Subscribe to get access
Read more of this content when you subscribe today.
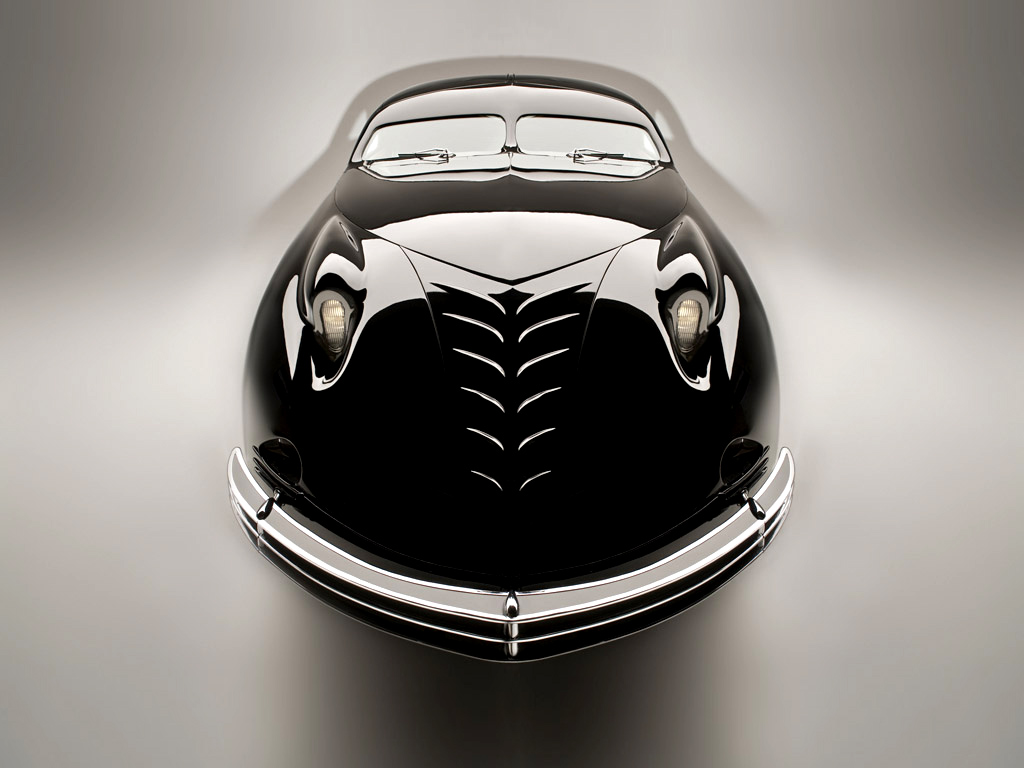

1938 Phantom Corsair

1938 Phantom Corsair

Subscribe to continue reading
Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.
Bringing You the Wonder of Yesterday – Today

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.

1938 Phantom Corsair

1938 Phantom Corsair

Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.

