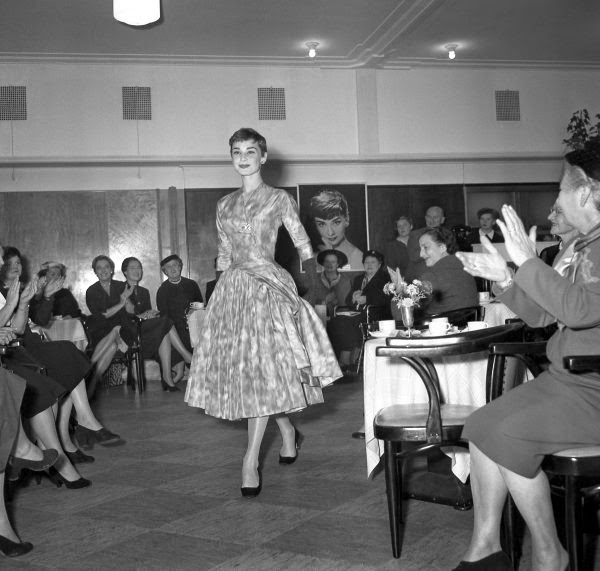
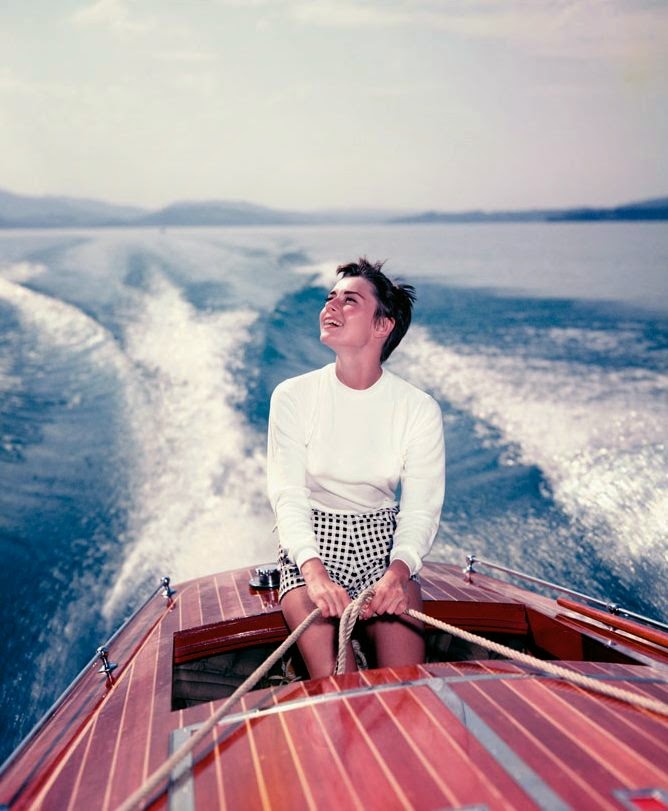
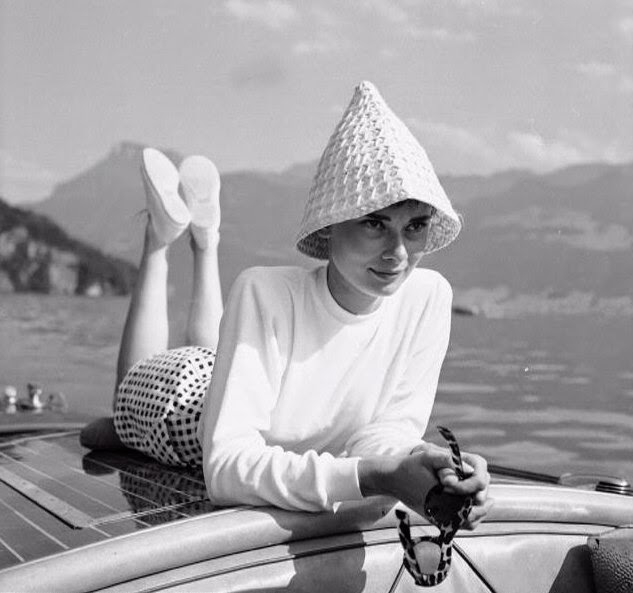
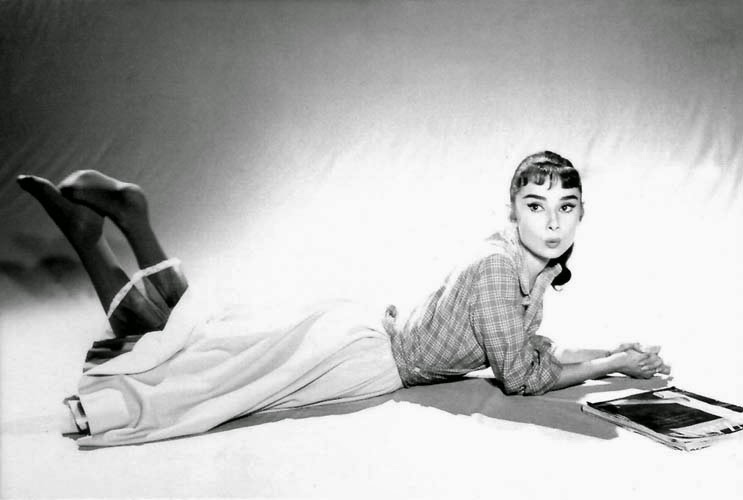
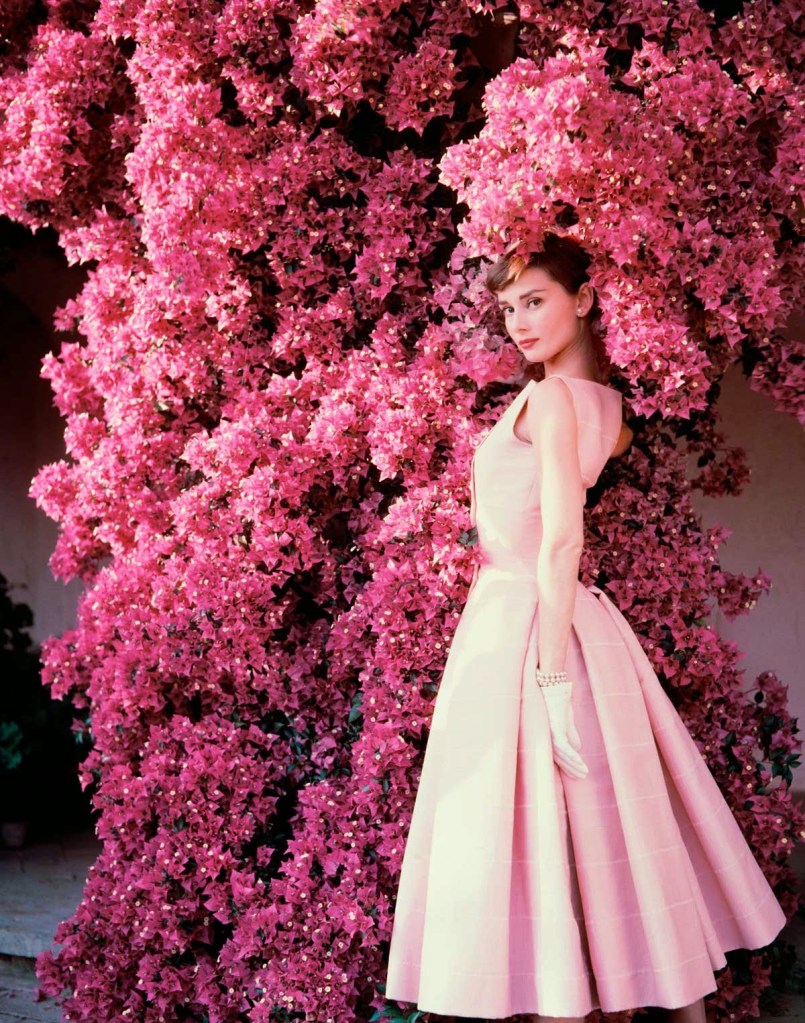
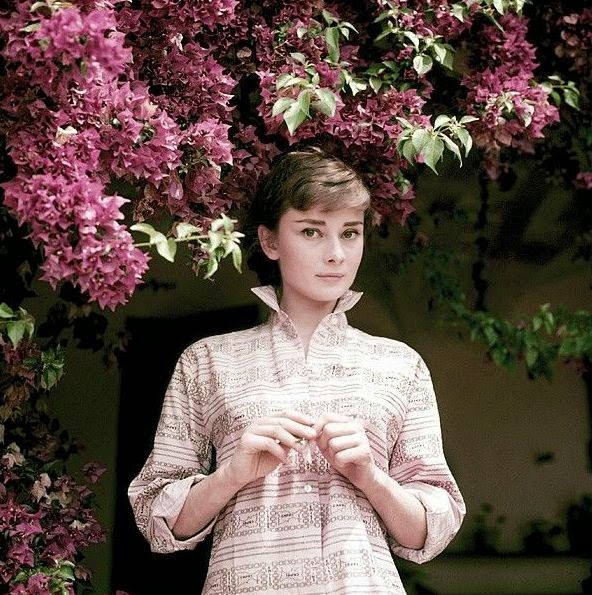
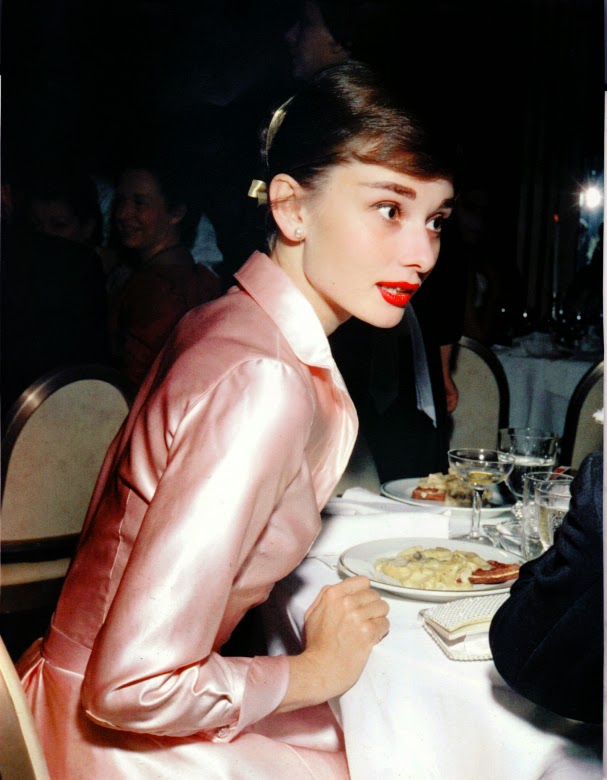
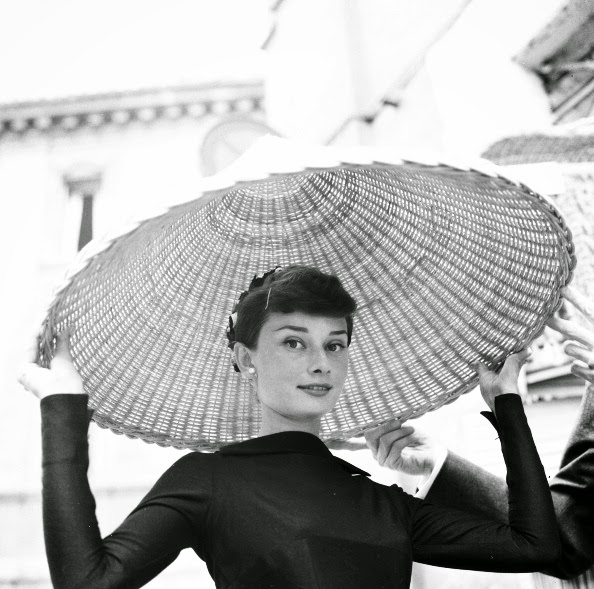
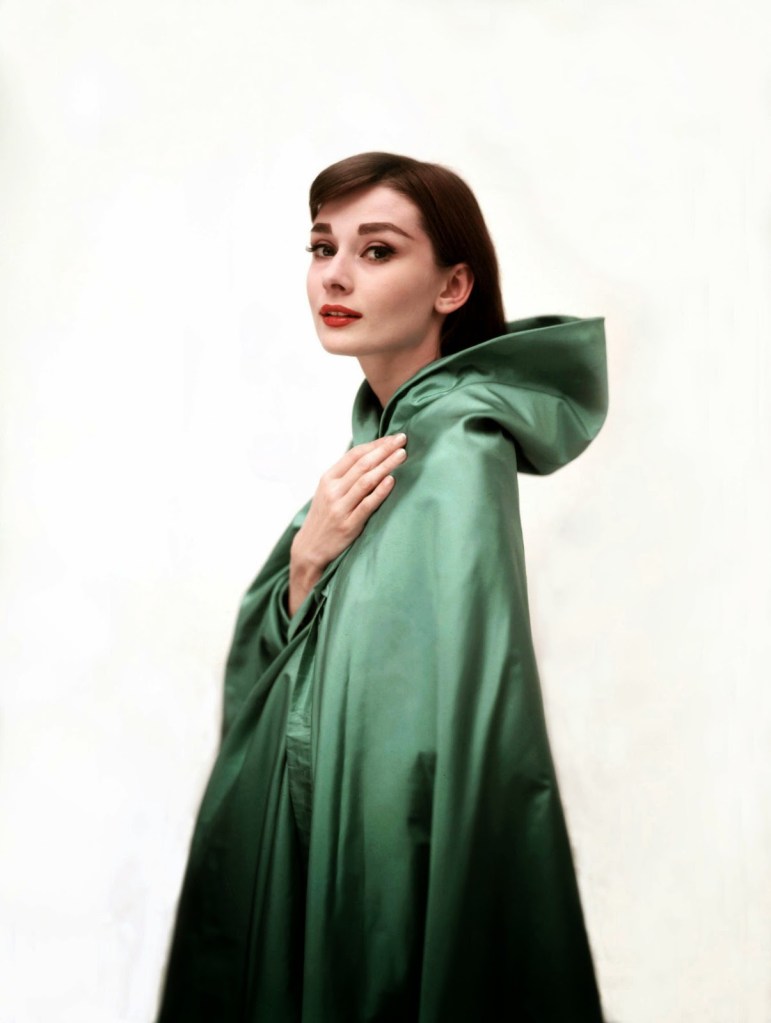
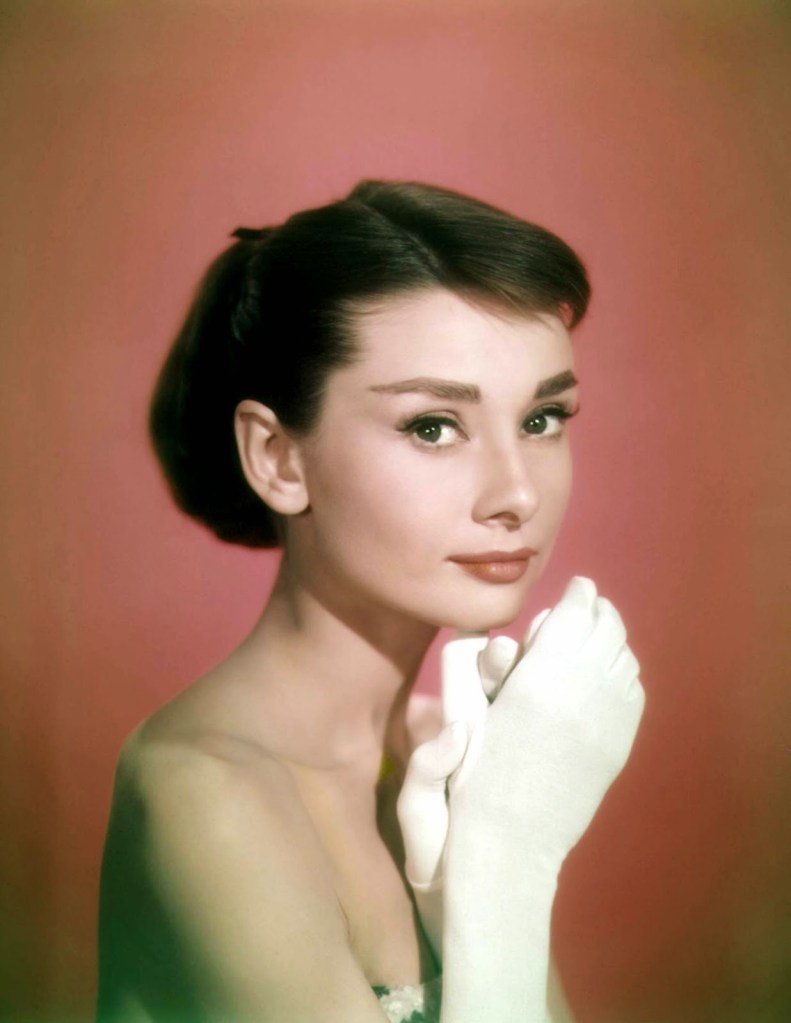
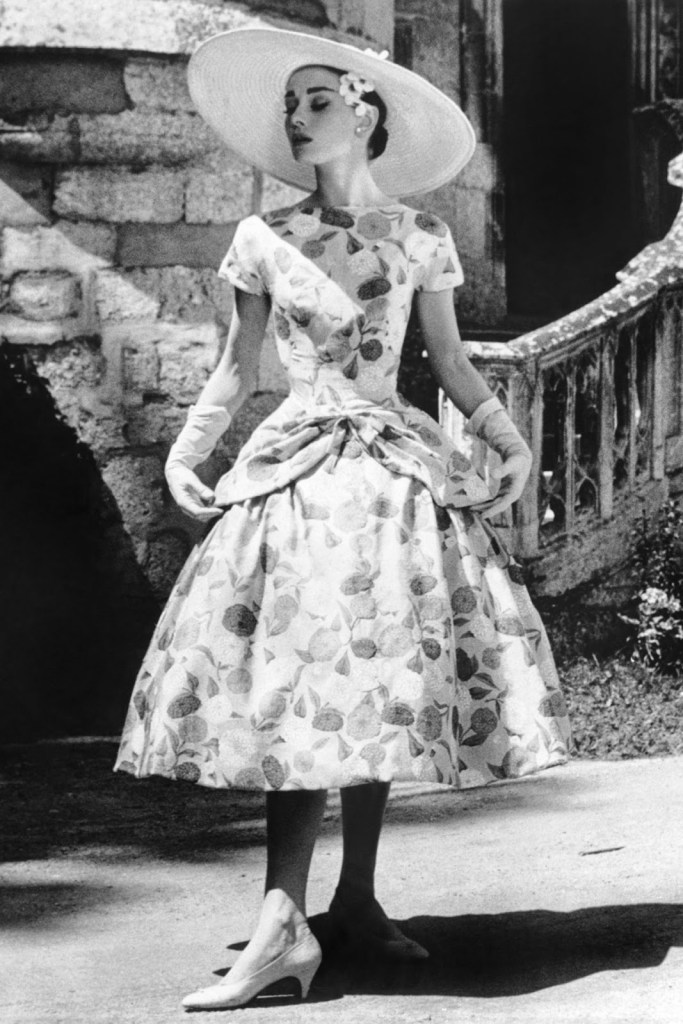
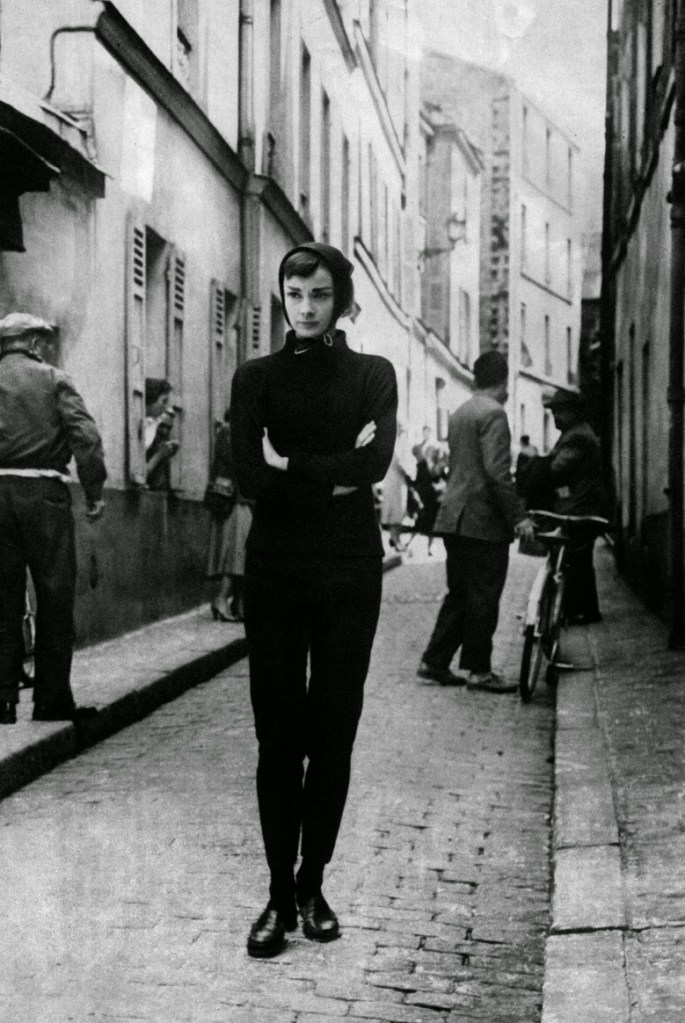
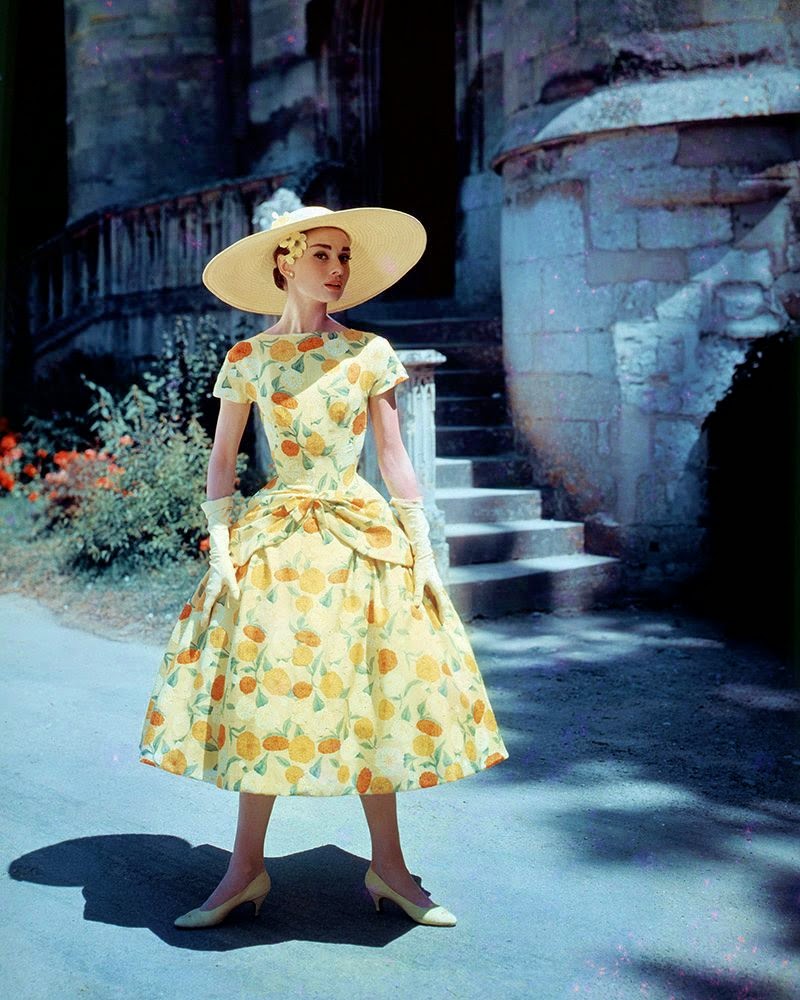
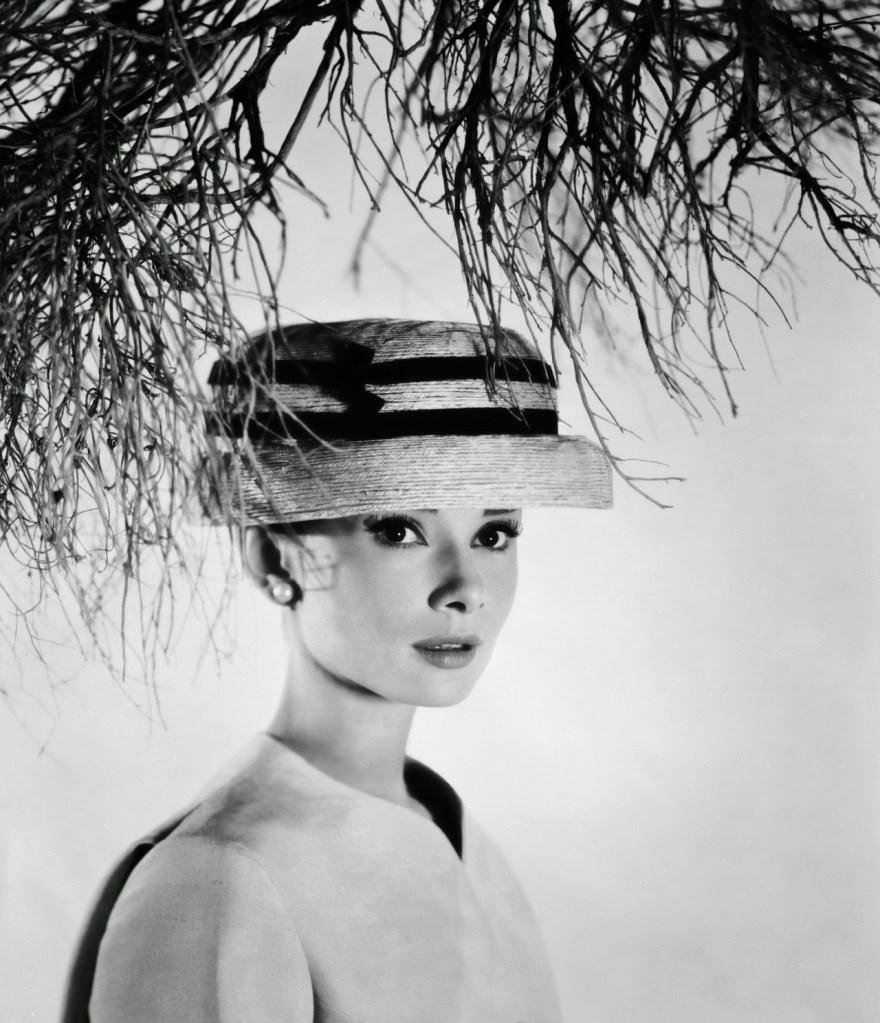
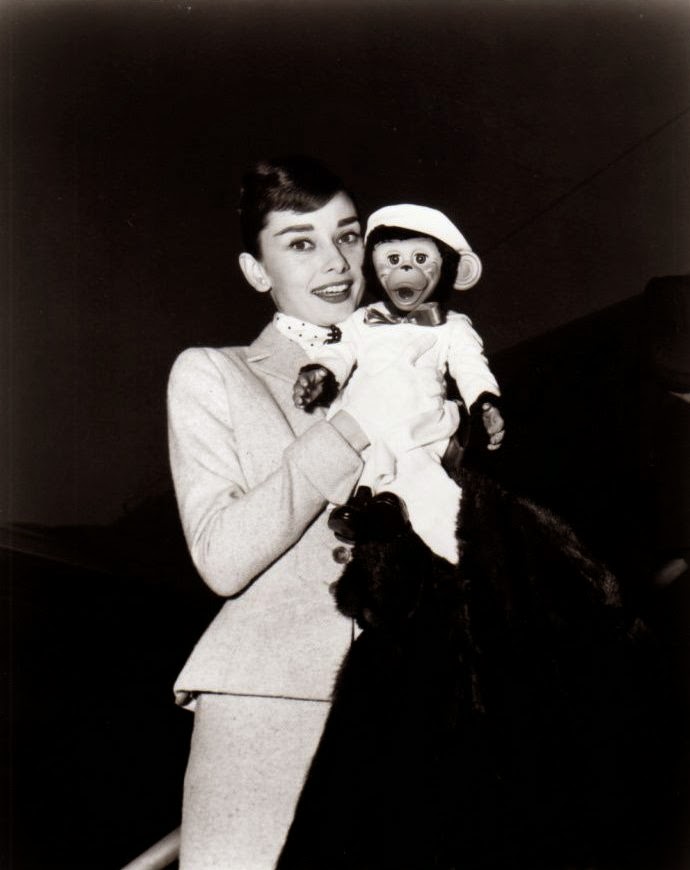
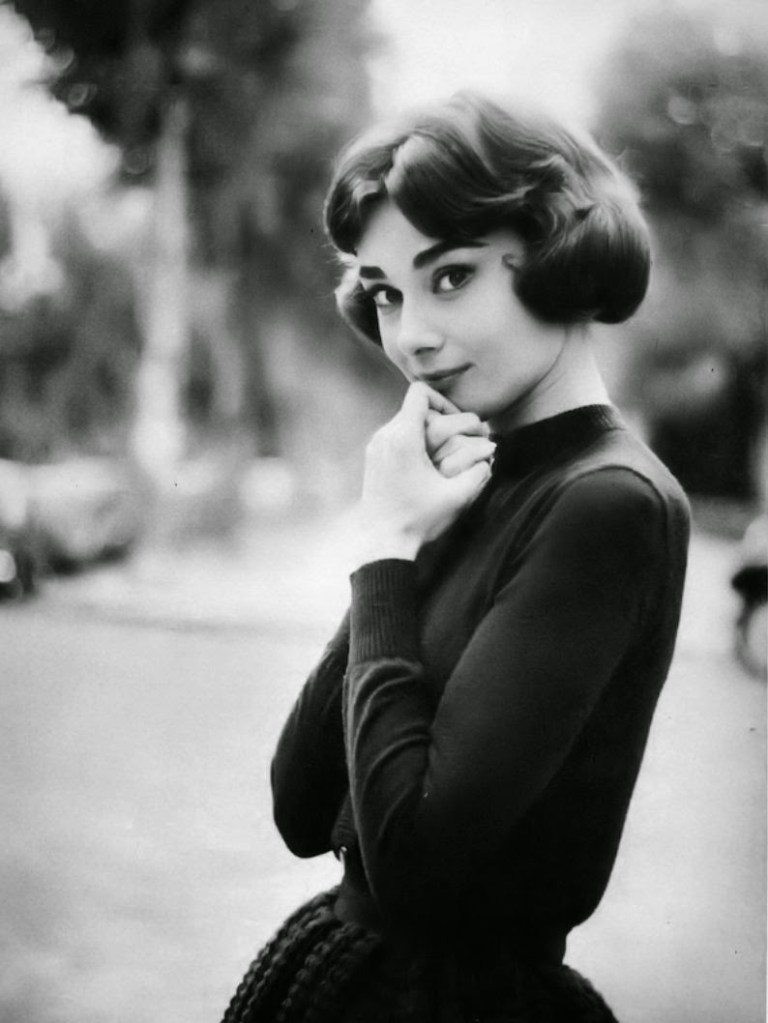
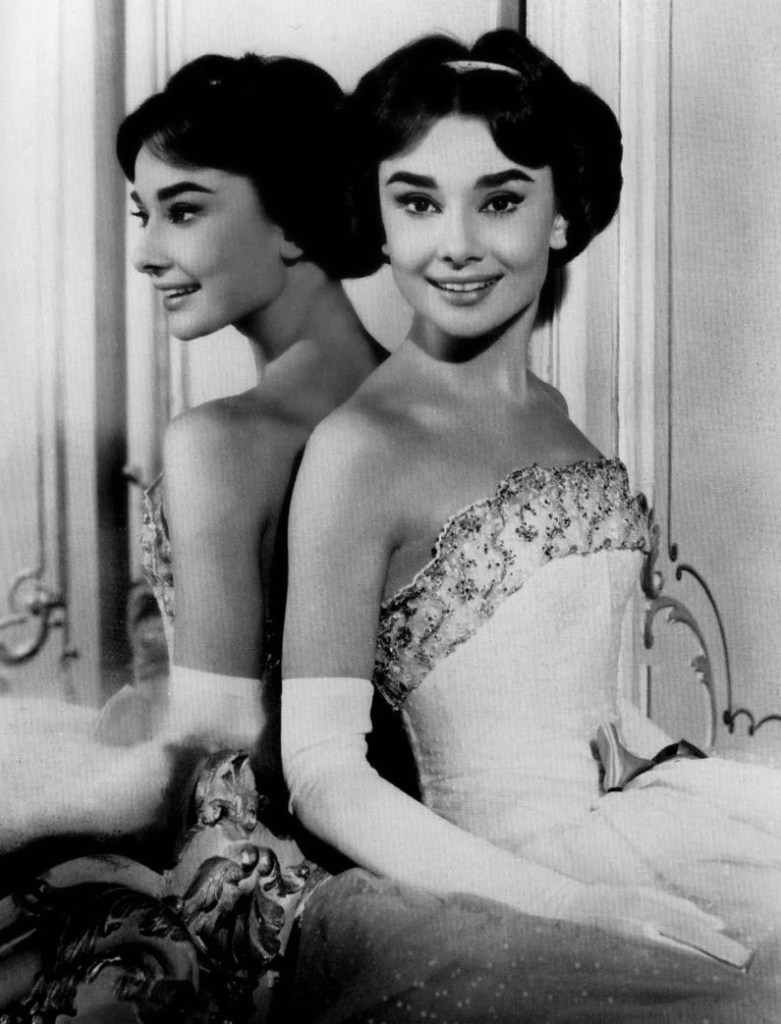
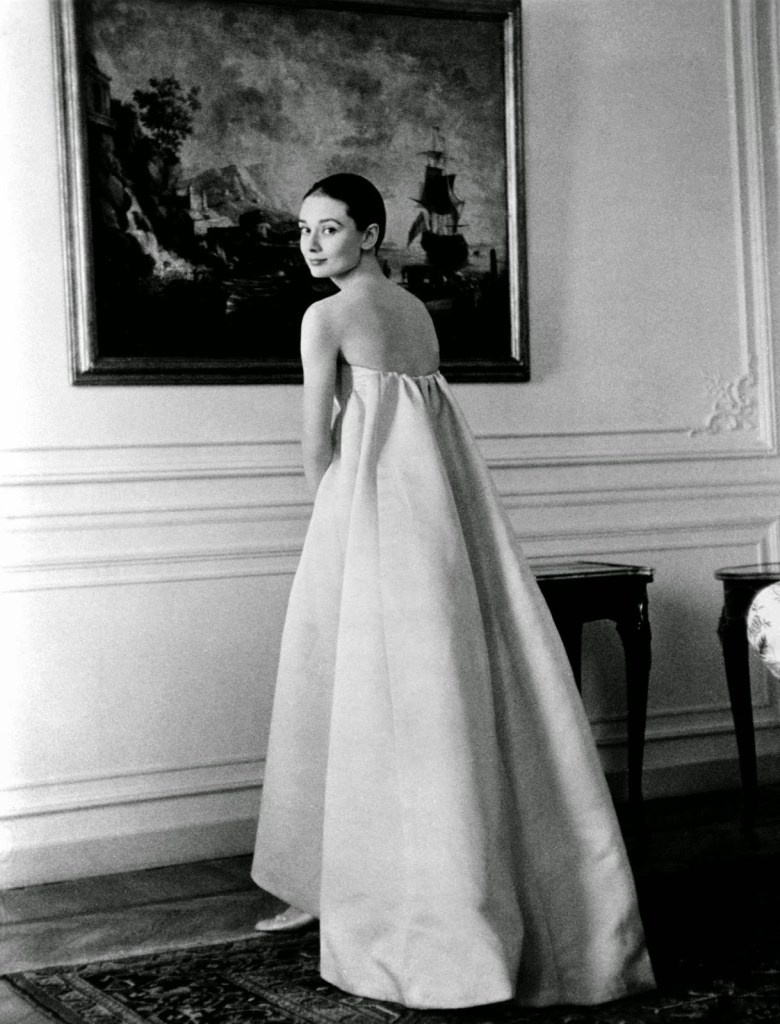
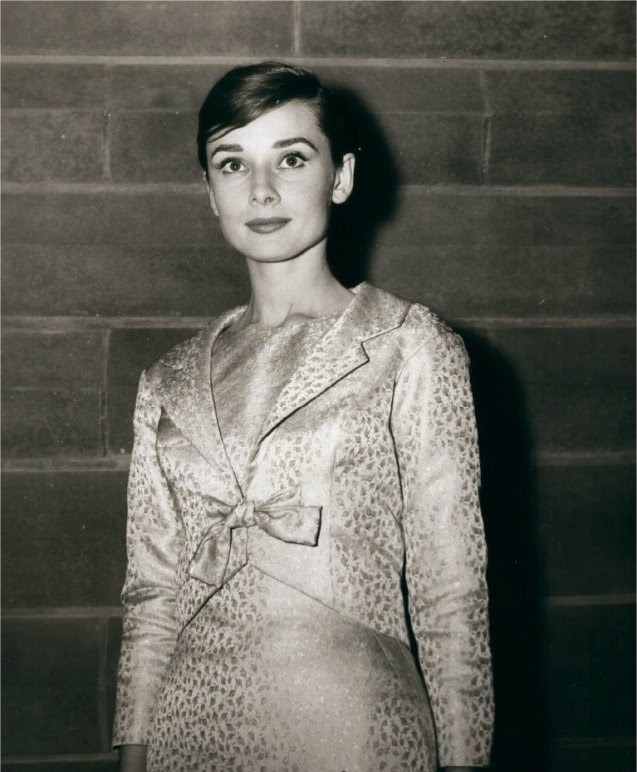
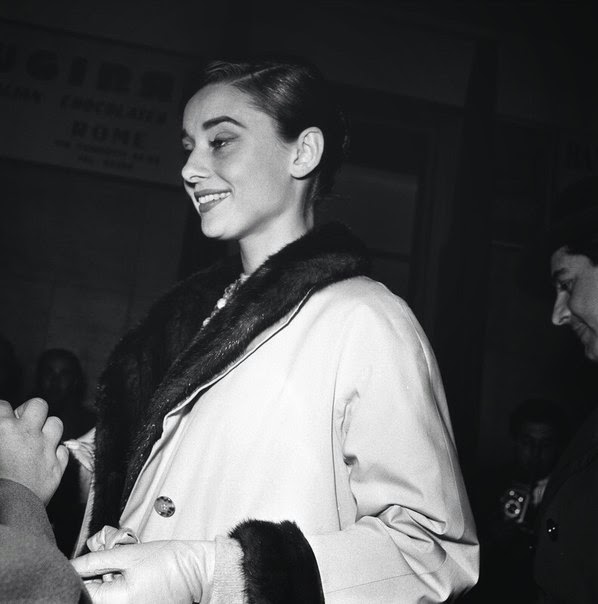
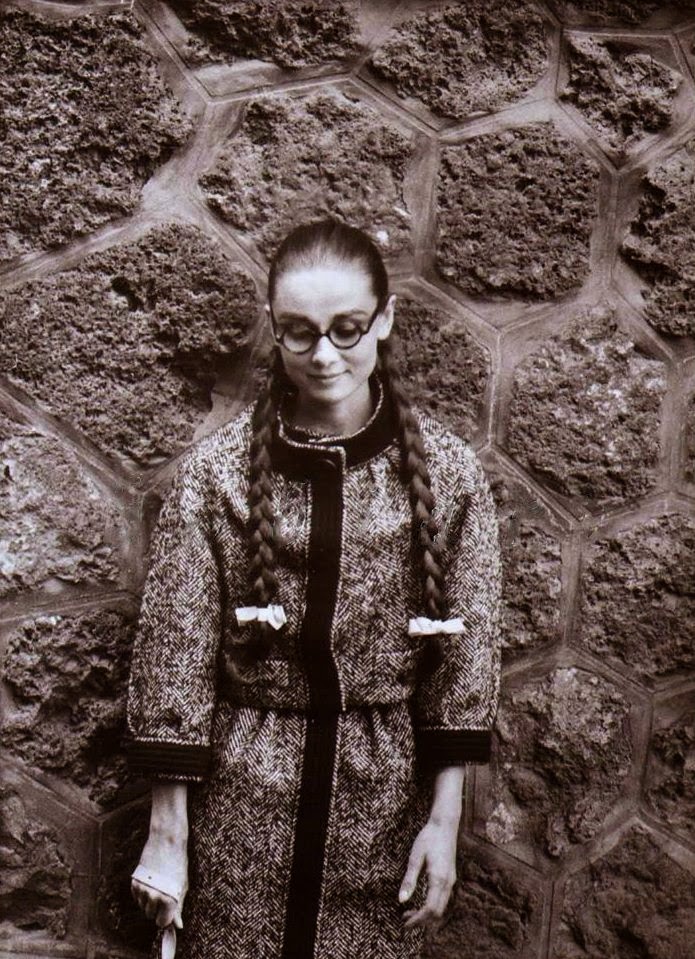
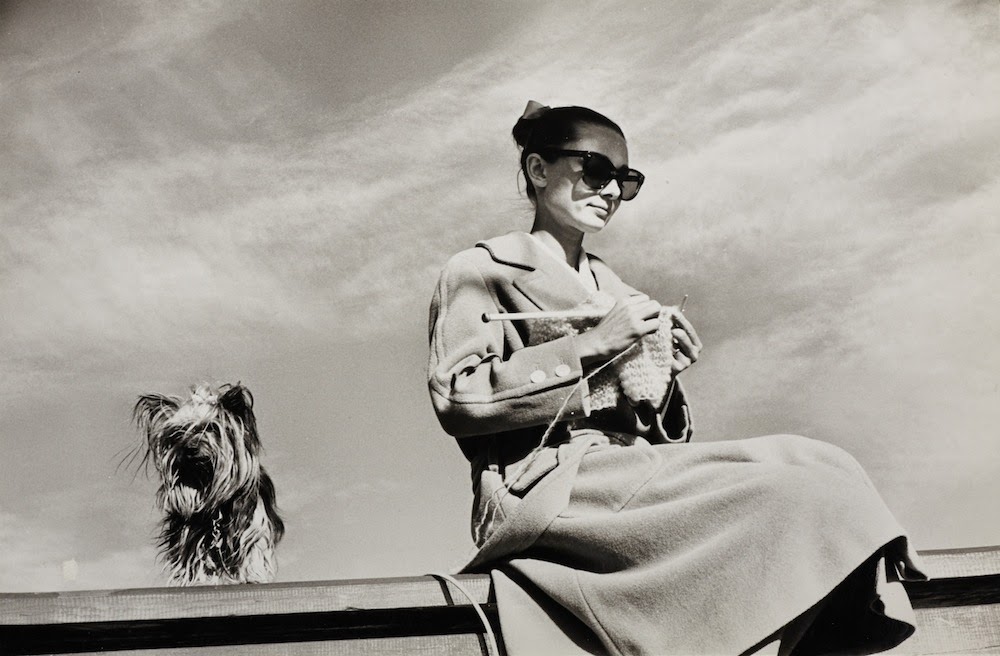
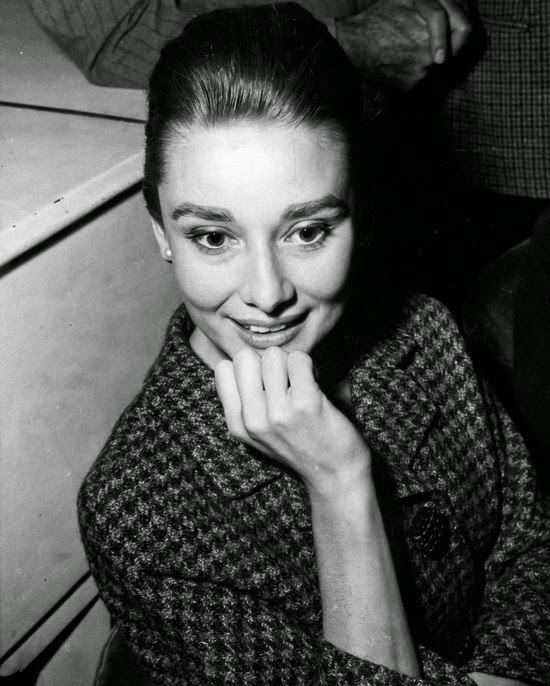
Audrey Hepburn (born Audrey Kathleen Ruston; 4 May 1929 – 20 January 1993) was a British actress and humanitarian. Recognised as both a film and fashion icon, she was ranked by the American Film Institute as the third-greatest female screen legend from the Classical Hollywood cinema and was inducted into the International Best Dressed List Hall of Fame.
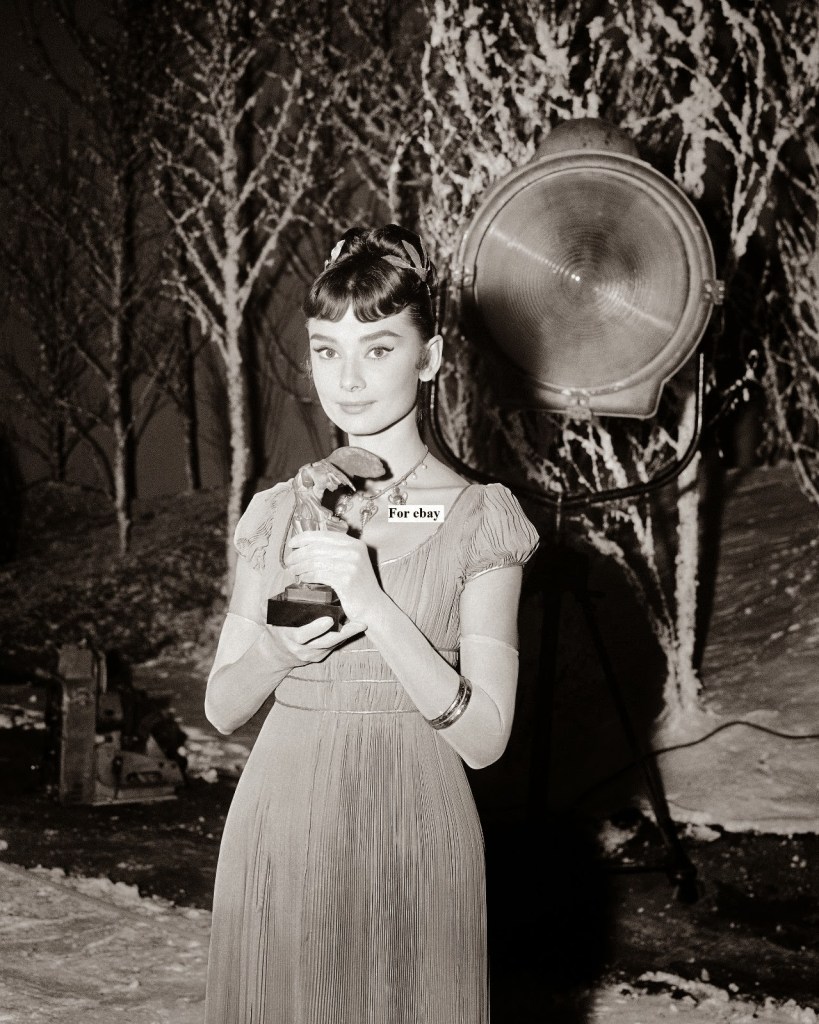
Born in Ixelles, Brussels, Hepburn spent parts of her childhood in Belgium, England, and the Netherlands. She studied ballet with Sonia Gaskell in Amsterdam beginning in 1945, and with Marie Rambert in London from 1948. She began performing as a chorus girl in West End musical theatre productions and then had minor appearances in several films. She rose to stardom in the romantic comedy Roman Holiday (1953) alongside Gregory Peck, for which she was the first actress to win an Oscar, a Golden Globe Award, and a BAFTA Award for a single performance. That year, she also won a Tony Award for Best Lead Actress in a Play for her performance in Ondine.