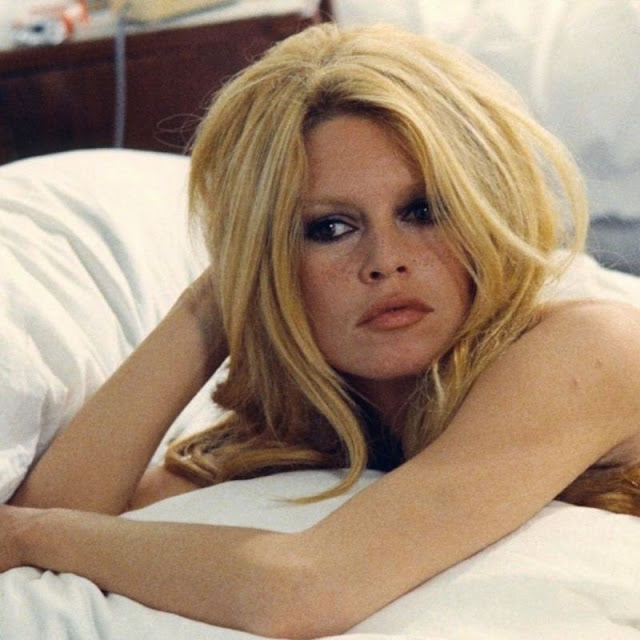
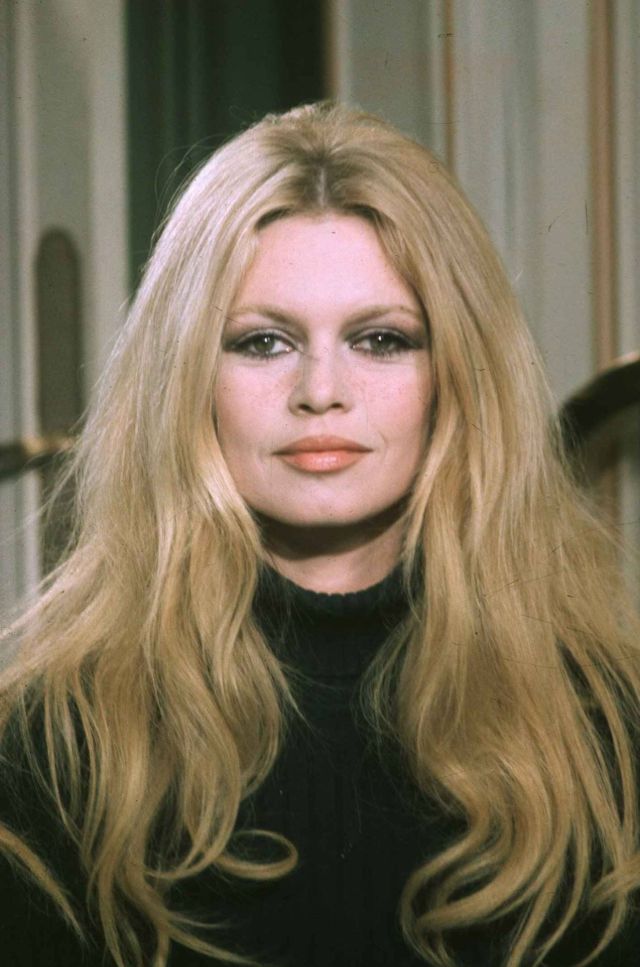
Les Femmes is a 1969 sex comedy film co-written and directed by Jean Aurel, starring Brigitte Bardot and Maurice Ronet. It recorded admissions of 505,292 in France.
When Les Femmes was first released in Italy in 1970, the Committee for the Theatrical Review of the Italian Ministry of Cultural Heritage and Activities rated it as VM18: not suitable for children under 18.
The reason for the age restriction, cited in the official documents, is that: even after the cuts, the movie is still imbued with eroticism and it is inappropriate to the sensitivity of a minor.
Brigitte Anne-Marie Bardot; born 28 September 1934, often referred to by her initials B.B., is a French former actress, singer and model. Famous for portraying sexually emancipated characters with hedonistic lifestyles, she was one of the best known sex symbols of the late 1950s and 1960s. Although she withdrew from the entertainment industry in 1973, she remains a major popular culture icon.
Born and raised in Paris, Bardot was an aspiring ballerina in her early life. She started her acting career in 1952. She achieved international recognition in 1957 for her role in And God Created Woman (1956), and also caught the attention of French intellectuals. She was the subject of Simone de Beauvoir’s 1959 essay The Lolita Syndrome, which described her as a “locomotive of women’s history” and built upon existentialist themes to declare her the first and most liberated woman of post-war France. She won a 1961 David di Donatello Best Foreign Actress Award for her work in The Truth. Bardot later starred in Jean-Luc Godard’s film Le Mépris (1963). For her role in Louis Malle’s film Viva Maria! (1965) she was nominated for the BAFTA Award for Best Foreign Actress.
Bardot retired from the entertainment industry in 1973. She had acted in 47 films, performed in several musicals, and recorded more than 60 songs. She was awarded the Legion of Honour in 1985. After retiring, she became an animal rights activist and created the Fondation Brigitte Bardot. Bardot is known for her strong personality, outspokenness, and speeches on animal defense; she has been fined twice for public insults. She has also been a controversial political figure, having been fined five times for inciting racial hatred when she criticised immigration and Islam in France. She is married to Bernard d’Ormale, a former adviser to Jean-Marie Le Pen, a French far-right politician. Bardot is a member of the Global 500 Roll of Honour of the United Nations Environment Programme and has received awards from UNESCO and PETA. Los Angeles Times Magazine ranked her second on the “50 Most Beautiful Women In Film”. (Wikipedia)
Here below is a set of vintage photos that shows portraits of Brigitte Bardot during the filming of Les Femmes in 1969.


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.

Though the history of color photography dates back more than a hundred years, the production and publication of color enlargements (photopositives) has only been widespread since the 1940s, when color film first entered mass use. These fascinating color photographs were taken by an unknown photographer using Agfacolor, they show everyday life in Budapest in 1939, just before the Second World War.
Agfacolor was the name of a series of color film products made by Agfa of Germany. The first Agfacolor, introduced in 1932, was a film-based version of their Agfa-Farbenplatte (Agfa color plate), a “screen plate” product similar to the French Autochrome. In late 1936 Agfa introduced Agfacolor Neu (New Agfacolor), a pioneering color film of the general type still in use today.
The new Agfacolor was originally a reversal film used for making “slides”, home movies and short documentaries. By 1939 it had also been adapted into a negative film and a print film for use by the German motion picture industry. After World War II, the Agfacolor brand was applied to several varieties of color negative film for still photography, in which the negatives were used to make color prints on paper. The reversal film was then marketed as Agfachrome. These films use Color Developing Agent 1 in their color developer.
Budapest is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on Danube river; the city has an estimated population of 1,752,286 over a land area of about 525 square kilometres (203 square miles). Budapest, which is both a city and county, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of 7,626 square kilometres (2,944 square miles) and a population of 3,303,786, comprising 33% of the population of Hungary.
The history of Budapest began when an early Celtic settlement transformed into the Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Lower Pannonia. The Hungarians arrived in the territory in the late 9th century, but the area was pillaged by the Mongols in 1241–42. Re-established Buda became one of the centres of Renaissance humanist culture by the 15th century. The Battle of Mohács, in 1526, was followed by nearly 150 years of Ottoman rule. After the reconquest of Buda in 1686, the region entered a new age of prosperity, with Pest-Buda becoming a global city after the unification of Buda, Óbuda and Pest on 17 November 1873, with the name ‘Budapest’ given to the new capital. Budapest also became the co-capital of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, a great power that dissolved in 1918, following World War I. The city was the focal point of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Battle of Budapest in 1945, as well as the Hungarian Revolution of 1956.
Budapest is a Beta + global city with strengths in commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education and entertainment. Hungary’s financial centre, it is the second richest capital and city in the region after Bucharest. Budapest is the headquarters of the European Institute of Innovation and Technology, the European Police College and the first foreign office of the China Investment Promotion Agency. Over 40 colleges and universities are located in Budapest, including the Eötvös Loránd University, the Corvinus University, Semmelweis University, University of Veterinary Medicine Budapest and the Budapest University of Technology and Economics. Opened in 1896, the city’s subway system, the Budapest Metro, serves 1.27 million, while the Budapest Tram Network serves 1.08 million passengers daily.
The central area of Budapest along the Danube River is classified as a UNESCO World Heritage Site and has several notable monuments of classical architecture, including the Hungarian Parliament and the Buda Castle. The city also has around 80 geothermal springs, the largest thermal water cave system, second largest synagogue, and third largest Parliament building in the world. Budapest attracts around 12 million international tourists per year, making it a highly popular destination in Europe. It also topped the Best European Destinations 2020 list by Big7Media. Budapest also ranks as the third-best European city in a similar poll conducted by Which?