She went on to star in a number of successful films such as Sabrina (1954), in which Humphrey Bogart and William Holden compete for her affection; Funny Face (1957), a musical where she sang her own parts; the drama The Nun’s Story (1959); the romantic comedy Breakfast at Tiffany’s (1961); the thriller-romance Charade (1963), opposite Cary Grant; and the musical My Fair Lady (1964). In 1967 she starred in the thriller Wait Until Dark, receiving Academy Award, Golden Globe, and BAFTA nominations. After that, she only occasionally appeared in films, one being Robin and Marian (1976) with Sean Connery. Her last recorded performances were in the 1990 documentary television series Gardens of the World with Audrey Hepburn.
Hepburn won three BAFTA Awards for Best British Actress in a Leading Role. In recognition of her film career, she received BAFTA’s Lifetime Achievement Award, the Golden Globe Cecil B. DeMille Award, the Screen Actors Guild Life Achievement Award, and the Special Tony Award. She remains one of only sixteen people who have won Academy, Emmy, Grammy, and Tony Awards. Later in life, Hepburn devoted much of her time to UNICEF, to which she had contributed since 1954. Between 1988 and 1992, she worked in some of the poorest communities of Africa, South America, and Asia. In December 1992, she received the Presidential Medal of Freedom in recognition of her work as a UNICEF Goodwill Ambassador. A month later, she died of appendiceal cancer at her home in Switzerland at the age of 63. (Wikipedia)
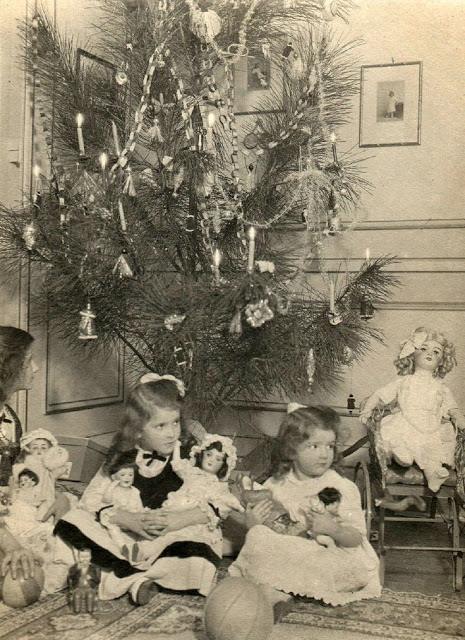





















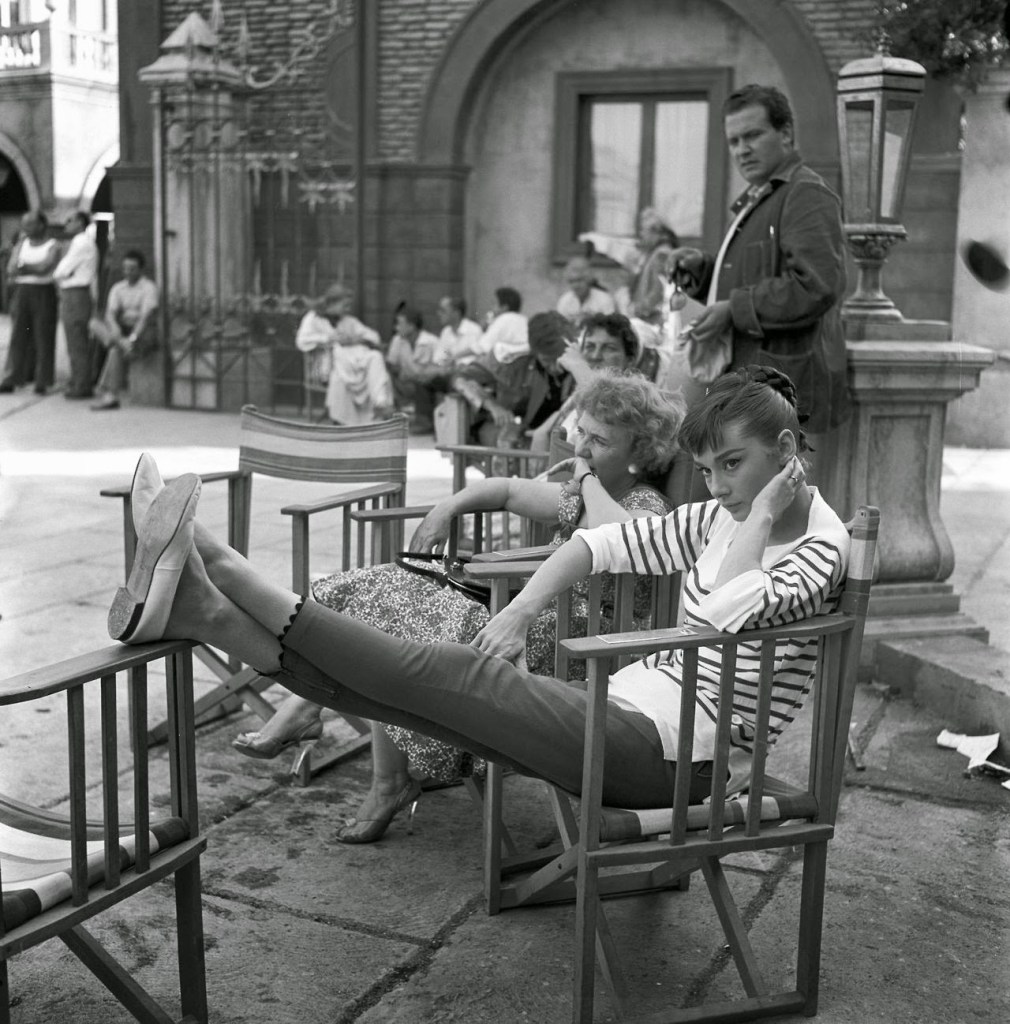





























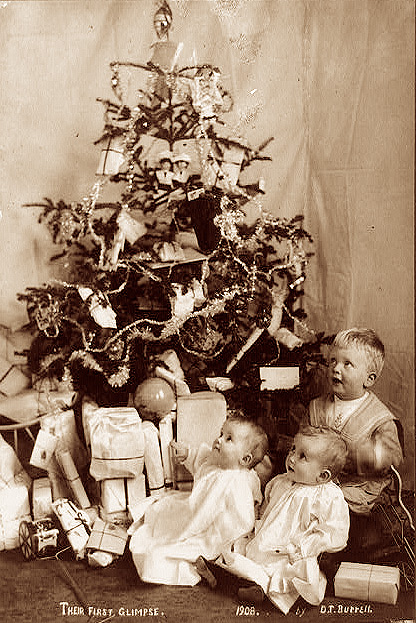
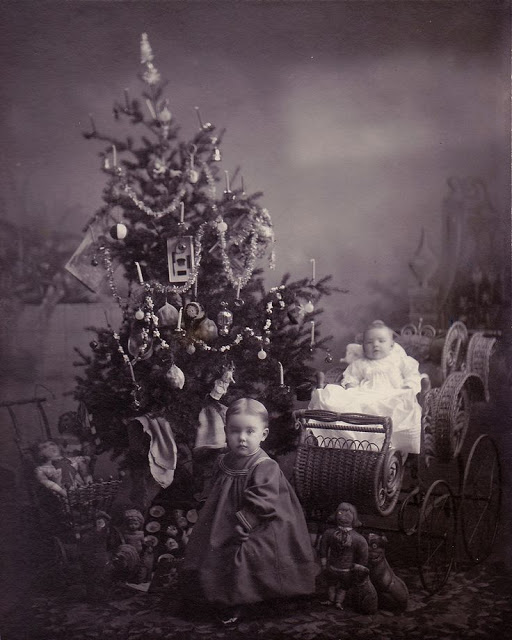
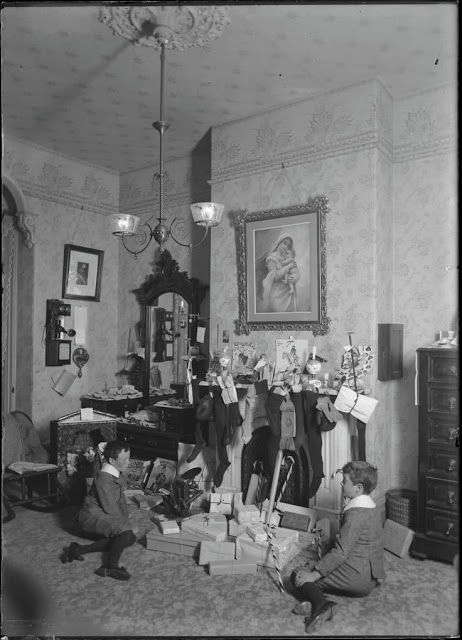
From lighting a real candle on the branch of an indoor Christmas tree, to a well-dressed family singing carols on a stairwell in the home, this lovely collection of nostalgic photos reveal how children from a bygone era celebrated the festive season.
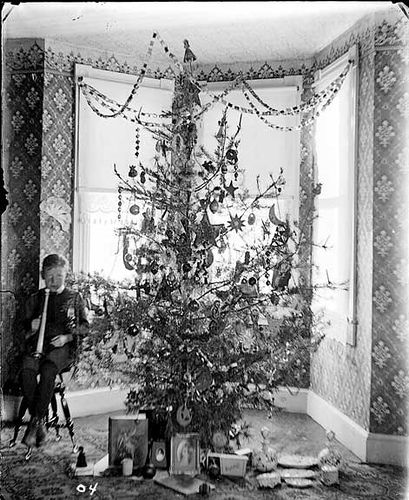
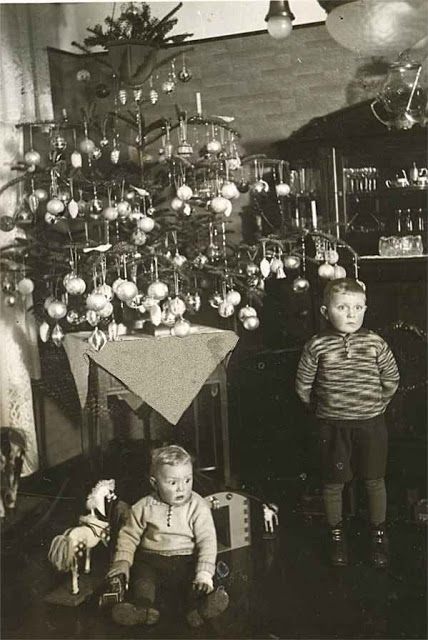
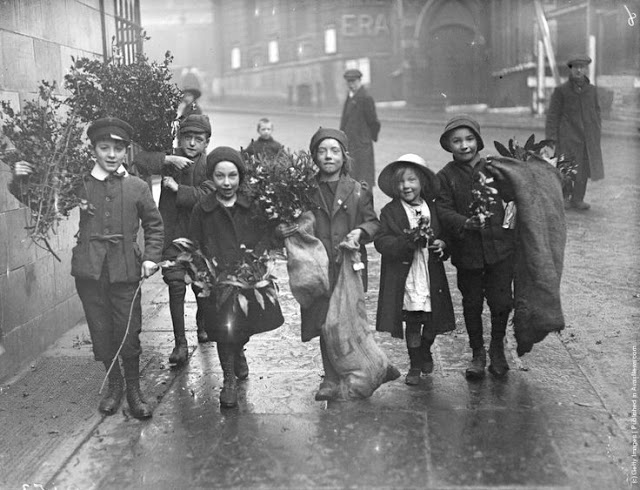
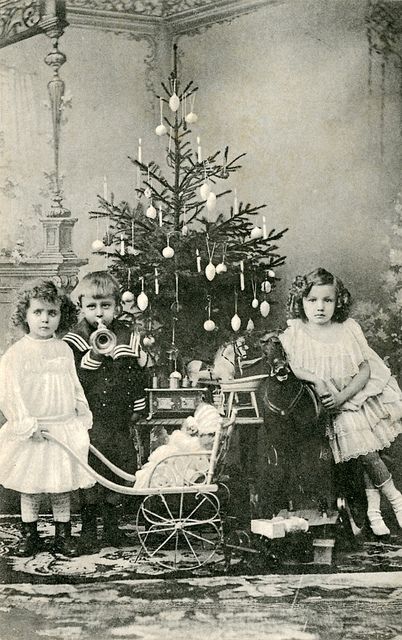
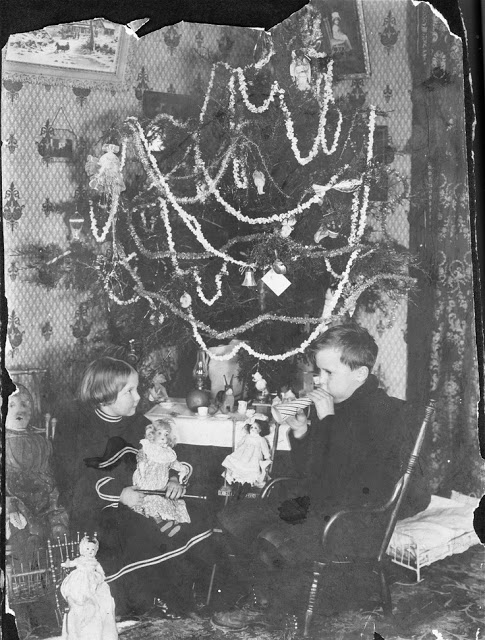























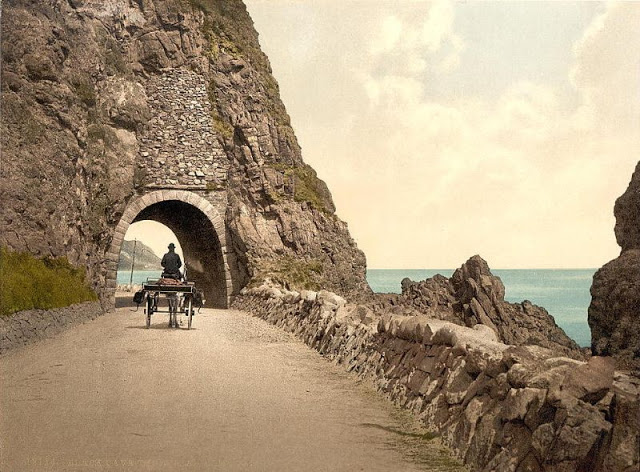
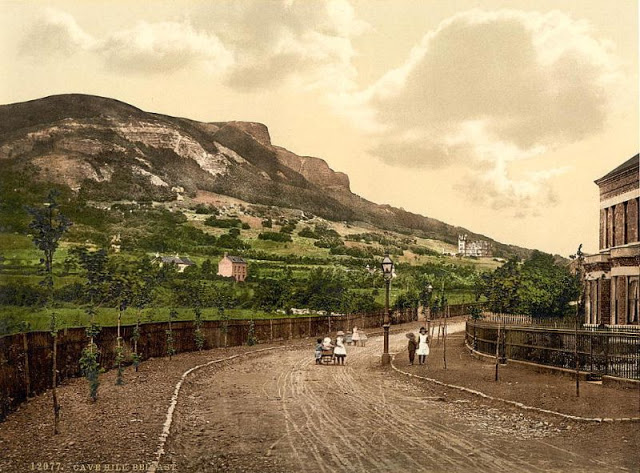
Ireland is an island in the North Atlantic. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George’s Channel. Ireland is the second-largest island of the British Isles, the third-largest in Europe, and the twentieth-largest on Earth.
Geopolitically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially named Ireland), which covers five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. In 2011, the population of Ireland was about 6.6 million, ranking it the second-most populous island in Europe after Great Britain. As of 2016, 4.8 million lived in the Republic of Ireland, and 1.8 million in Northern Ireland.
The geography of Ireland comprises relatively low-lying mountains surrounding a central plain, with several navigable rivers extending inland. Its lush vegetation is a product of its mild but changeable climate which is free of extremes in temperature. Much of Ireland was woodland until the end of the Middle Ages. Today, woodland makes up about 10% of the island, compared with a European average of over 33%, and most of it is non-native conifer plantations. There are twenty-six extant land mammal species native to Ireland. The Irish climate is influenced by the Atlantic Ocean and thus very moderate, and winters are milder than expected for such a northerly area, although summers are cooler than those in continental Europe. Rainfall and cloud cover are abundant.
Gaelic Ireland had emerged by the 1st century AD. The island was Christianised from the 5th century onwards. Following the 12th century Anglo-Norman invasion, England claimed sovereignty. However, English rule did not extend over the whole island until the 16th–17th century Tudor conquest, which led to colonisation by settlers from Britain. In the 1690s, a system of Protestant English rule was designed to materially disadvantage the Catholic majority and Protestant dissenters, and was extended during the 18th century. With the Acts of Union in 1801, Ireland became a part of the United Kingdom. A war of independence in the early 20th century was followed by the partition of the island, thus creating the Irish Free State, which became increasingly sovereign over the following decades, and Northern Ireland, which remained a part of the United Kingdom. Northern Ireland saw much civil unrest from the late 1960s until the 1990s. This subsided following the Good Friday Agreement in 1998. In 1973, the Republic of Ireland joined the European Economic Community while the United Kingdom, and Northern Ireland, as part of it, did the same. In 2020, the United Kingdom, Northern Ireland included, left what was by then the European Union (EU).
Irish culture has had a significant influence on other cultures, especially in the field of literature. Alongside mainstream Western culture, a strong indigenous culture exists, as expressed through Gaelic games, Irish music, Irish language, and Irish dance. The island’s culture shares many features with that of Great Britain, including the English language, and sports such as association football, rugby, horse racing, golf, and boxing. (Wikipedia)
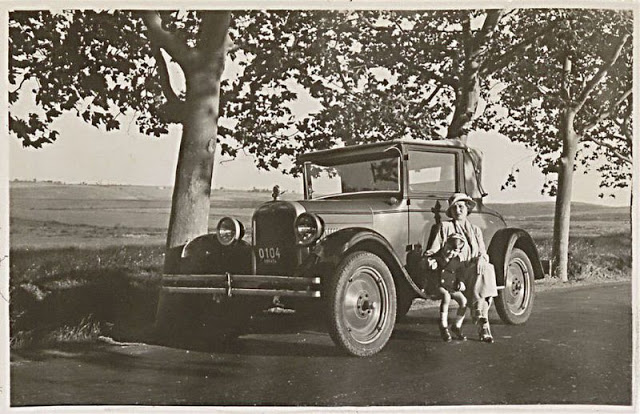
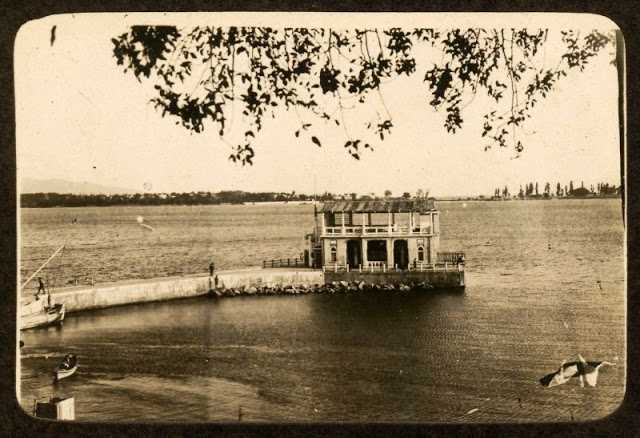
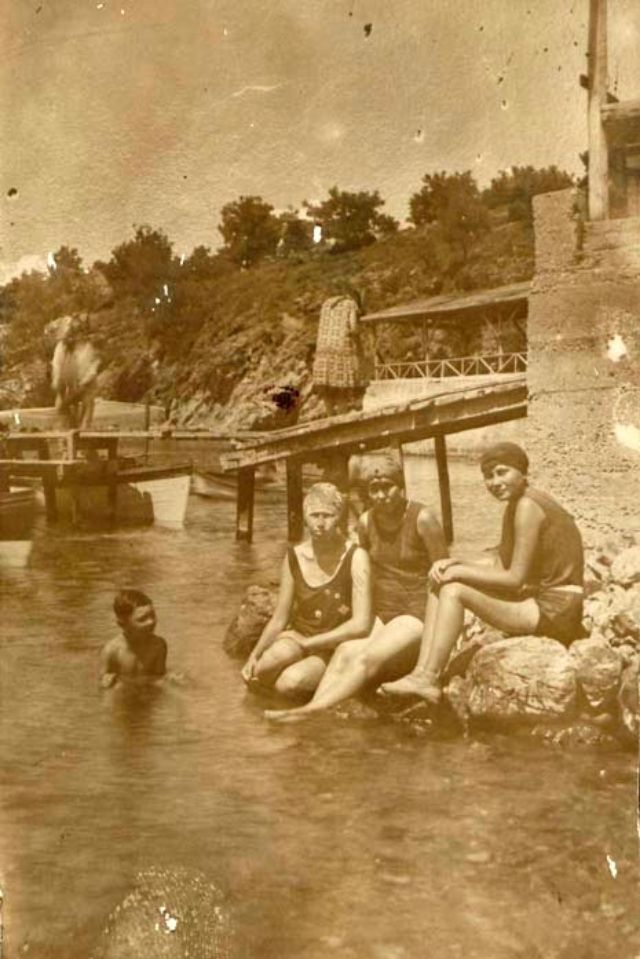
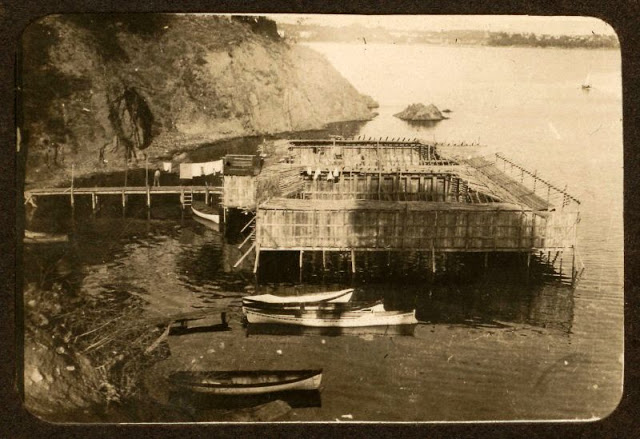
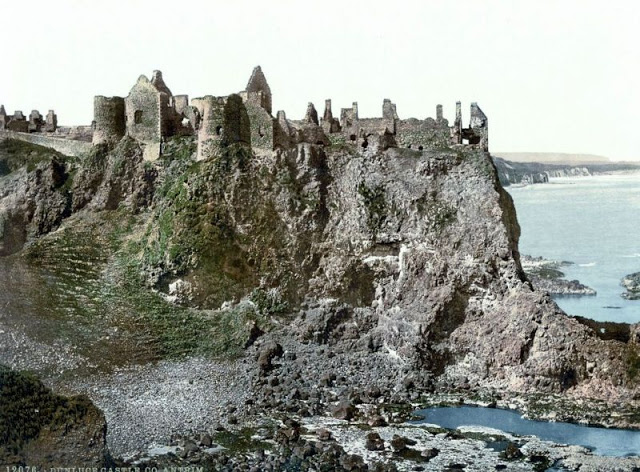
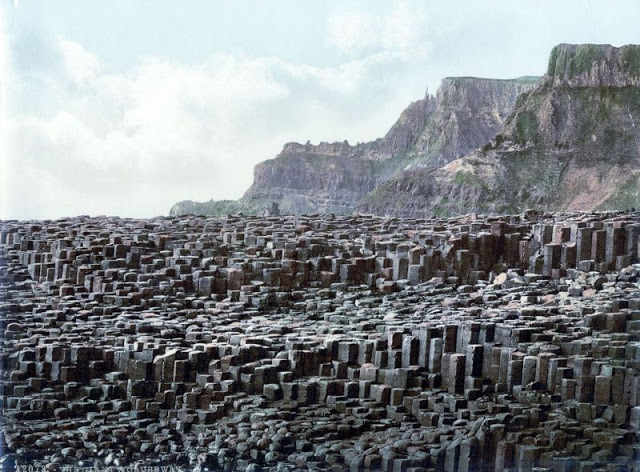
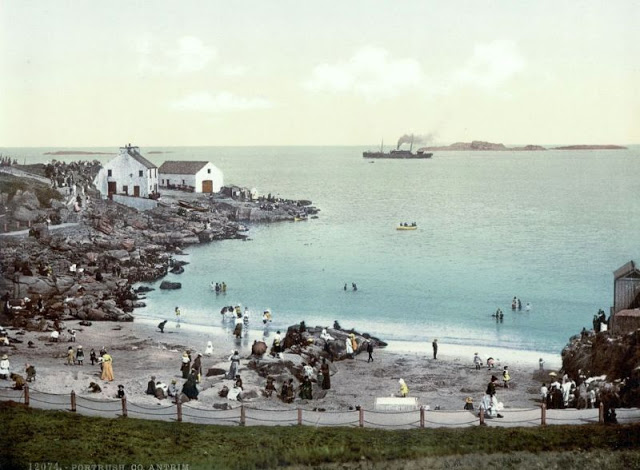
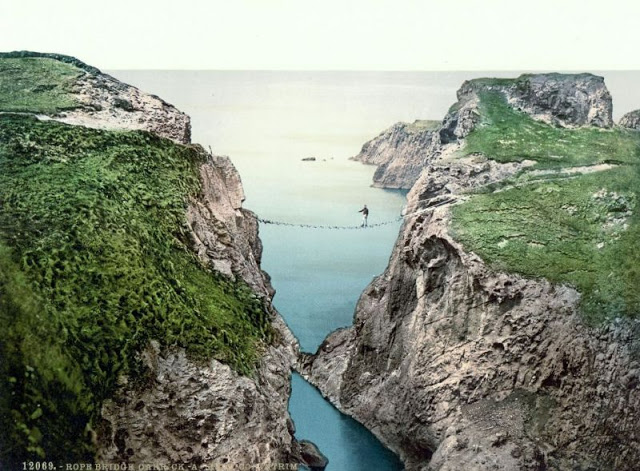
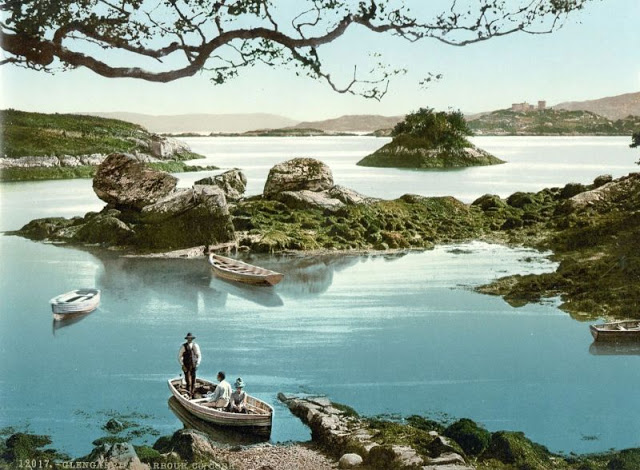
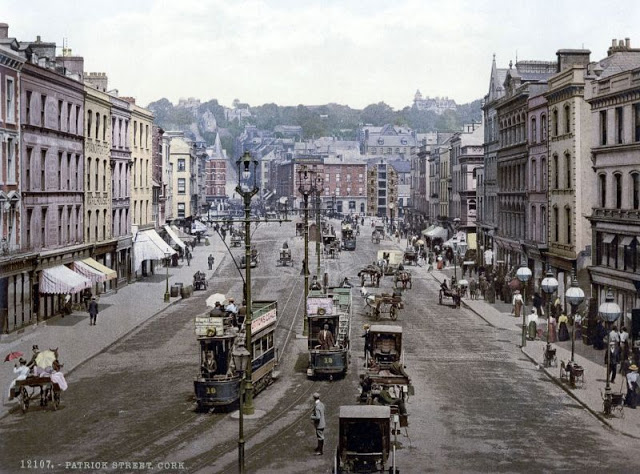
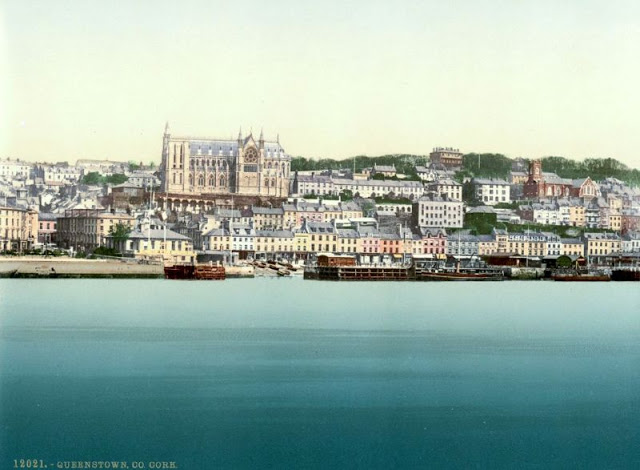
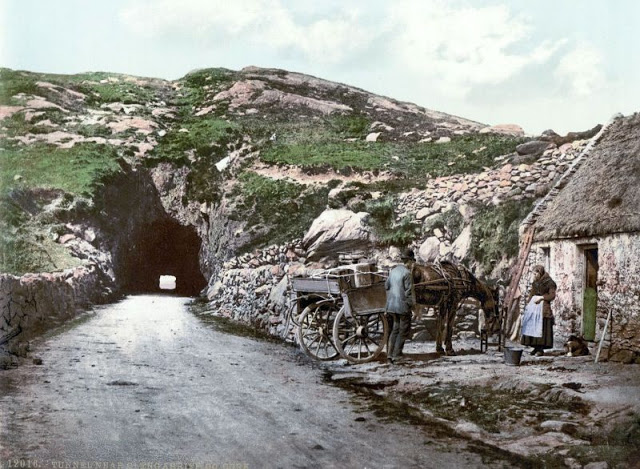
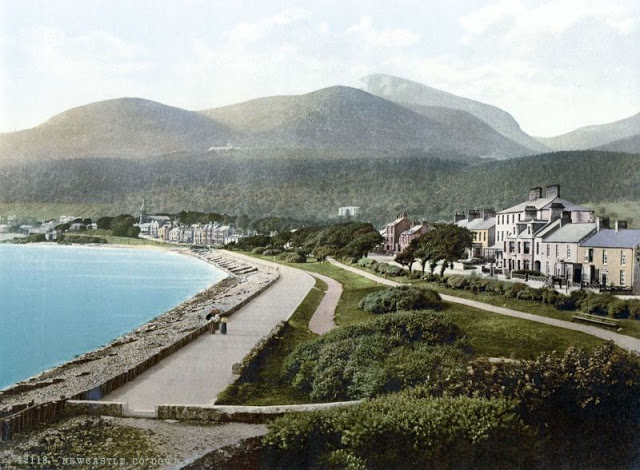
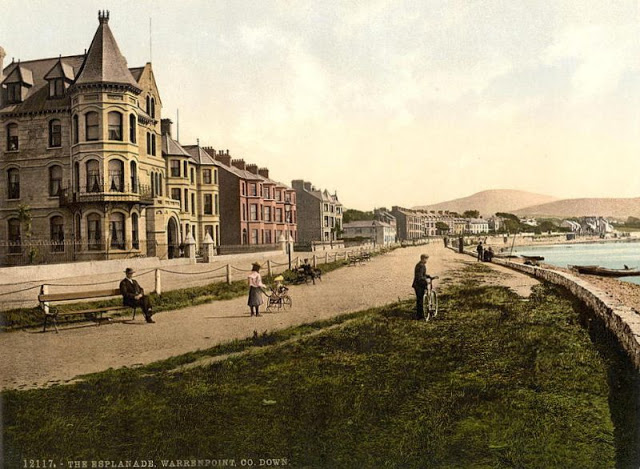
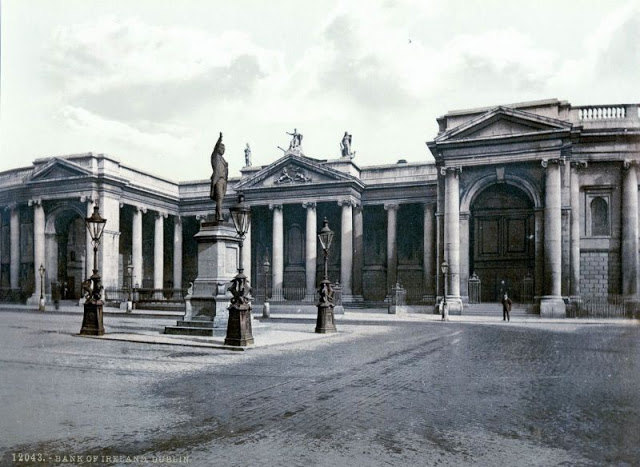
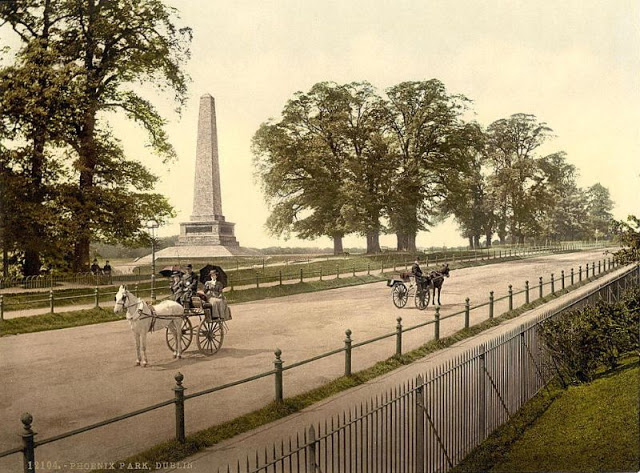
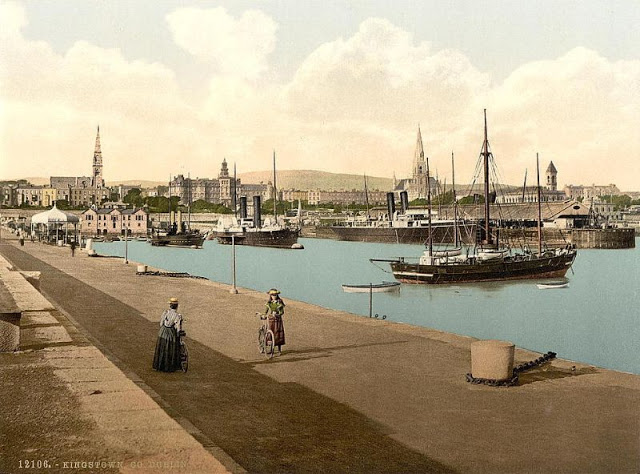
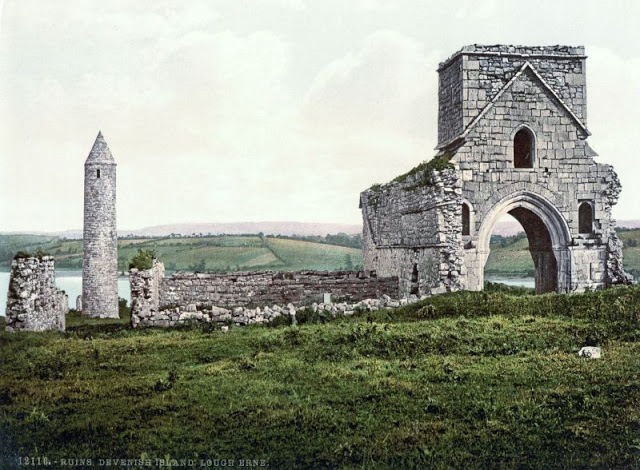
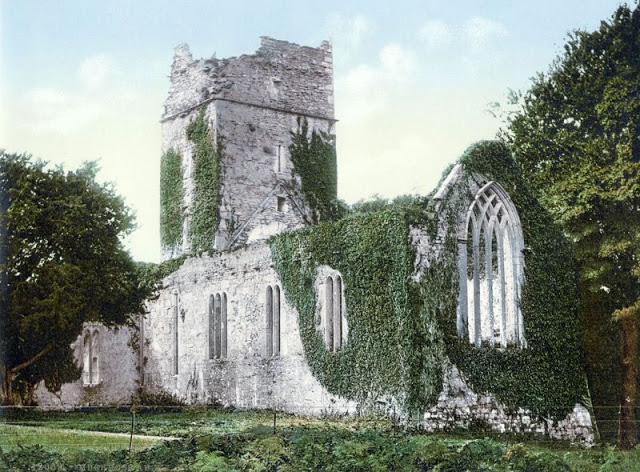
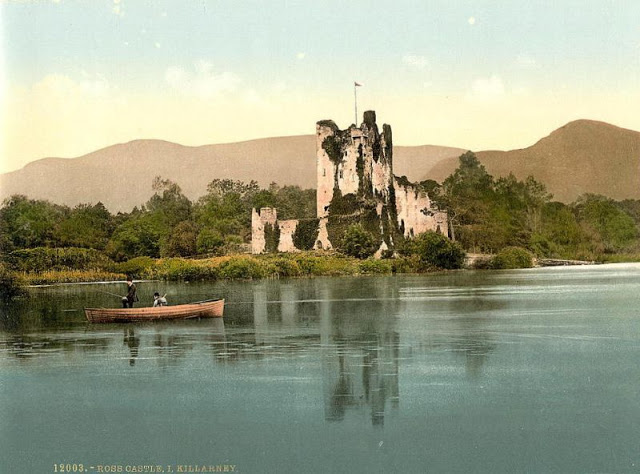
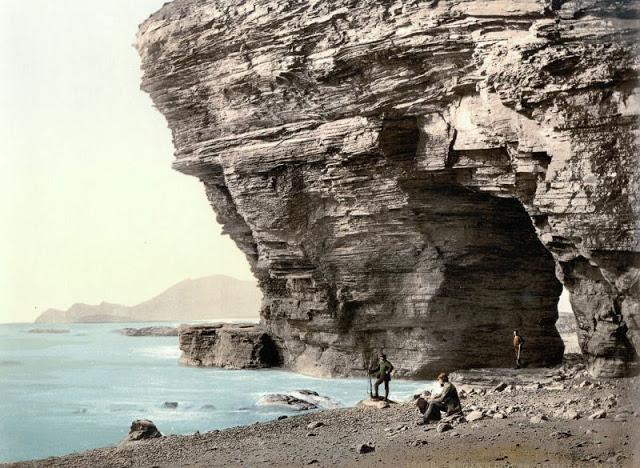
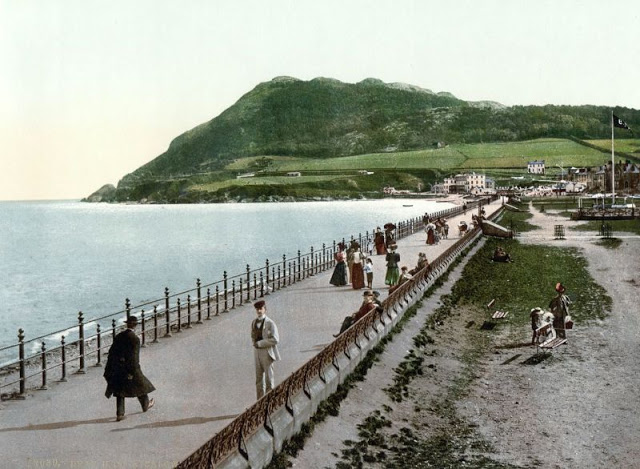
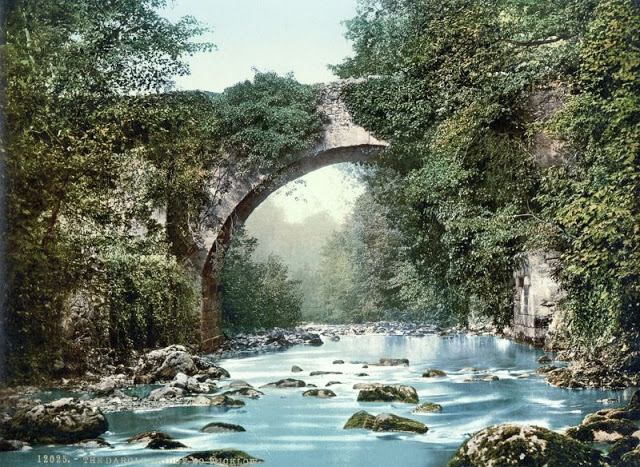
These postcards from The Library of Congress that captured landscapes and daily life of Ireland in the 1890s. They were created using the Photochrom process, a complex method of imbuing black-and-white photographs with relatively realistic color.
Though delicate and time-consuming, the Photochrom process resulted in color images of striking verisimilitude for a time when true color photography was in the earliest stages of development.