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.
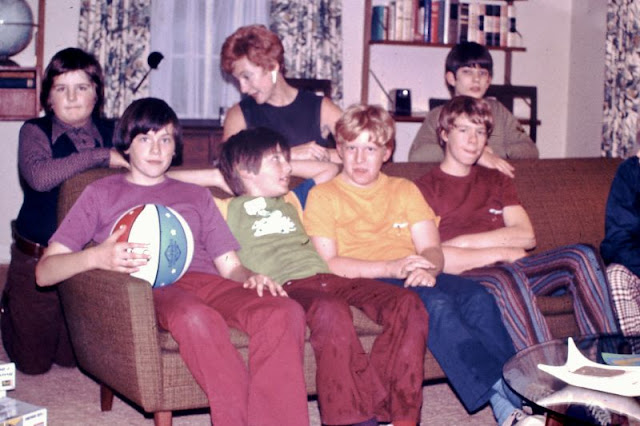
Read more of this content when you subscribe today.

If you grew up in the 1970s, chances are you had a rockin’ sense of style. Adults were donning leisure suits and bell bottoms, and stores adapted those trends to fit their littlest costumers, too.
At that time, it was impossible not to look good. But looking back, some of the best styles seem a bit ridiculous. Who could forget some of these funky styles? Take a look at these vintage photos to see what kids looked like from the 1970s.
The 1970s (pronounced “nineteen-seventies”; commonly shortened to the “Seventies” or the “’70s”) was a decade that began on January 1, 1970, and ended on December 31, 1979.
In the 21st century, historians have increasingly portrayed the 1970s as a “pivot of change” in world history, focusing especially on the economic upheavals that followed the end of the postwar economic boom. On a global scale, it was characterized by frequent coups, domestic conflicts and civil wars, and various political upheaval and armed conflicts which arose from or were related to decolonization, and the global struggle between the West, the Warsaw Pact, and the Non-Aligned Movement. Many regions had periods of high-intensity conflict, notably Southeast Asia, the Mideast, and Africa.
In the Western world, social progressive values that began in the 1960s, such as increasing political awareness and economic liberty of women, continued to grow. In the United Kingdom, the 1979 election resulted in the victory of its Conservative leader Margaret Thatcher, the first female British Prime Minister. Industrialized countries experienced an economic recession due to an oil crisis caused by oil embargoes by the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries. The crisis saw the first instance of stagflation which began a political and economic trend of the replacement of Keynesian economic theory with neoliberal economic theory, with the first neoliberal governments being created in Chile, where a military coup led by Augusto Pinochet took place in 1973.
The 1970s was also an era of great technological and scientific advances; since the appearance of the first commercial microprocessor, the Intel 4004 in 1971, the decade was characterised by a profound transformation of computing units – by then rudimentary, spacious machines – into the realm of portability and home accessibility.
On the other hand, there were also great advances in fields such as physics, which saw the consolidation of Quantum Field Theory at the end of the decade, mainly thanks to the confirmation of the existence of quarks and the detection of the first gauge bosons in addition to the photon, the Z boson and the gluon, part of what was christened in 1975 as the Standard Model.
Novelist Tom Wolfe coined the term “ ’Me’ decade” in his essay “The ‘Me’ Decade and the Third Great Awakening”, published by New York Magazine in August 1976 referring to the 1970s. The term describes a general new attitude of Americans towards atomized individualism and away from communitarianism, in clear contrast with the 1960s.
In Asia, affairs regarding the People’s Republic of China changed significantly following the recognition of the PRC by the United Nations, the death of Mao Zedong and the beginning of market liberalization by Mao’s successors. Despite facing an oil crisis due to the OPEC embargo, the economy of Japan witnessed a large boom in this period, overtaking the economy of West Germany to become the second-largest in the world. The United States withdrew its military forces from their previous involvement in the Vietnam War, which had grown enormously unpopular. In 1979, the Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan, which led to an ongoing war for ten years.
The 1970s saw an initial increase in violence in the Middle East as Egypt and Syria declared war on Israel, but in the late 1970s, the situation in the Middle East was fundamentally altered when Egypt signed the Egyptian–Israeli Peace Treaty. Anwar Sadat, President of Egypt, was instrumental in the event and consequently became extremely unpopular in the Arab world and the wider Muslim world. Political tensions in Iran exploded with the Iranian Revolution in 1979, which overthrew the Authoritarian Pahlavi dynasty and established an even more authoritarian Islamic republic under the leadership of the Ayatollah Khomeini.
Africa saw further decolonization in the decade, with Angola and Mozambique gaining their independence in 1975 from the Portuguese Empire after the restoration of democracy in Portugal. The continent was, however, plagued by endemic military coups, with the long-reigning Emperor of Ethiopia Haile Selassie being removed, civil wars and famine.
The economies of much of the developing world continued to make steady progress in the early 1970s because of the Green Revolution. However, their economic growth was slowed by the oil crisis, although it boomed afterwards. (Wikipedia)