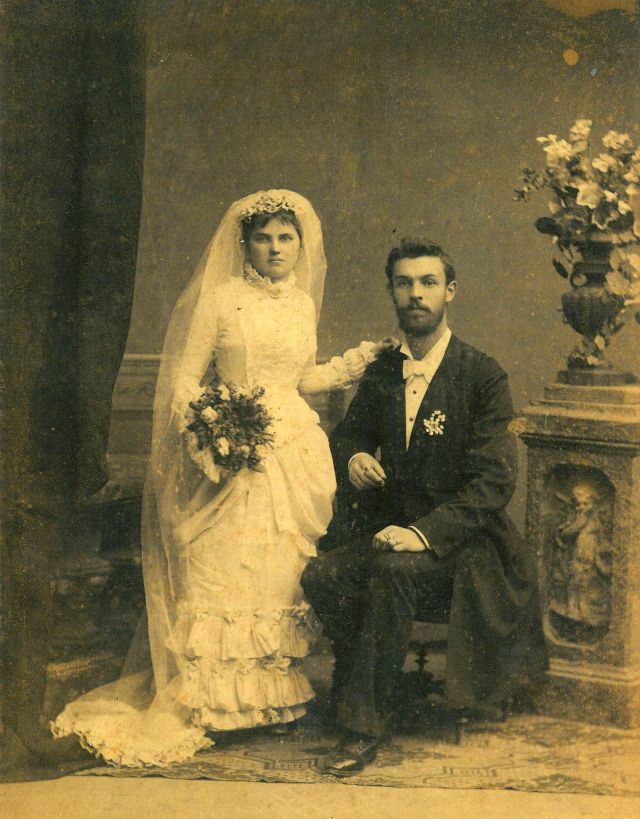




















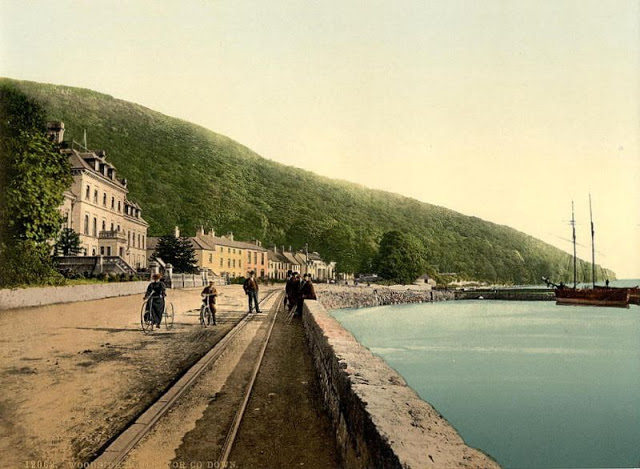




















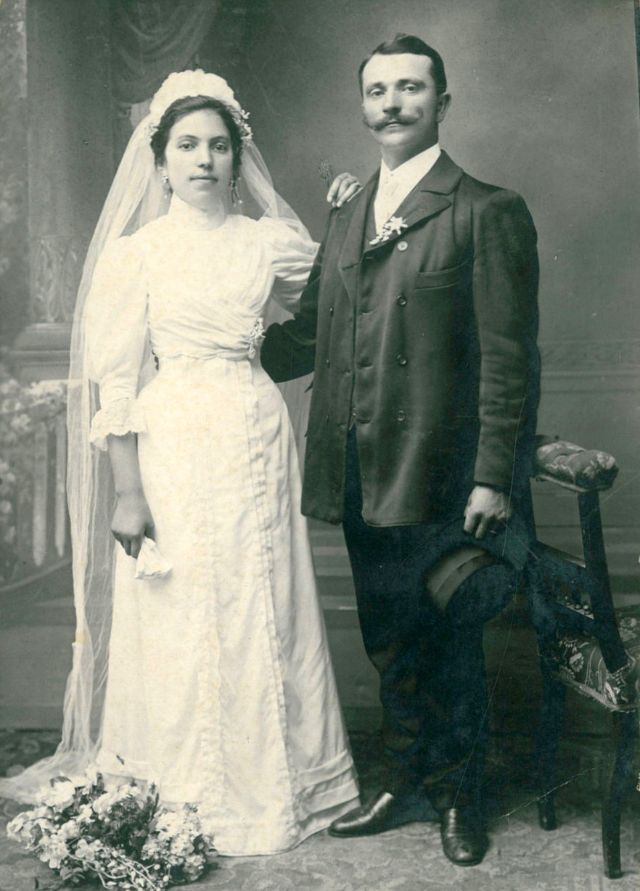
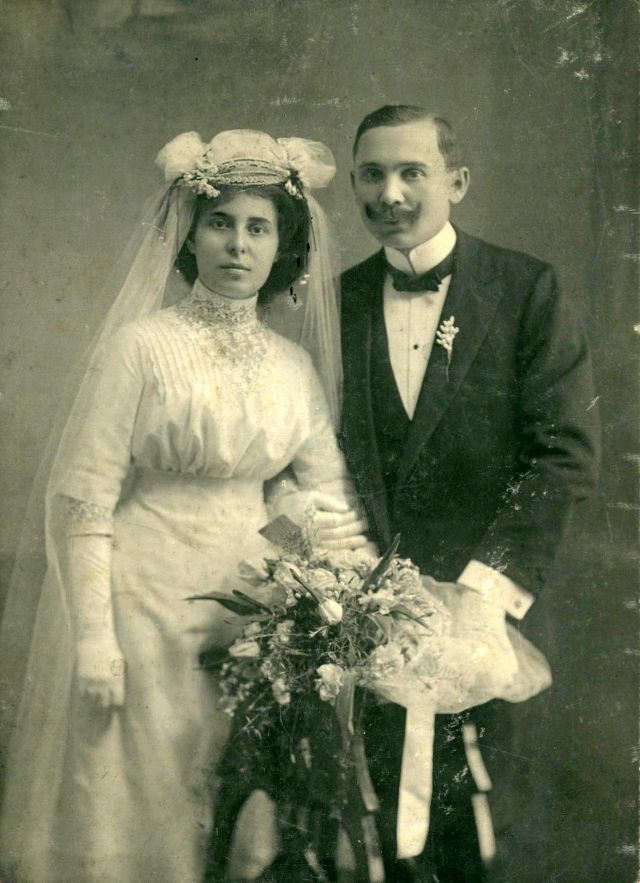
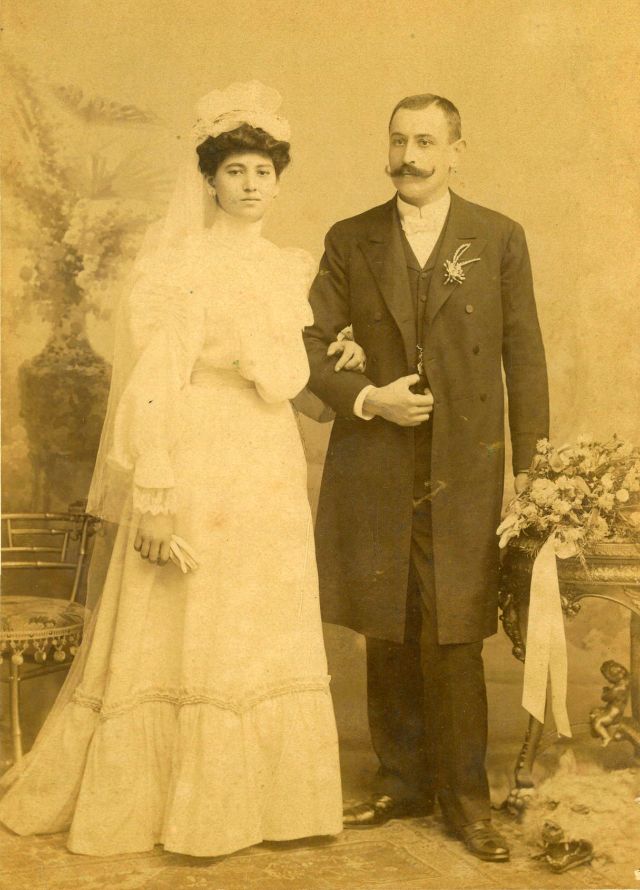
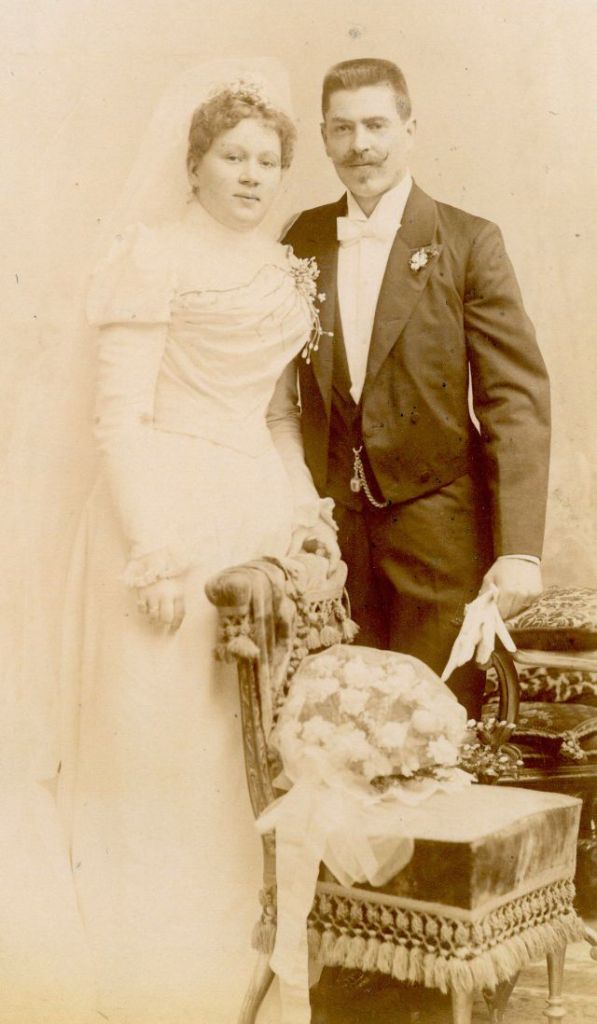
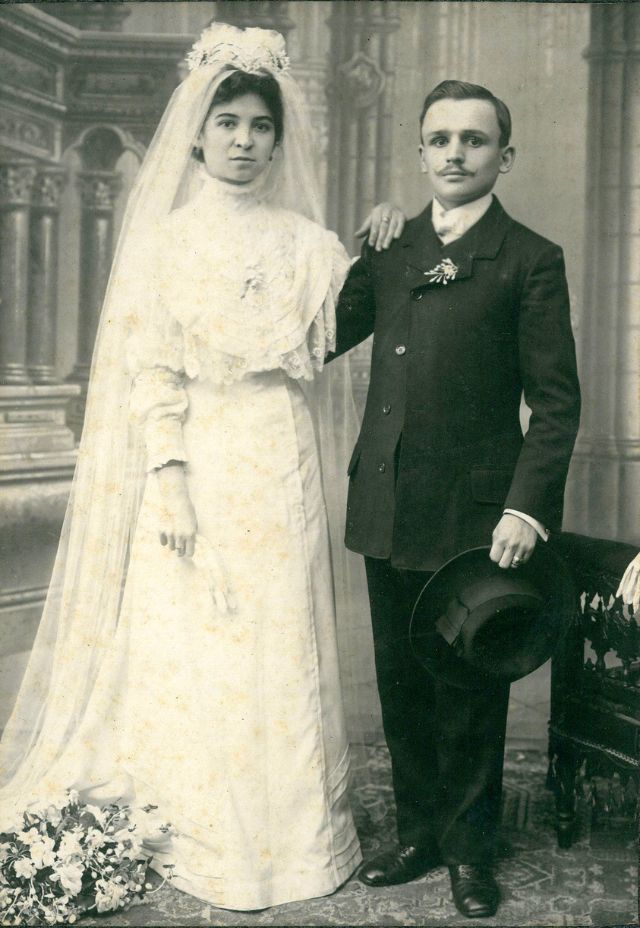
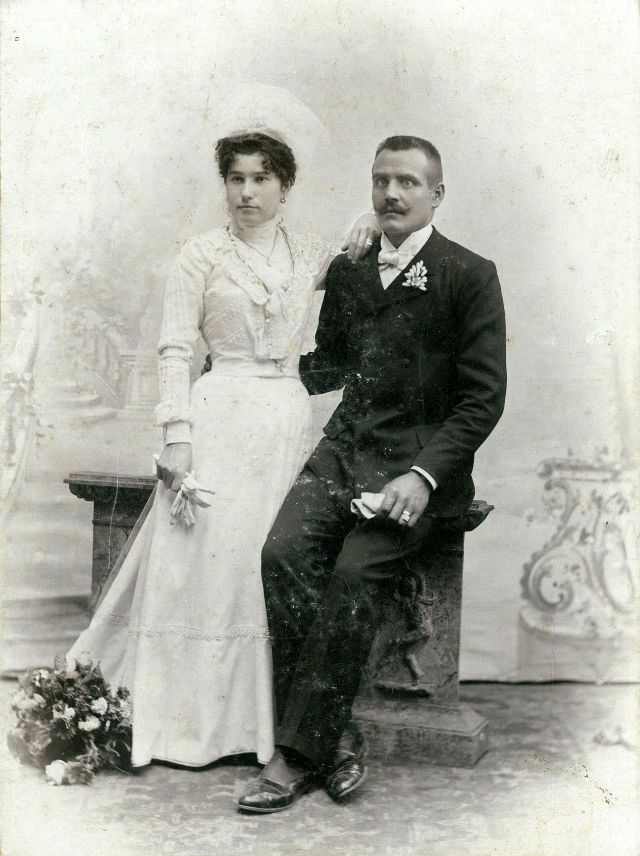
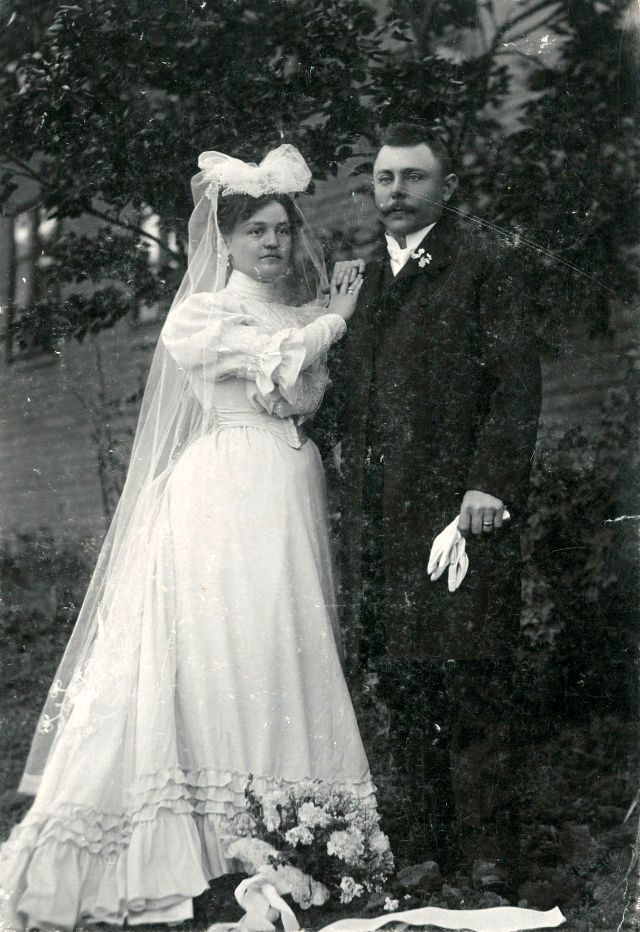
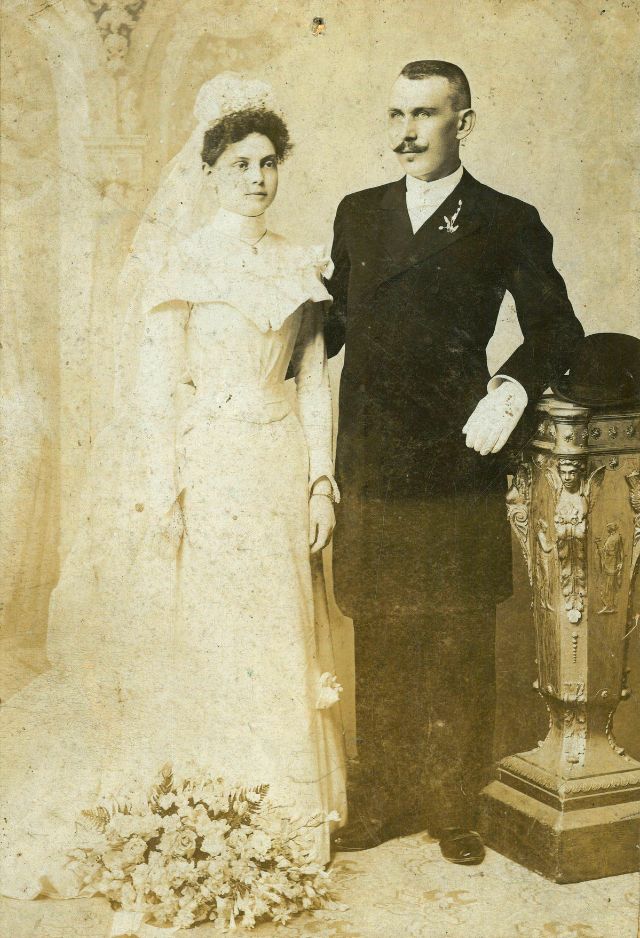
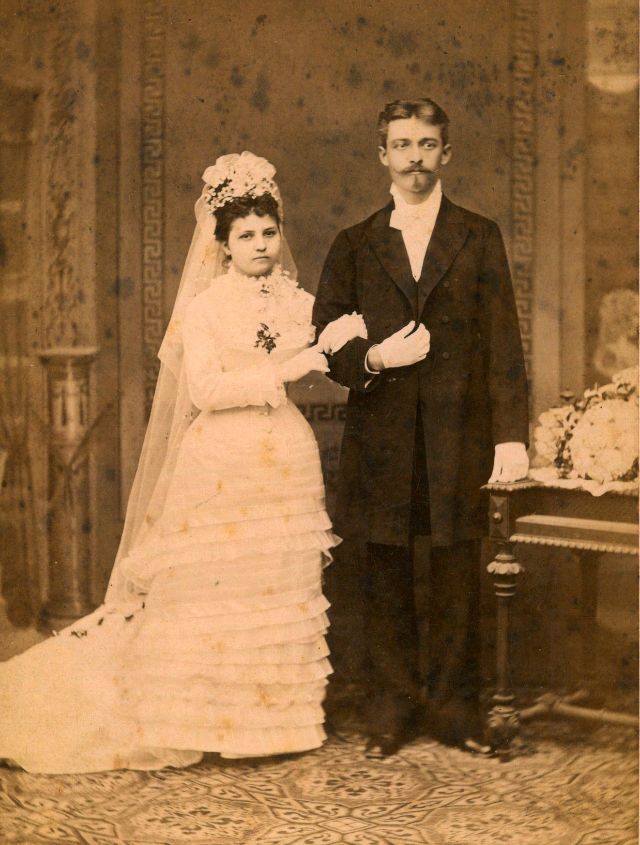
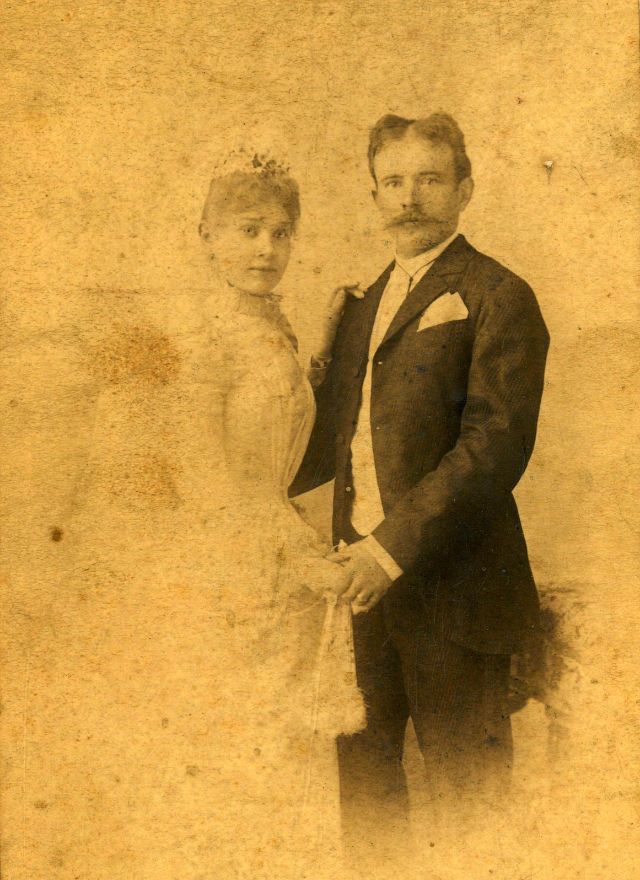
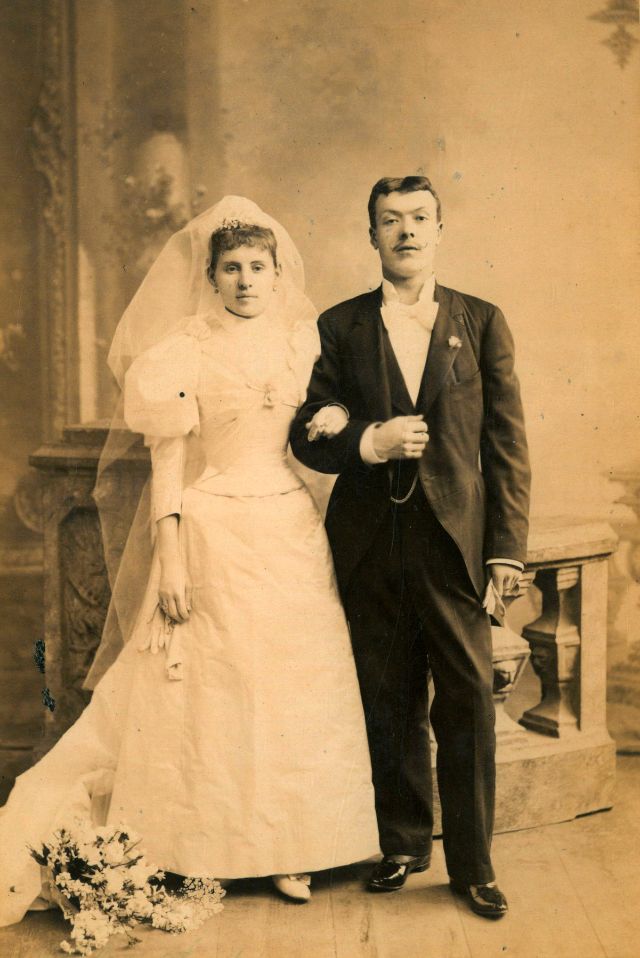
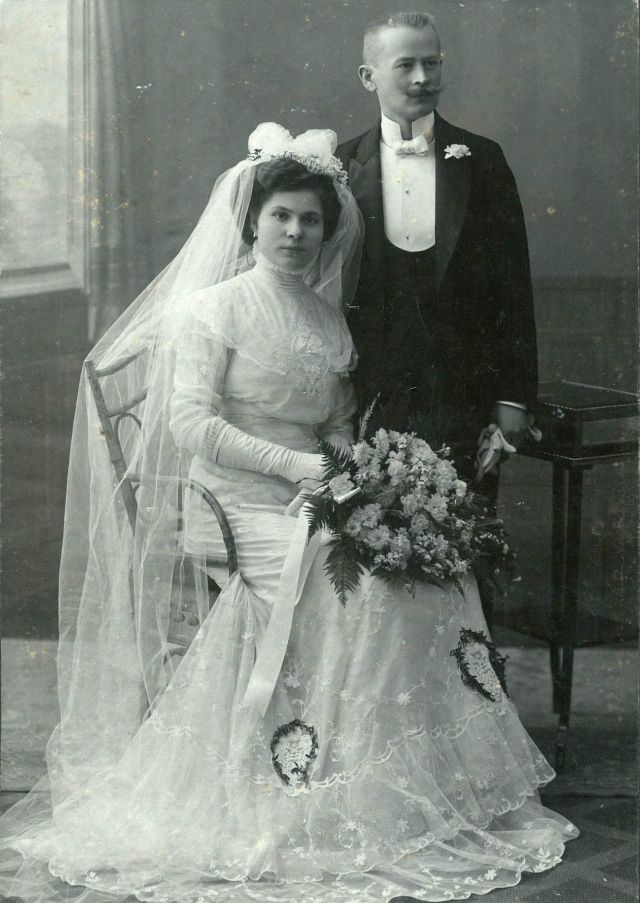
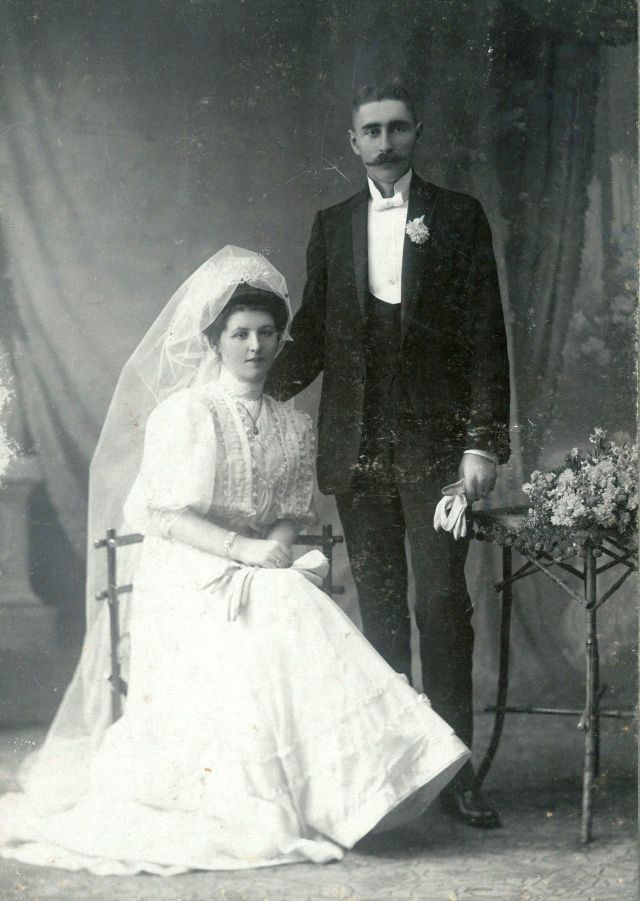
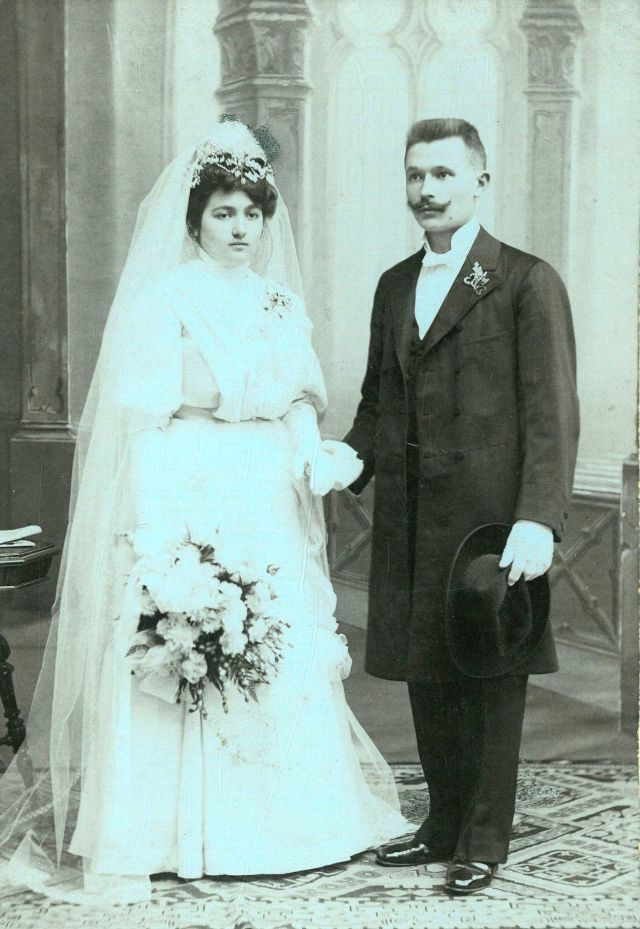
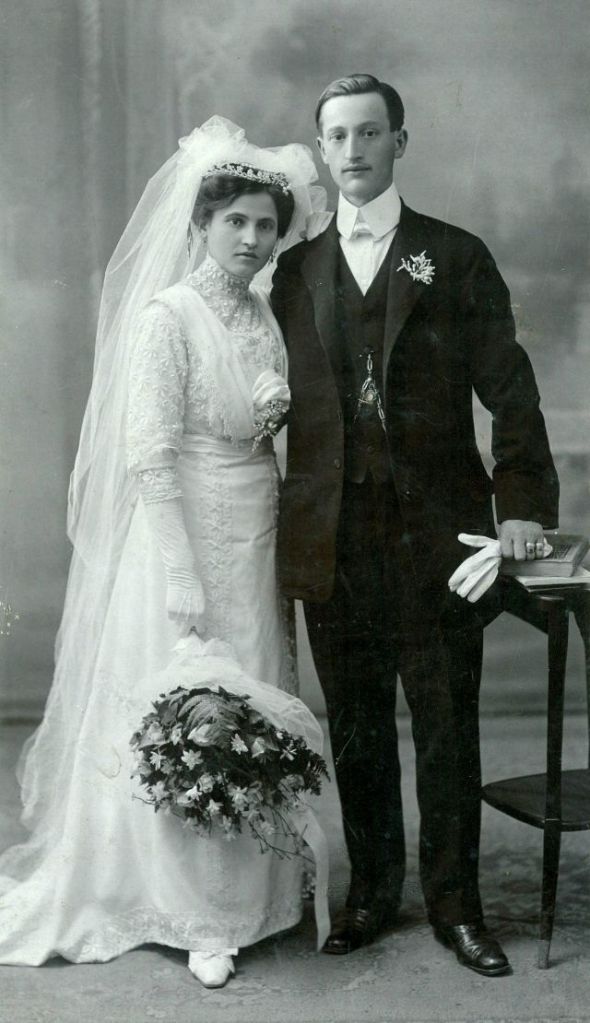
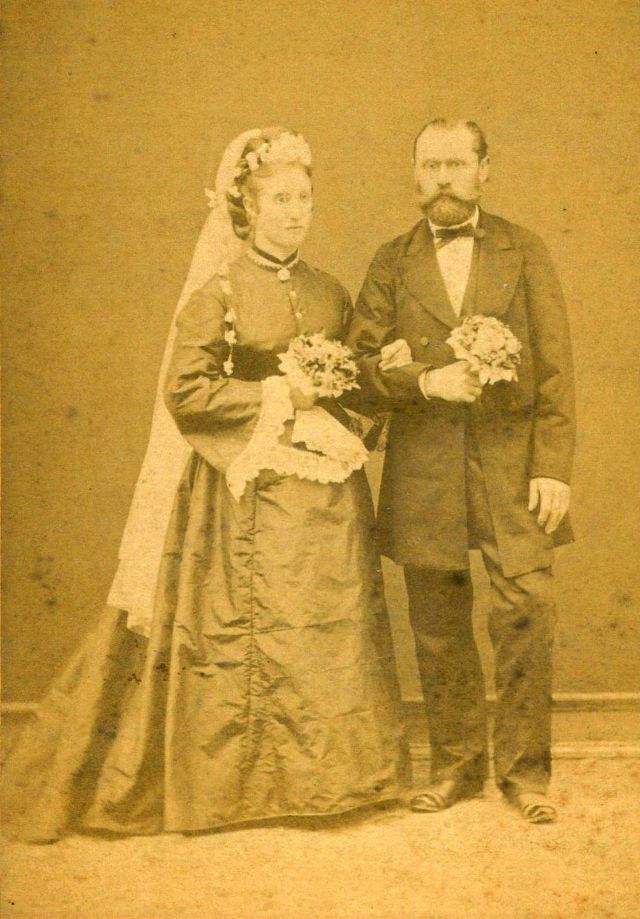
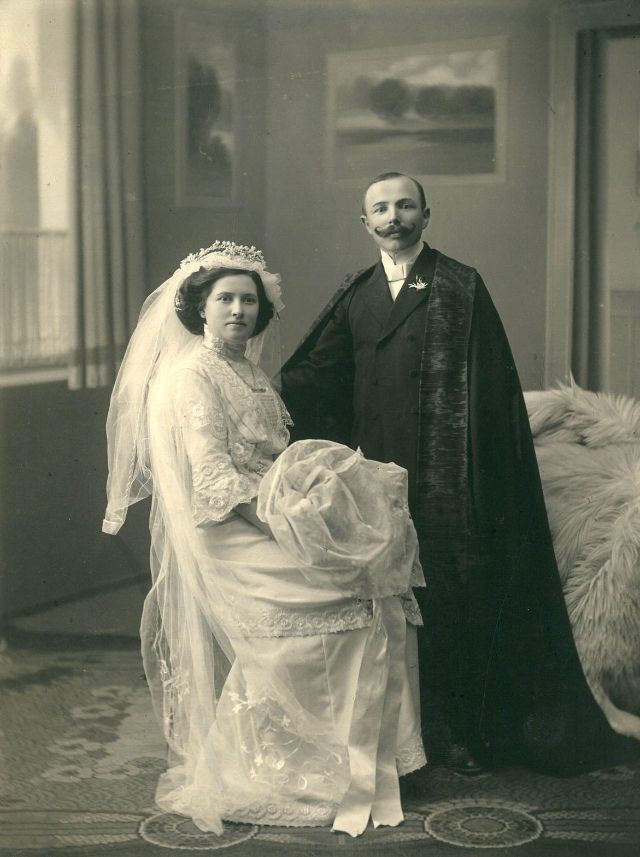
What did brides and grooms wear to their weddings in the 19th century? In most cases, not what we would think of as bridal wear, which actually is more like Victorian formal evening clothing. Instead, 19th-century couples wore their best day clothes, the clothing we would wear to church or a special daytime occasion.
A rare and amazing photo collection that shows Hungarian newlyweds from between the 1870s and 1890s.
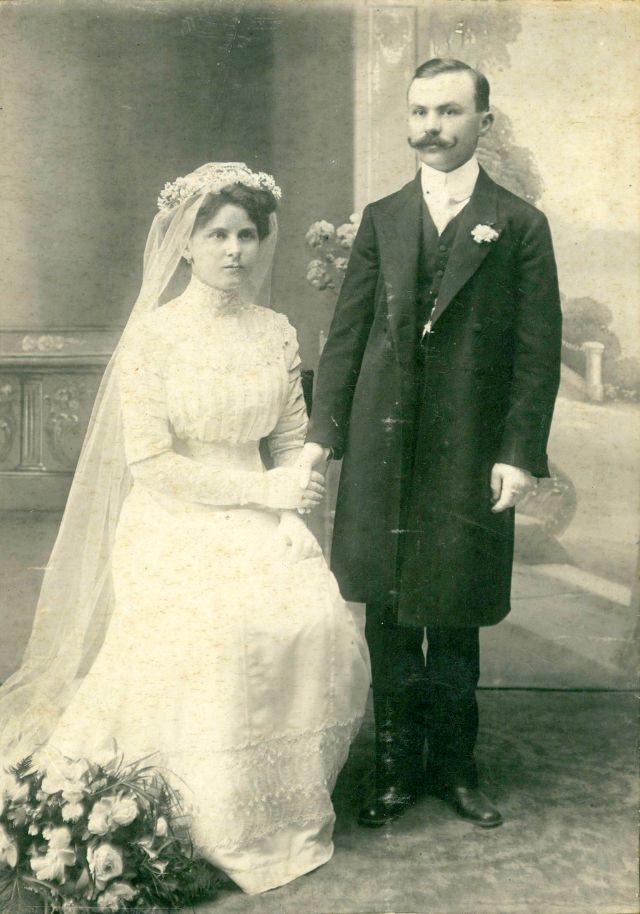
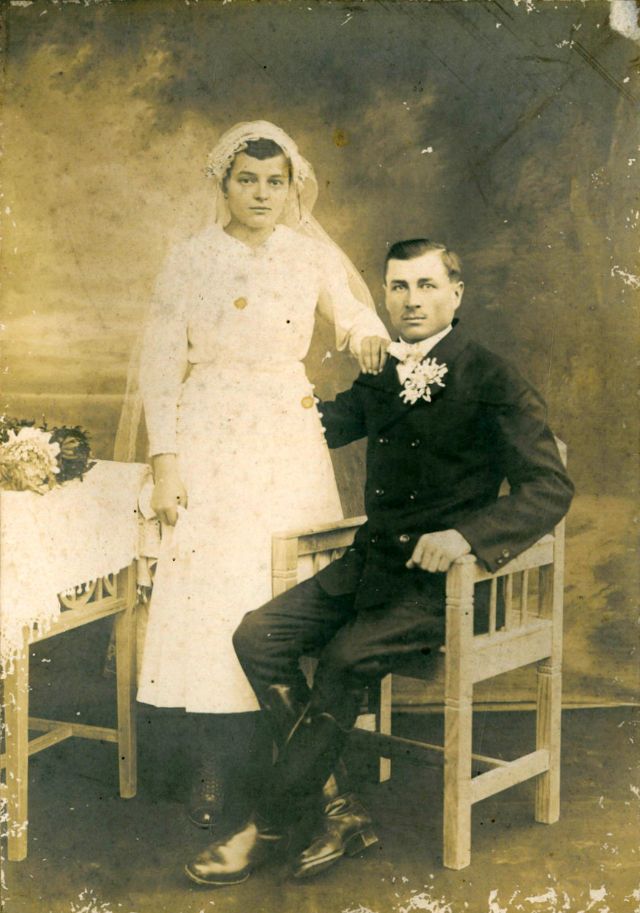
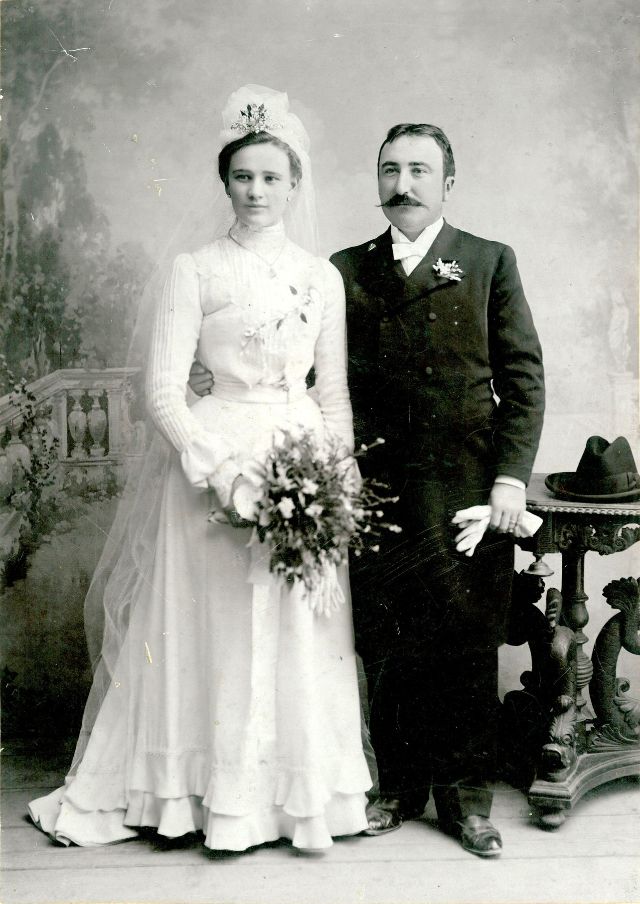
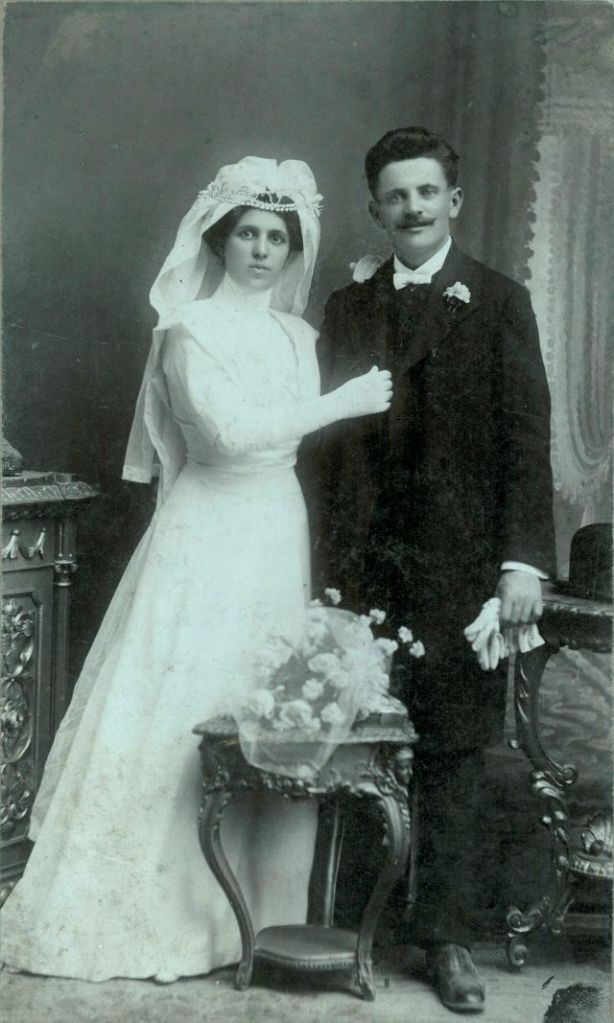
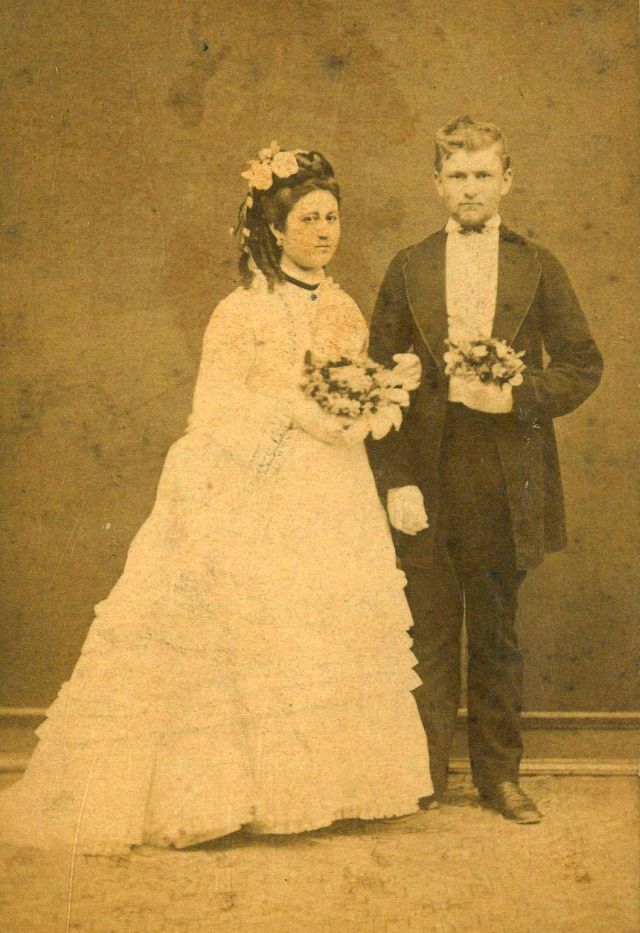
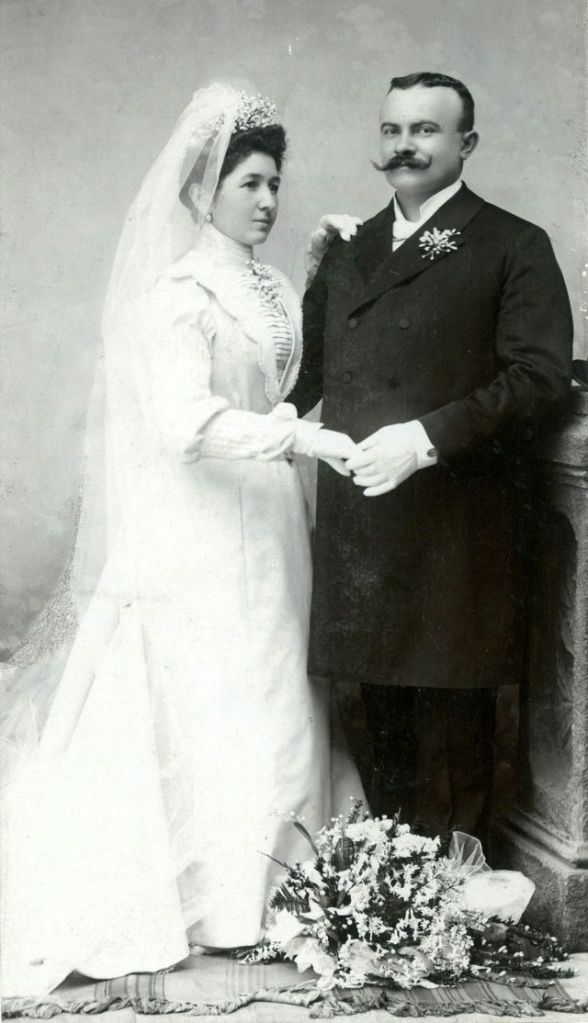
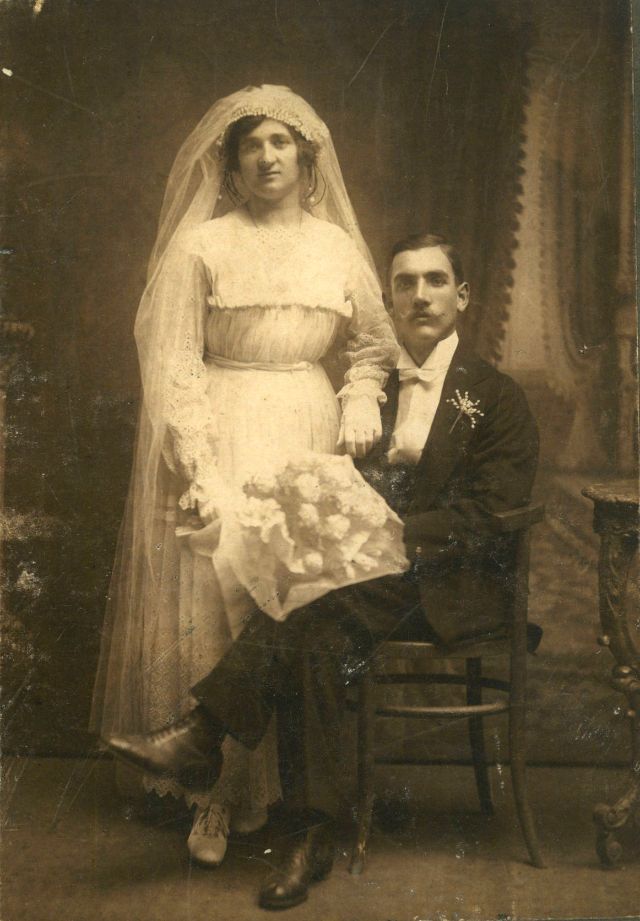
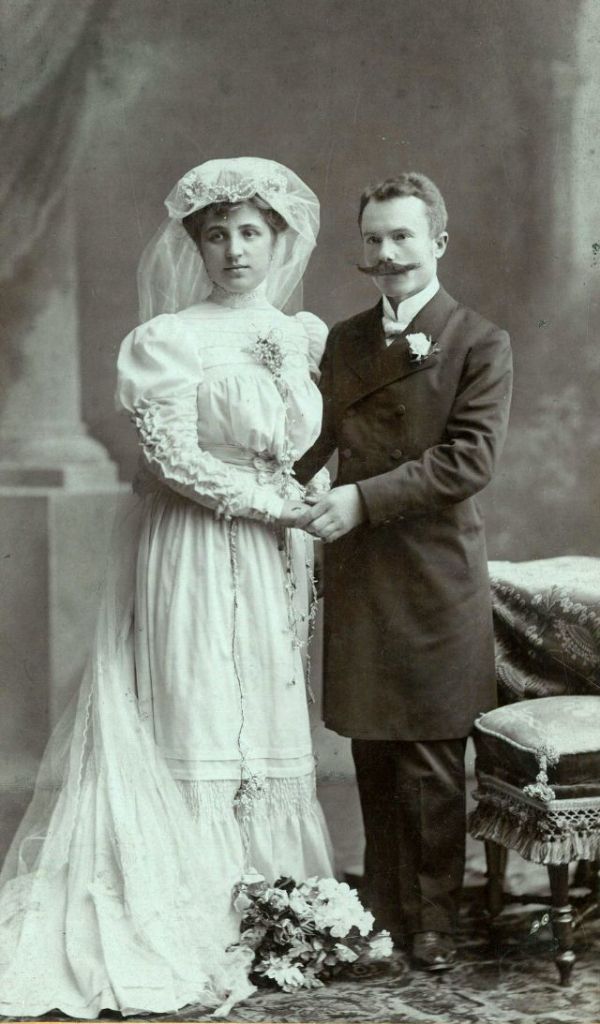
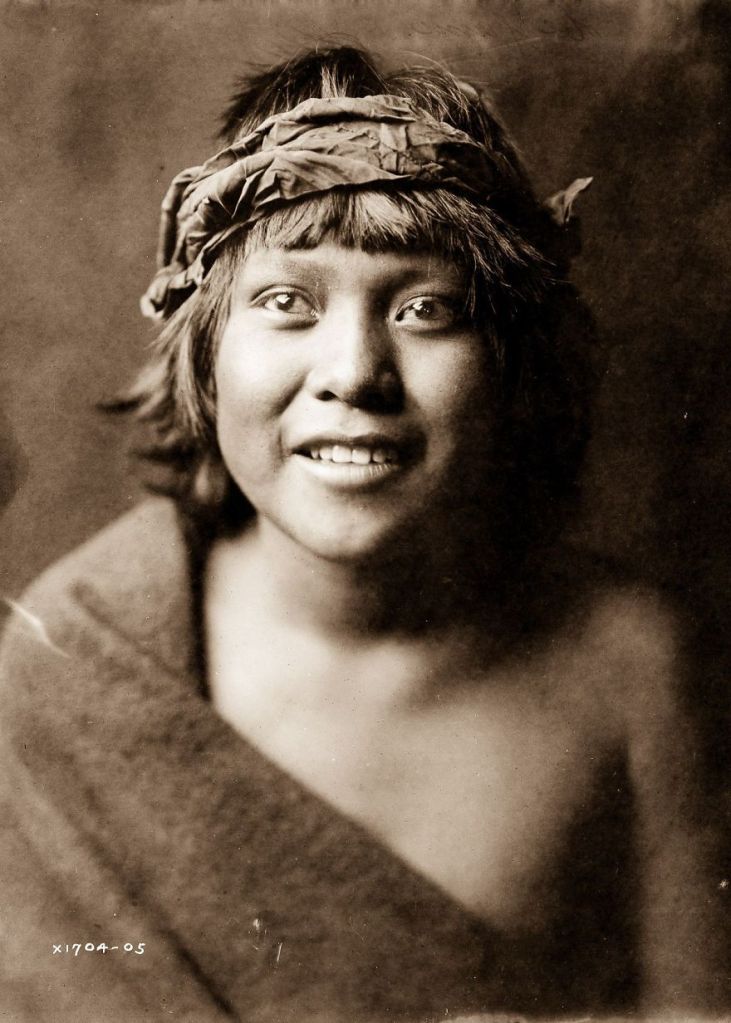
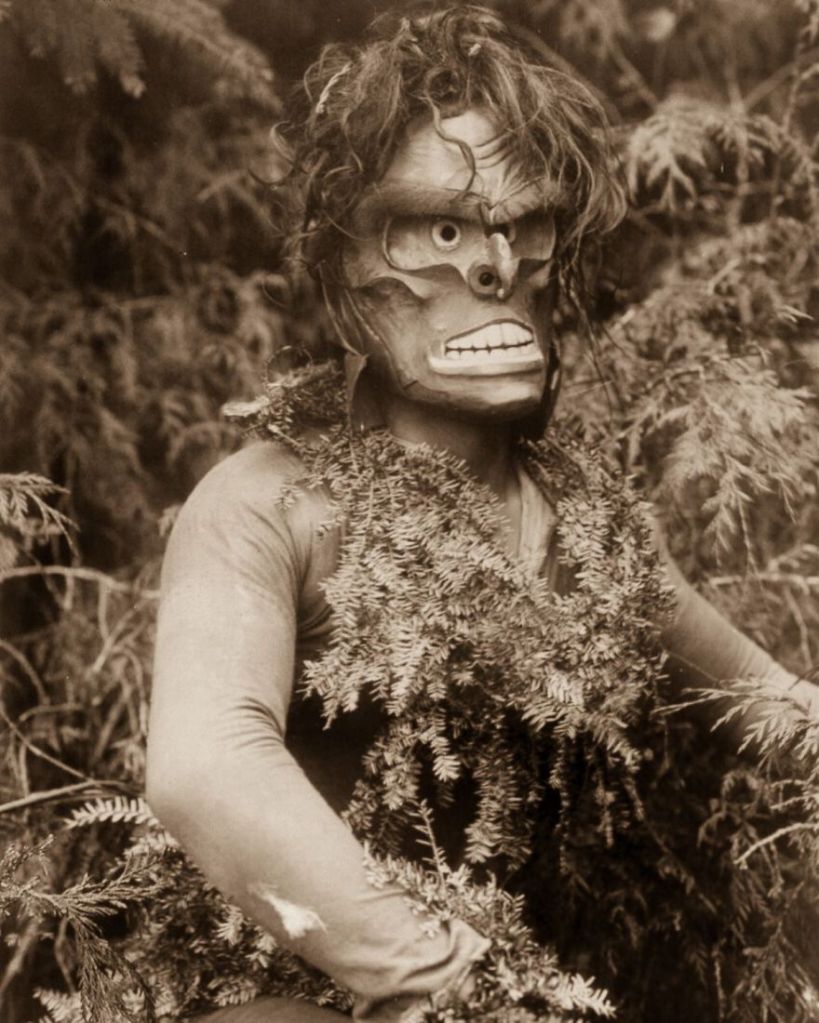
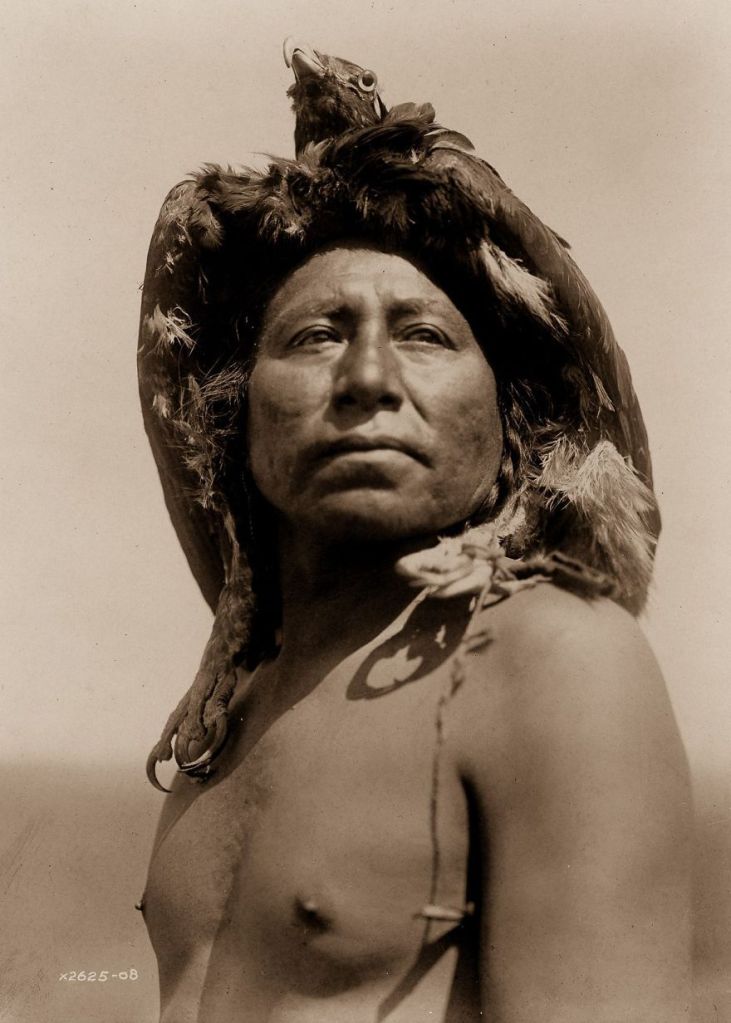
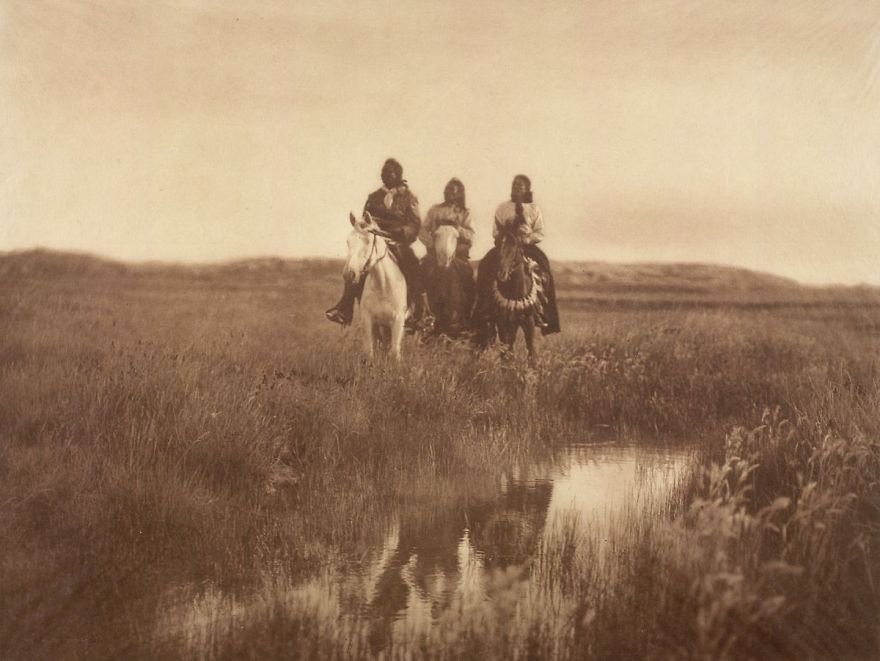
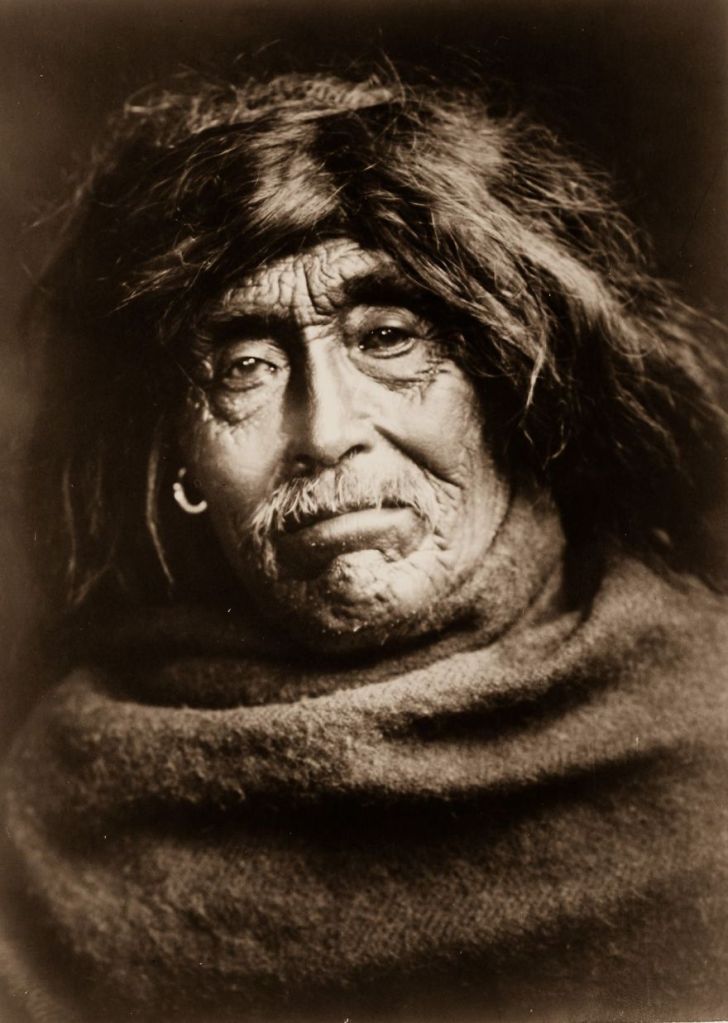
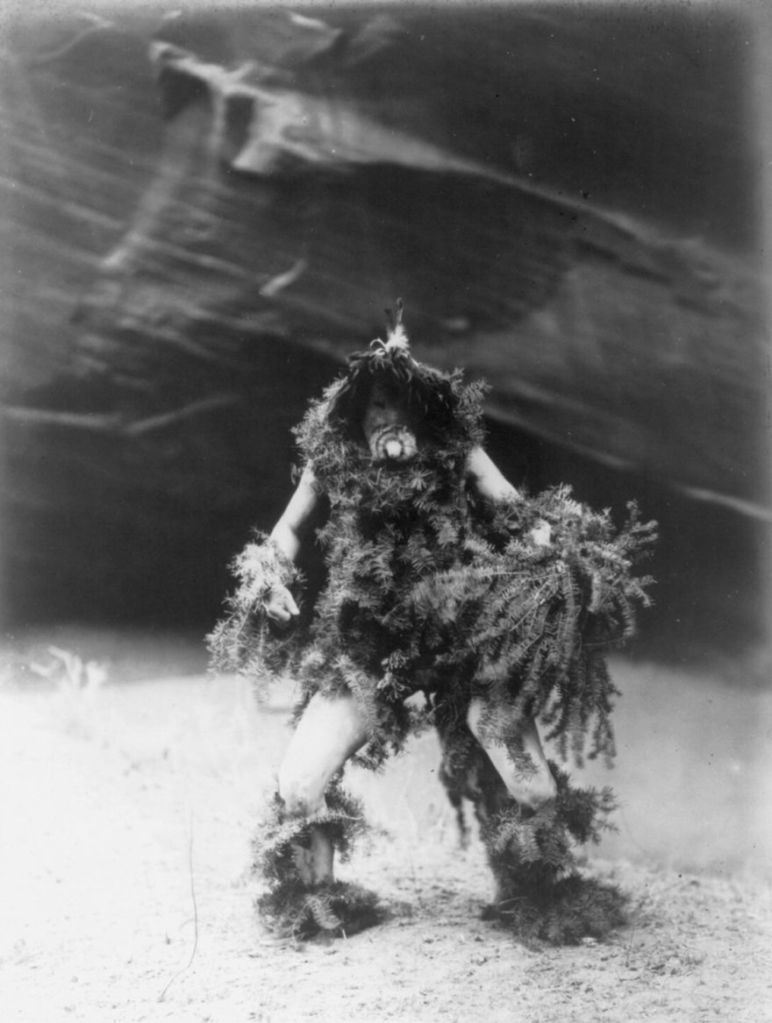















































































(Photos by Edward Sheriff Curtis)
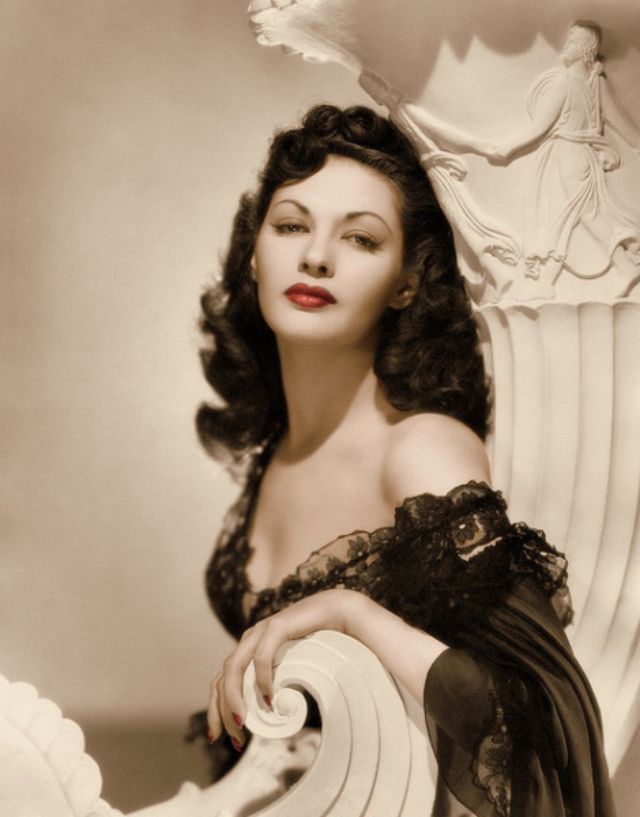

The Golden Age of Hollywood, sometimes referred to as the period of classical Hollywood cinema, started with the silent movie era and the first major feature-length silent movie called The Birth of a Nation (1915). The Golden Age of Hollywood ended with the demise of the studio system, theemergence of television, the rising costs and subsequent losses notably Cleopatra (1963).