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.

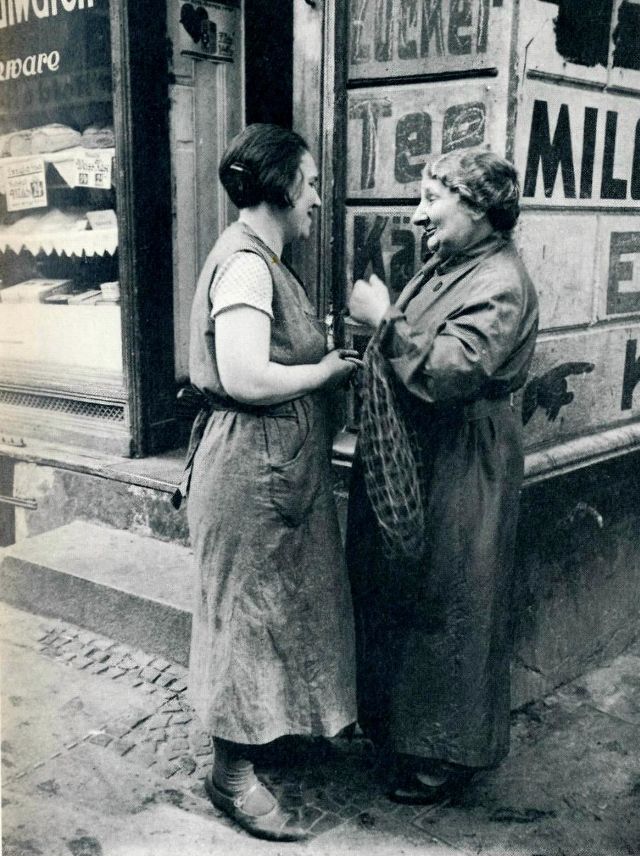
The Golden Twenties was a vibrant period in the history of Berlin, Germany, Europe and the world in general. After the Greater Berlin Act the city became the third largest municipality in the world and experienced its heyday as a major world city.
Berlin was known for its leadership roles in science, the humanities, music, film, higher education, government, diplomacy, industries and military affairs.
Berlin in the 1920s also proved to be a haven for English writers such as W. H. Auden, Stephen Spender and Christopher Isherwood, who wrote a series of ‘Berlin novels’, inspiring the play I Am a Camera, which was later adapted into a musical, Cabaret, and an Academy Award winning film of the same name. Spender’s semi-autobiographical novel The Temple evokes the attitude and atmosphere of the time.
Take a look at these amazing photos to see what Berlin looked like during the 1920s.