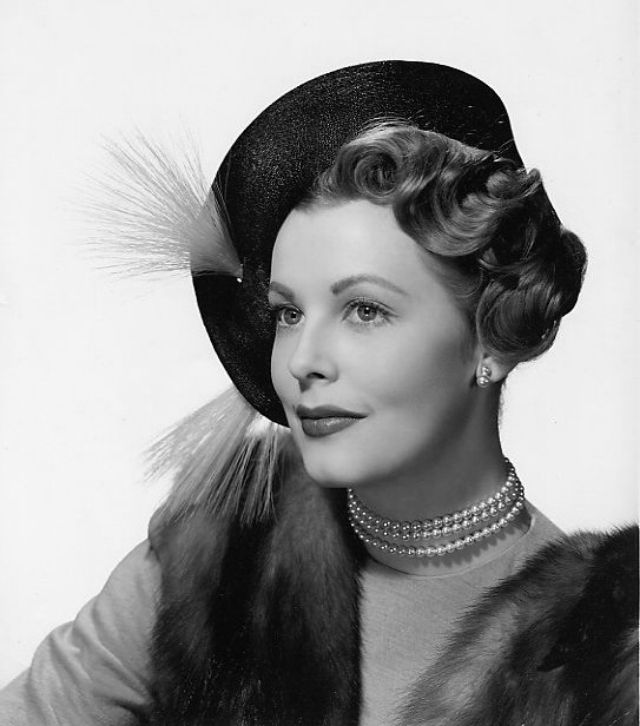
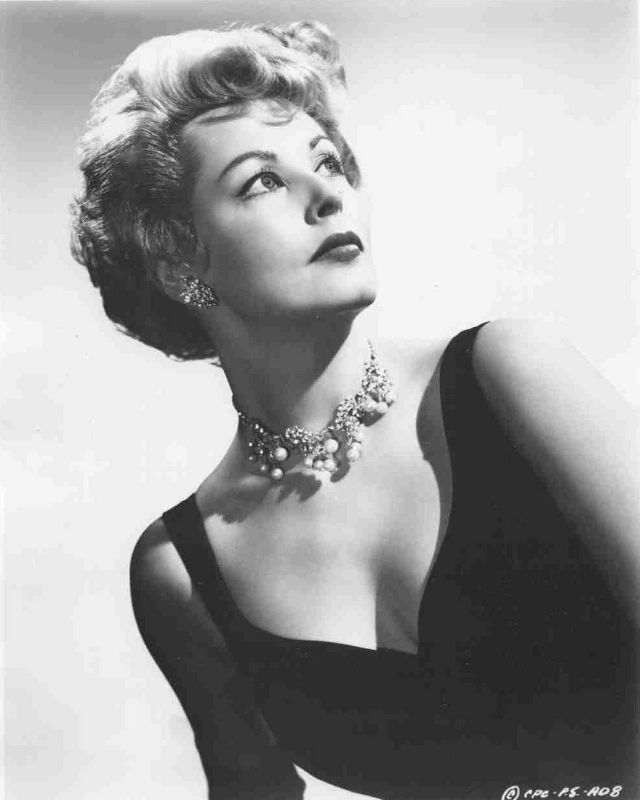
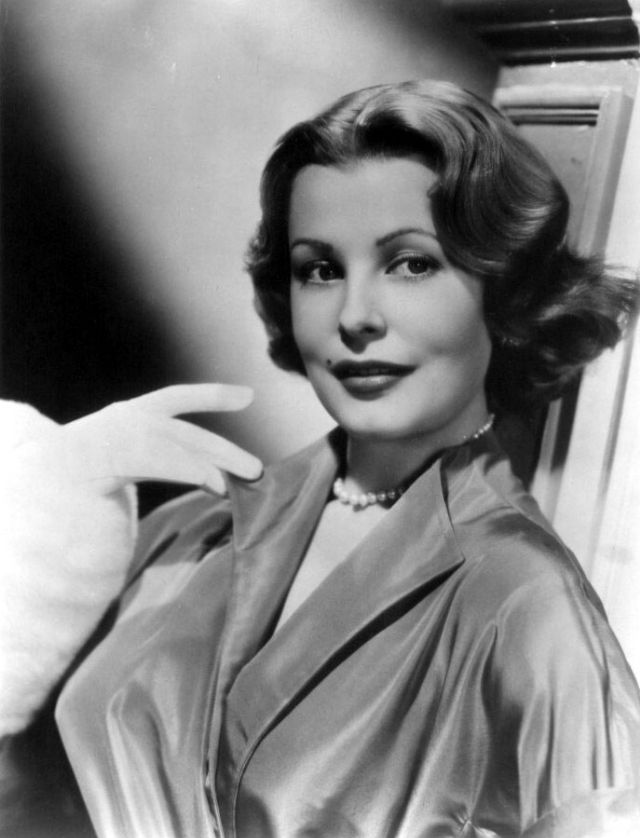
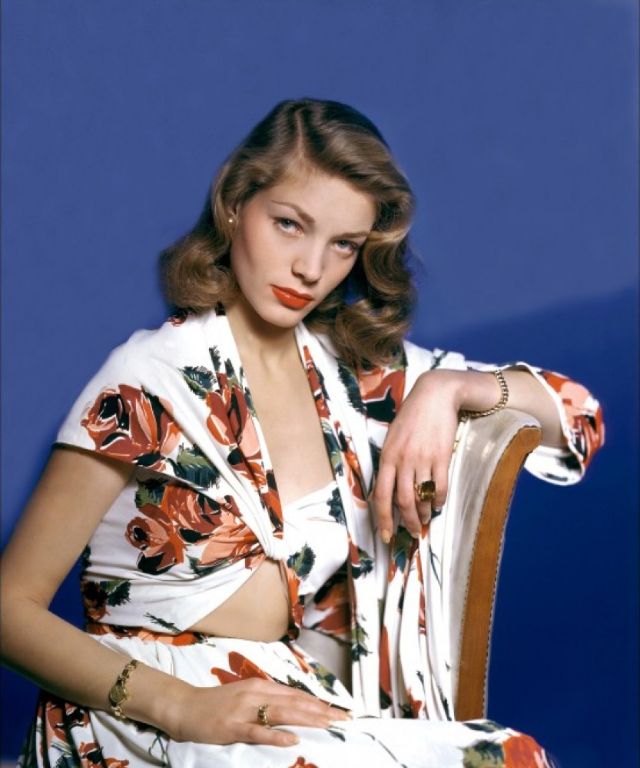
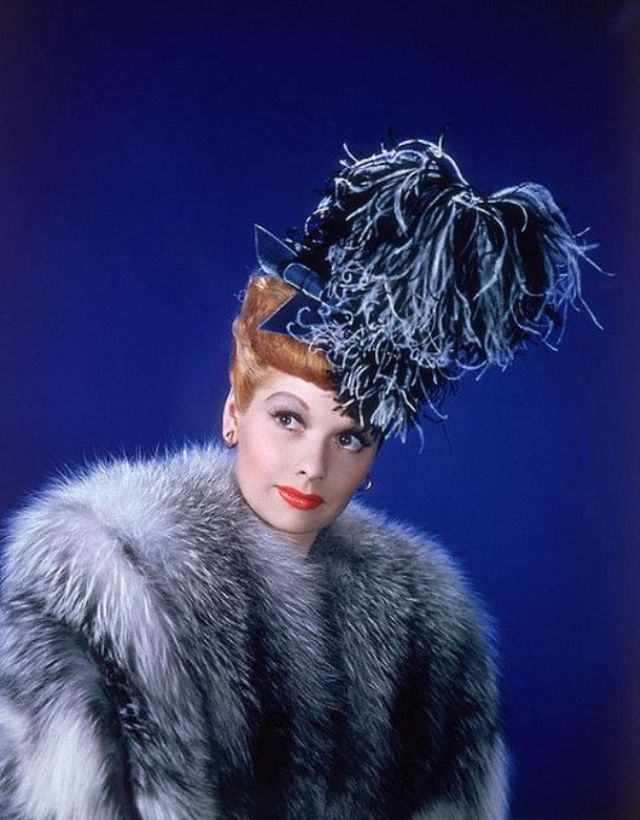
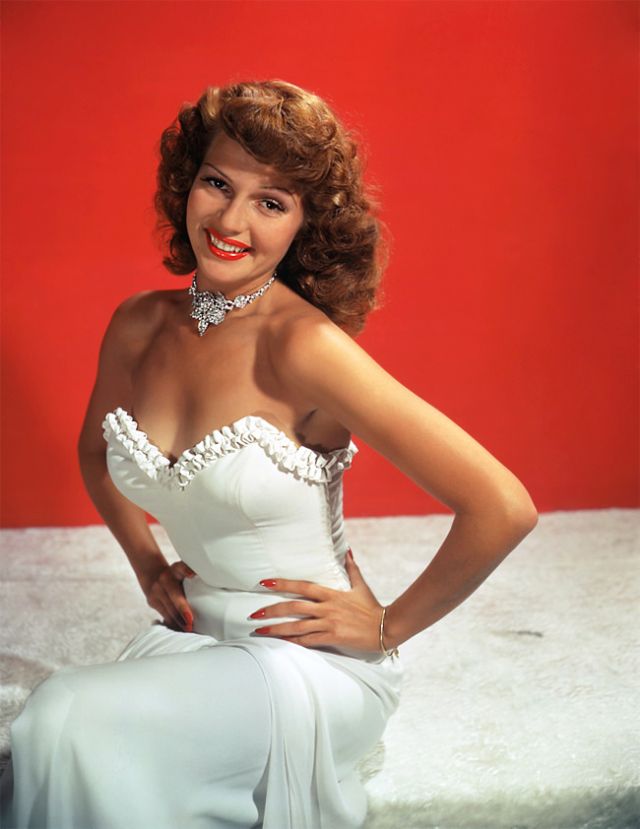
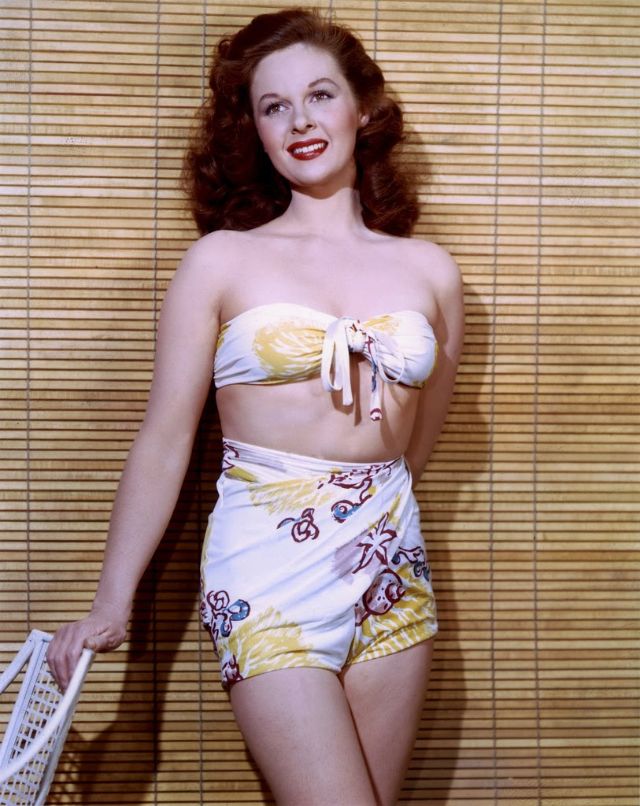
During the Golden Age of Hollywood, thousands of movies were issued from the Hollywood studios, and of course the classic beauties played very important roles in this era.
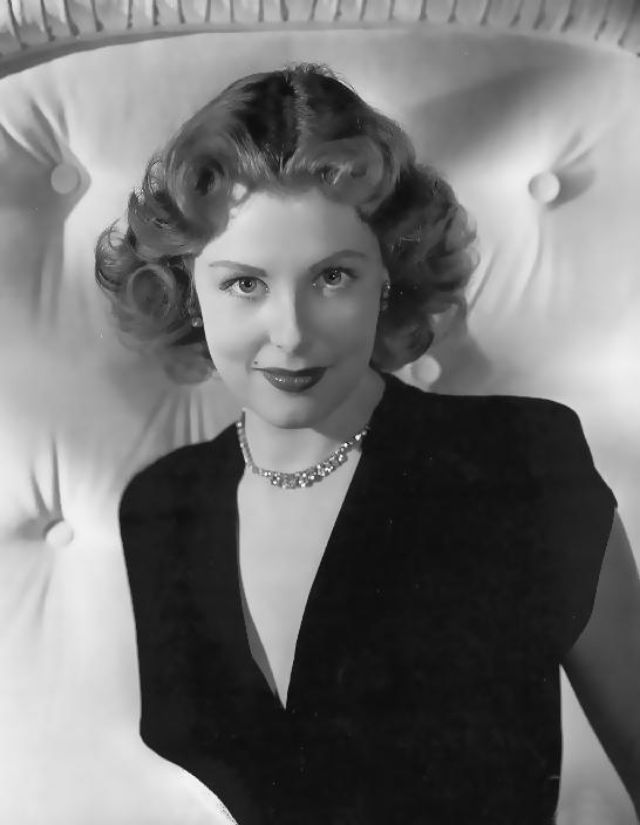
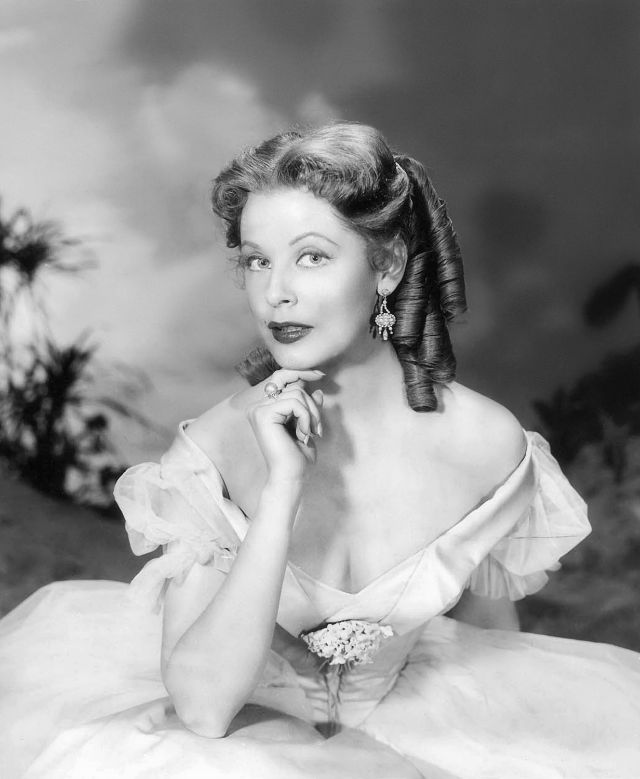
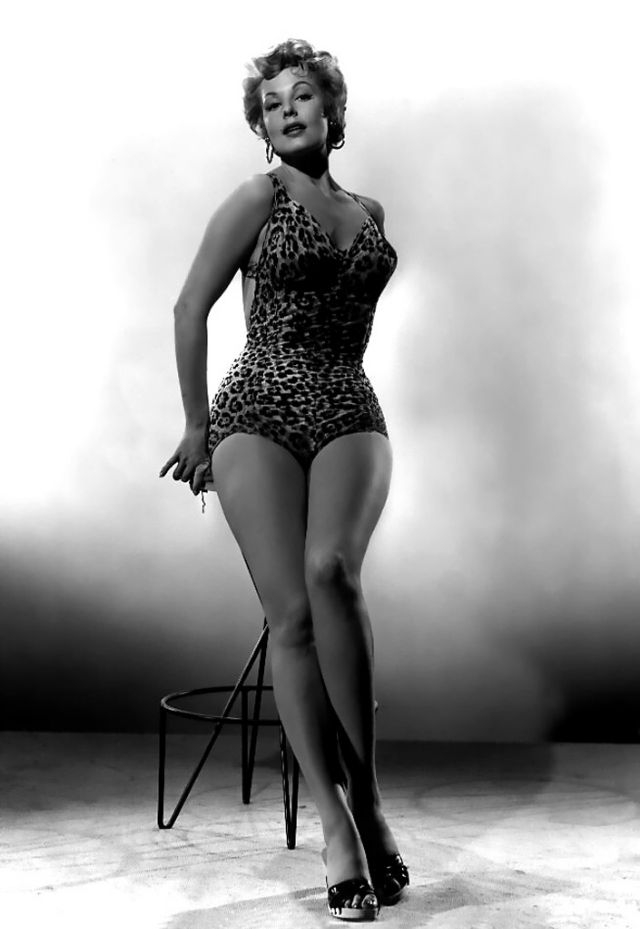
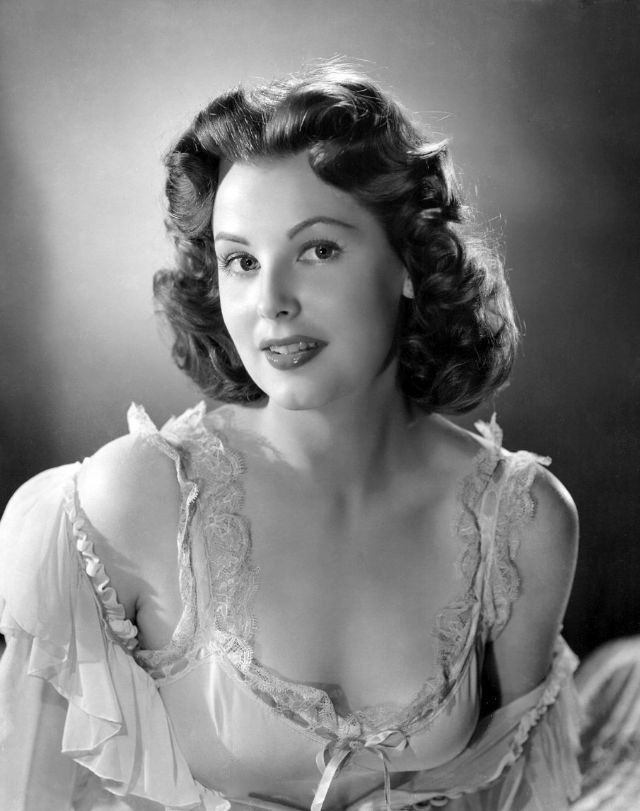
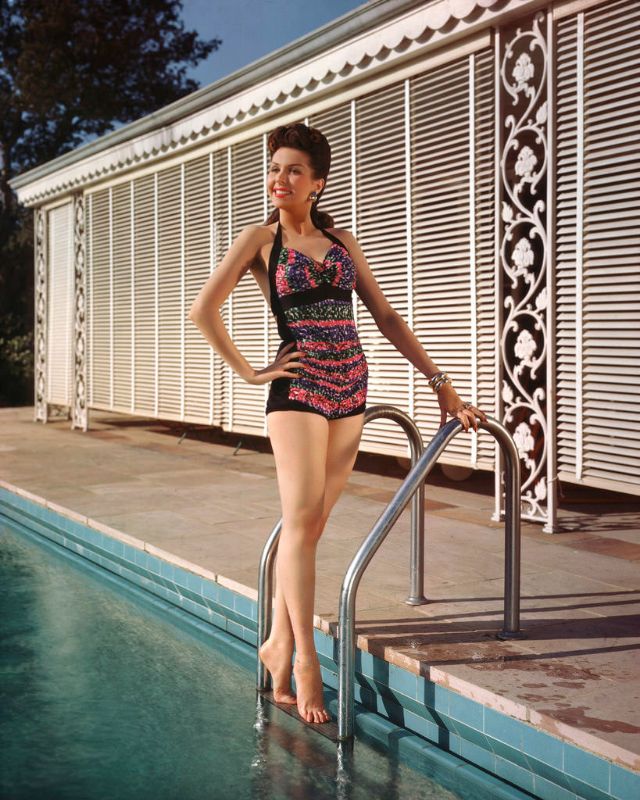
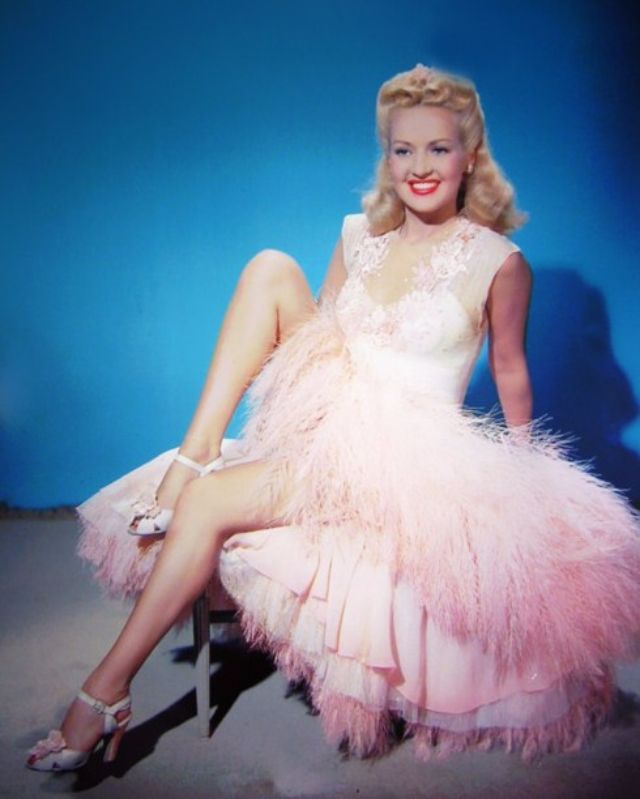
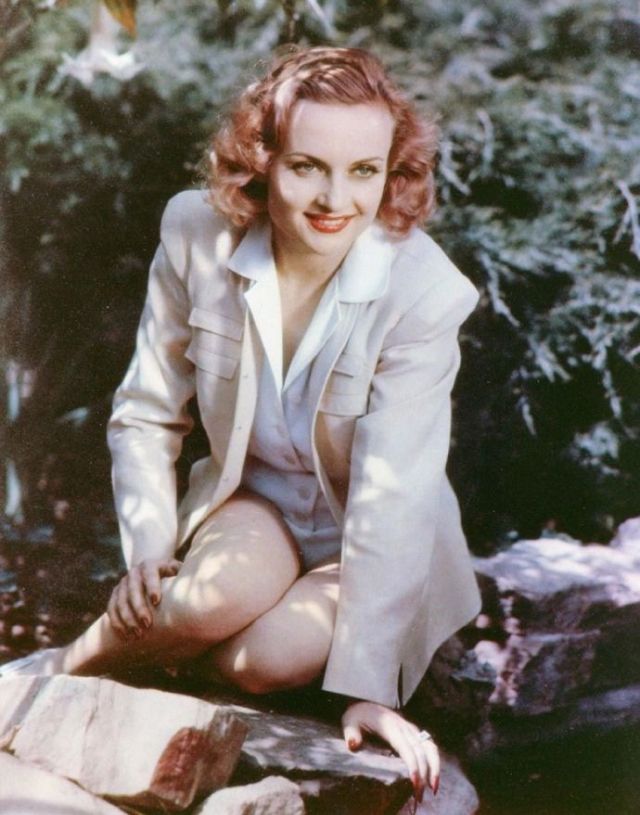
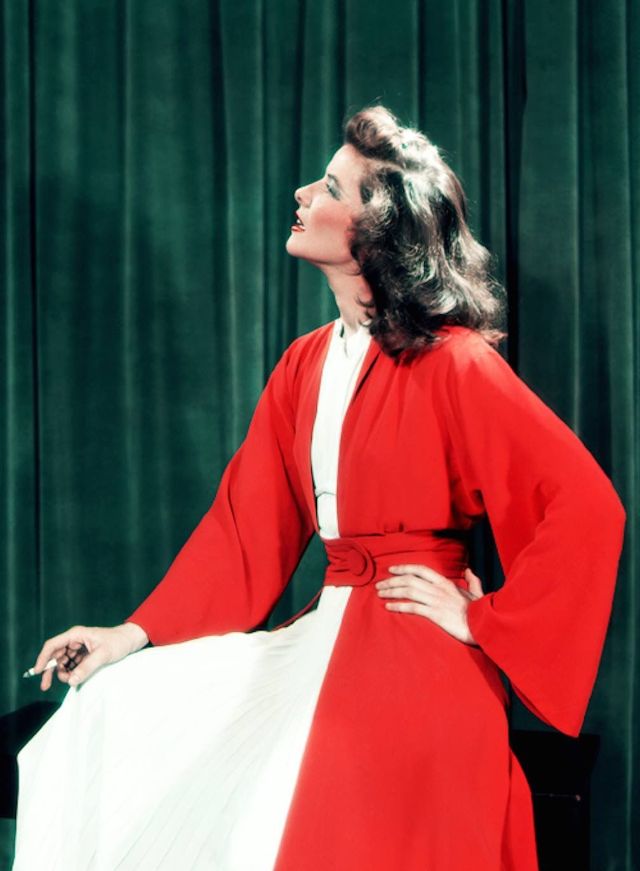
These rare and gorgeous color photographs that captured portraits of classic beauties in the late 1930s and 1940s.


























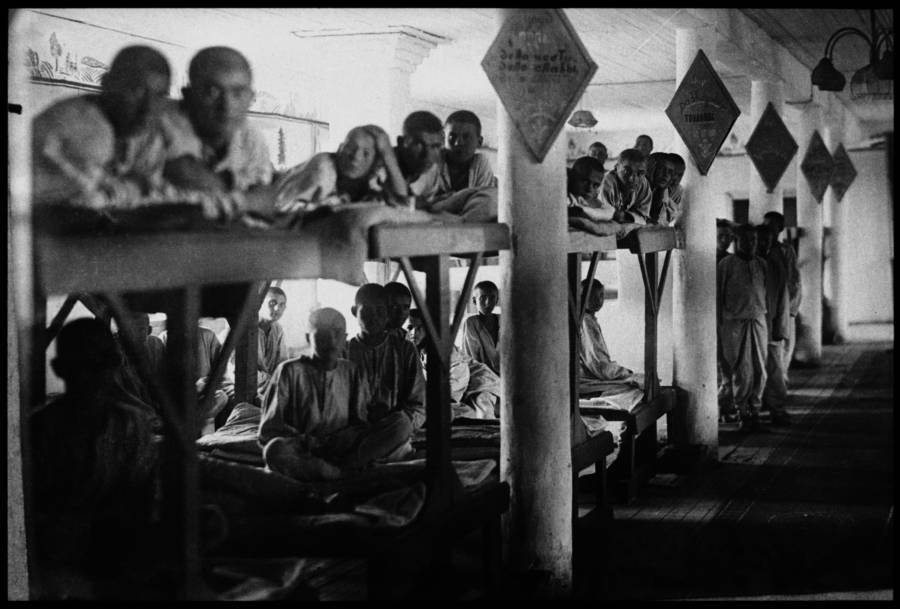
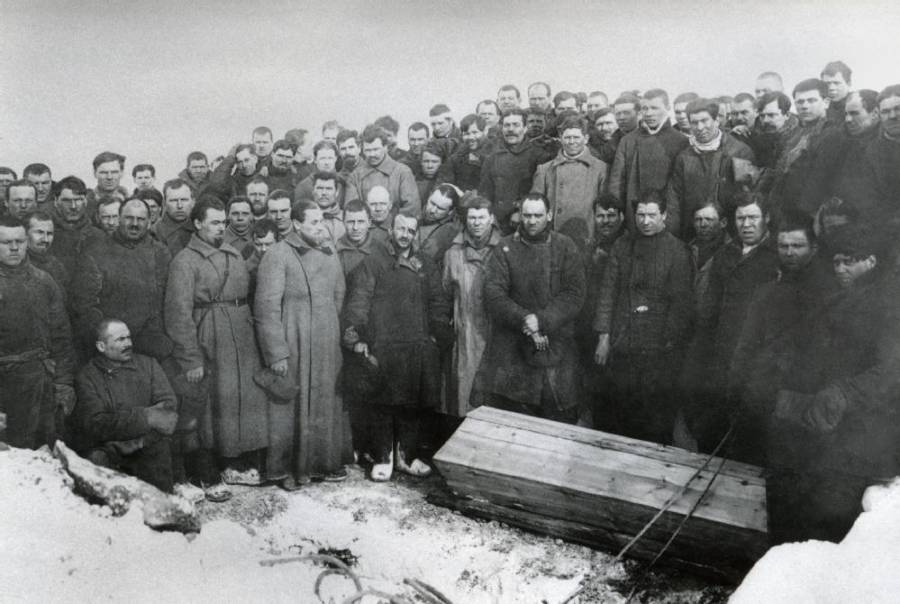
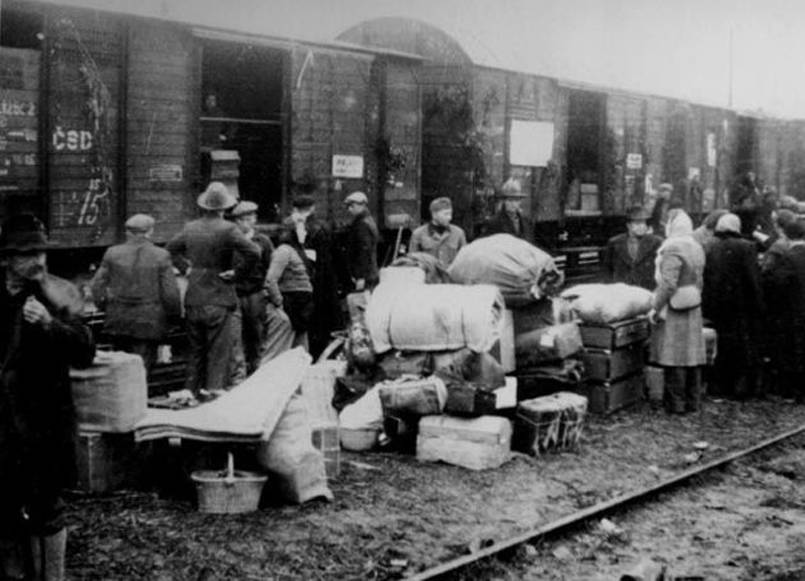
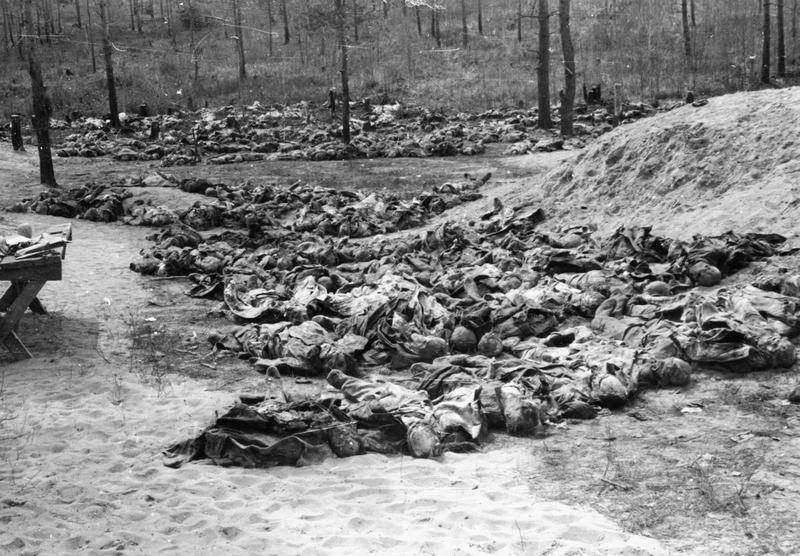
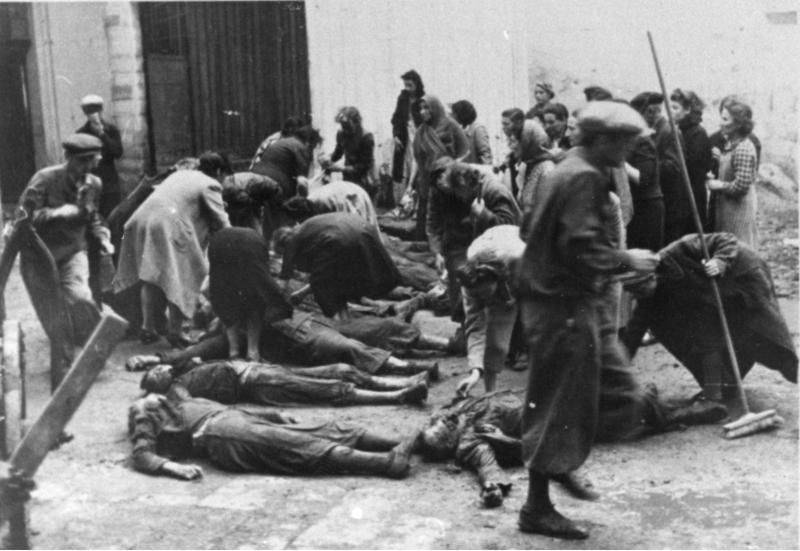
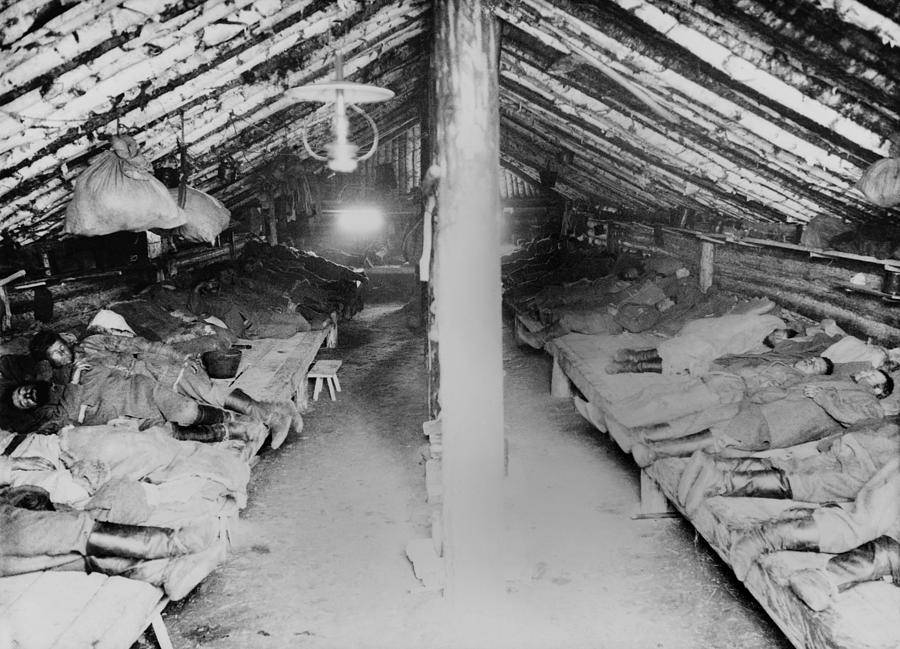
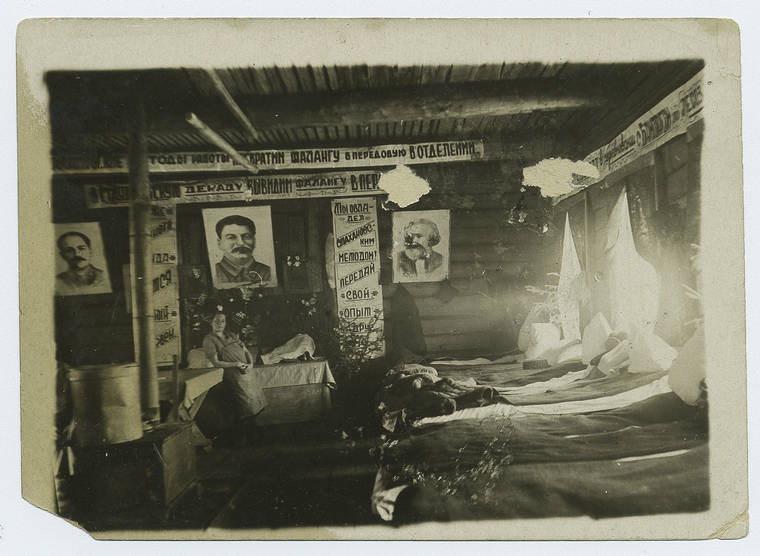
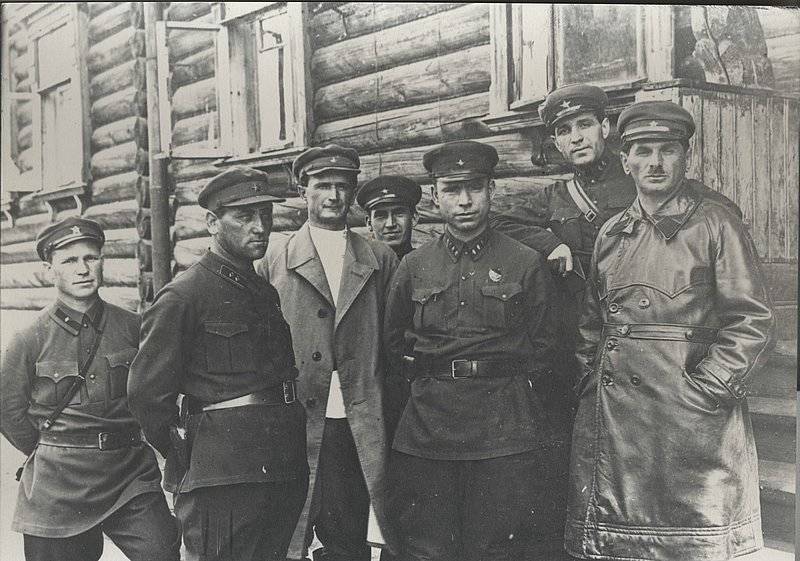
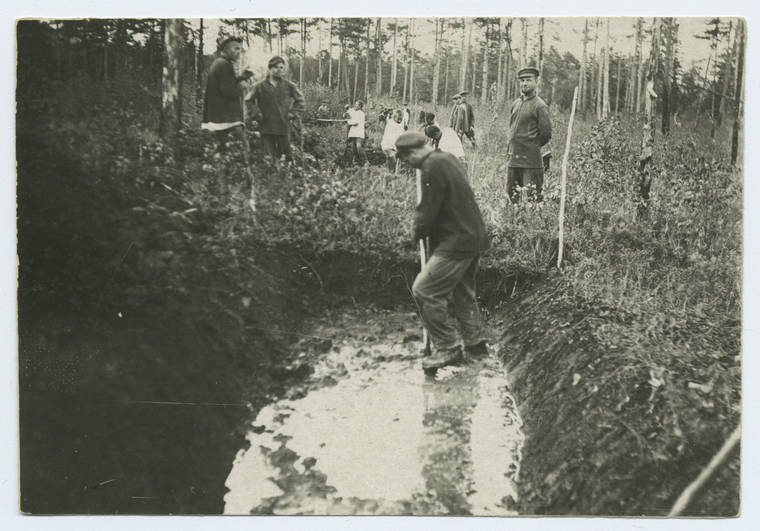
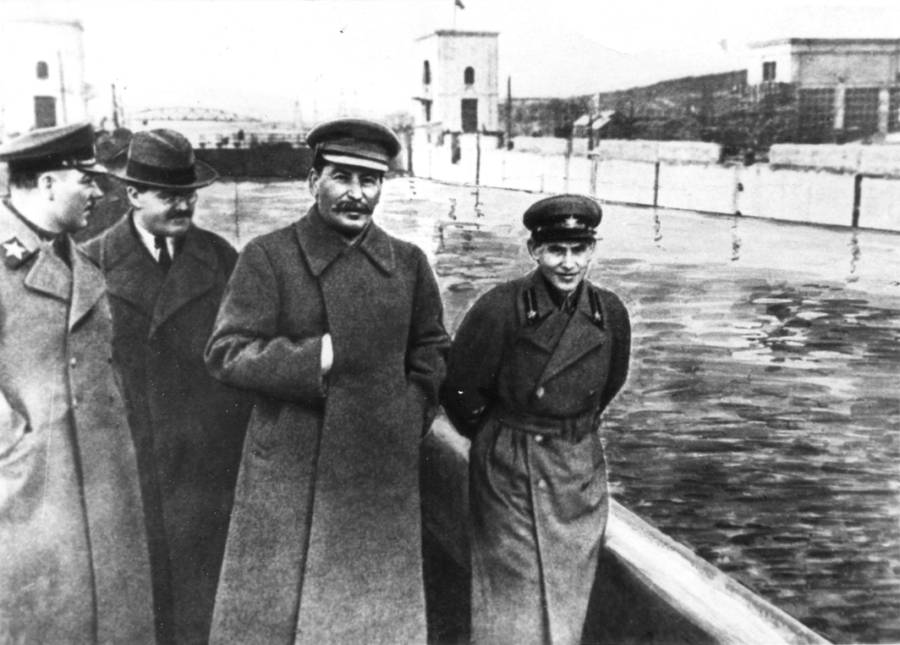
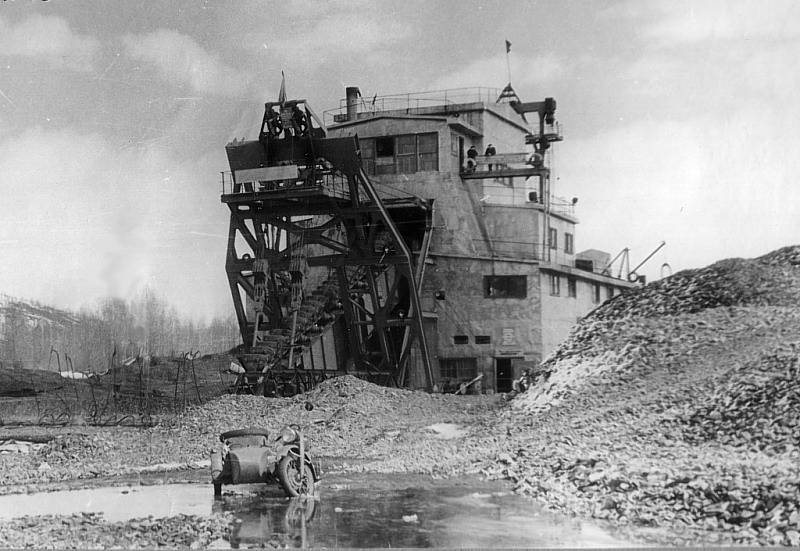
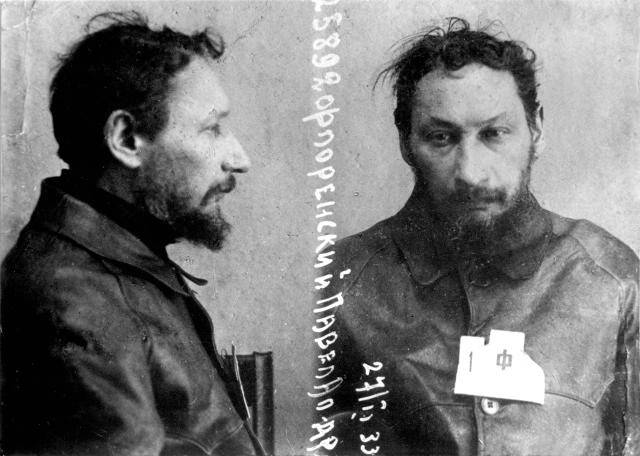
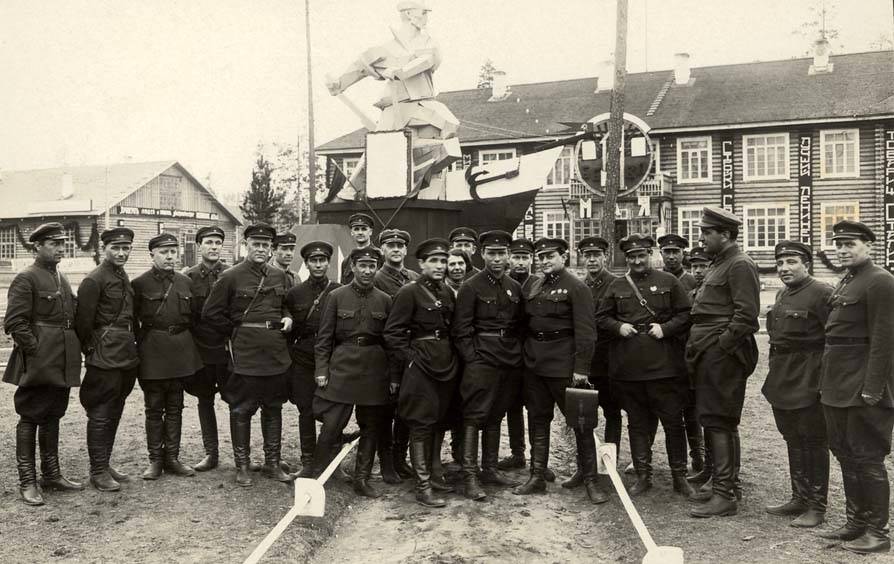
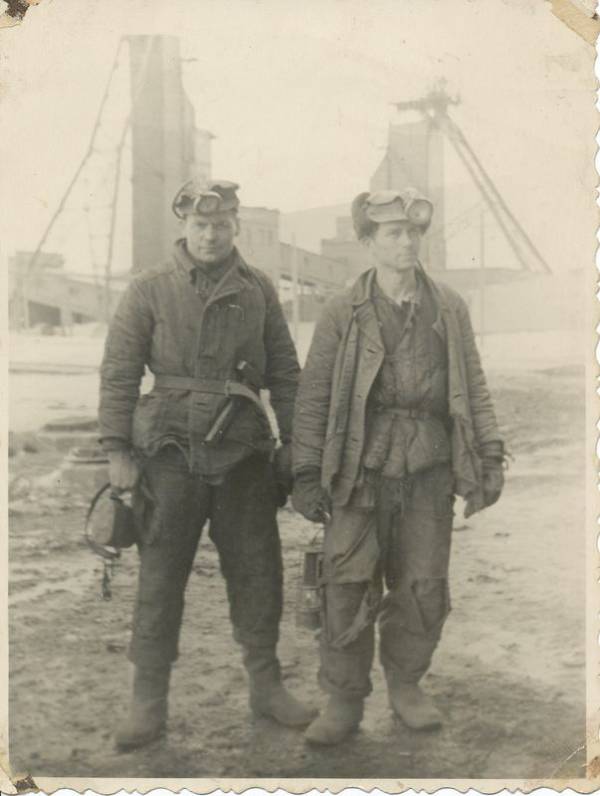
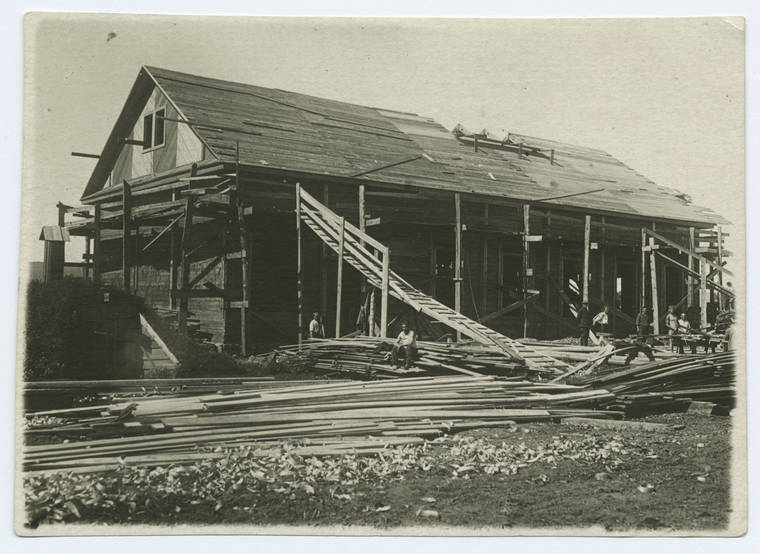
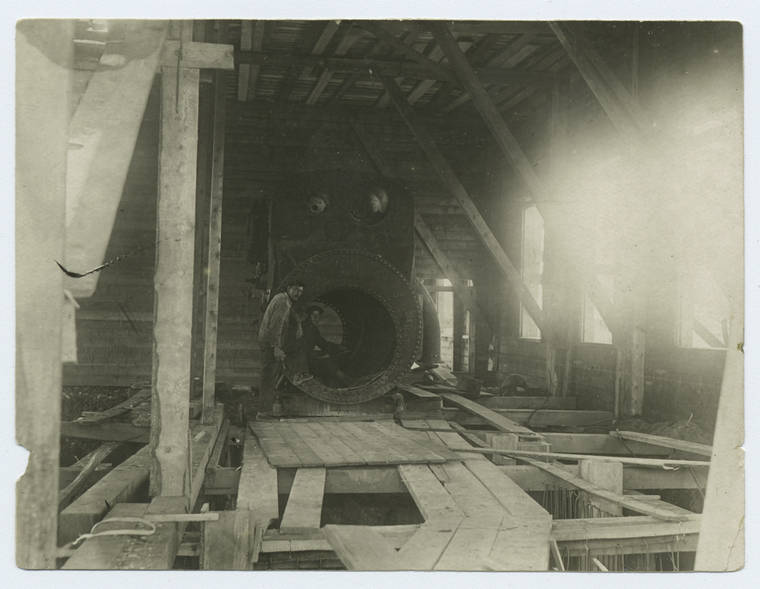
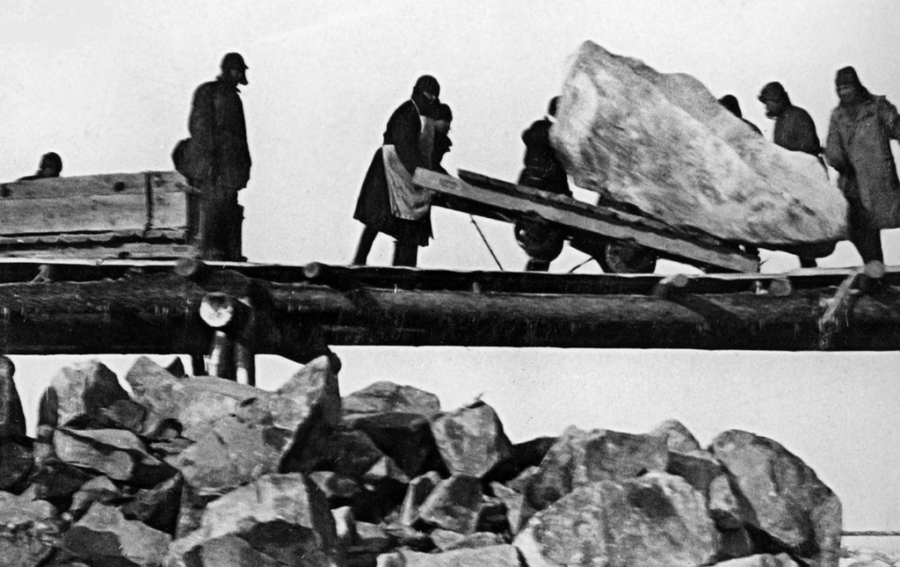
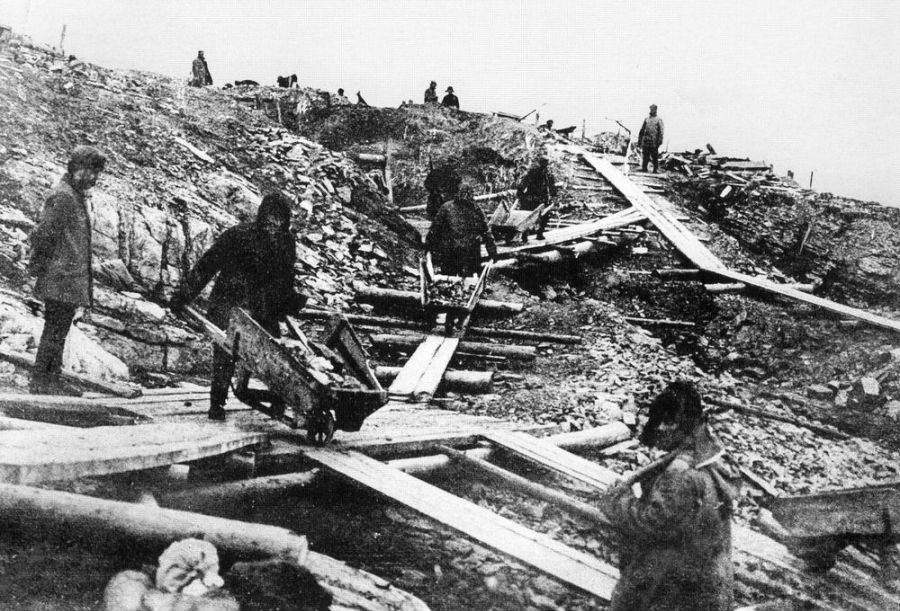
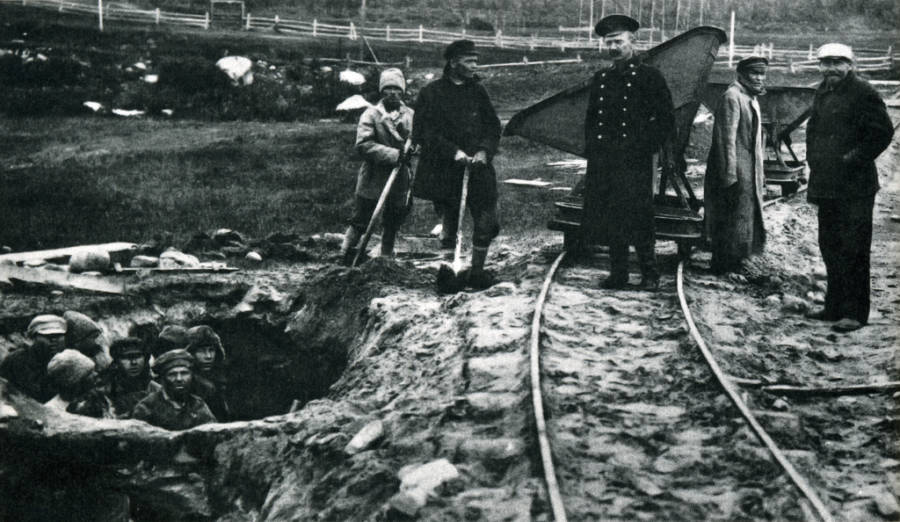
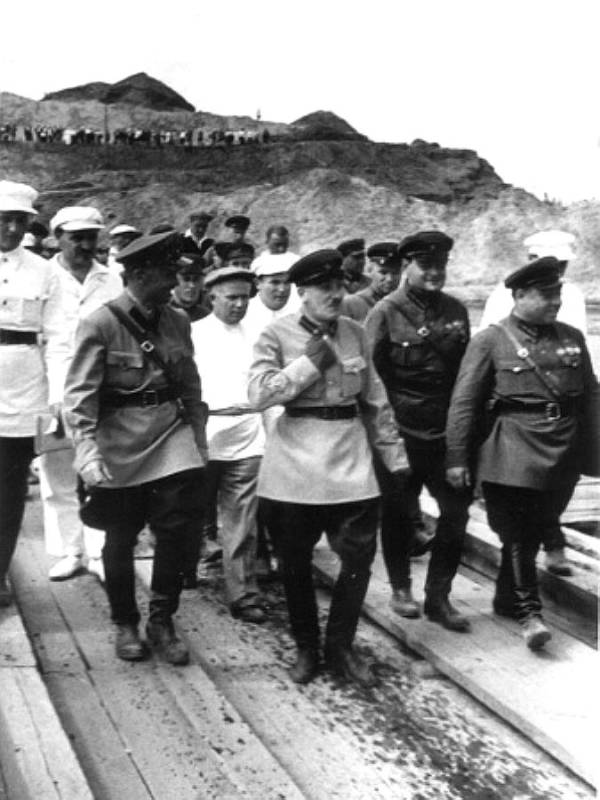
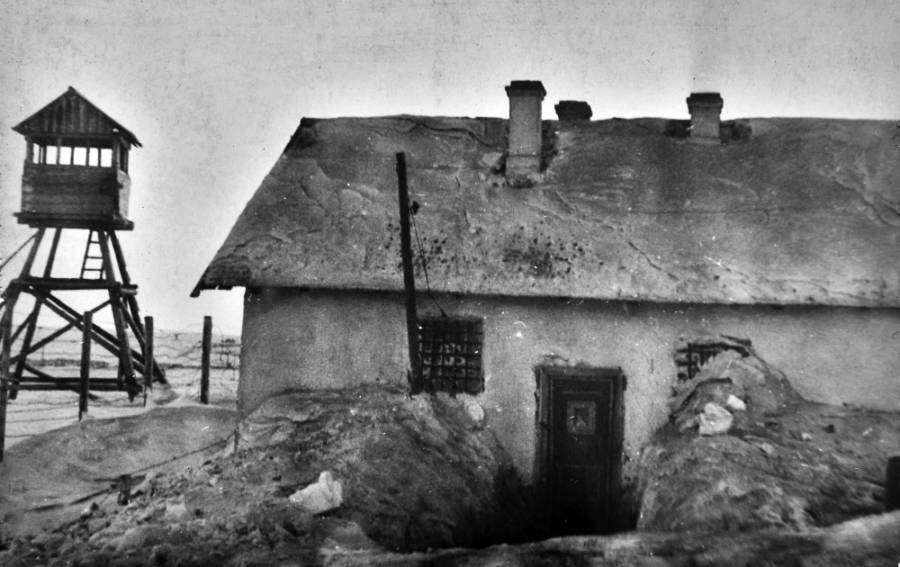
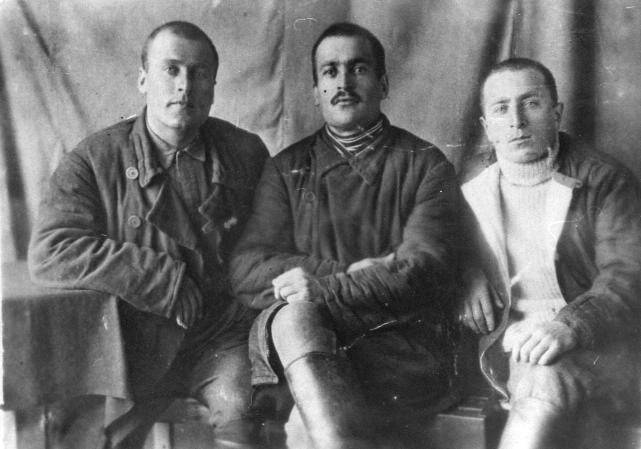
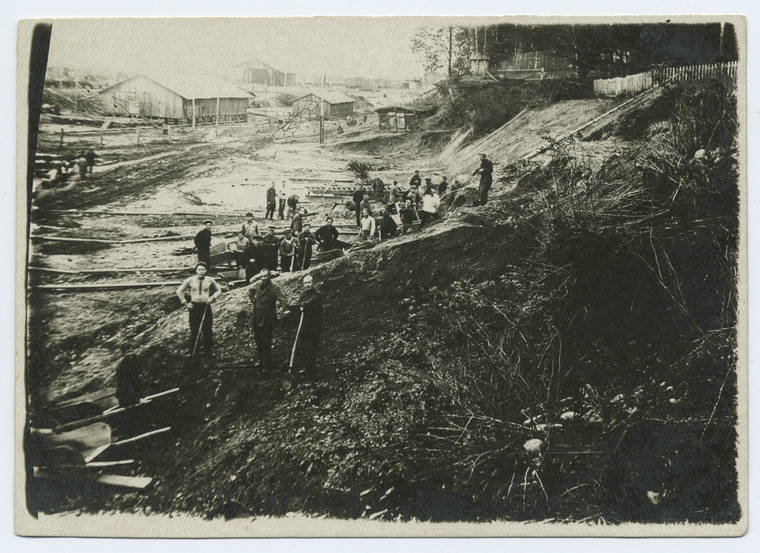
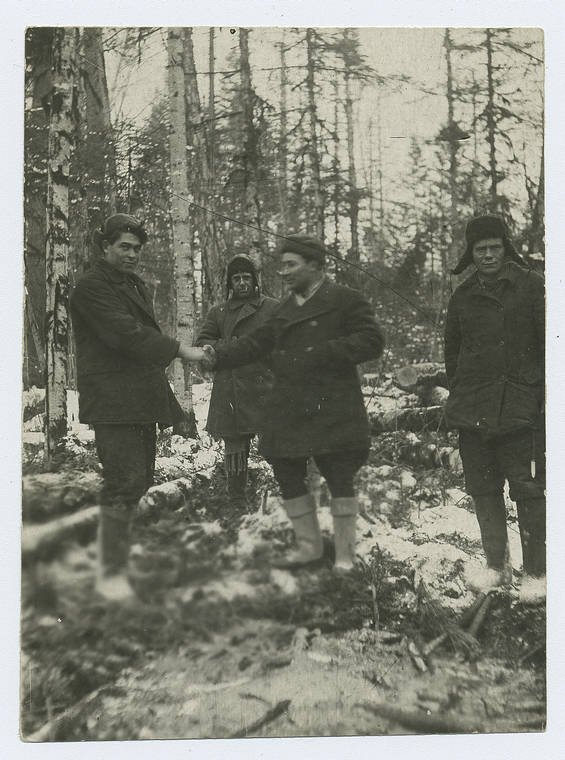
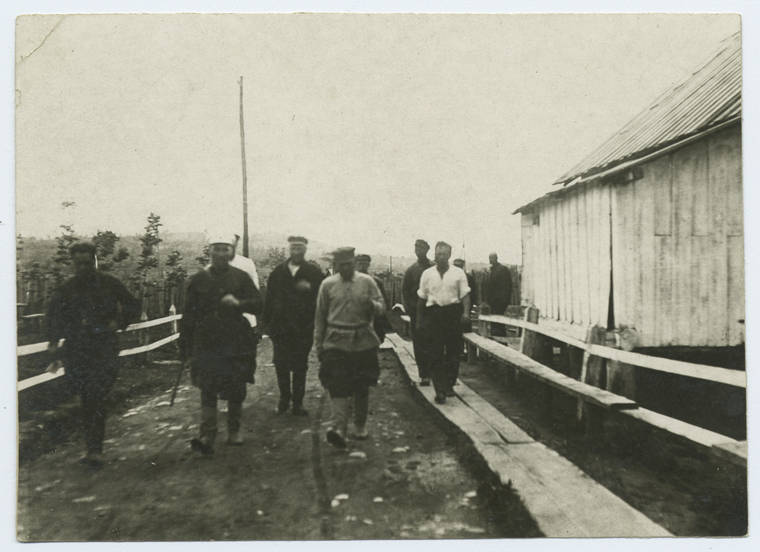
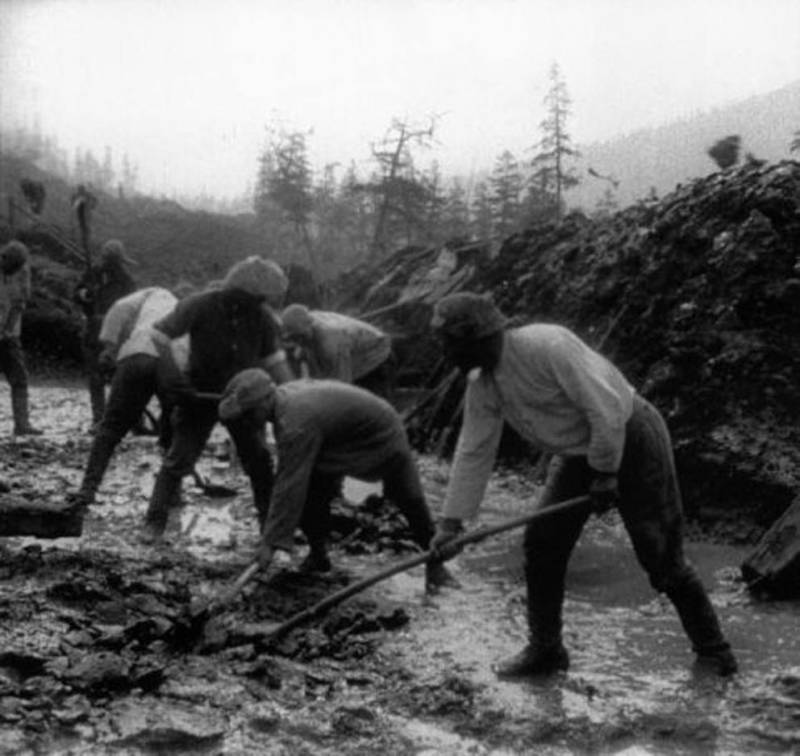
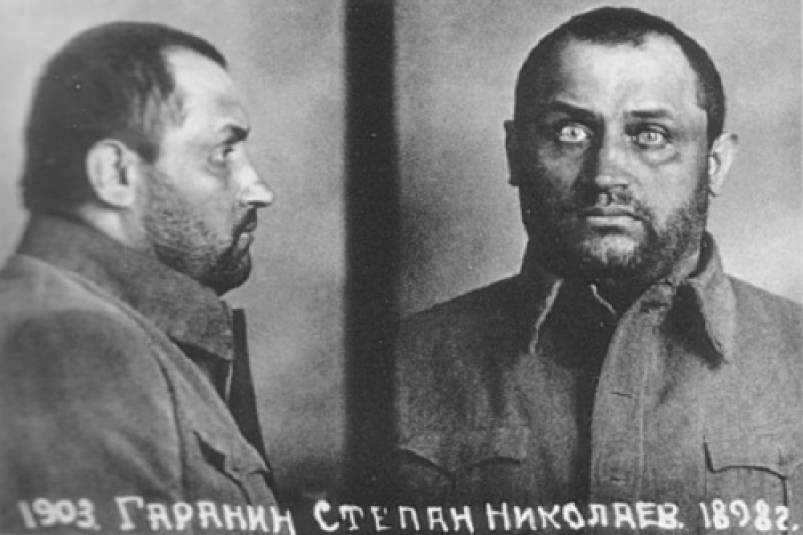
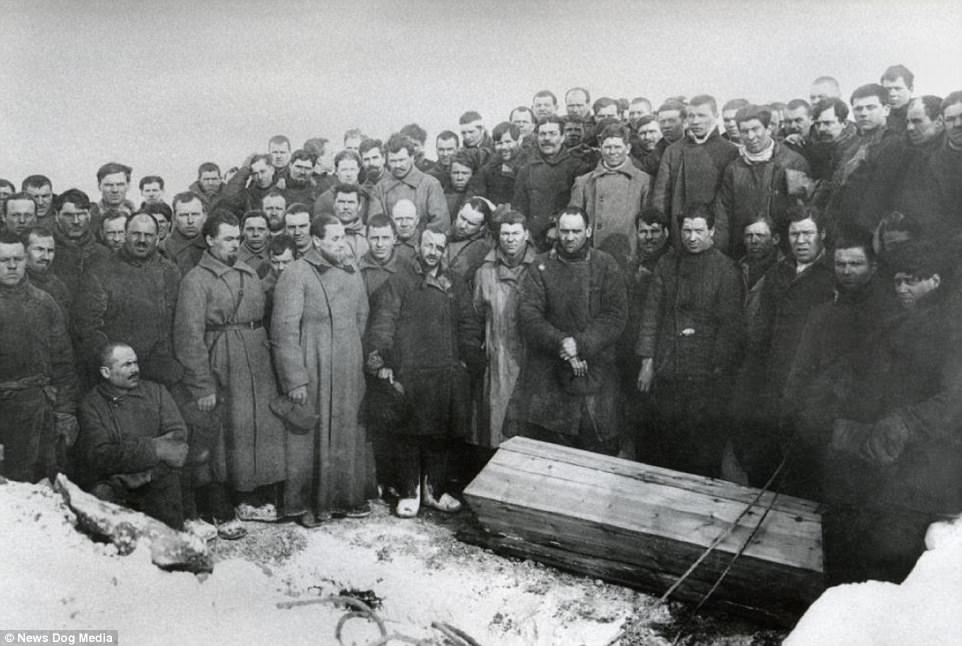
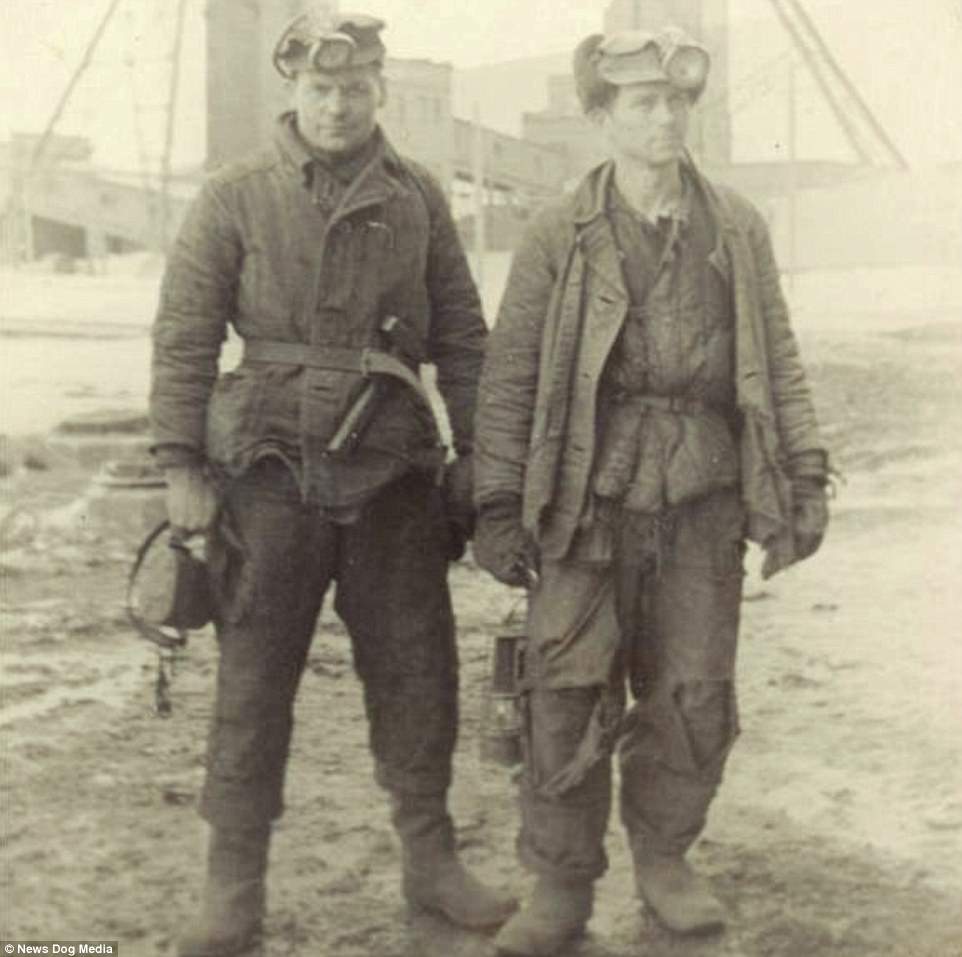
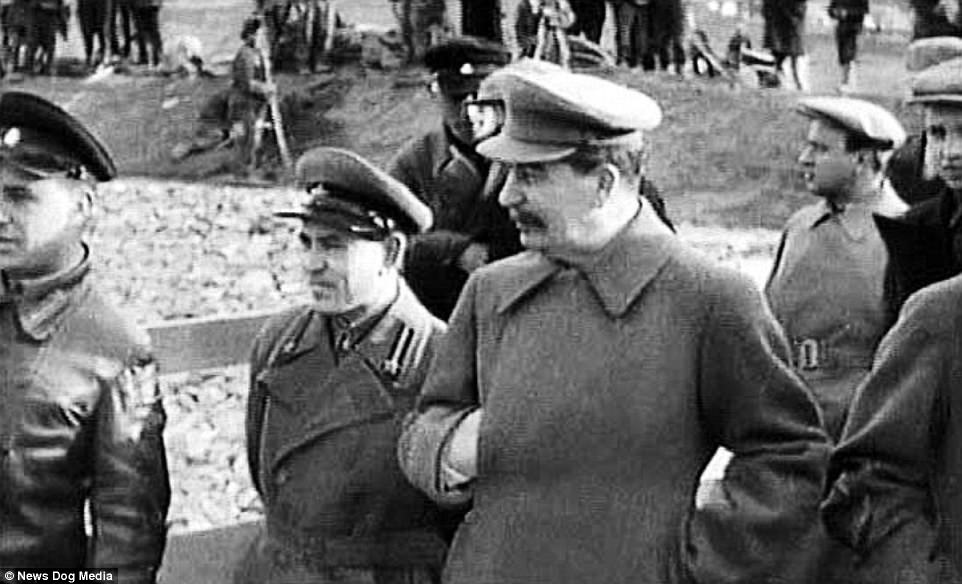
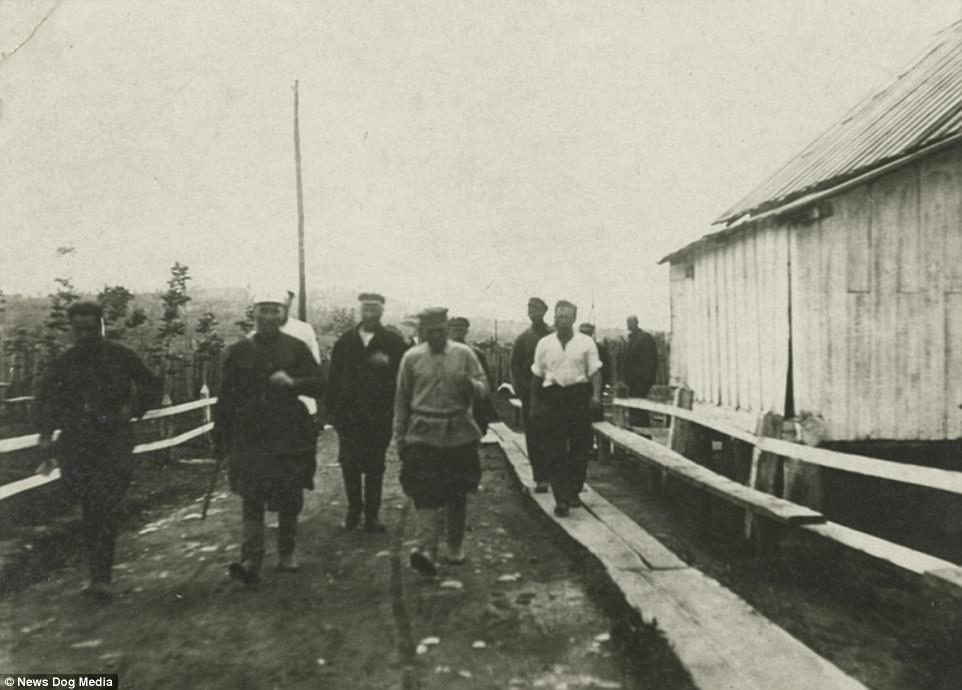
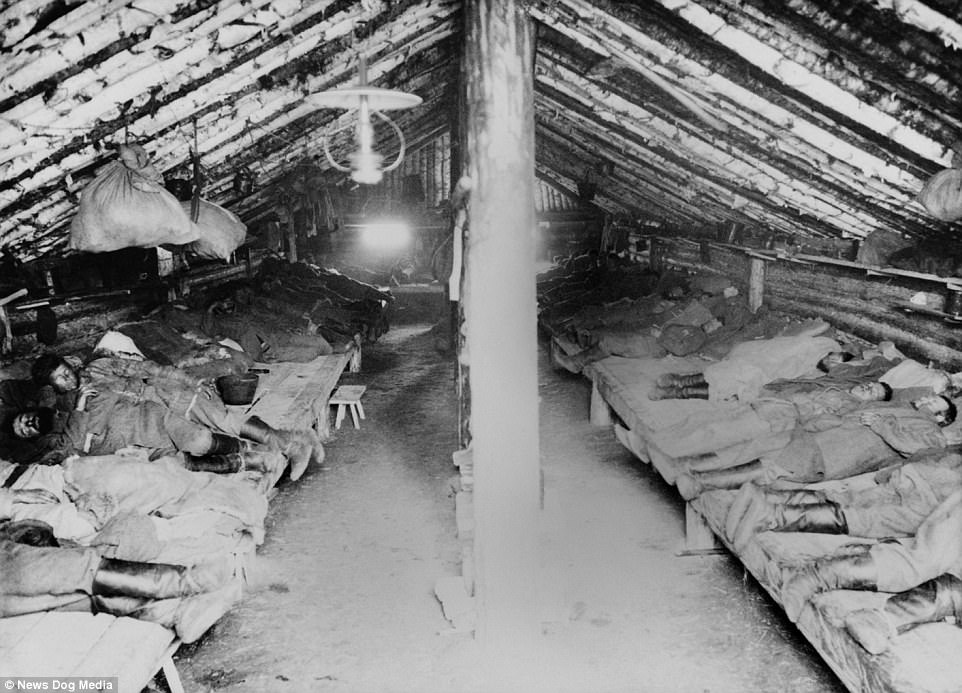
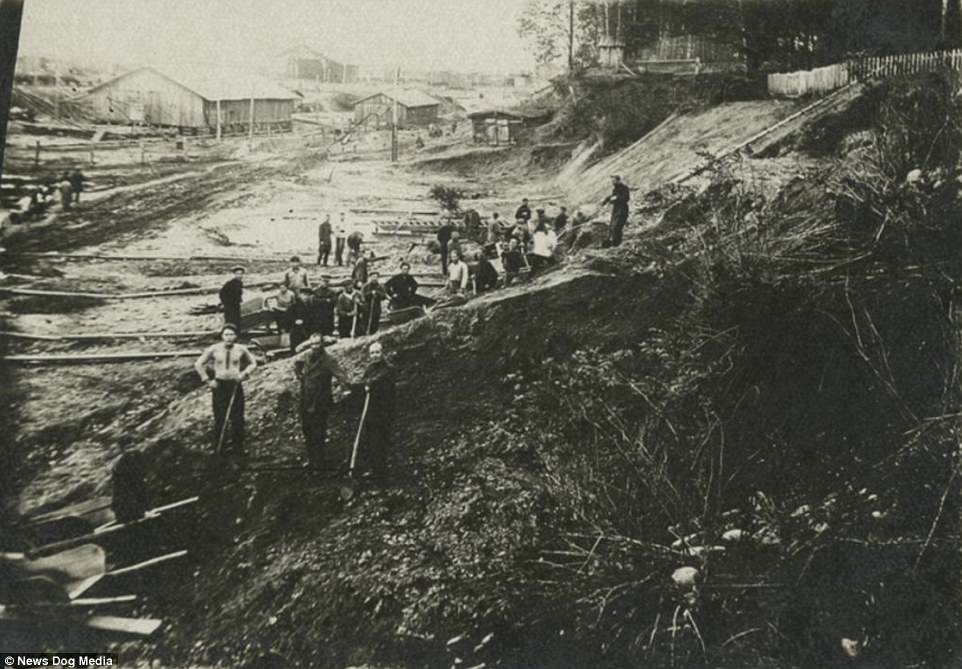
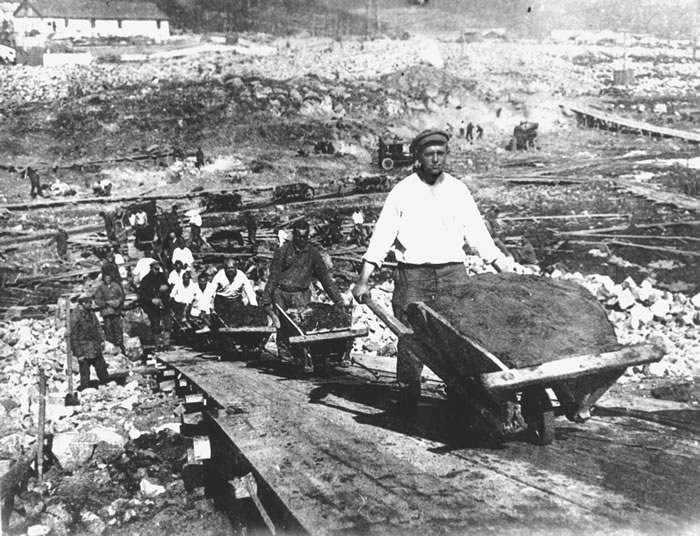
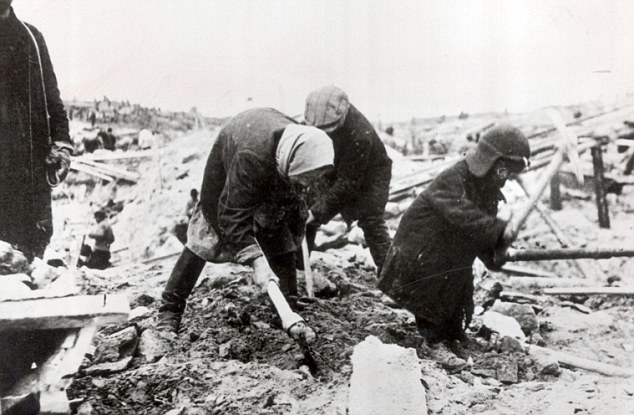
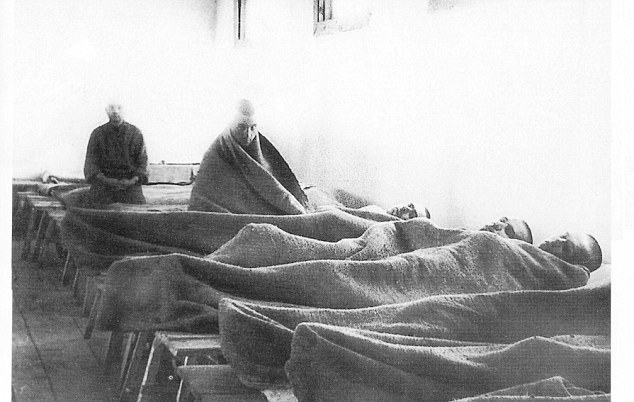
The Gulag was the government agency in charge of the Soviet forced-labour camp-system that was set up under Vladimir Lenin and reached its peak during Joseph Stalin’s rule from the 1930s to the early 1950s. English-language speakers also use the word gulag to refer to any forced-labor camp in the Soviet Union, including camps which existed in post-Stalin times. The camps housed a wide range of convicts, from petty criminals to political prisoners. Large numbers were convicted by simplified procedures, such as by NKVD troikas or by other instruments of extrajudicial punishment. The Gulag is recognized by many as a major instrument of political repression in the Soviet Union.