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.
Marilyn Monroe (born Norma Jeane Mortenson; June 1, 1926 – August 4, 1962) was an American actress, model and singer. Famous for playing comedic “blonde bombshell” characters, she became one of the most popular sex symbols of the 1950s and early 1960s and was emblematic of the era’s sexual revolution. She was a top-billed actress for a decade, and her films grossed $200 million (equivalent to $2 billion in 2020) by the time of her death in 1962. Long after her death, Monroe remains a major icon of pop culture. In 1999, the American Film Institute ranked her sixth on their list of the greatest female screen legends from the Golden Age of Hollywood.
Born and raised in Los Angeles, Monroe spent most of her childhood in foster homes and an orphanage; she married at age sixteen. She was working in a factory during World War II when she met a photographer from the First Motion Picture Unit and began a successful pin-up modeling career, which led to short-lived film contracts with 20th Century Fox and Columbia Pictures. After a series of minor film roles, she signed a new contract with Fox in late 1950. Over the next two years, she became a popular actress with roles in several comedies, including As Young as You Feel and Monkey Business, and in the dramas Clash by Night and Don’t Bother to Knock. She faced a scandal when it was revealed that she had posed for nude photographs prior to becoming a star, but the story did not damage her career and instead resulted in increased interest in her films.
By 1953, Monroe was one of the most marketable Hollywood stars; she had leading roles in the film noir Niagara, which overtly relied on her sex appeal, and the comedies Gentlemen Prefer Blondes and How to Marry a Millionaire, which established her star image as a “dumb blonde”. The same year, her nude images were used as the centerfold and on the cover of the first issue of Playboy. She played a significant role in the creation and management of her public image throughout her career, but she was disappointed when she was typecast and underpaid by the studio. She was briefly suspended in early 1954 for refusing a film project but returned to star in The Seven Year Itch (1955), one of the biggest box office successes of her career.
When the studio was still reluctant to change Monroe’s contract, she founded her own film production company in 1954. She dedicated 1955 to building the company and began studying method acting under Lee Strasberg at the Actors Studio. Later that year, Fox awarded her a new contract, which gave her more control and a larger salary. Her subsequent roles included a critically acclaimed performance in Bus Stop (1956) and her first independent production in The Prince and the Showgirl (1957). She won a Golden Globe for Best Actress for her role in Some Like It Hot (1959), a critical and commercial success. Her last completed film was the drama The Misfits (1961).
Monroe’s troubled private life received much attention. She struggled with addiction and mood disorders. Her marriages to retired baseball star Joe DiMaggio and to playwright Arthur Miller were highly publicized, and both ended in divorce. On August 4, 1962, she died at age 36 from an overdose of barbiturates at her Los Angeles home. Her death was ruled a probable suicide. (Wikipedia)
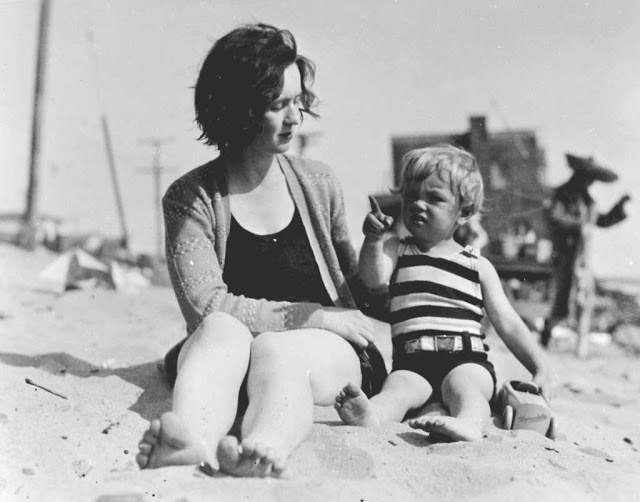
Here’s a gallery of three-year-old Norma at the beach. The photographs of a young Marilyn Monroe were taken in 1929.


Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.
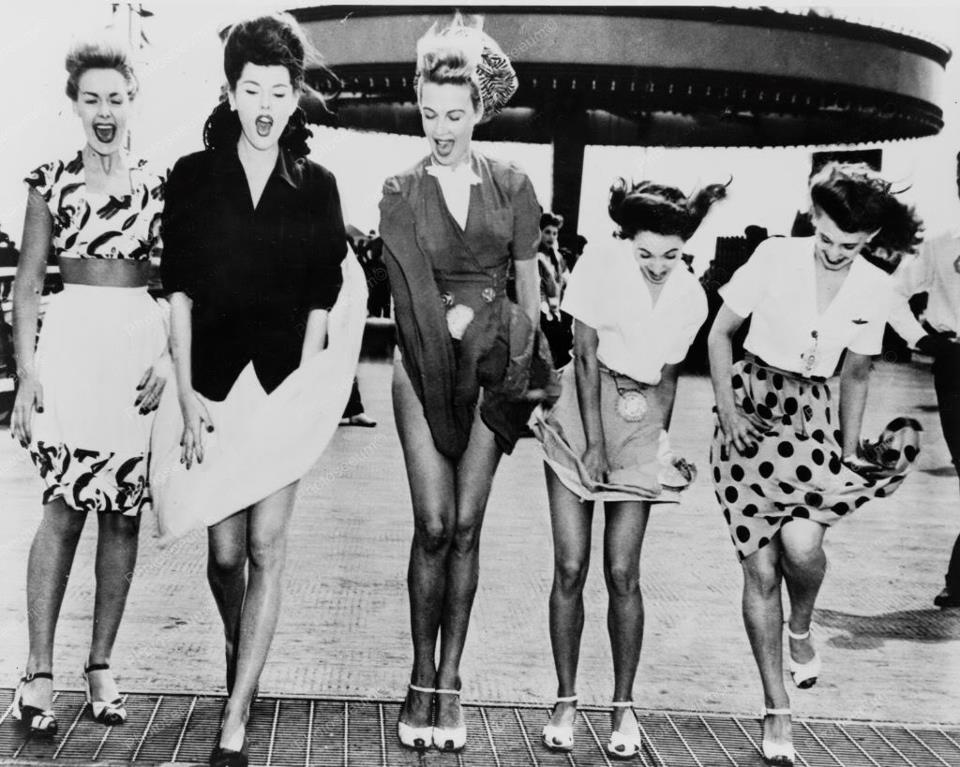


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.
Travel trailers and caravans vary from basic models which may be little more than a tent on wheels to those containing several rooms with all the furniture and furnishings and equipment of a home.
In the United States, the history of travel trailers can be traced back to the early 1920s, when those who enjoyed their use were often referred to as ‘tin can tourists’. As time progressed, trailers became more liveable and earned a new name in the 1930s and 1940s, which was the house trailer.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the industry seemed to split, creating the two types that we see today, that of the recreational vehicle (RV) industry and mobile home industry.
Today travel trailers are classified as a type of RV along with motorhomes, fifth-wheel trailers, pop-up trailers, and truck campers.
Here’s a collection of 20 vintage photos that show the golden age of travel trailers during the 1940s and 1950s.
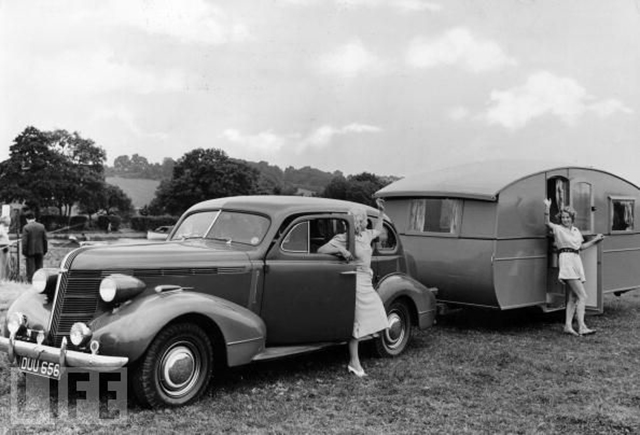


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.

Read more of this content when you subscribe today.

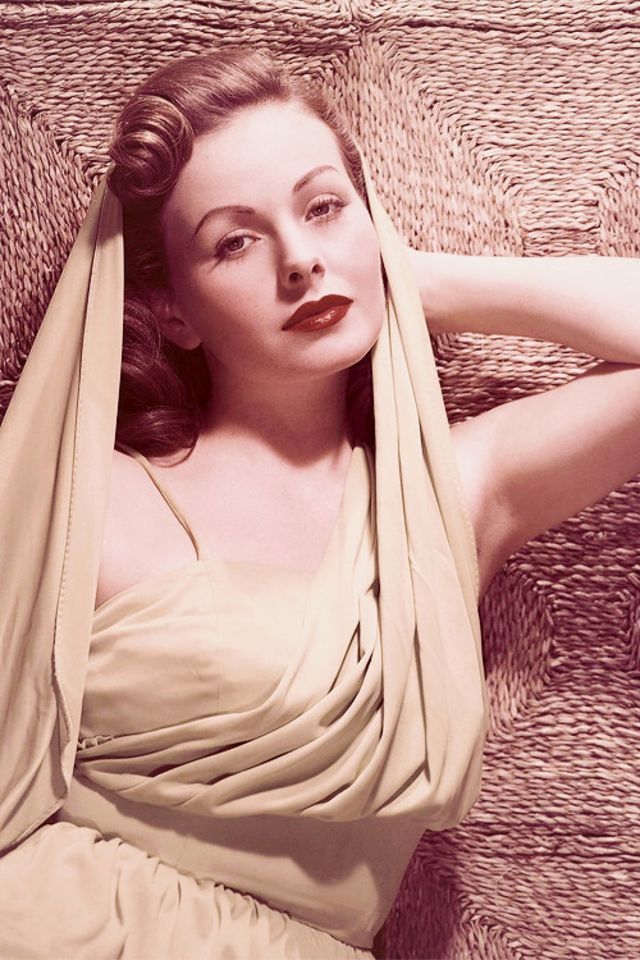
Born 1925 in Barstow, California, American actress Jeanne Crain had her first sizable role in Home in Indiana (1944). The film, shot in Technicolor, was popular at the box office and established Crain as a film name.
In 1949, Crain appeared in three films. A Letter to Three Wives (1949), in which Crain was one of several stars, quickly became established as a classic, winning Joseph L. Mankiewicz two Oscars and being a solid box office hit. The Fan, directed by Preminger and based on Lady Windemere’s Fan by Oscar Wilde, was received poorly. However Pinky earned Crain a nomination the Academy Award for Best Actress and was one of the more popular films of the year.
Crain continued to have success when appeared in some movies in the 1950s such as Cheaper by the Dozen (1950), starred in Take Care of My Little Girl (1951), People Will Talk (1951), starred in The Model and the Marriage Broker (1951), and showed her dancing skills in 1955’s Gentlemen Marry Brunettes.
At the height of her stardom, in the late 1940s and early 1950s, Crain was nicknamed “Hollywood’s Number One party girl”, and she was quoted as saying that she was invited to at least 200 parties a year.
Film roles became fewer in the 1960s as Crain went into semi-retirement. Her last films were Skyjacked (1972) and The Night God Screamed (1975).
Crain died in 2003, cause of a heart attack, at the age of 78.
Take a look at these glamorous photos to see the beauty of Jeanne Crain in the 1940s and 1950s.
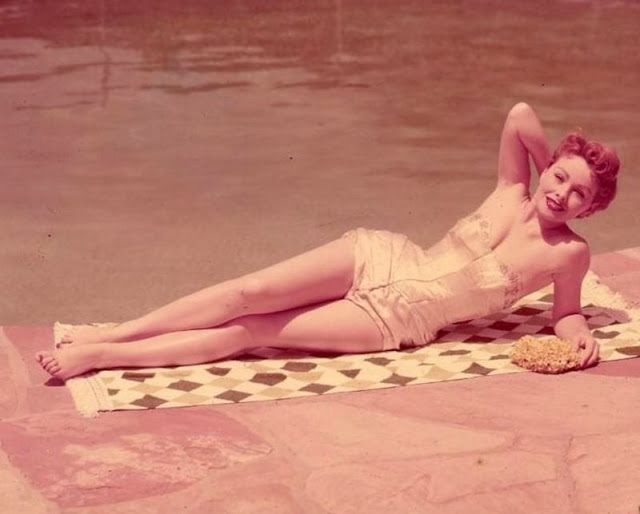


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.


Become a paid subscriber to get access to the rest of this post and other exclusive content.