The agency was first administered by the GPU, later by the NKVD and in the final years by the Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD). The Solovki prison camp, the first corrective labor camp constructed after the revolution, was established in 1918 and legalized by a decree “On the creation of the forced-labor camps” on April 15, 1919. The internment system grew rapidly, reaching a population of 100,000 in the 1920s. According to Nicolas Werth, author of The Black Book of Communism, the yearly mortality rate in the Soviet concentration camps strongly varied, reaching 5% (1933) and 20% (1942–1943) while dropping considerably in the post-war years (about 1 to 3% per year at the beginning of the 1950s). The emergent consensus among scholars who utilize official archival data is that of the 18 million who were sent to the Gulag from 1930 to 1953, roughly 1.5 to 1.7 million perished there or as a result of their detention. However, some historians question the reliability of such data and instead rely heavily on literary sources come to higher estimations. Archival researchers have found “no plan of destruction” of the gulag population and no statement of official intent to kill them, and prisoner releases vastly exceeded the number of deaths in the Gulag.
Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn, winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature, who survived eight years of Gulag incarceration, gave the term its international repute with the publication of The Gulag Archipelago in 1973. The author likened the scattered camps to “a chain of islands”, and as an eyewitness he described the Gulag as a system where people were worked to death. In March 1940, there were 53 Gulag camp directorates (colloquially referred to as simply “camps”) and 423 labor colonies in the Soviet Union. Many mining and industrial towns and cities in northern and eastern Russia and in Kazakhstan such as Karaganda, Norilsk, Vorkuta and Magadan, were originally blocks of camps built by prisoners and subsequently run by ex-prisoners.
(Wikipedia).